Table of Contents
A hot air oven is a laboratory appliance that is used to dry, sterilize, or heat materials. It works by circulating hot air inside the oven chamber to evenly distribute heat to the materials being processed. Hot air ovens are often used in a variety of settings, including research laboratories, industrial settings, and educational institutions.
Hot air ovens typically have a temperature range of ambient temperature to 250°C or higher and are equipped with a thermostat to maintain a consistent temperature. Some hot air ovens also have a fan to circulate the hot air inside the oven chamber, which can help to ensure that the materials being processed are heated or dried evenly.
Hot air ovens are commonly used to sterilize equipment and materials, as the high temperatures can kill microorganisms. They are also used to dry materials, such as chemicals, biological specimens, and glassware. In addition, hot air ovens can be used to heat materials for a variety of purposes, such as activating chemicals or heating materials to a specific temperature for testing.
It is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for your specific hot air oven and to use caution when working with hot materials.

What is Hot Air Oven?
- A hot air oven is a specialized electrical apparatus designed for the purpose of sterilization using dry heat. Rooted in the foundational work of the renowned scientist Louis Pasteur, this device has become an integral part of scientific and medical laboratories. Its primary function is to eliminate microbial life, including bacterial spores, from various heat-resistant materials.
- Constructed with a double-walled insulation system, the hot air oven is designed for energy efficiency. The inner layer, being a poor conductor, and the metallic outer layer work in tandem with an interspersed air-filled space to enhance insulation. This ensures that the heat remains confined within the chamber, optimizing energy utilization. Additionally, the oven is equipped with an air circulating fan, ensuring the even distribution of heat throughout its interior.
- The hot air oven operates within a temperature spectrum of 50 to 300ºC. The precise temperature and duration of sterilization are pivotal, as they determine the efficacy of the sterilization process. Commonly, temperatures of 170ºC for 30 minutes, 160ºC for 60 minutes, or 150ºC for 150 minutes are employed. These parameters ensure the thorough elimination of microorganisms without compromising the integrity of the materials being sterilized.
- The principle underlying the operation of the hot air oven is heat conduction. This method ensures that sterilization occurs progressively, layer by layer, from the exterior to the core of the material. The dry heat generated within the oven chamber induces oxidation of the cellular components of microorganisms, effectively neutralizing them. This mechanism is particularly suitable for sterilizing materials that are thermally stable and resistant to dry heat, such as certain metals, glassware, and specific powders.
- To monitor and verify the sterilization process’s success, the oven often employs temperature-sensitive tapes or biological indicators. These indicators, often based on bacterial spores, provide a tangible measure of the device’s sterilization efficacy during its operation.
- In summary, the hot air oven is a paramount instrument in the realm of scientific research and medical practice. Its ability to sterilize using dry heat makes it indispensable for treating heat-resistant materials. With its roots in Pasteur’s pioneering work, the hot air oven stands as a testament to the enduring value of scientific innovation.
Definition of Hot Air Oven
A hot air oven is an electrical apparatus that utilizes dry heat to sterilize heat-resistant materials, effectively eliminating microbial life, including bacterial spores, from the items placed within its chamber.
Working Principle of Hot air oven/Principle of Hot Air Oven
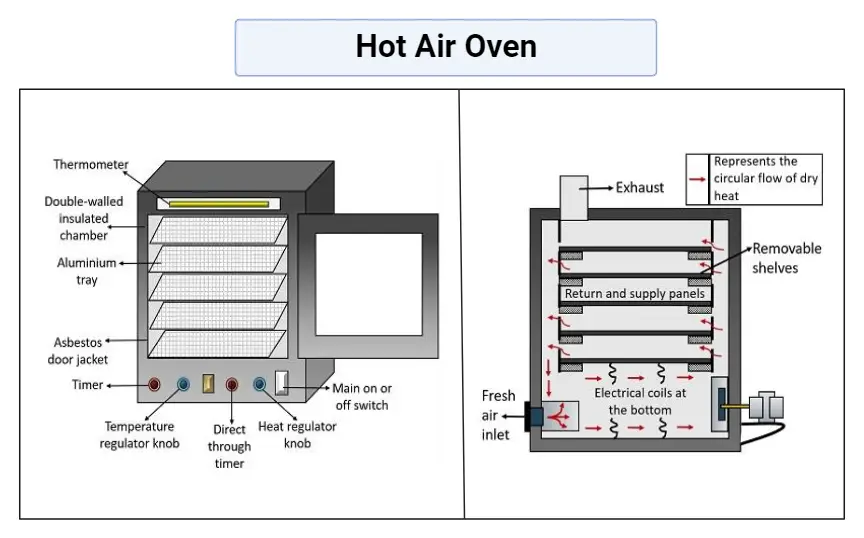
The hot air oven operates based on the principle of dry heat sterilization, employing a combination of convection, conduction, and radiation mechanisms. Scientifically, the process begins with the heating elements warming the air within the chamber. To ensure uniform heat distribution, fans circulate this heated air, ensuring all surfaces of the samples or items inside are uniformly exposed to the elevated temperatures.
The sterilization mechanism is primarily driven by conduction. As the external surfaces of items absorb the heat, it is progressively transferred inwards, layer by layer, until the entire item reaches the desired sterilization temperature. This methodical heat transfer ensures that even the core of the items is adequately sterilized.
