Table of Contents
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on Eastern blot protocol, principle, and applications. In the field of molecular biology, Eastern blot has emerged as a valuable technique for detecting post-translational modifications in proteins, as well as the presence of lipids and carbohydrates. In this article, we will delve into the step-by-step protocol of Eastern blotting, explore its underlying principles, and discuss its diverse applications in protein analysis. Whether you’re a researcher, scientist, or student, this guide will provide you with the essential knowledge to understand and implement Eastern blot in your experiments. Let’s dive in and unlock the potential of this powerful molecular biology tool.
What is Eastern blotting?
- Eastern blot is a powerful molecular biology technique used for detecting post-translational modifications in proteins, as well as the presence of lipids and carbohydrates. As an extension of the popular western blotting technique, Eastern blot has emerged as a valuable tool in protein analysis.
- The primary objective of Eastern blot is to identify and study the differences in post-translational modifications across various species. By detecting the presence of biomolecules in different proteins, researchers can gain insights into the intricate modifications occurring within these molecules.
- The principle and procedure of Eastern blotting are similar to other blotting techniques. However, the specific molecule or particle being detected may vary. Notably, Eastern blot has undergone modifications to develop a related technique called far-western blotting, which focuses on studying lipids separated by chromatography.
- Eastern blotting enables the analysis of proteins, lipids, and glycoconjugates, with a particular emphasis on detecting carbohydrate epitopes. It can be viewed as an extension of western blotting, which primarily detects protein post-translational modifications (PTMs). The technique involves transferring proteins or lipids from an SDS-PAGE gel onto a PVDF or nitrocellulose membrane.
- Once the proteins are transferred, they are subjected to analysis for post-translational modifications using specific probes. These probes can detect various modifications such as lipids, carbohydrates, phosphorylation, and other protein modifications. It’s important to note that Eastern blotting refers to methods that rely on the specific interaction between the PTM and the probe, distinguishing it from a standard far-western blot.
- While Eastern blotting is conceptually similar to lectin blotting, which detects carbohydrate epitopes on proteins or lipids, the term “lectin blotting” is more commonly used in the scientific literature.
- In summary, Eastern blot is a versatile technique in molecular biology that allows researchers to explore post-translational modifications and the presence of biomolecules in proteins. By utilizing specific probes, Eastern blotting offers valuable insights into the intricate world of protein modifications, paving the way for advancements in various biological studies.
Eastern blotting Definition
Eastern blotting is a molecular biology technique used to detect post-translational modifications in proteins and identify the presence of lipids and carbohydrates. It involves transferring proteins or lipids from a gel onto a membrane, followed by analysis using specific probes to detect various modifications. Eastern blotting provides valuable insights into protein modifications and is commonly used in research and biomedical applications.
Purposes of Eastern blotting
he purposes of Eastern blotting, a molecular biology technique, are as follows:
- Detection of post-translational modifications: Eastern blotting allows the identification and analysis of post-translational modifications (PTMs) in proteins. This technique helps researchers understand how proteins are modified after translation, such as the addition of lipids, carbohydrates, phosphates, or other modifications.
- Characterization of protein diversity: Eastern blotting enables the study of differences in post-translational modifications across different species or samples. By detecting and comparing the presence or absence of specific biomolecules in proteins, researchers can gain insights into the diversity and variations within protein populations.
- Identification of specific biomolecules: Eastern blotting can be used to identify the presence of specific biomolecules, such as lipids and carbohydrates, in proteins. This information is valuable for understanding the role of these molecules in protein function, signaling pathways, and disease processes.
- Comparative analysis: Eastern blotting allows for the comparison of protein modifications between different samples or experimental conditions. By analyzing the patterns and intensity of protein bands, researchers can draw comparisons and identify potential differences or similarities in PTMs.
- Research and biomedical applications: Eastern blotting is widely used in research and biomedical fields to study protein modifications, biomarker discovery, protein-protein interactions, and disease-related changes. It plays a crucial role in advancing our understanding of cellular processes, disease mechanisms, and potential therapeutic targets.
Eastern blot Principle
The principle of Eastern blotting, a potent immunoblotting method, is comparable to that of other blotting techniques. It relies on the specific interaction between the target biomolecule and a probe to distinguish it from a mélange of other biomolecules.
