Table of Contents
What is Light Microscope?
- The light microscope, an essential instrument in the realm of biological research, is designed to magnify and elucidate the intricate details of microorganisms and minuscule objects that remain invisible to the unaided human eye. This device operates by manipulating light rays through a series of lenses to produce an enlarged image of the specimen under study.
- To begin with, the specimen to be observed is meticulously placed on a designated platform, commonly referred to as the stage. Once positioned, light rays are directed onto the specimen. These rays then pass through the specimen and are subsequently captured and magnified by the microscope’s lenses, allowing the observer to view the specimen’s details through the eyepieces.
- There are primarily two categories of light microscopes: the simple and the compound. The simple light microscope relies on a single lens or sometimes a combination of lenses to magnify the object. On the other hand, the compound light microscope, often just termed as the “compound microscope,” employs multiple lenses. In this configuration, one lens is strategically positioned close to the specimen, while the other lens works in tandem to further magnify the image.
- Besides its lens system, another pivotal component of the light microscope is the condenser. This element gathers the light rays and disperses them uniformly onto the specimen, ensuring optimal illumination. Therefore, the quality of the image produced is significantly influenced by the efficiency of the condenser.
- However, it’s essential to note that while the light microscope offers a plethora of advantages, it does have its limitations. Specifically, its resolution and magnification capabilities are relatively modest, especially when compared to its counterpart, the electron microscope. The resolution of a typical light microscope is approximately 0.2 µm, and its magnification power ranges between 500 to 1000 times the actual size of the specimen.
- Then, to emphasize its functionality, the light microscope serves as a gateway to the microscopic world, granting researchers and enthusiasts alike a glimpse into the intricate and often mesmerizing realm of microorganisms. Whether it’s for the study of bacteria, fungi, or cellular structures, the light microscope remains an indispensable tool in the arsenal of biological exploration.
Principle of Light Microscope
The light microscope, as its name suggests, employs light as its primary medium of observation. At its core, this instrument is designed to visualize the fine details of an object by producing a magnified image. The process begins with the focusing of a beam of light either onto or through the specimen. This is achieved through a series of carefully crafted glass lenses. Once the light interacts with the specimen, it is then captured by convex objective lenses. These lenses play a pivotal role in enlarging the image formed, allowing the observer to discern the minute details of the specimen. Therefore, the light microscope essentially functions by manipulating light through lenses to generate a magnified representation of the object under study.
Parts of Light Microscope
- Eyepiece Lens: Situated closest to the observer’s eye, the eyepiece lens can be composed of a single lens or a combination of multiple lenses. Its primary function is to further magnify the image initially enlarged by the objective lens. In essence, it transforms the real, intermediate image produced by the objective lens into a larger, virtual image for the observer.
- Lens Tube: This cylindrical structure houses the eyepiece. Typically measuring around 160 mm in length, the exact dimensions can vary based on the microscope’s design.
- Objective Revolver: A crucial component, the objective revolver securely holds multiple objective lenses, each boasting different magnifying capabilities. Users can effortlessly rotate this component to select the desired magnification level for observing the specimen.
- Objective Lens: Positioned closest to the specimen, the objective lens plays a pivotal role in image formation. It gathers light rays, reflects them through the numerical aperture, and subsequently offers a clear and detailed view of the specimen.
- Clip: This simple yet essential component firmly holds the glass slide bearing the specimen, ensuring it remains stationary during observation.
- Microscope Stage: This platform provides the necessary surface area for placing and maneuvering the specimen slide. It allows users to adjust the specimen’s position to focus on specific areas of interest.
- Condenser: Situated beneath the stage, the condenser gathers incident light and redirects it onto the specimen, ensuring optimal illumination and visibility.
- Fine and Coarse Focus: These two knobs regulate the distance between the specimen and the objective lens by adjusting the position of the microscope stage. To achieve a sharp, clear image, users can fine-tune both the fine and coarse focus knobs.
- Diaphragm: This component is instrumental in controlling the amount of light reaching the specimen. By adjusting the diaphragm, users can modulate the light’s diameter, preventing excessive brightness that might obscure the image.
- Light Source: Modern light microscopes typically employ LED bulbs to illuminate the specimen, providing consistent and adjustable lighting.
- Stand or Body: This structural component supports and holds together all the other parts of the microscope, ensuring stability and alignment.
- Base: Serving as the foundation of the microscope, the base imparts stability, ensuring the instrument remains steady during use.
What is Electron Microscope?
- The electron microscope stands as a pinnacle of technological advancement in the realm of microscopic observation. Unlike traditional optical microscopes that utilize light rays, this instrument harnesses the power of accelerated electron beams to produce magnified images of specimens. Its design and functionality are rooted in the principles of electron optics, making it a marvel in the field of microscopy.
- To begin with, the core of the electron microscope is its electron source, typically a heated tungsten filament. This filament emits a stream of electrons, which are then accelerated and directed towards the specimen under observation. As these electrons interact with the specimen, they generate detailed images that are captured on a detector.
