Table of Contents
What is Indole test?
- The indole test, a biochemical assay, has its roots tracing back to 1889 and has been historically significant in differentiating bacterial species such as Escherichia coli and Enterobacter aerogenes. This test primarily focuses on the bacterial capability to metabolize the amino acid tryptophan, converting it into indole through the enzymatic action of tryptophanase.
- The essence of the indole test lies in its qualitative nature, which evaluates the transformation of tryptophan into indole. This conversion is pivotal in the IMViC series of tests, a set of biochemical assays designed to distinguish members within the Enterobacteriaceae family. Notably, the indole test has been instrumental in the identification of various bacterial strains, including but not limited to Escherichia coli, Proteus, and Morganella.
- Coliforms, which are gram-negative, non-sporulating bacilli that ferment lactose to produce acid and gas, have been extensively characterized using the indole test. The myriad adaptations of this test, either standalone or in conjunction with other biochemical assays, underscore its central role in bacterial characterization. In contemporary microbiology, the indole test remains a cornerstone method to discern indole-producing E. coli strains from those of indole-negative Enterobacter and Klebsiella.
- Furthermore, the test’s versatility is evident in its variations, such as the Ehrlich’s reagent adaptation. This particular modification, which employs ethyl alcohol in lieu of isoamyl alcohol, is tailored for non-fermenting bacteria and anaerobes.
- In conclusion, the indole test, with its rich historical significance and enduring relevance, continues to be a vital tool in the realm of microbiological research and diagnostics, offering insights into bacterial metabolism and aiding in precise bacterial identification.
Indole Test Definition
The indole test is a biochemical assay used to determine a bacterium’s ability to metabolize tryptophan into indole through the action of the enzyme tryptophanase, aiding in the differentiation and identification of certain bacterial species.
Purpose of Indol Test (Objectives of Indole Test)
The indole test serves a dual purpose in the realm of microbiological diagnostics:
- Detection of Indole Production: The primary objective of the indole test is to ascertain the ability of bacteria to metabolize the amino acid tryptophan into indole. This metabolic conversion is facilitated by the enzyme tryptophanase, and the test’s outcome provides insights into the presence or absence of this enzyme within the bacterial specimen.
- Differentiation within Enterobacteriaceae: The test is instrumental in distinguishing various members of the Enterobacteriaceae family. Specifically, it aids in differentiating Escherichia coli, which is indole-positive, from other genera like Enterobacter and Klebsiella, which typically do not produce indole.
Principle of Indole Test
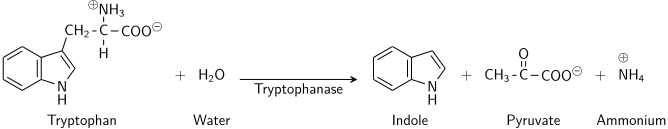
- The indole test operates on the foundational principle of detecting the enzymatic activity of tryptophanase, which facilitates the conversion of the amino acid tryptophan into indole. This enzymatic activity is pivotal in understanding the metabolic capabilities of various organisms, particularly within the context of amino acid degradation.
- Tryptophan, an essential amino acid, undergoes a two-step metabolic process in the presence of tryptophanase: deamination and hydrolysis. Initially, tryptophanase catalyzes the reductive deamination of tryptophan, wherein the amino group (-NH2) is excised from the molecule. This enzymatic action necessitates pyridoxal phosphate as a coenzyme. Subsequently, the resultant indole pyruvic acid undergoes hydrolysis, culminating in the production of indole, pyruvic acid, ammonium (NH4+), and energy.