At the cellular level, the elevated temperatures have a profound impact on microorganisms. The heat causes the water molecules within these organisms to evaporate. This dehydration process, coupled with the oxidative damage to cellular components, leads to the denaturation of vital proteins. Proteins, essential for the survival and function of microorganisms, lose their native structure and functionality when denatured. Additionally, the heat-induced increase in electrolyte concentrations exerts a toxic effect on the cells. These combined effects—oxidative damage, protein denaturation, and electrolyte imbalance—culminate in the effective elimination of microorganisms.
In essence, the hot air oven’s principle revolves around harnessing dry heat for sterilization. Through the systematic application of convection, conduction, and radiation, it ensures that items are not only surface-sterilized but are free from microorganisms even at their core. This method underscores the importance of precise temperature control and uniform heat distribution in achieving thorough sterilization.
What is Dry Heat Sterilisation?
Dry heat sterilization is a scientific method that utilizes the principle of heat conduction to achieve sterilization. In this process, heat is absorbed by the external surface of an item and subsequently transferred internally until the entire item reaches the predetermined sterilization temperature. The underlying mechanism by which dry heat sterilization eliminates microorganisms is through the oxidation of their molecular components. By inducing oxidative damage, the vital cellular structures and functions of the microorganisms are disrupted, leading to their inactivation. This method is distinct from moist heat sterilization and is particularly effective for materials that are moisture-sensitive or can withstand elevated temperatures. In essence, dry heat sterilization offers a precise and efficient means to ensure the safety and sterility of various items by leveraging the power of conducted heat and oxidative processes.
Features of a Hot Air Oven
Hot air ovens have several distinctive features that make them suitable for a variety of applications. Here are the key features of a hot air oven:
- Temperature Range: Hot air ovens can generate heat within a temperature range of ambient +10°C to 150°C, 200°C, or 250°C. This allows for versatile use in different drying, sterilization, and heat treatment processes.
- Forced Air Circulation: Hot air ovens utilize a blower-assisted air recirculation system to ensure even distribution of heat throughout the chamber. This forced air circulation promotes consistent temperature control and uniform drying or sterilization of materials.
- Wide Range of Applications: Hot air ovens find applications in various fields, including laboratories, life sciences, microbiology, MLSS analysis, research, and industries such as chemical, pharmaceutical, food and beverage, textile, electronic components, and steel manufacturing.
- Microprocessor-Based PID Controller: The ovens are equipped with a microprocessor-based PID temperature controller. This controller allows precise temperature regulation and displays both the set value (SV) and the process value (PV). Temperature measurement is performed using an RTD PT100 temperature sensor.
- Safety Features: Hot air ovens incorporate safety measures to protect the oven and samples. They include an overtemperature prevention system or safety thermostat that activates in case of controller failure, preventing overheating and potential damage.
- Interior Chamber Design: The interior chamber of hot air ovens is typically constructed with thick gauge stainless steel sheets (SS 304/SS 316). This choice of material ensures durability, easy cleaning, and meets the design requirements of the oven.
- Adjustable Shelves: The ovens feature removable stainless steel wire mesh cable shelves. These shelves can be adjusted in height to accommodate different sizes of materials or samples. The number of shelves varies depending on the internal chamber size.
- External Cabinet: The external cabinet of hot air ovens can be made of powder-coated GI sheet or stainless steel, based on customer specifications. Larger ovens often come equipped with caster wheels and brakes for convenient mobility.
- Optional Accessories: Hot air ovens offer optional accessories to enhance functionality and meet specific requirements. These may include an explosion-proof heater, digital timer, PLC-based HMI controller, RS485 computer interface, 21 CFR software, data logger and circle chart recorder, and HEPA filter air inlet.
Instrumentation of Hot Air Oven (Parts of Hot Air Oven and their Functions)
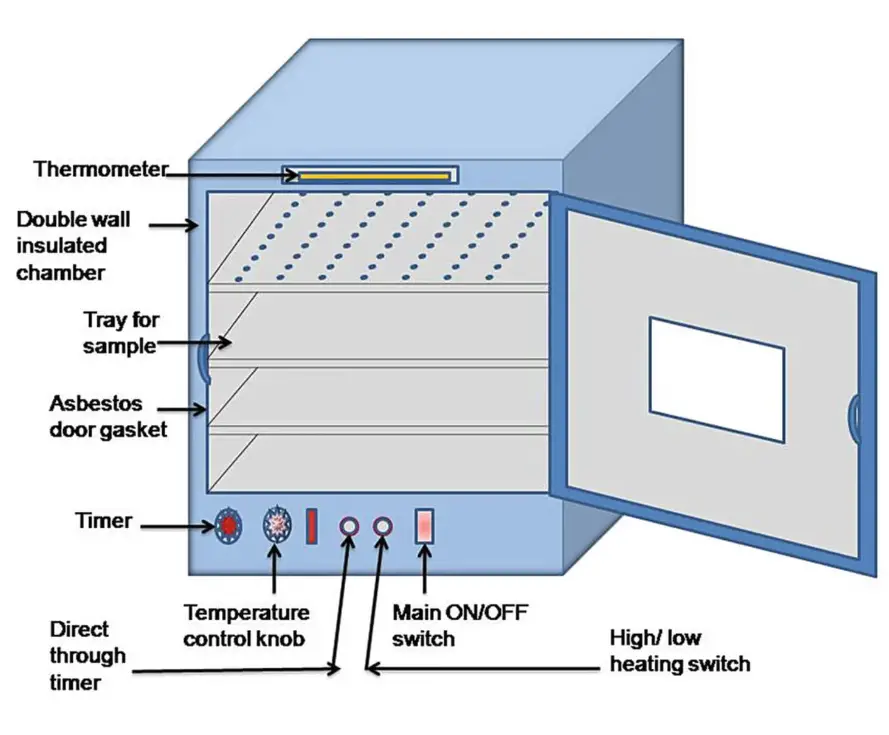
Mechanical parts of Hot air oven
The hot air oven is a sophisticated piece of equipment designed for sterilization purposes, and its functionality is attributed to its various mechanical components. Here’s a detailed overview of the primary mechanical parts of a hot air oven:
- Coat/Cabinet: This is the external protective layer of the oven, typically constructed from materials like aluminum or stainless steel. These materials are chosen for their resilience against mechanical impacts and resistance to oxidation. The cabinet serves a dual purpose: it provides a barrier between the internal and external environments and ensures minimal heat loss during the oven’s operation.