In Eastern blotting, proteins are initially separated on a polyacrylamide gel by electrophoresis, effectively isolating them from the complex mixture. The separated proteins are then transferred onto a nitrocellulose or nylon membrane, where their specific interaction with the probes enables the detection of target molecules.
Identification of this interaction is possible using a radioactive probe or a secondary molecule with a tag, analogous to ELISA. In both instances, the ultimate Eastern blot result is determined by the specificity and extent of antigen-antibody interactions.
Both Eastern blotting and lectin blotting are utilised to detect carbohydrate epitopes on proteins and lipids. This is a significant similarity between the two techniques. This is especially significant when studying smaller molecular compounds, whose detection cannot be accomplished using immunostaining alone.
Utilising the principles of specific interaction and detection, Eastern blotting provides researchers with a valuable instrument for exploring and gaining crucial insights into protein modifications and the presence of specific biomolecules.
Unlocking the potential of Eastern blotting provides researchers with a deeper understanding of complex biological processes and facilitates advances in a variety of disciplines, including biomarker discovery, disease research, and therapeutics.
Requirements for Eastern blot
To perform Eastern blotting effectively, certain requirements and materials are necessary. Here is a list of the key requirements for conducting an Eastern blot, ensuring accurate detection and analysis of target molecules.
- Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) Plate: A TLC plate serves as the initial platform for separating the components of interest. It is composed of a solid support, such as glass or aluminum, coated with a thin layer of adsorbent material, like silica gel or cellulose. The TLC plate allows for the separation of different molecules based on their chemical properties.
- Transfer Membrane: A transfer membrane, typically made of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), is used to transfer the components from the TLC plate onto its surface. The membrane should have good binding capacity and compatibility with subsequent steps in the Eastern blot protocol.
- NaIO4 Solution: Sodium periodate (NaIO4) solution is used to fix the components from the TLC plate onto the transfer membrane. This solution enables the stable attachment of molecules to the membrane surface, ensuring their retention for subsequent detection steps.
- Blotting Solution: A suitable blotting solution is required for the transfer of components from the TLC plate to the transfer membrane. This solution can be applied by pressing or heating the membrane against the plate or by utilizing an electroblotting apparatus to pass an electric current through the structure.
- Na2CO3/NaHCO3 Buffer: A buffer solution containing sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) and sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) is used for creating an alkaline condition necessary for the preparation of hapten-BSA conjugates on the transfer membrane. This buffer facilitates the formation of stable conjugates and enhances the sensitivity of the Eastern blot.
- Stainless Steel Plate: A stainless steel plate, often placed beneath the transfer membrane during the transfer process, serves as a support to ensure even pressure or uniform electric field distribution. It provides stability and assists in achieving a successful transfer of components onto the transfer membrane.
By having these essential requirements, including a TLC plate for initial separation, a transfer membrane for component transfer, a NaIO4 solution for fixation, a suitable blotting solution for transfer, a Na2CO3/NaHCO3 buffer for conjugate formation, and a stainless steel plate for support, researchers can conduct Eastern blotting accurately and efficiently. These materials are crucial in enabling the successful detection and analysis of specific molecules, thereby advancing scientific understanding in various fields of research.
