Casein Hydrolysis Test Principle, Procedure, Result
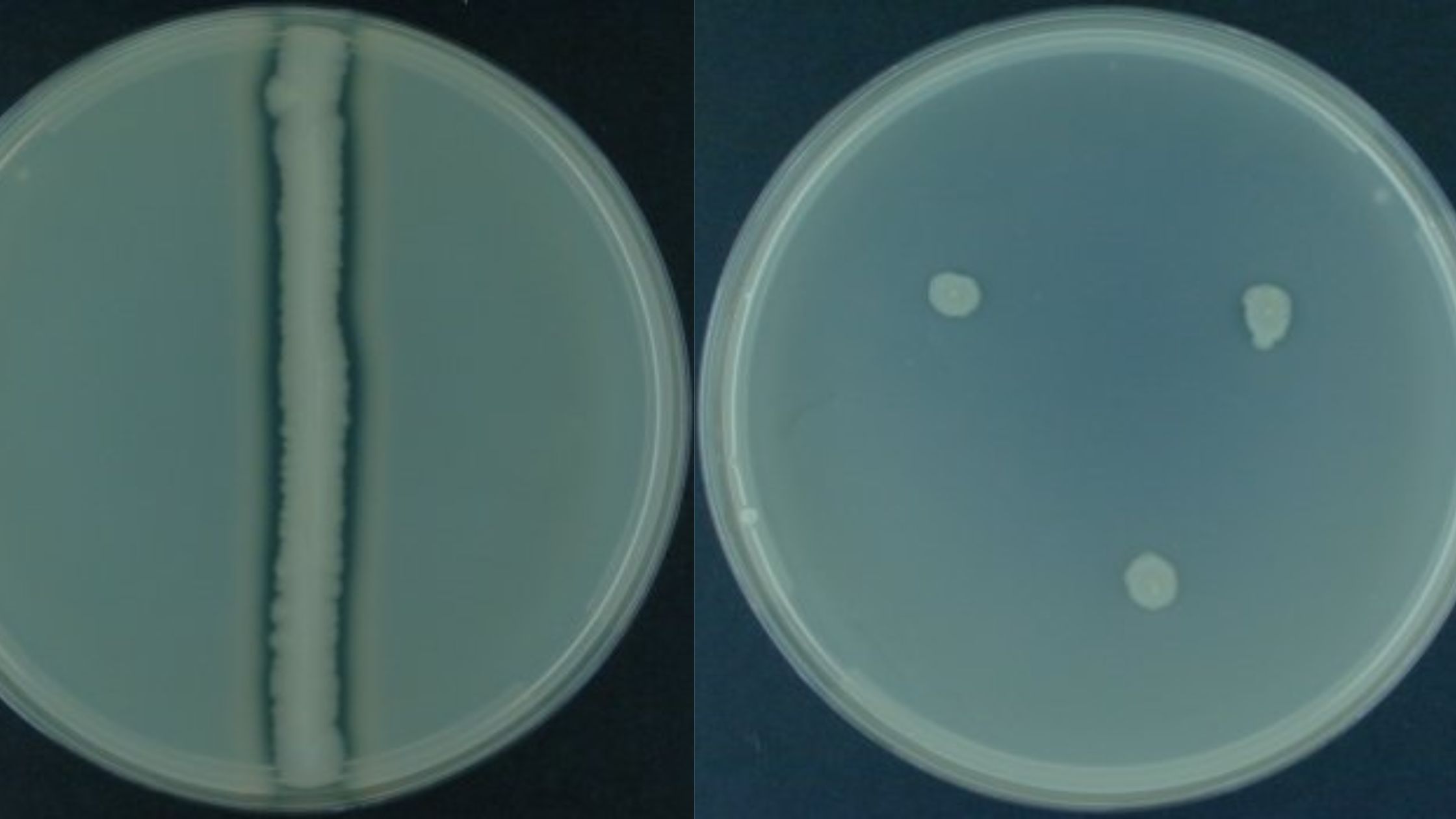
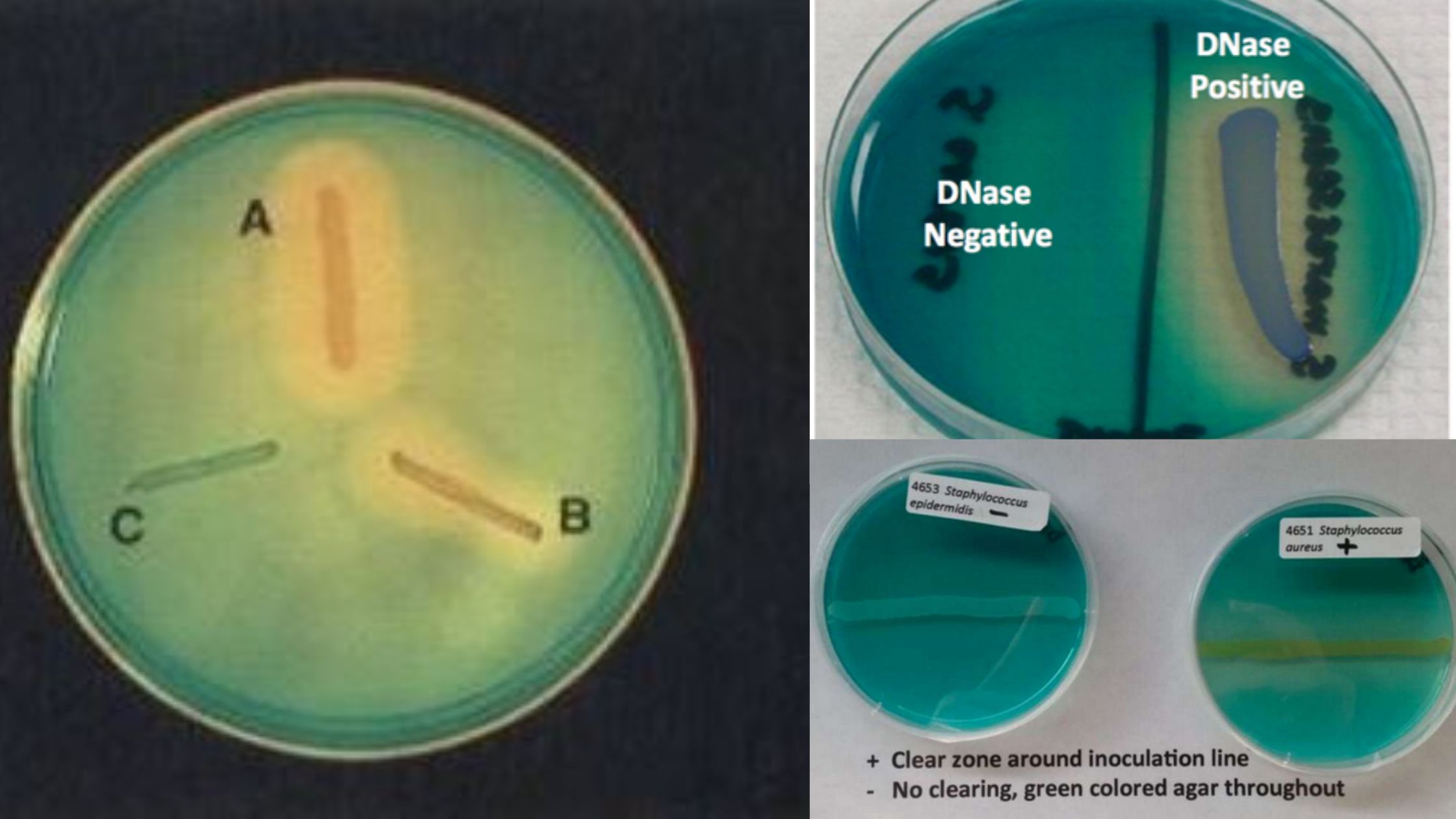