- Fiberglass Insulation: Situated between the outer cabinet and the inner chamber is a layer of thick glass wool insulation. There are two primary types of fiberglass used: brown and yellow. While brown fiberglass can lead to respiratory inflammation, yellow fiberglass might cause skin sensitivity. Due to these potential hazards, it’s advisable to handle fiberglass with protective gloves. The primary role of this insulation is to prevent heat loss, ensuring efficient operation of the oven.
- Chamber: The inner sanctum of the oven, this rectangular-shaped chamber is crafted from either aluminum or stainless steel. It is designed with ribs to support the placement of shelves at various levels, accommodating different sizes and numbers of objects.
- Shelves (Mesh): Constructed from aluminum, these shelves hold the items to be sterilized. The number and design of these shelves can vary based on the oven’s capacity and the objects’ size. Some shelves are designed with openings to promote air circulation, while others are elevated on ribs to facilitate even air movement.
- Motorized Fans/Blower: An integral component, the fan, powered by a motor, ensures the uniform distribution of hot air throughout the chamber. This even heat distribution is crucial for consistent and effective sterilization.
- Door: The oven is equipped with a single door, mounted on robust hinges. This door is crucial for accessing the chamber and ensuring a sealed environment during the sterilization process. To further enhance its efficiency, the door is fitted with an asbestos gasket, which minimizes heat loss during operation.
In summary, the hot air oven’s mechanical components work in harmony to create an efficient and effective sterilization environment. Each part, from the protective coat to the motorized fans, plays a pivotal role in ensuring the oven’s optimal performance.
Electric parts of Hot air oven
The hot air oven, a staple in many scientific and medical settings, relies on a combination of mechanical and electrical components to function effectively. Delving into the electrical components, we find a series of intricate parts that ensure the oven’s efficient and safe operation. Here’s an in-depth examination of the electrical components of a hot air oven:
- Power Supply: The oven operates on a power supply derived from a 220V-50Hz transformer and rectifier. This ensures a stable and consistent energy source for the oven’s operations.
- Heater: Central to the oven’s function, the heater generates heat when an electric current passes through a conductor. Key attributes of the heating element include high resistance, excellent electrical insulation, and superior thermal conductivity. There are various heater designs employed in hot air ovens, such as the One side circular, U type, wave type, square type, three sides type, and four sides type heaters. These heaters can function across a temperature range of 50 to 300 degrees Celsius.
- Thermostat: Acting as a heat sensor, the thermostat is directly linked to the heater. Designed to withstand extreme temperatures, it possesses a high negative temperature coefficient. This component allows users to set and maintain the desired temperature within the oven, ensuring that the temperature doesn’t exceed the set limit.
- Temperature Indicator: To monitor the internal temperature of the oven, a temperature indicator is employed. This can either be a traditional thermometer or a more advanced thermocouple, both of which provide accurate temperature readings.
- Timer: Depending on the model, the oven may be equipped with either an electrical or mechanical timer. These timers can be set for durations ranging from 5 to 60 minutes, depending on the sterilization requirements.
- Fuse: Safety is paramount, and the fuse plays a critical role in this regard. It is designed to break the circuit in the event of excessive current flow, such as during short circuits or high loads, thereby preventing potential electrical damage.
- Control Panel: This is the user interface of the oven. The control panel provides access to various parameter settings, including temperature and time. It typically features an indicator power lamp (usually green) to show when the oven is powered on, an indicator heater lamp (usually red) to indicate when the heater is active, and a switch knob for adjusting settings.
In essence, the electrical components of the hot air oven are meticulously designed to ensure efficient sterilization while prioritizing user safety. Each component, from the power supply to the control panel, plays a pivotal role in the oven’s overall functionality, ensuring precision and reliability in its operations.