Eastern blot Protocol/Procedure
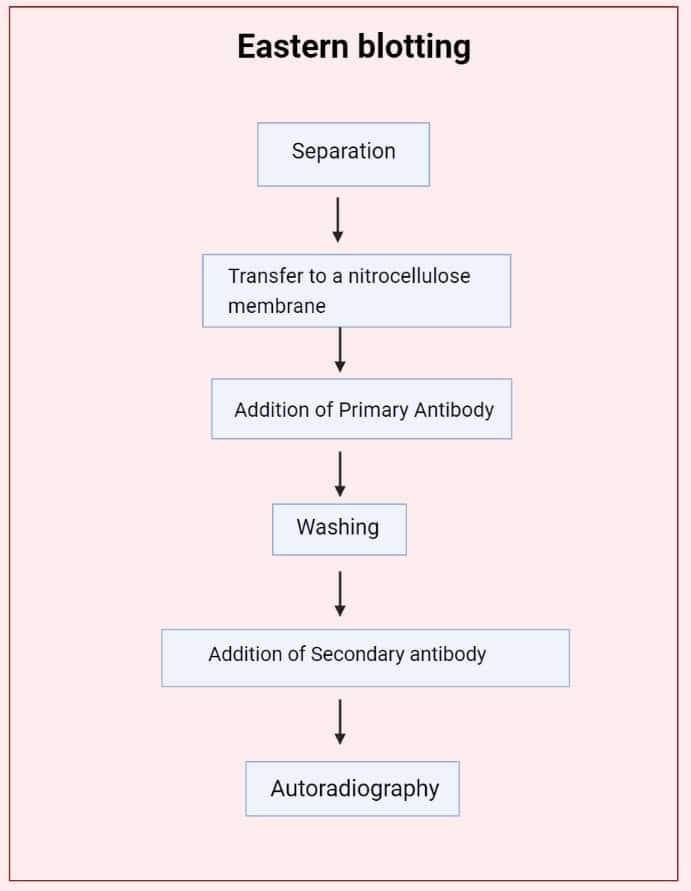
Eastern blotting is a technique used to detect and analyze specific molecules, such as haptens, on a membrane surface. It is a variation of the well-known Western blotting method. In this step-by-step guide, we will outline the protocol for performing an Eastern blot, highlighting its principle and key steps.

- TLC Plate Development: Begin by performing thin-layer chromatography (TLC) to separate the components of interest. The TLC plate is developed to reveal distinct spots representing different molecules.
- Membrane Transfer: Place a PVDF membrane on top of the developed TLC plate. The transfer of components from the plate to the membrane can be achieved by either pressing the membrane against the plate or applying heat. Alternatively, an electric current can be passed through the structure to facilitate the transfer.
- Sodium Periodide Treatment: Once the transfer is complete, treat the membrane with sodium periodide solution. This step fixes the components onto the membrane surface. Incubate the membrane in the solution for approximately 1 hour, followed by thorough washing with water to remove any excess reagents.
- Hapten-BSA Conjugate Formation: Prepare a solution of hapten-BSA conjugate by immersing the membrane in a buffer solution, typically Na2CO3/NaHCO3 at alkaline conditions. This step allows the formation of a conjugate between the hapten (target molecule) and BSA (bovine serum albumin), serving as a carrier protein.
- Blocking: Block any non-specific binding sites on the membrane by incubating it in a solution containing 5% skim milk or BSA in PBS (phosphate-buffered saline) for about 3 hours. This step reduces background noise and prevents unwanted interactions.
- Primary Antibody Incubation: Introduce a monoclonal antibody (MAb) onto the membrane surface. The MAb specifically recognizes and binds to the hapten conjugated with BSA. This interaction is crucial for the detection of the target molecule.
- Secondary Antibody Addition: Apply a second antibody labeled with peroxidase to the membrane. This secondary antibody recognizes and binds to the primary antibody, enabling signal amplification. The peroxidase label allows for subsequent visualization.
- Substrate Addition and Staining: Introduce a suitable substrate onto the membrane. The peroxidase label catalyzes a reaction with the substrate, resulting in the generation of a detectable signal (e.g., color change or chemiluminescence). This staining step allows visualization and quantification of the target molecule.
By following these steps, Eastern blotting enables the detection and analysis of specific molecules, such as haptens, on a membrane surface. The technique relies on the formation of hapten-BSA conjugates and the interaction between monoclonal antibodies and the target molecule. Finally, visualization of the antibodies’ binding is achieved through the addition of a peroxidase-labeled secondary antibody and subsequent staining with a suitable substrate. Eastern blotting provides a valuable tool for researchers studying various biological molecules and their interactions.
Result Interpretation
Interpreting the results of an Eastern blot is a crucial step in understanding the presence or absence of target molecules. The interpretation primarily depends on the type of label used in the second antibody. Here are the key aspects to consider when analyzing the Eastern blot results.
- Label Type: The second antibody used in the Eastern blot is typically labeled with a detection method, such as an enzyme (e.g., peroxidase) or a radioactive molecule (e.g., 32P). The choice of label depends on the specific requirements of the experiment and the desired detection sensitivity.
