Table of Contents
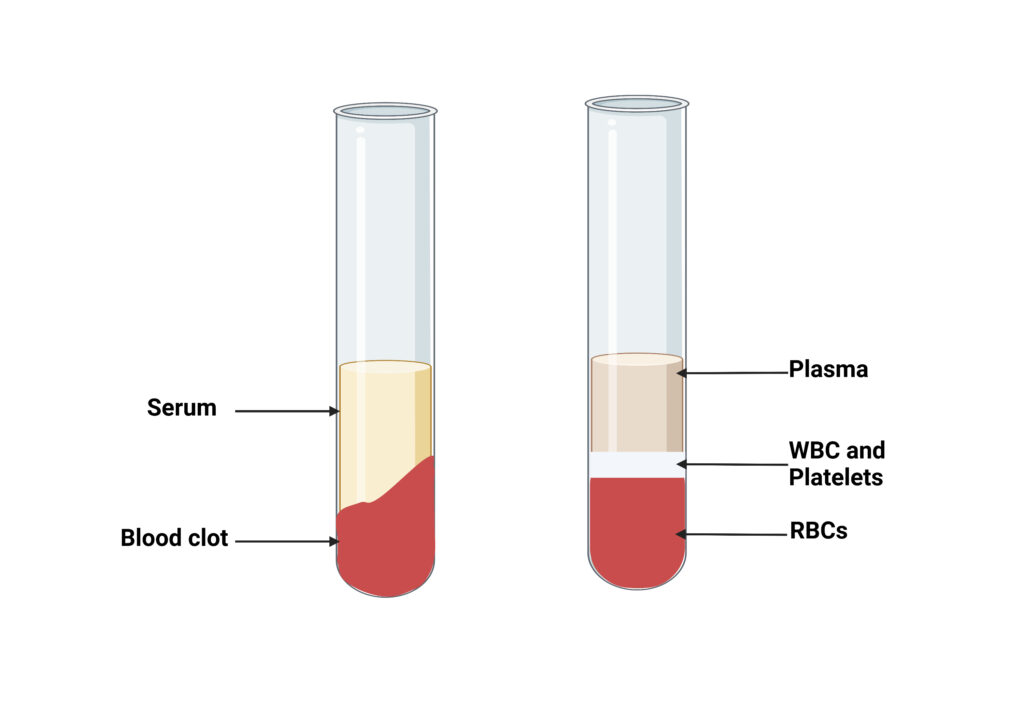
Plasma and serum are two blood derivatives which do not have blood cells such as red blood cells white blood cells and platelets. Both are enriched with proteins, drugs hormones, toxins and electrolytes. Both plasma and serum can be used to treat and diagnose. They are separated from blood using centrifugation, which eliminates the blood’s cellular component. Blood is infused with anticoagulants when it has been transfused to stop the clotting. The serum color is amber, while the plasma color is straw. The primary difference between serum as well as plasma lies in the fact that the latter is a protein-rich liquid that separates when blood is coagulated, whereas plasma forms the liquid part of blood that holds blood cells suspended.
What is Serum?
It is an amber colored fluid portion of blood of animals that persists after blood coagulation. Thus, the serum is devoid of blood cells such as white blood cells, as well as platelets. Also, it is deficient in fibrinogen, a coagulation factor, in. However, serum has all the proteins , including albumin and globulin, which aren’t involved in blood coagulation. Additionally, it contains antibodies, antigens, electrolytes and medications, hormones and microorganisms. The study of serology involves the study of the serum. Blood is isolated from serum through centrifugation. This eliminates the cellular component of blood. This is followed by the process of coagulation. The process removes the clotting agents like prothrombin, fibrinogen and tissue thromboplastin from blood. The serum is a great supply of electrolytes. It can be used in different tests to determine enzymes and hormones. It is also used for determination of blood group as well. Animal sera are utilized as an anti-venom, antitoxins, or vaccinations. The serum is kept at 2-6 degrees Celsius for a period of time.
What is Plasma?
The plasma is the liquid component of blood. It’s a straw-colored salt-protein solution that suspends platelets and blood cells. Therefore, plasma functions as an extracellular fluid. It is responsible for 55 percent of the total amount of blood. The content of water in plasma is approximately 92 percent. Plasma contains dissolved proteins such as albumin, globulin and fibrinogen glucose, clotting factors, glucose hormones, electrodelytes, carbon dioxide and oxygen. It helps maintain a healthy blood volume and pressure, and balances the body’s pH and acts as a medium to exchange minerals such as potassium and sodium.
Plasma can be separated from the cell portion through centrifugation. Four plasma units are reduced by one component of the anticoagulant citrate phosphate dextrose (CPD) up to 300 milliliters. If the plasma sample is frozen within eight hours of its collection, it’s called freshly frozen plasma (FFP). If it’s frozen for more than 8 hours, but not more that 24 hours in duration, then the sample is referred to as frozen plasma (FP). After preservation with antioxidants, freeze-dried plasma may be stored for up to one year at -18oC. Plasma transfusions are performed for patients suffering from trauma, who suffer from severe liver disorders as well as for patients with multiple clotting factors deficiency. Plasma derivatives such as specific plasma proteins are extracted through fractionation. The viruses that are responsible for HIV Hepatitis B as well as C are destroyed through treatment by heating or solvent detergents.