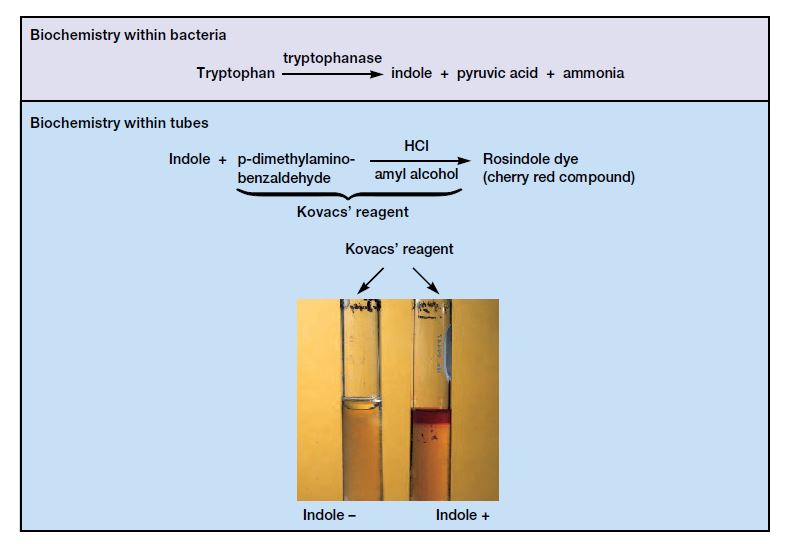
- The detection of indole, the metabolic byproduct of this process, is achieved through its chemical interaction with specific reagents. In the presence of indole, the aldehyde within the benzaldehyde reagent forms a quinoidal compound, manifesting as a pink to red-violet coloration. Alternatively, with the cinnamaldehyde reagent, a blue to green color is observed. Kovac’s reagent, comprising hydrochloric acid and p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde in amyl alcohol, interacts with indole to yield a yellow or cherry red coloration, with the amyl alcohol forming a distinct, red-colored oily layer atop the broth due to its water-insolubility.
- In the rapid spot test, indole detection is executed directly from a colony cultivated on a tryptophan-rich medium. Indole reacts with the p-dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde (DMACA) on the filter paper under acidic conditions, producing a blue to blue-green compound.
- In essence, the indole test is not merely a detection method but a reflection of an organism’s metabolic capabilities, specifically regarding tryptophan degradation. The presence of indole, when an organism is cultured in a tryptophan-abundant medium, signifies the organism’s ability to metabolize tryptophan, thereby providing a valuable metric for microbial characterization and differentiation. This principle, underpinned by the chemical reactions between indole and various reagents, continues to be a vital tool in microbiological investigations.
Reagents Used in Indole Test
In the realm of microbiological diagnostics, the indole test necessitates specific media, reagents, and supplies to ensure accurate and reliable results. Below is a comprehensive overview of these components:
Reagents Employed:
- Spot Test Reagents:
- A 5% solution of p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde or a 1% solution of p-dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde, both prepared in 10% (v/v) concentrated hydrochloric acid (HCl).
- Tube Method Reagents:
- For Aerobic Organisms: Kovac’s reagent is the reagent of choice.
- Kovac’s Reagent Composition:
- p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde: 50 grams
- Hydrochloric acid: 250 ml
- Amyl Alcohol: 750 ml
- Associated Media: Broth enriched with tryptophan, motility-indole-ornithine agar, or sulfide-indole-motility agar (SIM) are typically used in conjunction with Kovac’s reagent.
- Kovac’s Reagent Composition:
- For Anaerobes and Weak Indole Producers: Ehrlich’s reagent is preferred.
- Ehrlich’s Reagent Composition:
- p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde: 1 gram
- Hydrochloric acid: 20 ml
- Ethyl alcohol: 95 ml
- Associated Media: Heart infusion or an anaerobic medium supplemented with tryptophan is employed alongside Ehrlich’s reagent.
- Ehrlich’s Reagent Composition:
- For Aerobic Organisms: Kovac’s reagent is the reagent of choice.
Supplies Employed:
- Inoculation Tools: Sterile instruments such as loops, swabs, or sticks are essential for transferring and inoculating bacterial samples.