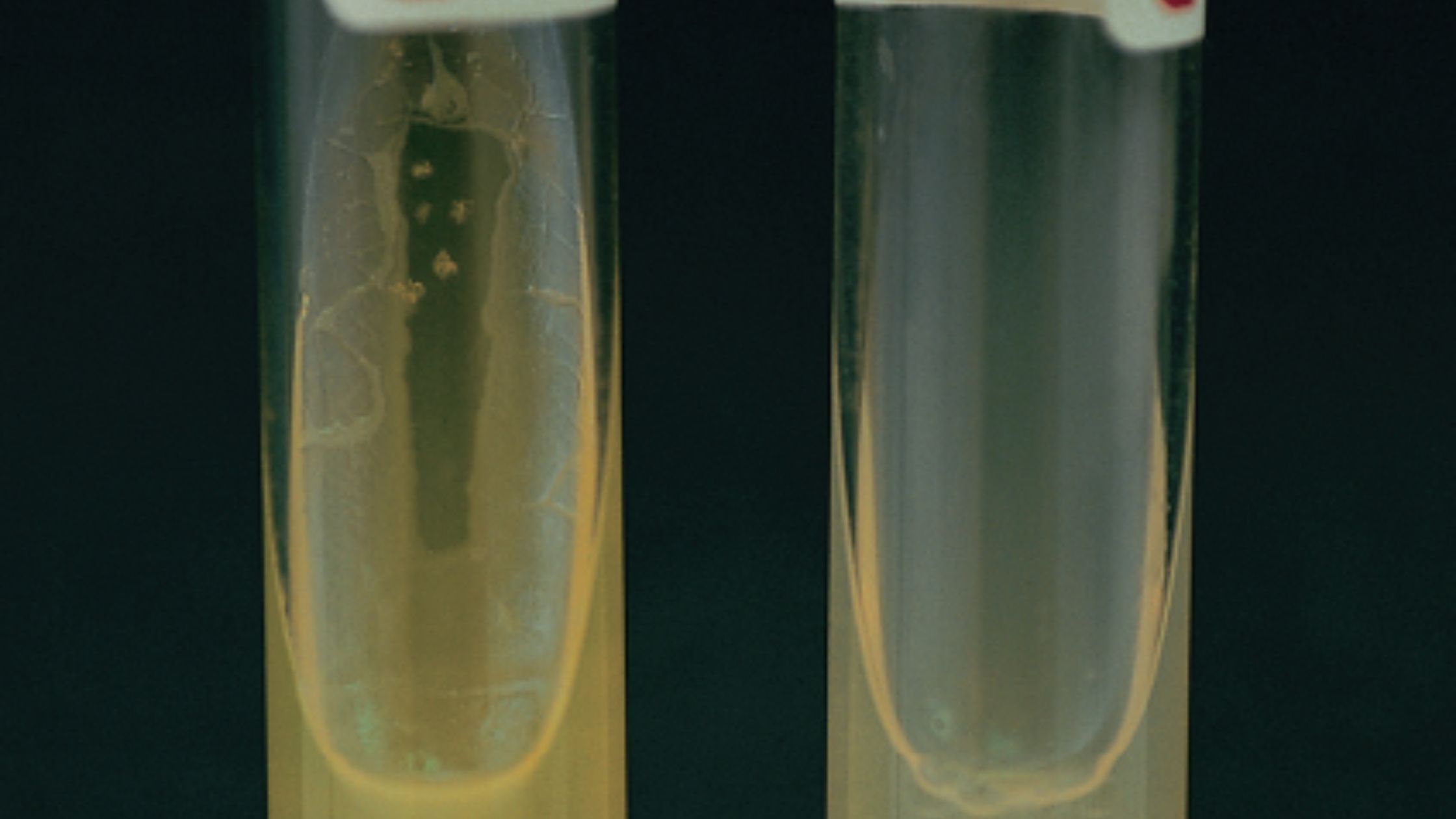
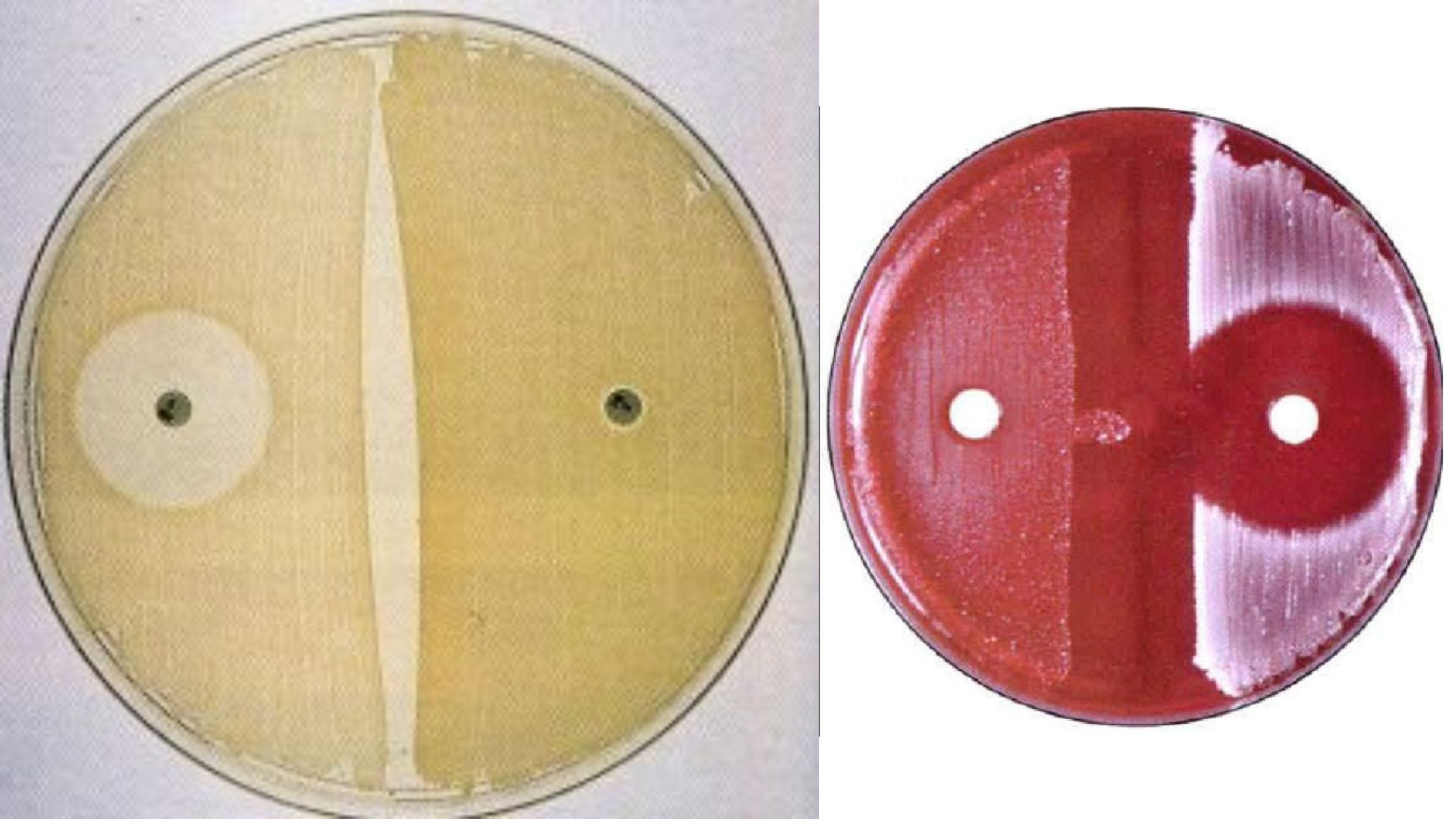
Test Name Casein Hydrolysis Test Detection Enzyme caseinase producing microorganisms Uses To show that some microorganisms can make enzymes outside of their cells that can break down the milk protein casein. Result A clear, transparent zone can be seen around the area where the colonies are growing, or sometimes under the area where the colonies … Read more