| Part | Function |
|---|---|
| Mechanical Components | |
| Coat/Cabinet | External protective layer made of aluminum or stainless steel, provides a barrier and minimizes heat loss. |
| Fiberglass Insulation | Insulation between the outer cabinet and inner chamber, prevents heat loss. |
| Chamber | Inner chamber made of aluminum or stainless steel with ribs for shelf placement. |
| Shelves (Mesh) | Aluminum shelves for holding items, with variations in design for air circulation. |
| Motorized Fans/Blower | Powered fan ensures even heat distribution throughout the chamber. |
| Door | Single door with asbestos gasket for chamber access and heat retention. |
| Electrical Components | |
| Power Supply | 220V-50Hz transformer and rectifier for stable energy supply. |
| Heater | Generates heat when an electric current passes through a conductor. Various heater designs available. |
| Thermostat | Heat sensor linked to the heater, allows temperature control and regulation. |
| Temperature Indicator | Monitors internal temperature using a thermometer or thermocouple. |
| Timer | Electrical or mechanical timer for setting sterilization duration. |
| Fuse | Breaks the circuit in case of excessive current flow for safety. |
| Control Panel | User interface for parameter settings including temperature and time. Features indicator lamps and switch knob. |
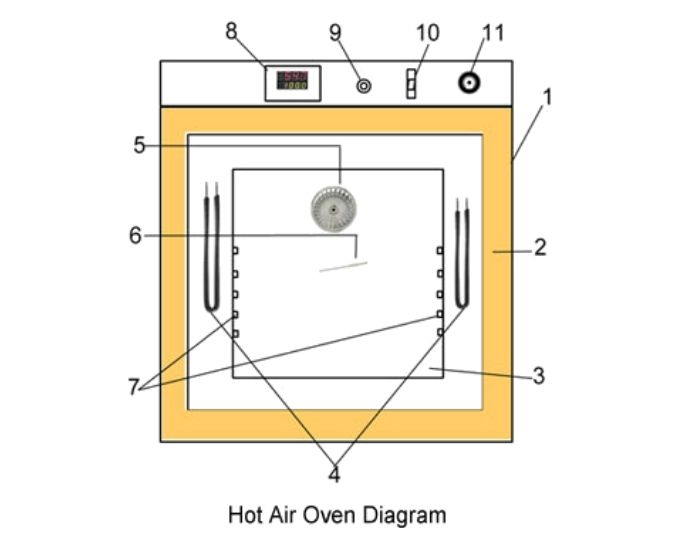
Types of Hot Air Oven
Hot air ovens are essential tools in various scientific and medical settings, primarily used for sterilization purposes. These ovens utilize dry heat to kill microorganisms and achieve sterilization. Based on their operational mechanisms and design, hot air ovens can be categorized into several types:
- Natural Convection Oven (Gravity Convection Oven): This type of oven operates based on the principle of natural convection. The mechanism involves the heated air at the oven’s bottom rising towards the top. As the air reaches the ceiling, it cools and descends back to the floor. This continuous cycle of heating and cooling occurs naturally within the oven. Due to the absence of a mechanism for uniform temperature distribution, the natural convection oven is best suited for sterilizing powder samples.
- Forced Convection Oven: Distinct from the natural convection oven, the forced convection oven incorporates a motorized fan or blower. This fan ensures the even distribution of hot air throughout the oven’s chamber. As a result, samples placed inside the oven are consistently exposed to hot air, enabling faster heat absorption and drying.
- Side Draught Oven: Characterized by its unidirectional airflow, the side draught oven directs air from one side of the chamber to the other. This design ensures that samples achieve optimal heat absorption in a relatively short duration. It is particularly beneficial for specific applications, such as preheating plastic garments in medical settings or evenly heating flat sheets or plates.
- Forced Air Oven: Superior to its static counterpart, the forced-air hot air oven utilizes a fan to maintain consistent air circulation within the chamber. This continuous movement of hot air ensures a uniform temperature distribution, preventing the natural tendency of hot air to rise and cooler air to settle at the bottom.
- Static Air Oven: Operating as an open sterilizer, the static air oven features a heating coil positioned at its base. Relying on gravity convection, the hot air naturally ascends within the chamber. However, this type of oven does not guarantee as uniform a temperature distribution as the forced air variant.
In summary, hot air ovens come in various designs and operational mechanisms to cater to specific sterilization needs. Whether relying on natural convection or employing fans for forced air circulation, each type of hot air oven offers unique advantages suited to particular applications in scientific and medical fields.
Operating Procedure of Hot Air Oven / Hot air oven procedure
The hot air oven is a vital instrument in scientific and medical laboratories, primarily used for sterilization purposes. To ensure its effective operation and achieve optimal sterilization results, it is essential to follow a systematic operating procedure. Here is a detailed guide on the operating procedure of a hot air oven:
- Initialization: Begin by connecting the oven to the power source and activating the switch to turn it on.
- Preheating Phase: Prior to introducing any items for sterilization, preheat the oven for a duration of 30 minutes. This step ensures that the oven reaches a stable temperature, suitable for the sterilization process.
- Setting the Temperature: Utilize the temperature gauge to designate the desired temperature. The specific temperature setting is contingent on the volume and nature of the contents that require sterilization.
- Loading the Oven: Position the items to be sterilized on the oven’s shelves or trays. It is crucial to maintain adequate spacing between individual articles. This spacing facilitates efficient circulation of heat, ensuring uniform exposure of all items to the sterilizing temperature.
- Securing the Oven: Once the items are appropriately placed inside, close the oven door. Ensure it is securely fastened using the provided screws. With the door sealed, the internal temperature of the oven will begin to rise.
- Monitoring Temperature and Holding Time: Possessing a comprehensive understanding of the required sterilizing temperature and holding time for specific items is paramount. Regularly monitor the thermometer to ascertain if the oven has reached the predetermined temperature. Once achieved, maintain this temperature for the specified holding time to ensure effective sterilization.
- Completion and Cooling: After the designated holding period has elapsed, deactivate the oven and allow it to cool down. It is essential to wait until the oven has sufficiently cooled before attempting to open the door. This precautionary measure ensures safety and prevents potential thermal injuries.
- Retrieving Sterilized Items: Once the oven has cooled, carefully open the door. Using protective equipment such as oven mitts or tongs, remove the sterilized items from the shelves or trays.
- Final Step: After retrieving all items, close the oven door to maintain its internal cleanliness and readiness for subsequent operations.
In conclusion, the hot air oven is a sophisticated instrument that requires meticulous operation to achieve optimal sterilization results. Adhering to the outlined procedure ensures safety, efficiency, and the effective sterilization of items.
