Table of Contents
What is ELISA test ?
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) is a powerful and widely used molecular technique for detecting and quantifying the interaction between antigens and antibodies. It plays a crucial role in clinical diagnosis, research, and various fields of biotechnology.
- The principle behind ELISA involves the use of an enzyme system to detect the specific binding of an antigen and its corresponding antibody. The assay is performed by immobilizing the antigen on a solid surface, such as a plastic tube or a microtiter plate well. Then, a specific antibody labeled with an enzyme is added to the system. The binding of the antibody to the immobilized antigen forms an antigen-antibody complex.
- After the antigen-antibody reaction, a chromogenic substrate specific to the enzyme is added. This substrate is designed to be acted upon by the enzyme attached to the antigen-antibody complex, resulting in a color change. The intensity of the color is directly proportional to the amount of antigen present in the sample, allowing for quantification. The reaction can be visually observed or measured using a spectrophotometer or an ELISA reader.
- The choice of enzyme used in ELISA depends on the specific requirements of the assay. Commonly used enzymes include peroxidase, alkaline phosphatase, and β-galactosidase. Each enzyme has its own compatible substrate, and the appropriate substrate is selected based on the enzyme used.
- ELISA tests find widespread applications in clinical laboratories and research settings. They are employed for diagnosing various diseases and conditions, such as infections like HIV, detecting autoimmune disorders, and identifying allergic responses, including food allergies. ELISA tests are also used in the pharmaceutical industry for drug development and quality control.
- To ensure accuracy and reliability, ELISA tests often include a standard curve. This curve is created by measuring known concentrations of the antigen or antibody and plotting them against the corresponding optical density values. By comparing the optical density of the unknown sample to the standard curve, the quantity of the antigen or antibody can be determined.
- In summary, ELISA is a versatile and sensitive technique that utilizes an enzyme system to detect and quantify the interaction between antigens and antibodies. Its wide range of applications and its ability to provide accurate and reproducible results make it an indispensable tool in clinical diagnosis, research, and biotechnology.
Definition of ELISA
ELISA, short for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay, is a widely used laboratory technique that detects and measures the presence of specific antibodies or antigens in a sample. It involves the binding of target molecules (antibodies or antigens) to a solid surface, followed by the addition of enzymes or fluorescent markers to generate a detectable signal. ELISA is commonly employed in medical diagnostics, research, and various fields of science to identify and quantify substances of interest, such as proteins, hormones, viruses, and bacteria.
Principle of ELISA test
The principle of the Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) test revolves around the specific interaction between antigens and antibodies. When an antigen, such as a pathogen or a molecule of interest, is present in a sample, it can bind to its corresponding antibody. This binding forms the antigen-antibody complex (Ag-Ab complex).
In the ELISA test, antibodies are often linked or attached to enzymes. This linkage allows the enzyme-linked antibodies to modify specific substrates, resulting in a color change within the test preparation. The enzyme’s activity is measured using a colorimeter, which detects the magnitude of the infection or the concentration of the target molecule in the patient’s sample.
Types of ELISA
There are presently four types of ELISA test such as;
- Direct ELISA Test (For Antigen Detection)
- Indirect ELISA Test (For Antigen Detection)
- Sandwich ELISA (For Antibody Detection)
- Combined ELISA (For Antibody Detection)
1. Direct ELISA Test
- The Direct Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) is a simple and efficient variant of ELISA that involves the direct interaction between a single enzyme-linked antibody and the antigen of interest present in the sample.
- In a Direct ELISA, the first step is to immobilize the antigen or sample directly onto a solid surface, such as a microtiter plate. This immobilization can be achieved by physically adsorbing or covalently attaching the antigen to the plate. The antigen-coated surface serves as a capture platform for the subsequent steps.
- Once the antigen is immobilized, a conjugated detection antibody is added to the plate. This detection antibody is typically labeled with an enzyme, such as peroxidase or alkaline phosphatase. The detection antibody specifically binds to the target protein or antigen present on the plate, forming an antigen-antibody complex.
- After incubation to allow the antibody-antigen binding to occur, the plate is washed to remove any unbound or non-specifically bound substances. This washing step helps reduce background noise and ensures the specificity of the assay.