- One of the most salient features of the electron microscope is its unparalleled resolution. It boasts a remarkable resolving power of 0.001 µm, which is a staggering 250 times greater than that of a light microscope. This superior resolution allows researchers to discern structures at the nanometer scale, revealing intricate details that would otherwise remain obscured.
- Besides its impressive resolution, the electron microscope also offers an astounding magnification capability. It can magnify specimens up to 1,000,000 times their actual size, granting scientists the ability to delve deep into the microcosm and explore entities that are beyond the reach of conventional microscopes.
- Then, to emphasize its functionality, the electron microscope serves as a window into the ultra-microscopic world. It has revolutionized various scientific disciplines, from biology to materials science, by providing unparalleled insights into the structure and composition of materials at the atomic and molecular levels.
- Therefore, in the realm of microscopy, the electron microscope stands as a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of knowledge. It has not only expanded our understanding of the microscopic world but has also paved the way for groundbreaking discoveries and innovations in numerous scientific fields.
Principle of Electron Microscope
Venturing into the realm of electron microscopy, one encounters a vastly different operational principle. Electrons, due to their minuscule nature, exhibit wave-like properties, akin to photons in light. The electron microscope harnesses a beam of these electrons, directing them through the specimen. As these electrons traverse the specimen, they are scattered by the atoms present within. This scattering forms the basis of the image generation in electron microscopy.
Besides the use of electrons for illumination, another distinguishing feature of the electron microscope is its lens system. Instead of the traditional glass lenses found in light microscopes, electron microscopes employ either electrostatic or electromagnetic lenses. These specialized lenses are adept at manipulating the electron beam, ensuring optimal image formation.
Then, to emphasize the differences, while light microscopes utilize photons or light energy, electron microscopes rely on electrons. The shorter wavelengths of electrons grant them a significant advantage in terms of magnification. This results in the electron microscope achieving a resolution far superior to that of its optical counterpart.
Parts of Electron Microscope
- Electron Gun: Situated at the topmost part of the microscope, the electron gun is responsible for generating the beam of accelerated electrons. This is achieved primarily through the heating of a tungsten filament, which emits electrons when subjected to voltages ranging from 100 to 1000 kV.
- Condenser Lens: The electron microscope is equipped with two magnetic condenser lenses. Their primary function is to converge the electron beam, directing it precisely onto the specimen.
- Objective Lens: This magnetic lens plays a crucial role in focusing the electron beam onto the specimen. In doing so, it forms the first real, intermediate magnified image, which can be enlarged up to 2000 times the actual size of the specimen.
- Projector Lens: Situated below the objective lens, the projector lens takes on the task of further magnifying the real intermediate image. Its capabilities are impressive, with the potential to magnify the image up to 240,000 times or even more.
- Viewing Screen: To visualize the magnified image, the electron microscope employs a specialized viewing screen. Typically, this screen is made of zinc sulphate, which exhibits fluorescent properties. Alternatively, a photographic plate can also be used to capture and view the image.
- Camera: Located beneath the viewing screen is the camera, specifically a charged coupled device (CCD). This component captures the magnified images, allowing for detailed analysis and documentation.
- Specimen Holder: The specimen to be observed is meticulously placed on a thin film, either made of carbon or collodion. This film is then securely held by a metal grid, ensuring the specimen remains stationary during the imaging process.
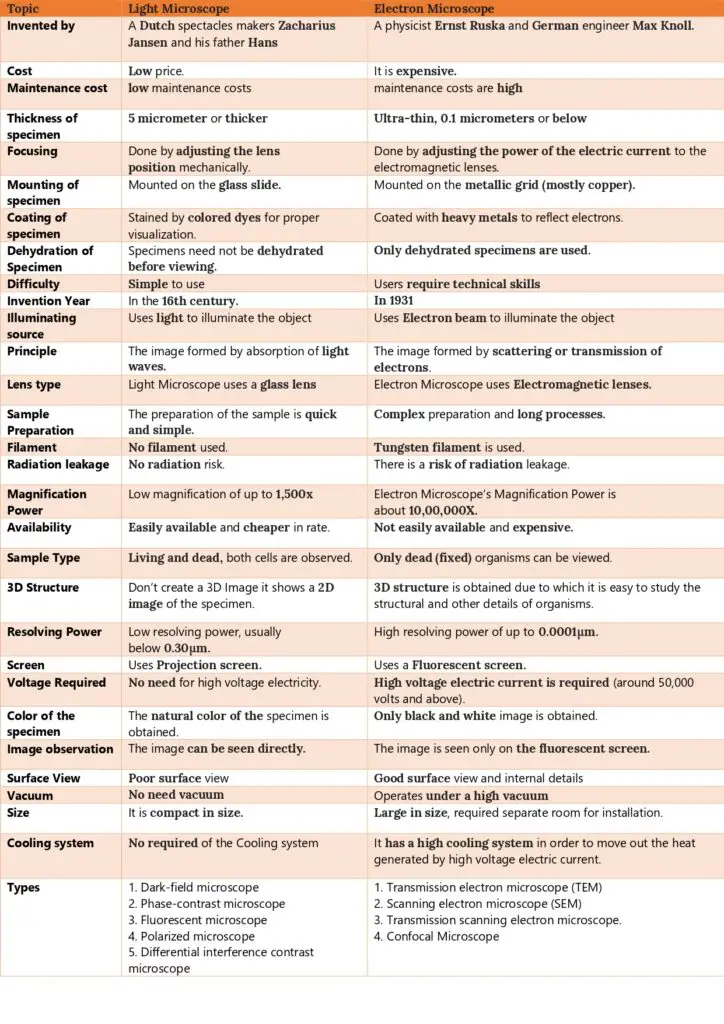
Difference Between Light Microscope and Electron Microscope
- Source of Illumination: The light microscope utilizes light rays to illuminate the specimen, typically with wavelengths ranging from 400-700 nm. In contrast, the electron microscope harnesses a beam of electrons for this purpose, with an approximate equivalent wavelength of 1 nm.