Calibration of Hot air Oven
Calibration is a pivotal procedure in ensuring the precision and reliability of the hot air oven, particularly in its ability to achieve and maintain the requisite temperature for effective microbial eradication. This process is essential for validating the oven’s temperature accuracy and ensuring consistent performance over time. Here’s a detailed overview of the calibration process for the hot air oven:
- Initiation: Begin by connecting the hot air oven to its power source, ensuring a stable and uninterrupted power supply.
- Placement of Thermometer: Position a calibrated thermometer at the central region of the oven’s sterilization chamber. This central location is chosen to obtain a representative temperature reading, reflecting the average temperature within the chamber.
- Activation: Activate the hot air oven by switching it on. Subsequently, input the desired temperature setting using the oven’s control interface.
- Monitoring: Once the oven is operational, it’s crucial to closely monitor the temperature readings. Every 15 minutes, observe the calibrated thermometer’s reading.
- Comparison: Continuously compare the thermometer’s reading with the set temperature on the oven’s control panel. This step is vital in determining any discrepancies between the desired temperature and the actual temperature within the chamber.
- Achievement of Set Temperature: The calibration process is deemed complete once the thermometer consistently displays a reading that matches the set temperature, indicating that the oven has reached and stabilized at the desired temperature.
- Frequency: To ensure the consistent accuracy and reliability of the hot air oven, it is recommended that this calibration procedure be conducted annually. Regular calibration not only ensures the efficacy of the sterilization process but also prolongs the lifespan of the equipment.
In essence, the calibration of the hot air oven is a systematic process that verifies the instrument’s temperature accuracy, ensuring its optimal performance in microbial sterilization. Regular calibration is indispensable in upholding the standards of scientific and medical practices.
Sterilization Control of Hot air Oven
Sterilization control is a critical aspect of ensuring the efficacy and reliability of the hot air oven. This control is achieved through a combination of biological, chemical, and physical methods to validate the sterilization process. Here’s an in-depth examination of the sterilization control mechanisms for the hot air oven:
- Biological Control:
- Indicator Organism: The primary biological indicator employed for assessing the sterilization efficacy of the hot air oven is the spores of the nontoxigenic strain of Clostridium tetani.
- Procedure: Paper strips are impregnated with approximately 10^6 spores and then enclosed within suitable envelopes or packaging. Following the sterilization process, these strips are carefully extracted and introduced into specific growth media, such as thioglycollate or cooked meat media.
- Incubation: The inoculated media are then incubated under strictly anaerobic conditions at a temperature of 37°C for a duration of five days.
- Evaluation: Effective sterilization is indicated by the absence of microbial growth in the media. The eradication of the Clostridium tetani spores signifies that the sterilization process was successful.
- Chemical Control:
- Indicator: Browne’s tube No. 3 serves as the chemical indicator for the hot air oven’s sterilization process.
- Color Change: Initially red, the indicator undergoes a color transformation to green after being subjected to a sterilization temperature of 160°C for 60 minutes. This color change is a clear indication of successful sterilization.
- Physical Control:
- Temperature Monitoring: Thermocouples, which are temperature-sensitive devices, are employed to continuously monitor the internal temperature of the oven.
- Recording: A temperature chart recorder is utilized to provide a visual representation of the temperature variations throughout the sterilization process. This chart offers a comprehensive overview of the temperature consistency and aids in verifying that the desired sterilization temperature was maintained for the requisite duration.
In summation, the hot air oven’s sterilization control is a multifaceted process that integrates biological, chemical, and physical methods to ensure its effectiveness. Regular quality control testing, encompassing all these control mechanisms, is imperative to guarantee the reliability and safety of the sterilization process.
What can be Sterilized by using a Hot Air Oven?
A hot air oven can be used to sterilize a variety of materials, including:
- Glassware: Glassware, such as test tubes and beakers, can be sterilized in a hot air oven.
- Laboratory equipment: Laboratory equipment, such as pipettes and Petri dishes, can be sterilized in a hot air oven.
- Medical instruments: Medical instruments, such as scalpels and forceps, can be sterilized in a hot air oven.
- Fabric: Fabric, such as lab coats and towels, can be sterilized in a hot air oven.
- Chemicals: Some chemicals can be sterilized in a hot air oven by heating them to a high enough temperature to kill any microorganisms present.
It is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for your specific hot air oven and to use caution when sterilizing materials. Some materials may be sensitive to high temperatures or may release harmful fumes when heated. It is also important to allow the materials to cool down before handling them after they have been sterilized.
Maintenance of Hot air Oven
The hot air oven, a pivotal instrument in scientific and medical laboratories, necessitates meticulous maintenance to ensure its optimal functionality and longevity. Proper upkeep not only guarantees accurate temperature regulation but also prolongs the equipment’s operational lifespan. Here’s a comprehensive guide on the maintenance of the hot air oven:
- Regular Cleaning: To prevent the accumulation of dust, debris, and contaminants, it’s imperative to clean the hot air oven routinely. At least once a week, the interior and exterior surfaces of the oven should be wiped down using appropriate cleaning agents, such as lint-free wipes or paper towels. This ensures a hygienic environment for sterilization.
- Power Regulation: The hot air oven should be connected to a stable power source that matches its specifications. Operating the oven on an inappropriate power supply can lead to suboptimal performance, potential damage to the heating elements, and even compromise the sterilization process.
- Optimal Placement: The positioning of the hot air oven plays a crucial role in its performance. It’s essential to place the oven in a location where there’s unrestricted airflow, especially around the blower motor. This placement ensures uniform heat distribution within the chamber and prevents overheating of the motor. Additionally, it’s advisable to keep the oven away from direct sunlight and moisture-prone areas.