- Following the washing step, a substrate specific to the enzyme linked to the detection antibody is added. The substrate undergoes a reaction with the enzyme, leading to the production of a detectable signal, such as a colored or fluorescent product. The intensity of the signal is directly proportional to the amount of antigen present in the sample.
- Finally, the signal generated by the enzymatic reaction is measured using a colorimeter or a fluorescence reader. The optical density or fluorescence intensity is quantified, providing information about the concentration of the target antigen in the sample.
- Direct ELISA has several advantages. It is a faster assay compared to other ELISA techniques since fewer steps are involved. It also requires fewer reagents and is less prone to error, as there is no need for a potentially cross-reacting secondary antibody. This simplicity makes direct ELISA a suitable choice for situations where a rapid analysis of the immune response to an antigen is needed.
- However, there are some limitations to consider. The antigen immobilization in a direct ELISA is not as specific as in other techniques, which may result in higher background noise due to non-specific protein binding. Additionally, the direct ELISA is less flexible as it requires a specific conjugated primary antibody for each target protein, limiting its versatility. Furthermore, direct ELISA lacks signal amplification, resulting in reduced assay sensitivity compared to other ELISA formats.
- In summary, the Direct ELISA is a straightforward and quick method for detecting and quantifying antigens in a sample. It involves the direct interaction between an enzyme-linked antibody and the target antigen. While it has some limitations, the direct ELISA is a valuable tool for analyzing immune responses and providing rapid results in various research and diagnostic applications.
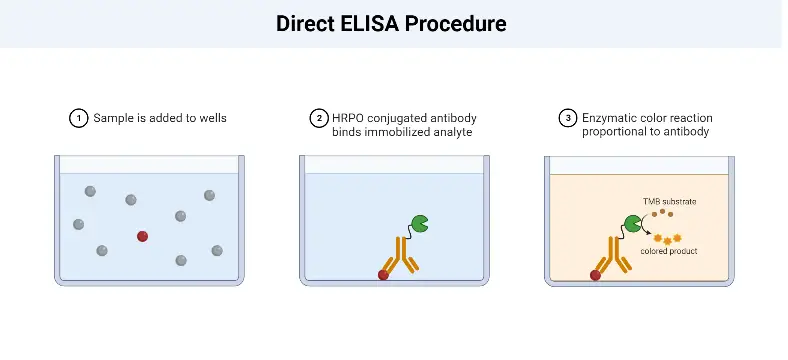
Direct ELISA Procedure
The Direct Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) procedure involves several key steps to detect and quantify the antigen of interest in a sample. The following outlines the general procedure for a Direct ELISA:
- Sample Addition: The first step is to add the sample, which contains the antigen, to the wells of a microtiter plate. The plate is coated with a solid surface that allows the antigen to adsorb or bind to it.
- Antigen Adsorption: The antigens present in the sample adsorb to the surface of the well through non-specific interactions. The plate is then incubated to ensure sufficient binding between the antigens and the plate surface.
- Washing: After the incubation period, the plate is washed to remove any unbound or non-specifically bound antigens. This washing step helps to reduce background noise and increase the specificity of the assay.
- Enzyme-Linked Antibody Addition: Next, an enzyme-linked antibody specific to the target antigen is added to the wells. This antibody is typically conjugated with an enzyme, such as peroxidase or alkaline phosphatase. The antibody binds specifically to the antigens immobilized on the plate, forming an antigen-antibody complex.
- Washing: Similar to the previous step, the plate is washed again to remove any unbound or non-specifically bound antibodies. This washing step is crucial for removing any excess or unwanted antibodies that could interfere with the assay’s accuracy.
- Chromogenic Substrate Addition: A chromogenic substrate specific to the enzyme linked to the antibody is added to the wells. This substrate undergoes a reaction with the enzyme, resulting in a color change. The reaction typically involves the conversion of a colorless substrate to a colored product.
- Visualization and Result Interpretation: The final step involves visualizing the color change or the formation of a colored product. This can be done by observing the wells visually or by using a spectrophotometer to measure the absorbance at a specific wavelength. The intensity of the color or the absorbance is proportional to the amount of antigen present in the sample. The results are then interpreted based on a standard curve or known concentrations of the antigen to determine the concentration of the antigen in the sample.