- Optional Supplies: Filter paper may be utilized, especially in the context of the spot test.
Procedure of Indole Test
The indole test, a pivotal biochemical assay, can be conducted using two primary methods: the Rapid Spot Test and the Tube Test. Each method has its distinct steps and procedures, as detailed below:
A. Rapid Spot Test:
- Preparation: Begin by obtaining a piece of filter paper and moistening it with the appropriate reagent.
- Sample Collection: Using an inoculating loop, carefully pick a well-isolated colony from a culture that has been grown for 18-24 hours.
- Application: Gently rub the collected colony onto the moistened filter paper.
- Observation: Examine the filter paper for any color changes, which would indicate the presence or absence of indole.
B. Tube Test:
- Inoculation:
- If using a broth medium, extract a small portion of the inoculated broth and place it in a separate tube.
- If using an agar medium, stab the medium in the tube using a colony from an 18-24-hour culture.
- Incubation: Place the inoculated tubes in an incubator set at 37°C and allow them to incubate for 24 hours.
- Reagent Addition and Observation:
- For Kovac’s Reagent:
- After incubation, carefully add three drops of Kovac’s reagent down the side of the tube.
- Observe for any color changes, particularly at the meniscus, which would indicate the presence or absence of indole.
- For Ehrlich’s Reagent:
- To the tube, add 0.5 ml of xylene and invert the tube several times to ensure thorough mixing.
- Subsequently, add six drops of Ehrlich’s indole reagent down the side of the tube.
- Carefully observe the region below the xylene layer for any color changes, which would signify the presence or absence of indole.
- For Kovac’s Reagent:
In conclusion, the indole test, whether conducted via the Rapid Spot Test or the Tube Test, offers a systematic approach to determine the ability of bacteria to produce indole from tryptophan. Adherence to the outlined procedure ensures accurate and reliable results, aiding in the differentiation and identification of bacterial species.
Conventional Indole Method Limitations
- Time-Consuming: The conventional tube method is relatively slow, necessitating a minimum of 24 hours to yield results.
- Inability to Differentiate Certain Bacteria: This method struggles to distinguish between non-fermentative and anaerobic bacteria. In such cases, Ehrlich’s reagent is employed as an alternative to Kovacs’ reagent.
- Formation of Skatole: During the reaction, a compound known as “Skatole” is produced, which can complicate result interpretation due to its potential to mask the presence of indole.
- False Results with Clostridium: Species of the genus Clostridium can rapidly degrade indole, leading to inaccurate results.
Spot Indole Method Limitations
- Reduced Sensitivity: The spot indole test is inherently less sensitive compared to other methods.
- Inoculum Source: It’s imperative to source the inoculum from an isolated colony to prevent indole diffusion, which can lead to false results.
- Aerobic Incubation Requirement: Bacterial cultures for this method must be incubated under aerobic conditions.
- Glucose-Free Medium: Cultures should be derived from a medium devoid of glucose, as glucose can expedite the breakdown of indole.
- Erroneous Results from Selective Media: Inoculum sourced from selective media, such as MacConkey’s agar or Eosin methylene blue agar, may yield inaccurate results.
- Tryptophan Degradation: Bacteria isolated from Mueller Hinton agar have the potential to degrade tryptophan due to the acid hydrolysis of casein.
- Limitations with Weak Indole Producers: The spot indole method is unsuitable for examining weak indole-positive bacteria, such as Cardiobacterium hominis.