- Positive Result: A positive result in Eastern blotting is indicated by the appearance of color or radioactivity on the membrane. This occurs when the second antibody, labeled with the chosen detection method, successfully binds to the primary antibody that recognizes the target molecule (hapten-BSA conjugate). The signal generated by the label allows for the visualization and identification of the target molecule.
- Negative Result: Conversely, a negative result in Eastern blotting is indicated by the absence of color or radioactivity on the membrane. This implies that the second antibody did not bind to the primary antibody and, therefore, the target molecule was not detected. It is important to note that a negative result could also arise from technical issues, such as insufficient washing steps or improper antibody incubation.
In both positive and negative results, the presence or absence of color or radioactivity provides valuable information about the target molecule’s presence or absence on the transfer membrane. By comparing the results to appropriate controls and standards, researchers can draw conclusions about the expression, abundance, or other characteristics of the target molecule in the studied sample.
Proper result interpretation in Eastern blotting requires careful consideration of the labeling method, the appearance or absence of color or radioactivity, and the establishment of appropriate positive and negative controls. By understanding and analyzing these results, researchers can gain insights into the presence or absence of target molecules, contributing to the advancement of scientific knowledge in various fields of research.
What is Far-estern Blotting?
Far-Eastern blotting is a specialized technique used for the detection and analysis of lipid-linked oligosaccharides. It is a variation of the traditional Eastern blotting method, specifically tailored to study these complex carbohydrate structures. In this brief explanation, we will outline the basic principles and key aspects of Far-Eastern blotting.
Developed by Taki and colleagues in 1994, Far-Eastern blotting involves several essential steps to visualize and analyze lipid-linked oligosaccharides.
- HPTLC Separation: The process begins with High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography (HPTLC), where the lipid-linked oligosaccharides are separated based on their chemical properties. This technique enables the isolation of different oligosaccharide components, allowing for subsequent analysis.
- Transfer to Blotting Matrix: Once the separation is complete, the lipid-linked oligosaccharides are transferred from the HPTLC plate to a blotting matrix. The choice of matrix can vary but typically includes materials such as nitrocellulose or PVDF membranes, similar to those used in traditional Eastern blotting.
- Specific Binding Protein Detection: The key step in Far-Eastern blotting is the detection of lipid-linked oligosaccharides using specific binding proteins, such as antibodies or lectins. These proteins have a high affinity for the target oligosaccharides and facilitate their detection on the blotting matrix. Antibodies can be generated against specific lipid-linked oligosaccharides, while lectins are proteins that naturally recognize specific sugar structures.
- Visualization and Analysis: After the binding of specific binding proteins, the presence of lipid-linked oligosaccharides on the blotting matrix can be visualized and analyzed. Various techniques can be employed for visualization, including enzyme-based colorimetric or chemiluminescent reactions.
Far-Eastern blotting allows researchers to gain insights into the presence, abundance, and structure of lipid-linked oligosaccharides in a sample. By utilizing specific binding proteins, such as antibodies or lectins, the technique offers a valuable tool for studying complex carbohydrates and their role in biological processes.
In summary, Far-Eastern blotting is a specialized variant of Eastern blotting that focuses on the detection and analysis of lipid-linked oligosaccharides. It involves HPTLC separation, transfer to a blotting matrix, and subsequent detection using specific binding proteins. This technique provides researchers with a powerful method to explore the complexity of carbohydrate structures and their functional implications in various biological systems.
Limitations of Eastern Blot
Eastern blotting, despite its utility as a method for detecting and analyzing specific molecules, has certain limitations that researchers should consider. Here are some key limitations of the Eastern blot technique:
- Complexity and Prone to Errors: Eastern blotting involves multiple steps and requires careful execution. The technique can be challenging, especially for beginners, and is susceptible to errors at various stages. It demands attention to detail and precision during sample preparation, membrane handling, antibody incubation, and detection steps. Any mistakes in these processes can lead to inaccurate or unreliable results.
- Training and Expertise: Performing Eastern blotting requires trained personnel who are familiar with the technique and its nuances. Adequate training and expertise are necessary to ensure proper execution and interpretation of results. The involvement of skilled researchers adds to the complexity and cost of implementing the technique in a laboratory setting.