Applications
- When analyzing the immune response to an antigen.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Faster than other ELISA – the technique has fewer steps | Antigen immobilization is not specific – may cause higher background noise than indirect ELISA. Mainly because all proteins in the sample, including the target protein, will bind to the plate Less flexible – each target protein needs a specific conjugated primary antibody No signal amplification – reduces assay sensitivity |
| Less prone to error – as less reagents and fewer steps are required |
2. Indirect ELISA
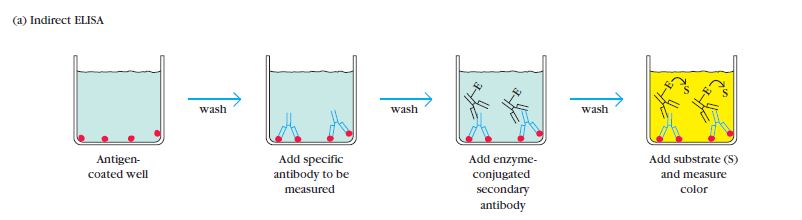
Indirect ELISA is a widely used variant of the Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) that was developed in 1978 and has become the most popular type of ELISA technique in use.
In an indirect ELISA, the primary focus is on the detection of antibodies. It involves the use of a primary antibody that specifically binds to the target antigen. This primary antibody is unlabeled and does not have an enzyme attached to it.
To detect the primary antibody, a secondary antibody is introduced. This secondary antibody is labeled with an enzyme, such as peroxidase or alkaline phosphatase. The secondary antibody recognizes and binds to the primary antibody, forming an antibody-antibody complex.
The advantage of indirect ELISA is its high sensitivity. Since multiple labeled secondary antibodies can bind to each primary antibody, signal amplification occurs, resulting in a stronger and more detectable signal. This increased sensitivity makes indirect ELISA suitable for detecting low levels of antibodies.
In terms of cost-effectiveness, indirect ELISA is more economical than direct ELISA. It requires fewer labeled antibodies since a single labeled secondary antibody can be used with multiple primary antibodies, offering greater flexibility in experimental design.
However, there are some disadvantages associated with indirect ELISA. One potential drawback is the possibility of cross-reactivity between the secondary antibody and the adsorbed antigen, leading to increased background noise. This cross-reactivity can affect the assay specificity and accuracy.
Additionally, indirect ELISA assays typically take longer to run than direct ELISAs. This is because an additional incubation step is required to allow the secondary antibody to bind to the primary antibody. The extended incubation time contributes to the longer overall assay duration.
Overall, indirect ELISA is particularly suitable for determining the total antibody concentration in samples. Its sensitivity, flexibility, and ability to detect low levels of antibodies make it a valuable tool in various research and diagnostic applications. However, careful optimization and selection of appropriate antibodies are necessary to ensure reliable and accurate results.
PIndirect ELISA Procedurerocedure
The Indirect Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) procedure involves several important steps to detect and quantify specific antibodies in a sample. The following outlines the general procedure for an Indirect ELISA:
- Antigen Addition: Known antigens that are specific to the antibody of interest are added to the wells of a microtiter plate. These antigens will be used to capture the specific antibodies present in the sample.
- Washing: Careful washing is performed to remove any unadsorbed antigens or potential contaminants that may have adsorbed to the plate. This washing step helps to reduce background noise and increase the specificity of the assay.
- Sample Addition: Serum samples or other test samples are added to their respective wells. If the sample contains specific antibodies that recognize the antigens on the plate, they will bind to the antigens during the incubation period.
- Washing: Similar to the previous step, the plate is washed again to remove any unbound or non-specifically bound substances, such as unbound antibodies or other components present in the sample.
- Secondary Antibody Addition: An enzyme-linked secondary antibody, specific to the species and isotype of the primary antibody, is added to the wells. This secondary antibody recognizes and binds to the primary antibody that is already bound to the antigens on the plate. The secondary antibody is conjugated with an enzyme, such as peroxidase or alkaline phosphatase.
- Washing: The plate is washed once more to remove any unbound or non-specifically bound secondary antibodies.
- Substrate Addition: A chromogenic substrate specific to the enzyme linked to the secondary antibody is added to the wells. The substrate undergoes a reaction with the enzyme, resulting in a color change or the generation of a fluorescent or chemiluminescent signal.