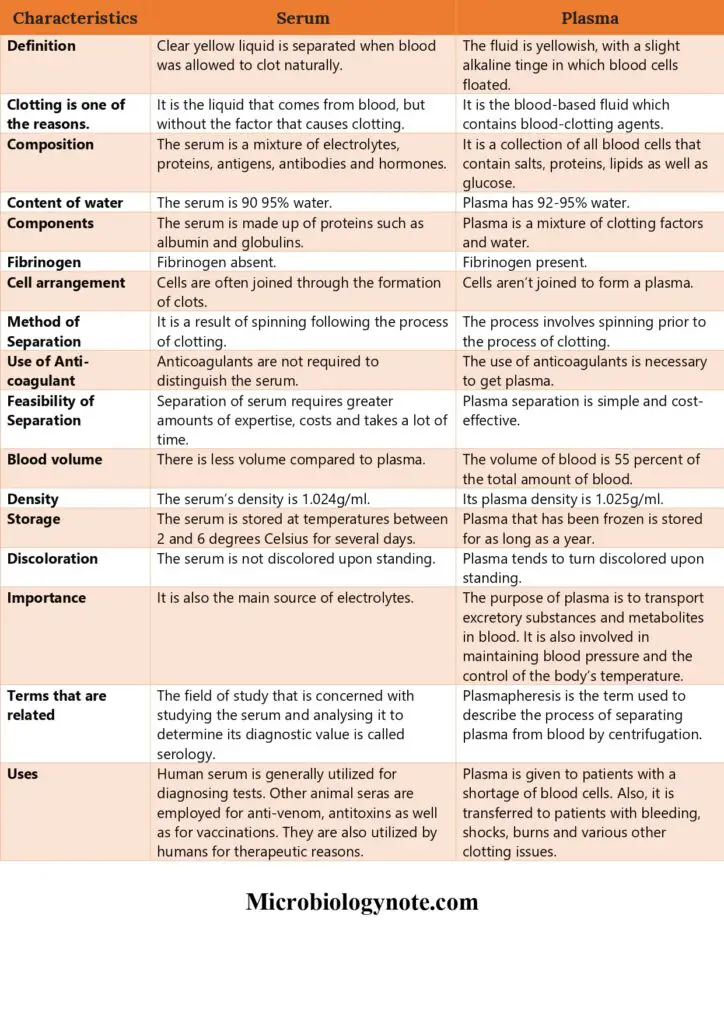
Differences between Serum and Plasma – Serum vs Plasma
| Characteristics | Serum | Plasma |
| Definition | Clear yellow liquid is separated when blood was allowed to clot naturally. | The fluid is yellowish, with a slight alkaline tinge in which blood cells floated. |
| Clotting is one of the reasons. | It is the liquid that comes from blood, but without the factor that causes clotting. | It is the blood-based fluid which contains blood-clotting agents. |
| Composition | The serum is a mixture of electrolytes, proteins, antigens, antibodies and hormones. | It is a collection of all blood cells that contain salts, proteins, lipids as well as glucose. |
| Content of water | The serum is 90 95% water. | Plasma has 92-95% water. |
| Components | The serum is made up of proteins such as albumin and globulins. | Plasma is a mixture of clotting factors and water. |
| Fibrinogen | Fibrinogen absent. | Fibrinogen present. |
| Cell arrangement | Cells are often joined through the formation of clots. | Cells aren’t joined to form a plasma. |
| Method of Separation | It is a result of spinning following the process of clotting. | The process involves spinning prior to the process of clotting. |
| Use of Anti-coagulant | Anticoagulants are not required to distinguish the serum. | The use of anticoagulants is necessary to get plasma. |
| Feasibility of Separation | Separation of serum requires greater amounts of expertise, costs and takes a lot of time. | Plasma separation is simple and cost-effective. |
| Blood volume | There is less volume compared to plasma. | The volume of blood is 55 percent of the total amount of blood. |
| Density | The serum’s density is 1.024g/ml. | Its plasma density is 1.025g/ml. |
| Storage | The serum is stored at temperatures between 2 and 6 degrees Celsius for several days. | Plasma that has been frozen is stored for as long as a year. |
| Discoloration | The serum is not discolored upon standing. | Plasma tends to turn discolored upon standing. |
| Importance | It is also the main source of electrolytes. | The purpose of plasma is to transport excretory substances and metabolites in blood. It is also involved in maintaining blood pressure and the control of the body’s temperature. |
| Terms that are related | The field of study that is concerned with studying the serum and analysing it to determine its diagnostic value is called serology. | Plasmapheresis is the term used to describe the process of separating plasma from blood by centrifugation. |
| Uses | Human serum is generally utilized for diagnosing tests. Other animal seras are employed for anti-venom, antitoxins as well as for vaccinations. They are also utilized by humans for therapeutic reasons. | Plasma is given to patients with a shortage of blood cells. Also, it is transferred to patients with bleeding, shocks, burns and various other clotting issues. |