In summary, while the indole test remains a cornerstone in microbiological diagnostics, it’s essential to be cognizant of its limitations. Recognizing these constraints ensures that the test is employed judiciously, and results are interpreted with the necessary caution, upholding the integrity of microbial characterization.
| Method | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Conventional Indole Method | – Time-consuming (minimum of 24 hours for results) |
| – Cannot differentiate non-fermentative and anaerobic bacteria (Ehrlich’s reagent used as an alternative to Kovacs’ reagent) | |
| – Skatole formation can obscure result interpretation | |
| – Clostridium species can rapidly degrade indole, leading to false results | |
| Spot Indole Method | – Less sensitive |
| – Inoculum must be from an isolated colony to prevent indole diffusion | |
| – Bacterial culture must be incubated aerobically | |
| – Culture should be from a glucose-free medium (glucose can rapidly break down indole) | |
| – Inoculum from selective media (e.g., MacConkey’s agar, Eosin methylene blue agar) may yield erroneous results | |
| – Bacteria from Mueller Hinton agar can degrade tryptophan due to acid hydrolysis of casein | |
| – Unsuitable for weak indole-positive bacteria like Cardiobacterium hominis |
Result Interpretation of Indole Test
The indole test, a biochemical assay, provides insights into the metabolic capabilities of bacteria, specifically their ability to produce indole from tryptophan. The interpretation of results, whether derived from the Spot Test or the Tube Test, is crucial for accurate bacterial identification and differentiation.
A. Spot Test Interpretation:
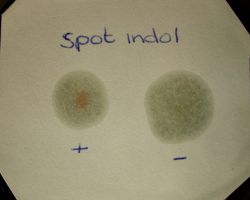
- Positive Result: The emergence of a blue color on the filter paper within a span of 20 seconds signifies the presence of indole, indicating that the bacterium possesses the enzyme tryptophanase and can metabolize tryptophan to produce indole.
- Negative Result: The absence of color or the manifestation of a faint pink hue on the filter paper denotes the absence of indole, suggesting that the bacterium lacks the enzymatic capability to convert tryptophan into indole.
B. Tube Test Interpretation:
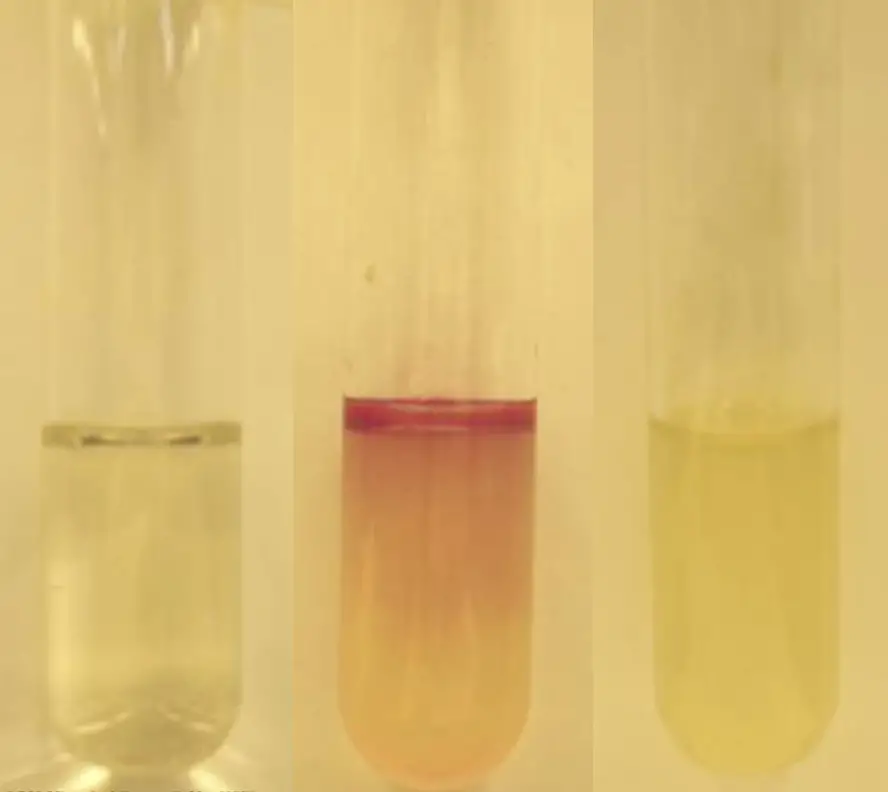
- Positive Result: A pink-red hue, often described as a cherry red ring, at the interface between the reagent and the medium is indicative of a positive result. This coloration confirms the presence of indole, suggesting that the bacterium can metabolize tryptophan through the action of tryptophanase.