- Visualization and Result Interpretation: The color change or the generated signal is observed and quantified. This can be done visually or by using a spectrophotometer or a suitable instrument that measures the optical density or fluorescence intensity. The intensity of the signal is proportional to the amount of specific antibodies present in the sample.
It is important to note that the specific details and conditions of the Indirect ELISA procedure may vary depending on the specific antigens, antibodies, and detection systems used. Optimization and validation may be required for each individual experiment to ensure accurate and reliable results.
Applications
- Determining total antibody concentration in samples.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| High sensitivity – more than one labeled secondary antibody can bind the primary antibody | Possibility of background noise – secondary antibody may be cross-reactive Longer procedure than direct ELISA technique – additional incubation step for secondary antibody needed |
| Economical – fewer labeled antibodies are needed | |
| Greater flexibility – different primary antibodies can be used with a single labeled secondary antibody |
3. Sandwich ELISA
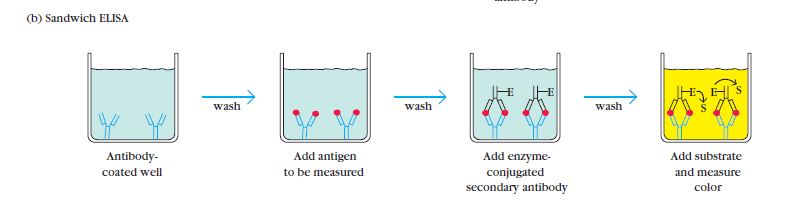
Sandwich ELISA, developed in 1977, is a widely used technique for the detection of antigens. It involves the use of two different antibodies: capture antibodies and enzyme-linked secondary antibodies.
In a sandwich ELISA, the antigen of interest is first captured by the immobilized capture antibodies, which are specific to different epitopes on the antigen. This creates a “sandwich” structure where the antigen is sandwiched between the capture antibodies and the detection antibodies.
To perform a sandwich ELISA, the well of an ELISA plate is coated with the capture antibody. The sample or analyte containing the antigen is then added to the well, allowing the capture antibodies to bind to the antigen. Next, the enzyme-linked secondary antibodies are introduced. These secondary antibodies recognize and bind to a different epitope on the antigen, forming the sandwich structure.
The use of matched antibody pairs is crucial in a sandwich ELISA to ensure accurate results. The capture and detection antibodies should target different epitopes on the antigen, avoiding overlap. This specificity ensures the accurate detection and quantification of the antigen.
There are two types of sandwich ELISAs: direct and indirect. In a direct sandwich ELISA, the detection antibody is directly conjugated to an enzyme. In an indirect sandwich ELISA, an unlabeled detection antibody is used, followed by the addition of a secondary enzyme-conjugated detection antibody.
Sandwich ELISAs offer several advantages. They provide high sensitivity, being 2-5 times more sensitive than direct or indirect ELISAs. This increased sensitivity makes them suitable for the analysis of low-concentration antigens. The use of two antibodies also enhances the specificity of the assay. Sandwich ELISAs are flexible and can be performed using both direct and indirect methods.
However, there are some disadvantages to consider. If a standardized ELISA kit or tested antibody pair is not available, antibody optimization is necessary to minimize cross-reactivity between the capture and detection antibodies. Additionally, the complexity of the sandwich ELISA procedure can make it more time-consuming and labor-intensive compared to other ELISA formats.
Sandwich ELISAs are particularly well-suited for the analysis of complex samples, as they allow for the direct detection of antigens without the need for prior purification. This makes them valuable in various research and diagnostic applications, including the measurement of cytokine levels in immune responses.