- Historical Context: The light microscope’s origins trace back to the 16th century, with Dutch spectacles makers Zacharius Jansen and his father Hans credited for its invention. On the other hand, the electron microscope was introduced much later, in 1931, by physicist Ernst Ruska and German engineer Max Knoll.
- Operational Principle: In a light microscope, images are formed based on the absorption of light waves. Conversely, the electron microscope forms images through the scattering or transmission of electrons.
- Structural Aspects: Light microscopes are generally smaller and lighter, making them more portable. Electron microscopes, due to their intricate components, are heftier and larger.
- Lens Composition: The lenses in a light microscope are crafted from glass. In contrast, the electron microscope employs electromagnetic lenses, adept at manipulating electron beams.
- Vacuum Requirement: While light microscopes operate without the need for a vacuum, electron microscopes necessitate a high vacuum environment for optimal functioning.
- Specimen Considerations: Light microscopes offer the flexibility to observe both live and dead specimens, whether they’re fixed, stained, or unstained. Electron microscopes, due to their operational constraints, are limited to observing fixed, stained,
- and non-living specimens.
- Specimen Preparation: Preparing specimens for a light microscope is relatively straightforward and less tedious. However, for electron microscopy, the process is more complex, often involving harsh chemicals and requiring more skill. Moreover, while light microscopy can handle specimens that are 5 micrometers or thicker, electron microscopy demands ultra-thin specimens, typically 0.1 micrometers or below.
- Image Visualization: Images from a light microscope can be viewed directly through the eyepiece, producing colored images. In contrast, electron microscopes project images onto a fluorescent screen or photographic plate, resulting in grayscale or “black and white” images.
- Magnification and Resolution: Light microscopes offer a magnification of up to 1,500x with a resolving power below 0.30µm. Electron microscopes, however, boast a magnification of up to 1,000,000x and a superior resolving power of up to 0.001µm.
- Operational Complexity: Light microscopes are simpler to use, making them suitable for educational settings and basic research. Electron microscopes, due to their complexity, require technical expertise and are primarily used in specialized research environments.
- Cost Implications: Light microscopes are more affordable, both in terms of purchase and maintenance. Electron microscopes, given their advanced technology, are significantly more expensive.
- Applications: While light microscopes are versatile, suitable for studying a range of specimens from pond life to cell division, electron microscopes are employed for more specialized tasks. They are invaluable in studying the ultrastructure of cells, tiny organisms, and surface structures in great detail.
- Safety and Infrastructure: Electron microscopes, due to their high voltage requirements, pose a risk of radiation leakage and necessitate controlled room settings. Light microscopes, being less complex, do not have such requirements.
Light Microscope vs Electron Microscope Chart
| Parameter | Light Microscope | Electron Microscope |
|---|---|---|
| Source of Illumination | Uses light rays (400-700 nm wavelength) | Uses a beam of electrons (~1 nm wavelength) |
| Historical Context | Invented by Zacharius Jansen in the 16th century | Introduced in 1931 by Ernst Ruska and Max Knoll |
| Operational Principle | Forms images by absorbing light waves | Forms images through scattering or transmission of electrons |
| Structural Aspects | Smaller and lighter | Heavier and larger |
| Lens Composition | Glass lenses | Electromagnetic lenses |
| Vacuum Requirement | No vacuum needed | Requires a high vacuum |
| Specimen Considerations | Can observe live and dead, fixed, stained, or unstained specimens | Observes fixed, stained, non-living specimens |
| Specimen Preparation | Straightforward and less tedious | Complex, often involving harsh chemicals |
| Image Visualization | Directly viewed through eyepiece, colored images | Viewed on a fluorescent screen, grayscale images |
| Magnification & Resolution | Up to 1,500x, resolving power below 0.30µm | Up to 1,000,000x, resolving power up to 0.001µm |
| Operational Complexity | Simple to use | Requires technical expertise |
| Cost Implications | Affordable, low maintenance costs | Expensive to purchase and maintain |
| Applications | Versatile, suitable for various specimens | Specialized; for studying ultrastructure of cells and tiny organisms |
| Safety & Infrastructure | No radiation risk, no special room settings required | Risk of radiation leakage, requires controlled room settings |