- Inspection of Components: Periodically, components such as heating elements, thermostats, and fans should be inspected for any signs of wear or malfunction. Any defective parts should be promptly replaced to prevent disruptions in the oven’s operation.
- Avoid Overloading: While loading items for sterilization, ensure that they are evenly spaced and do not overcrowd the chamber. Overloading can hinder proper air circulation, leading to uneven heating and potentially compromising the sterilization process.
- Consult the Manual: Always refer to the manufacturer’s manual for specific maintenance guidelines and troubleshooting tips tailored to the particular model of the hot air oven.
In summary, the maintenance of the hot air oven is a systematic process that requires regular attention and adherence to best practices. Proper care ensures the equipment’s reliability, accuracy, and extended service life, making it an indispensable asset in scientific endeavors.
Technical Specification of a Hot air oven
| Temperature range | Ambient +10°C to 250°C |
| Temperature accuracy | ±05°C or better |
| Temperature sensor | RTD PT100 |
| Temperature controller | PID temprature controllerDisplay of SV & PV |
| Construction | Double walled |
| Inner chamber | Stainless steel 304 |
| Exterior | Powder coated steel sheet |
| Insulation | Ceramic wool insulation |
| Shelves | Chrome plated wire mesh cable trays (removable) |
| Door | Insulated solid door with spring latchp |
| Door gasket | High temperature silicone rubber gasket |
| Air circulation | Motor driven blower assembly |
| Vent port | fume vent port |
| Safety | Over temperature thermostat |
| Power supply | 220 Volts / 50 Hz |
| Optional | Horizontal air flowPass through (two side doors)Port hole for sensors & data monitoringDigital timer 99 hours 99 minutesProgrammable controller (Ramp & Soak)Toughened glass windowStainless steel exterior (GMP model)Data logger with USB interfaceHMI & PLC automationEUROTHERM controllerCaster wheels with lock |
Advantages of Hot Air Oven
The hot air oven, a widely utilized sterilization device in scientific and medical laboratories, offers a plethora of advantages that make it a preferred choice over other sterilization methods. Here are the key benefits of employing a hot air oven:
- Water-Free Sterilization: Unlike autoclaves, which rely on steam and water for sterilization, the hot air oven utilizes dry heat, eliminating the need for water. This feature ensures that materials are sterilized without the risk of moisture-related complications.
- Economical Operation: The hot air oven is cost-effective in terms of both acquisition and operation. Its simple design and mechanism translate to lower maintenance costs and energy consumption.
- High-Temperature Efficiency: Capable of operating at elevated temperatures, the hot air oven achieves sterilization faster than autoclaves, ensuring rapid and effective elimination of microbial contaminants.
- Compact Design: Typically designed in smaller sizes, the hot air oven occupies minimal space, making it suitable for laboratories with space constraints. Its compactness also facilitates easy installation.
- Preservation of Instruments: The dry heat method ensures that metal instruments and sharp objects are not subjected to corrosion or rust, preserving their integrity and lifespan.
- Safety Measures: With minimal pressure build-up during its operation, the hot air oven offers enhanced safety, reducing the risk of accidents or malfunctions.
- Non-Toxic Operation: Sterilization in a hot air oven leaves no chemical residues, ensuring that the sterilized items remain uncontaminated and safe for use.
- Deep Penetration: The dry heat generated in the oven can penetrate deep into thick objects, ensuring comprehensive sterilization even for dense materials.
- Versatility: The hot air oven is adept at sterilizing a variety of materials, including oils and powders. Such materials, which might form clumps in moist environments, are effectively sterilized without any aggregation.
- Inactivation of Endotoxins: The oven’s dry heat is capable of inactivating bacterial endotoxins, ensuring a higher level of sterilization.
- Low Maintenance: With its straightforward design and mechanism, the hot air oven requires minimal maintenance, making it a hassle-free choice for many laboratories.
In conclusion, the hot air oven stands out as an indispensable tool in sterilization processes, offering a combination of efficiency, safety, and versatility. Its unique attributes make it a valuable asset in ensuring the sterility of equipment and materials in various scientific and medical settings.
Limitations of Hot air oven
The hot air oven, while advantageous in many respects, also has certain limitations that restrict its applicability in some sterilization scenarios. Here are the primary constraints associated with the use of a hot air oven:
- Material Restrictions: The hot air oven is not apt for sterilizing materials like rubber, plastics, and surgical dressings. The elevated temperatures used in dry heat sterilization can lead to the melting or deformation of these materials due to their low melting points.
- Inefficacy Against Resistant Microorganisms: One of the significant limitations of the hot air oven is its inability to effectively destroy certain heat-resistant endospores and prions. These microbial agents can withstand the dry heat, making them challenging to eliminate entirely.
- Time-Consuming Process: Dry heat sterilization in a hot air oven is relatively more time-intensive compared to other methods such as steam sterilization, flaming, chemical sterilization, or radiation. This extended duration can be a drawback in scenarios requiring rapid sterilization.
- Limited Heat Penetration: The rate of heat penetration and microbial inactivation in a hot air oven is slower compared to moist heat sterilization methods. This can result in uneven sterilization, especially for dense or thick materials.
- Incompatibility with Certain Equipment: Not all types of equipment or instruments are suitable for dry heat sterilization. Some materials may be adversely affected by the high temperatures used in the oven.
- Potential for Residue: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures in the oven can cause glassware to develop a smoky or cloudy residue, affecting its clarity and usability.
- Risk with Prions: Certain microbial agents, particularly prions, may not be effectively eradicated using the dry heat method of sterilization. This poses a risk for specific medical and research applications.