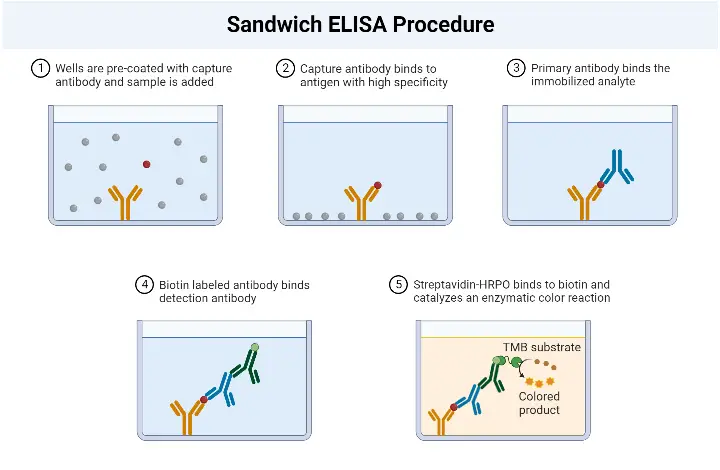
Sandwich ELISA Procedure
The Sandwich Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) procedure involves several key steps to detect and quantify specific antigens in a sample. The following outlines the general procedure for a Sandwich ELISA:
- Addition of Capture Antibodies: Capture antibodies, specific to the target antigen, are added to the wells of a microtiter plate. These antibodies are immobilized on the surface of the plate and will bind to the antigen in the sample.
- Washing: The plate is carefully washed to remove any unbound capture antibodies, as well as any other substances that may be present in the sample but are not specifically bound to the capture antibodies. This washing step helps to reduce background noise and increase the specificity of the assay.
- Addition of Sample: The serum sample or other test sample containing the antigen of interest is added to the wells. The capture antibodies on the plate will bind to the antigen present in the sample, forming the first layer of the “sandwich” structure.
- Washing: Similar to the previous step, the plate is washed again to remove any unbound or non-specifically bound substances, such as unbound antigens or other components present in the sample.
- Addition of Enzyme-Linked Antibodies: Enzyme-linked antibodies, also known as detection antibodies, are added to the wells. These antibodies are specific to a different epitope on the antigen than the capture antibodies. The enzyme linked to the detection antibodies can be a peroxidase, alkaline phosphatase, or another enzyme that can generate a detectable signal.
- Washing: The plate is washed once more to remove any unbound or non-specifically bound detection antibodies.
- Addition of Substrate: A chromogenic substrate specific to the enzyme linked to the detection antibodies is added to the wells. The substrate undergoes a reaction with the enzyme, resulting in the development of a colored or fluorescent signal.
- Visualization and Result Interpretation: The color development or fluorescence intensity is observed and measured. This can be done visually or using a spectrophotometer or a suitable instrument that detects the generated signal. The intensity of the signal is proportional to the amount of antigen present in the sample.
Application
- The sandwich ELISA technique allows for the analysis of complex samples without the requirement of antigen purification prior to measurement.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| High sensitivity – 2-5 times more sensitive than direct or indirect ELISA | Antibody optimization can be difficult – cross-reactivity may occur between the capture and detection antibodies. Needs a standardized ELISA kit or tested antibody pair. |
| High specificity – two antibodies are involved in capture and detection | |
| Flexibility – both direct and indirect detection can be used |
4. Competition/Inhibition ELISA
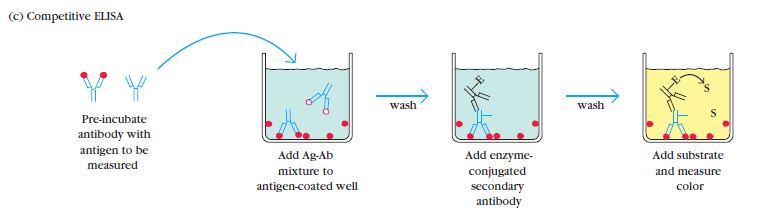
Competition/Inhibition ELISA, also known as blocking ELISA, was developed in 1976 and is primarily used for the detection of antibodies. This ELISA technique is based on the principle of competition between sample antibodies (if present) and enzyme-linked secondary antibodies for binding to the antigens.
The concept behind competition/Inhibition ELISA is straightforward. If the sample contains specific antibodies of interest, they will bind to the antigens, preventing the enzyme-linked antibodies from binding to the same antigens. As a result, the enzyme-linked antibodies are washed away during the washing steps. Therefore, when the substrate is added, there won’t be a color change, indicating a positive test result (absence of competition) for the specific antibodies. Conversely, if the sample does not contain specific antibodies, the enzyme-linked antibodies will bind to the antigens, leading to a color change and a negative test result (presence of competition).