- Sample Amount Requirement: Eastern blotting often requires a relatively large amount of sample for analysis. This can be problematic in cases where the target molecules or proteins have limited yield, such as rare or low-abundance compounds. Insufficient sample quantity may compromise the sensitivity and reliability of the technique.
- Challenges in Quantification: Accurate quantification of proteins and biomolecules using Eastern blotting can be challenging. Unlike some other methods, such as Western blotting, Eastern blotting does not provide a straightforward and precise quantification of target molecules. The detection signal obtained from the labeling and staining process may not directly correlate with the abundance or concentration of the target molecule, making quantitative analysis more difficult.
- Potential Protein Structure Alteration: The interaction between the probe (antibody or other binding protein) and the biomolecules on the membrane may occasionally disrupt the tertiary structure of proteins. This alteration could affect the functionality and stability of the proteins, leading to potential artifacts or misinterpretation of results. Careful consideration should be given to choosing appropriate probes and optimizing experimental conditions to minimize such effects.
It is important to be aware of these limitations when planning and conducting Eastern blot experiments. Researchers should carefully address potential sources of error, optimize conditions, and consider alternative techniques if the limitations significantly impact their study objectives. By acknowledging and working around these limitations, researchers can make the most of Eastern blotting as a valuable tool for molecular analysis.
Eastern blot Application
Eastern blotting finds widespread application in various areas of research due to its ability to detect and analyze post-translational modifications and other molecular interactions. Here are some key applications of Eastern blotting:
- Analysis of Post-Translational Modifications: Eastern blotting is particularly valuable for studying post-translational modifications (PTMs) in proteins. It allows researchers to identify and characterize modifications such as phosphorylation, glycosylation, acetylation, and more. This information helps in understanding the functional significance of PTMs and their role in cellular processes.
- Identification and Purification of Plant Products: Eastern blotting has been utilized in the identification and purification of different plant products. It enables the detection of specific compounds or molecules in plant extracts, aiding in the isolation and characterization of plant-derived bioactive compounds or natural products.
- Detection of Protein Modifications in Different Origins: Eastern blotting can be applied to detect modifications in proteins from diverse sources, including bacteria, plants, animals, and human samples. It offers a versatile platform for studying modifications and their implications in different biological systems.
- Investigation of Molecular Interactions: By employing ligands or specific binding proteins, Eastern blotting allows researchers to study the nature of interactions between different molecules. It can provide insights into protein-protein interactions, protein-lipid interactions, and other molecular binding events.
- Comparative Analysis of Protein Modifications: Eastern blotting has been extensively used to compare protein modifications among different bacterial species or strains. This comparative analysis helps in understanding the variation in post-translational modifications and their potential correlation with virulence or pathogenicity.
- Detection of Carbohydrate Epitopes: Eastern blotting is a valuable tool for detecting carbohydrate epitopes in proteins. It enables the identification and characterization of specific carbohydrate structures, contributing to our understanding of glycosylation patterns and their functional implications.
For example, in a specific application, Eastern blotting was used to detect protein modifications in two bacterial species, Ehrlichia muris and IOE. Ganglioside-binding cholera toxin B subunit, mannose-containing glycan-detecting concanavalin A, and phosphoprotein-detecting nitrophospho molybdate-methyl green were employed to identify protein modifications. The study revealed differences in post-translational modifications between the non-virulent E. muris and the highly virulent IOE.
In summary, Eastern blotting has diverse applications, including the analysis of post-translational modifications, identification of plant products, detection of protein modifications in various origins, study of molecular interactions, comparative analysis of protein modifications, and detection of carbohydrate epitopes. This technique continues to be a valuable tool in molecular biology and biochemical research, providing insights into the intricate world of protein modifications and molecular interactions.
FAQ
What is Eastern blotting?
Eastern blotting is a laboratory technique used to detect and analyze specific molecules, such as proteins or carbohydrates, based on their interactions with labeled probes. It is a variation of the Western blotting technique, with the key difference being the target molecules and the probes used.
How does Eastern blotting differ from Western blotting?
Eastern blotting differs from Western blotting in terms of the target molecules and the probes used. While Western blotting primarily focuses on the detection of proteins, Eastern blotting is particularly useful for detecting and studying post-translational modifications, glycosylation patterns, and other biomolecular interactions.