In summary, while the hot air oven offers a range of benefits for sterilization, it is essential to be aware of its limitations. Proper assessment of the materials and equipment to be sterilized, as well as the specific sterilization requirements, is crucial to determine the suitability of the hot air oven for a given application.
Applications of Hot Air Oven
The hot air oven is a versatile instrument with a wide range of applications, particularly in scientific and research settings. Its primary function is to utilize dry heat for sterilization and other processes. Here are the primary applications of the hot air oven:
- Sterilization of Laboratory Equipment: The hot air oven is extensively used for the sterilization of various laboratory apparatus. This includes glassware such as flasks, pipettes, Petri-plates, and test tubes. Its efficacy in ensuring the sterility of these tools is paramount for accurate and uncontaminated experimental results.
- Sterilization of Metal Instruments: Instruments made of metal, including forceps, spatulas, scalpels, and scissors, can be effectively sterilized in a hot air oven. This ensures that these tools are free from microbial contaminants when used in surgical or experimental procedures.
- Sterilization of Non-Volatile Compounds: The oven is also employed to sterilize non-volatile substances like sulfonamide, zinc, and starch powder. The dry heat ensures that these compounds remain stable and uncontaminated during the sterilization process.
- Testing Temperature Stability: The hot air oven is used to assess the temperature stability of various products, including food items and pharmaceuticals. This testing ensures that these products maintain their quality and efficacy throughout their shelf life.
- Research Applications: The oven finds extensive use in research domains, including biology, chemistry, and material science. Researchers utilize it for various experimental procedures that require controlled temperature conditions.
- Heat Treatment and Drying: The oven is employed for the heat treatment of samples, including metals and alloys. It is also used for drying samples like soil, ensuring the removal of moisture content, which is crucial for specific analytical procedures.
- Baking, Curing, and Annealing: The hot air oven has applications in baking, curing, and annealing processes. Its ability to provide consistent and controlled heat makes it suitable for these applications.
- Research in Life Sciences: Given its precision and reliability, the hot air oven is widely used in life science research. It ensures that experimental conditions are maintained, and results are accurate.
In conclusion, the hot air oven is an indispensable tool in various scientific and industrial domains. Its ability to provide consistent dry heat makes it ideal for a plethora of applications, from sterilization to research.
Precautions
In the realm of scientific and laboratory procedures, the use of a hot air oven is commonplace. However, to ensure its safe and effective operation, certain precautions must be meticulously observed. Here are the essential precautions to consider when using a hot air oven:
- Material Compatibility: Only materials that can withstand dry heat sterilization should be placed in the oven. It’s imperative to ensure that the materials are not susceptible to heat damage.
- Prohibition of Combustibles: Combustible items, including volatile substances, are strictly forbidden inside the oven. Their presence can lead to hazardous situations.
- Proper Packaging: Items intended for sterilization should be appropriately wrapped, preferably in paper or newspaper. Containers made of cardboard or metal are ideal for holding these items. For items like test tubes, flasks, and pipettes, cotton wool can serve as an effective plug.
- Temperature Caution: Before opening the oven door post-sterilization, it’s crucial to let the oven cool down to approximately 40°C. This cooling process prevents potential breakage of glassware due to sudden temperature changes.
- Use of Protective Gear: When retrieving items from the oven, always use thermal gloves or tongs to prevent burns or injuries.
- Avoid Overloading: The oven should never be overloaded. Proper spacing between items ensures unobstructed circulation of hot air, which is vital for effective sterilization.
- Proper Placement: Articles should be positioned on the shelves with adequate spacing. This ensures that hot air circulates freely, leading to uniform heating.
- Preparation of Glassware: Before placing glassware in the oven, ensure it is completely dry. Wrapping them in paper can offer additional protection.
- Safety Attire: When operating the oven, wearing heat-resistant gloves is a must to prevent accidental burns.
- Avoid Overcrowding: Overcrowding can hinder the efficient circulation of hot air. Ensure that there’s ample space between items for optimal sterilization.
- Cooling Precaution: After the sterilization process, it’s advisable to cool the oven to around 60°C before opening its door. This measure prevents the cracking or breakage of glassware due to rapid temperature fluctuations.
In summary, while hot air ovens are invaluable in scientific settings, their safe operation hinges on adhering to these precautions. Proper usage not only ensures effective sterilization but also guarantees the safety of the operator and the longevity of the equipment.
Hot Air Oven Working Principle Video
Quiz
What is the primary mechanism of sterilization in a hot air oven?
a) Moist heat
b) Ultraviolet radiation
c) Dry heat
d) Chemical disinfection
Which of the following is NOT suitable for sterilization in a hot air oven?
a) Glassware
b) Metal instruments
c) Rubber items
d) Zinc powder
What is the recommended temperature range for sterilization in a hot air oven?
a) 100-120°C
b) 121-130°C
c) 160-180°C
d) 200-220°C
How does a hot air oven primarily kill microorganisms?
a) By denaturing proteins
b) By disrupting cell membranes
c) By oxidizing cell components
d) By inducing DNA mutations
Which of the following is a key advantage of using a hot air oven over an autoclave?
a) Faster sterilization
b) Sterilization of liquids
c) Non-corrosiveness for metals
d) Killing of all types of microorganisms
How often should a hot air oven be calibrated to ensure accurate temperature settings?
a) Once a week
b) Once a month
c) Once every six months
d) Once a year
Which biological indicator is commonly used for quality control testing of a hot air oven?
a) Escherichia coli
b) Clostridium tetani spores
c) Bacillus subtilis
d) Staphylococcus aureus
What is the primary disadvantage of dry heat sterilization compared to moist heat sterilization?
a) Higher temperature requirement
b) Longer exposure time
c) Less penetration power
d) All of the above
In a hot air oven, what ensures proper airflow inside the oven?
a) Keeping the door slightly open
b) Placing the oven near a window
c) Ensuring airflow around the blower motor is not restricted
d) Using a fan inside the oven
Which of the following cannot be sterilized in a hot air oven due to its low melting point?
a) Surgical steel instruments
b) Glass pipettes
c) Plastic Petri dishes
d) Zinc powder
FAQ
What is hot air oven?