The competition/inhibition ELISA is commonly used to measure the concentration of an antigen or antibody in a sample by detecting interference in the expected signal output. It is a complex ELISA technique but can be adapted from other assay types. In this format, the sample antigen or antibody competes with a reference for binding to a limited amount of labeled antibody or antigen, respectively. The strength of the output signal is inversely correlated with the amount of antigen in the sample: the higher the antigen concentration, the weaker the output signal.
For example, in a direct detection-based competition ELISA, a known antigen is coated on a multiwell plate. After blocking and washing steps, samples containing unknown antigens are added to the wells. Labeled detection antibodies specific to the antigens are then applied, followed by the addition of relevant substrates, such as 3,3′,5,5′-Tetramethylbenzidine (TMB). If the sample contains a high concentration of antigen, there will be a significant reduction in the signal output compared to the control. On the other hand, if the sample contains a low concentration of antigen, there will be minimal reduction in the expected signal output. The reduction in signal output indicates the presence of competition and can be quantified to determine the concentration of the antigen in the sample.
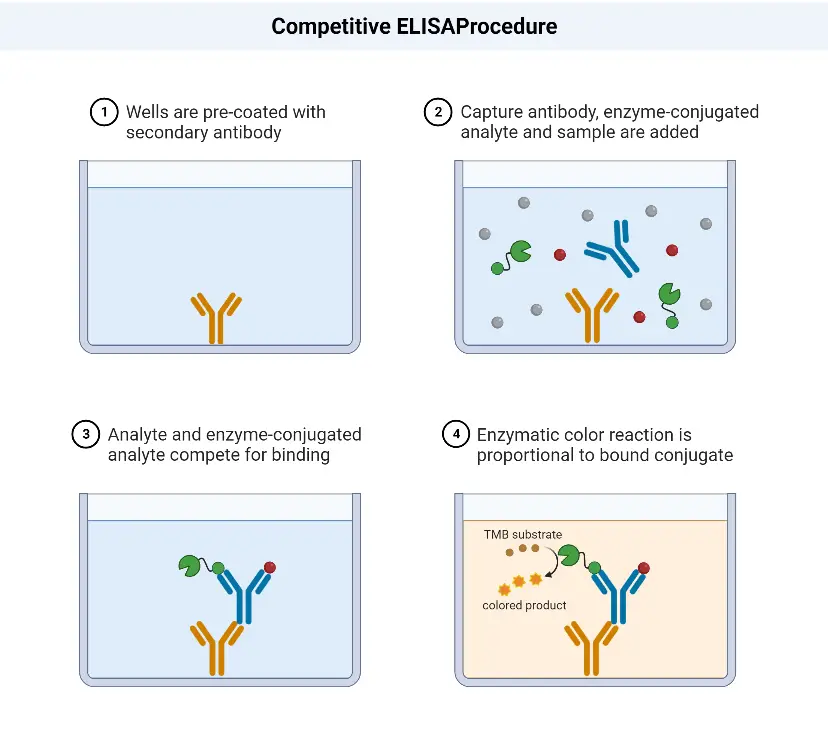
Competitive ELISA Procedure
The competitive ELISA procedure involves the following steps:
- Addition of HIV antigens: The first step is to add the HIV antigens to the wells of a microtitre plate. These antigens will coat the surface of the well.
- Washing: After the antigens have been added, the plate is washed to remove any unbound or excess antigens.
- Addition of serum sample: The next step is to add the serum sample, which may contain antibodies against HIV, to the wells. The antibodies in the sample will compete with the enzyme-linked HIV-specific antibodies for binding to the HIV antigens.
- Washing: After a suitable incubation period, the plate is washed again to remove any unbound serum proteins or antibodies.
- Addition of enzyme-linked HIV-specific antibodies: In this step, enzyme-linked HIV-specific antibodies are added to the wells. These antibodies can bind to the HIV antigens that were not occupied by the antibodies present in the serum sample.
- Washing: Once again, the plate is washed to remove any unbound enzyme-linked antibodies.
- Addition of substrate: A substrate specific to the enzyme linked to the HIV-specific antibodies is added to the wells. When the substrate reacts with the enzyme, it produces a measurable signal, usually a color change.