What are the key steps involved in Eastern blotting?
The key steps in Eastern blotting include separation of molecules by techniques like thin-layer chromatography, transfer of separated molecules to a blotting membrane, incubation with specific probes (antibodies, lectins, or other binding proteins), detection of the bound probes, and visualization of the target molecules using appropriate methods.
What are the common applications of Eastern blotting?
Eastern blotting finds applications in various areas of research. It is commonly used for studying post-translational modifications, analyzing glycosylation patterns, investigating molecular interactions, identifying specific carbohydrate epitopes, and comparing protein modifications among different species or strains.
What are the advantages of using Eastern blotting over other techniques?
Eastern blotting offers several advantages, including its ability to detect and study specific biomolecular interactions, post-translational modifications, and glycosylation patterns. It provides valuable insights into the functional implications of these modifications and allows for comparative analysis among different samples or organisms.
Can Eastern blotting be used for quantitative analysis?
Eastern blotting is primarily a qualitative technique and is not typically used for precise quantitative analysis. While the intensity of the detection signal can provide a semi-quantitative estimation, other techniques, such as densitometry or ELISA, are better suited for accurate quantitative analysis.
What are the limitations of Eastern blotting?
Eastern blotting has certain limitations, including its complexity and potential for errors, the requirement for a significant amount of sample, challenges in accurate quantification, and the possibility of protein structure alteration due to probe interactions. These limitations should be considered when planning and interpreting experiments.
What are the different detection methods used in Eastern blotting?
Various detection methods can be used in Eastern blotting, depending on the nature of the target molecules and the probes. Common detection methods include enzyme-based colorimetric reactions, chemiluminescence, fluorescence, or radioactive labeling, which facilitate the visualization and analysis of the bound probes.
Is Eastern blotting suitable for detecting specific post-translational modifications?
Yes, Eastern blotting is well-suited for detecting and analyzing post-translational modifications (PTMs) in proteins. It allows for the identification and characterization of PTMs, such as phosphorylation, glycosylation, acetylation, and more, providing insights into their functional significance and regulatory roles.
What are the critical factors to consider when performing Eastern blotting experiments?
Several factors are crucial for successful Eastern blotting experiments. These include sample preparation, optimization of transfer conditions, selection of appropriate probes, optimization of probe concentration and incubation conditions, appropriate controls, and careful interpretation of results. Attention to these factors ensures reliable and meaningful outcomes from Eastern blotting experiments.
References
- Morinaga, Osamu & Li, Xiao-Wei & Fujii, Shunsuke. (2011). Quality Control of Bupleurum Species by Newly Established Eastern Blotting. 10.5772/24223.
- Nicholas MW, Nelson K. North, south, or east? Blotting techniques. J Invest Dermatol. 2013 Jul;133(7):e10. doi: 10.1038/jid.2013.216. PMID: 23760052.
- Jonathan M. Gershoni, George E. Palade. Protein blotting: Principles and applications. Analytical Biochemistry. Volume 131, Issue 1. 1983. Pages 1-15. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(83)90128-8.
- Hiroyuki Tanaka, Waraporn Putalun, Yukihiro Shoyama, “Fingerprinting of Natural Product by Eastern Blotting Using Monoclonal Antibodies”, Chromatography Research International, vol. 2012, Article ID 130732, 7 pages, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/130732
- Gershoni, J. M., & Palade, G. E. (1983). Protein blotting: Principles and applications. Analytical Biochemistry, 131(1), 1–15. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(83)90128-8
- Taki T., Gonzalez T., Goto-Inoue N., Hayasaka T., Setou M. (2009) TLC Blot (Far-Eastern Blot) and Its Applications. In: Kurien B., Scofield R. (eds) Protein Blotting and Detection. Methods in Molecular Biology (Methods and Protocols), vol 536. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-542-8_55
- https://bitesizebio.com/639/southern-northern-western-and-eastern/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Far-eastern_blot
- https://www.aaas.org/southern-northern-western-and-eastern-blots
- https://www.scientificlib.com/en/Biology/Molecular/EasternBlotting.html
- https://www.slideshare.net/ZoqiaTariq/eastern-blotting-technique