A hot air oven is a laboratory instrument that uses dry heat to sterilize laboratory equipment and other materials.
What temperature of hot air oven used for sterilization?
The commonly-used temperatures and time that hot air ovens need to sterilize materials is 170 degrees Celsius for 30 minutes, 160 degrees Celsius for 60 minutes, and 150 degrees Celsius for 150 minutes.
What is the principle of hot air oven?
Hot air ovens use extremely high temperatures over several hours to destroy microorganisms and bacterial spores. The ovens use conduction to sterilize items by heating the outside surfaces of the item, which then absorbs the heat and moves it towards the center of the item.
hot air oven act on which principle?
Sterilization by conduction of dry heat. Heat is absorbed by the material from outer layer towards center until finally the entire item reaches the temperature of sterilization.
What is the use of hot air oven?
Hot air sterilization is one method of effectively killing microbes of all kinds, especially bacteria, viruses and molds on heat-resistant materials. Contamination control during the incubation of cell cultures in a CO₂ incubator is of the greatest importance.
What is the temperature of hot air oven?
The standard settings for a hot air oven are: 1.5 to 2 hours at 160 °C (320 °F) 6 to 12 minutes at 190 °C (374 °F)
Which one cannot be sterilized by hot air oven?
Examples of items that aren’t sterilized in a hot air oven are surgical dressings, rubber items, or plastic material.
hot air oven is which type of sterilization?
A hot air oven is a type of dry heat sterilization.
What items can go into a hot air oven?
Items that are sterilized in a hot air oven include:
Glassware (like petri dishes, flasks, pipettes, and test tubes)
Powders (like starch, zinc oxide, and sulfadiazine)
Materials that contain oils
Metal equipment (like scalpels, scissors, and blades)
Who invented hot air oven?
Hot air ovens are electrical devices which use dry heat to sterilize. They were originally developed by Louis Pasteur. Generally, they use a thermostat to control the temperature.
What is pv and sv in hot air oven?
The oven begin to heat automatically with ‘PV’ showing present temperature in the chamber and ‘SV’ showing the target temperature the oven will reach to.
Which instrument is used for validation of hot air oven?
For the calibration of hot air oven use a standard thermometer ranging up to 300º C. 5.2 Start the calibration procedure after 1 hour of staring the oven. Set the oven at desired temperature. 5.4 Put the standard thermometer for 30 minutes on the upper shelf of the oven and close the door of the oven.
what is the difference between autoclave and hot air oven?
Autoclaving refers to a process of instrument sterilization that uses time, temperature and pressure to kill all forms of microbial life, whereas dry heat sterilization is basically sterilizing using an oven that uses time and heat to kill all forms of microbial life, including microbial spores and viruses.
how to check efficiency of hot air oven?
Due to the excessive temperatures used in dry heat, Bacillus atrophaeus spores are used to monitor the efficiency of the sterilization process.
What is the Temperature Range of Hot air oven?
A laboratory hot air oven has a normal temperature range of ambient+10°C to 150°C, but we can additionally reach 200°C and 250°C.
What are the uses of hot air oven in histopathology?
A hot air oven is a type of laboratory equipment used in histopathology to dry and fix biological samples, such as tissue samples, prior to staining and examination under a microscope. The samples are placed in the oven and exposed to high temperatures, which removes any water or other solvents and helps to preserve the samples for further analysis. The temperature and duration of heating can vary depending on the type of sample and the specific staining technique being used.

Wow this is awesome on hot air oven pls types more others
Your blog post on hot air ovens is incredibly informative and well-written. I appreciate the clear and concise definitions of the parts, principle, and applications of hot air ovens. Your post provides valuable information for those who are new to using this type of equipment or who are looking to refresh their knowledge.
I particularly like how you included a step-by-step procedure for using a hot air oven, as this can be very helpful for those who may not be familiar with the process. Your explanations are easy to understand, and the use of visuals adds an extra level of clarity to the content.
Great post on hot air ovens! You have covered all the essential aspects of this essential laboratory equipment, from its definition to its principle of operation, parts, and applications. I particularly appreciate the detailed procedure you provided, which is sure to help anyone looking to use a hot air oven.
Your post is informative, well-structured, and easy to understand, making it an excellent resource for students and researchers alike. It is evident that you put a lot of effort into researching and writing this post, and it shows in the quality of the content.
Your article about hot air ovens provided me with a comprehensive understanding of the principles and applications of this equipment in laboratory settings. The explanation of the heat transfer mechanism in hot air ovens and its role in sterilizing equipment and media was particularly insightful, highlighting the importance of preventing contamination in microbiology experiments. Thank you for sharing this informative and useful piece!
I found your article on hot air ovens to be very informative and useful in understanding the principles and applications of hot air ovens in laboratory settings.The article explains the mechanism of heat transfer in hot air ovens and how it helps in sterilising equipment and media, which is crucial in preventing contamination in microbiology experiments. Thank you for sharing!