- Visualization of color change and result interpretation: The final step involves observing any color change that occurs in the wells. The intensity of the color change is proportional to the amount of enzyme activity, which in turn reflects the amount of enzyme-linked antibodies bound to the HIV antigens. The color change can be visually assessed or measured using a spectrophotometer. Based on the results, the presence or absence of HIV antibodies in the serum sample can be determined.
Applications
- The competitive ELISA is commonly employed in situations where only a single antibody is available for the target antigen. It is particularly useful for detecting small antigens that cannot be captured by two distinct antibodies, as required in the sandwich ELISA method.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Main advantage – no sample processing is required and crude or impure samples can be used | Same limitations as base ELISA – as each ELISA technique can be adapted to a competitive format |
| More robust – less sensitive to sample dilution and sample matrix effects than the sandwich ELISA | |
| More consistent – less variability between duplicate samples and assays | |
| Maximum flexibility – it can be based on direct, indirect or sandwich ELISA |
ELISA Result Interpretation
- ELISA result interpretation involves both qualitative and quantitative analysis of the antigen or antibody being detected.
- Qualitative interpretation focuses on determining the presence or absence of the antigen. This is done by observing the color change in the solution. If the antigen-antibody reaction occurs and the enzyme-linked antibodies remain bound in the solution, they will modify the substrate, resulting in a visible color change.
- Quantitative interpretation involves determining the concentration of the antigen or antibody. This is achieved by measuring the optical density of the solution using an ELISA reader spectrophotometer. A standard curve is prepared using known concentrations of the antigen or antibody, and the optical density values of the unknown sample are compared to this curve. By correlating the optical density with the concentration of the standard samples, the concentration of the antigen or antibody in the unknown sample can be determined.
Application of ELISA test
The ELISA test finds wide application in various fields due to its sensitivity and effectiveness in detecting infections, as well as its ability to quantify substances. Some of the key applications of ELISA include:
- Detection of Infections: ELISA is commonly used for the detection of viral, bacterial, and fungal infections. It is especially used as a screening test for HIV infection. Additionally, there are specific ELISA test kits available for the detection of infections such as dengue fever, tuberculosis (TB), and Hepatitis B.
- Pregnancy Testing: ELISA-based pregnancy test kits are widely used for the detection of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) hormone in urine or blood, providing a reliable and convenient method for confirming pregnancy.
- Protein and Hormone Estimation: ELISA allows for qualitative and quantitative estimation of various proteins and hormones in samples. It is extensively used in research, clinical laboratories, and pharmaceutical industries to measure the concentration of specific proteins and hormones in body fluids.
- Toxin Detection: ELISA plays a crucial role in the detection of toxins produced by microorganisms or toxins present in food. It enables the identification and quantification of these harmful substances, aiding in food safety testing and toxin screening.
- Allergen Detection: ELISA is utilized in the detection of food allergens, helping to identify the presence of specific allergenic proteins in food products. This is particularly important for individuals with food allergies who need to avoid certain ingredients.
The wide range of applications of ELISA highlights its versatility and significance in various fields, including medical diagnostics, research, food safety, and pharmaceutical development.
Advantages of ELISA
ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) offers several advantages that contribute to its widespread use in various fields. Some of the key advantages of ELISA are as follows:
- Simple Protocols: ELISA protocols are relatively simple and easy to perform. The assay steps are well-established and standardized, making it accessible to researchers, laboratory technicians, and clinicians.
- Specific and Sensitive: ELISA is highly specific, meaning it can accurately detect and differentiate the target analyte of interest from other substances present in the sample. It achieves high sensitivity, enabling the detection of very low concentrations of the target molecule, such as antigens or antibodies, in the sample.
- High Efficiency: ELISA allows for the analysis of multiple samples simultaneously in a high-throughput manner. This makes it a time-efficient technique, particularly when analyzing a large number of samples.
- Low-Cost Reagents: ELISA utilizes commercially available reagents that are generally affordable and cost-effective. This makes it a cost-efficient option for laboratories and research facilities, especially when compared to other analytical techniques.
- Non-Radioactive Assay: Unlike Radioimmunoassay (RIA), ELISA does not require the use of radioactive substances. This eliminates the safety concerns associated with handling and disposal of radioactive materials, making ELISA a safer alternative.
- Versatility: ELISA can be adapted to detect a wide range of analytes, including proteins, hormones, antibodies, antigens, and various other molecules. It can be used in diverse fields such as medical diagnostics, research, environmental monitoring, and food safety.
Overall, the simplicity, specificity, sensitivity, efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and safety of ELISA make it a highly valuable and widely utilized technique in the scientific community. Its versatility and reliable performance have contributed to its prominence in various applications, from disease diagnosis to drug development and quality control.
Limitations of ELISA
ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) is a powerful technique; however, it does have certain limitations that need to be considered. Here are some of the limitations associated with ELISA:
- Work-Intensive: ELISA can be a labor-intensive technique, especially when processing a large number of samples. It involves several steps, including sample preparation, coating plates, incubation, washing, and data analysis. The workload increases as the number of samples to be analyzed grows.
- Preparation of Enzyme-Linked Antibodies: The preparation of enzyme-linked antibodies can be a complex and time-consuming process. It requires the conjugation of the enzyme to the antibody, which may involve specific conditions and optimization. This process can be technically challenging and may require expertise, making it expensive and time-consuming.
- Antibody Stability: Antibodies used in ELISA can be sensitive to environmental conditions, such as temperature and pH. They can degrade or lose activity over time, affecting the reliability and reproducibility of the assay. Proper storage and handling of antibodies are crucial to maintain their stability and activity. Refrigeration is often required during transportation and storage to preserve antibody integrity.
- Cross-Reactivity: ELISA assays can sometimes exhibit cross-reactivity, where antibodies may bind to molecules other than the intended target. This can lead to false-positive or false-negative results and compromise the specificity of the assay. Careful selection and validation of antibodies are essential to minimize cross-reactivity.
- Detection Limit: While ELISA is highly sensitive, it does have a detection limit. Extremely low concentrations of the analyte may not be detectable, limiting its applicability in certain scenarios where ultra-sensitive detection is required.
- Limited Multiplexing: ELISA is typically designed to measure one analyte at a time in a single assay. Multiplexing, which refers to simultaneous detection of multiple analytes in a single sample, can be challenging to achieve with traditional ELISA techniques. This limitation restricts the ability to analyze multiple targets in a single experiment, requiring separate assays for each analyte of interest.
FAQ
What is ELISA?
ELISA, or Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay, is a laboratory technique used to detect and measure the presence of specific antibodies or antigens in a sample.
How does ELISA work?
ELISA involves the binding of target molecules (antibodies or antigens) to a solid surface, followed by the addition of enzymes or fluorescent markers to generate a detectable signal.
What are the different types of ELISA?
There are several types of ELISA, including direct ELISA, indirect ELISA, sandwich ELISA, and competitive ELISA, each with its own variations and applications.
What is the purpose of ELISA?
ELISA is used for various purposes, such as medical diagnostics, research, and monitoring the presence of specific substances like proteins, hormones, viruses, or bacteria in a sample.
What are the advantages of ELISA?
Some advantages of ELISA include its high sensitivity and specificity, simplicity of protocols, efficiency, and availability of low-cost reagents.
What are the limitations of ELISA?
Limitations of ELISA include being work-intensive, the difficulty and expense of preparing enzyme-linked antibodies, and the requirement for proper refrigeration to maintain antibody stability during transport and storage.
What are the applications of ELISA?
ELISA has various applications, including the detection of viral, bacterial, and fungal infections, screening for diseases like HIV and hepatitis, protein and hormone quantification, allergen detection, and pregnancy testing.
How long does an ELISA test take?
The time required for an ELISA test can vary depending on the specific assay and the number of steps involved. It can range from a few hours to overnight incubations.
What are the key components of an ELISA kit?
An ELISA kit typically includes pre-coated plates, antibodies or antigens, detection reagents (enzyme or fluorescent markers), buffers, and substrate solutions for generating a detectable signal.
Can ELISA be automated?
Yes, ELISA can be automated using specialized ELISA instruments or robotic systems, which can increase throughput, reduce human error, and streamline the process of performing multiple tests simultaneously.
Reference
- Kuby Immunology by Thomas J. Kindt (Author), Barbara A. Osborne (Author), Richard Goldsby (Author).
- Healthline, “What is an ELISA test?“
- Wkipedia,”ELISA test“
- MyBiosource, “What is ELISA? (Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay)“