- Negative Result: A lack of color change or the appearance of a slightly yellow tint in the medium denotes a negative result. This suggests that the bacterium does not produce indole from tryptophan, indicating the absence or insufficient activity of the enzyme tryptophanase.
In summation, the interpretation of the indole test results, whether from the Spot Test or the Tube Test, offers a systematic approach to discern the metabolic attributes of bacteria. Recognizing the significance of these color changes is paramount for accurate microbial characterization and subsequent clinical or research applications.
Uses of Indole Test
The indole test, rooted in microbiological diagnostics, is a biochemical assay designed to ascertain an organism’s metabolic capability, specifically its ability to metabolize tryptophan into indole. The significance and applications of this test span various domains of microbiology, as detailed below:
- Tryptophan Utilization Assessment: The primary purpose of the indole test is to evaluate an organism’s capacity to utilize the amino acid tryptophan and subsequently produce indole.
- Differentiation within Enterobacteriaceae: The test is an integral component of the IMViC series, a set of biochemical assays tailored to distinguish members of the Enterobacteriaceae family.
- Species Differentiation: The indole test plays a pivotal role in differentiating various bacterial species based on their indole production:
- Escherichia coli: Differentiates indole-positive E. coli strains from indole-negative strains of Enterobacter and Klebsiella.
- Klebsiella species: Distinguishes between indole-positive Klebsiella oxytoca and indole-negative Klebsiella pneumoniae.
- Citrobacter species: Segregates indole-positive Citrobacter koseri from indole-negative Citrobacter freundii.
- Proteus species: Differentiates indole-positive Proteus vulgaris from indole-negative Proteus mirabilis.
- Rapid Identification: The spot indole test, in conjunction with gram stain results and colony characteristics, facilitates swift identification of bacterial isolates. For instance, a lactose-fermenting colony on MacConkey agar that is spot indole positive and oxidase negative can be presumptively identified as E. coli.
- Multitest Agar in Diagnostic Laboratories: Diagnostic labs often employ multitest agar media for the indole test. The most prevalent ones include:
- Sulfide-Indole-Motility (SIM) Medium: This multitest agar evaluates indole production, motility, and the ability of the isolate to produce hydrogen sulfide.
- Motility-Indole-Urease (MIU) Medium: This medium assesses indole and urease production capabilities, along with motility.
- Motility-Indole-Ornithine (MIO) Medium: Beyond indole production assessment, MIO agar tests for motility and the presence of ornithine decarboxylase.
In essence, the indole test, with its multifaceted applications, remains a cornerstone in microbiological diagnostics. Its ability to differentiate bacterial species, combined with its integration into multitest agars, underscores its enduring relevance in the realm of microbial research and clinical diagnostics.
Quality Control for Indole Test
Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the indole test necessitates stringent quality control (QC) measures. These measures are pivotal in maintaining the test’s integrity and ensuring that the results are both reproducible and consistent. Here’s a detailed overview of the quality control procedures for the indole test:
- Reagent Quality Assurance:
- Color Check: Benzaldehyde reagents, encompassing both Ehrlich’s and Kova´cs’ reagents, should be pale yellow in color. If any deviation from this hue is observed, the reagent should not be used.
- Frequency of QC: For in-house-prepared reagents, quality control should be conducted weekly. This is crucial as these reagents can deteriorate over time, especially if not stored at an optimal temperature of 4°C. If the reactions elicited by these reagents appear weak or inconsistent, they should be promptly discarded.
- Reference Strains for Quality Control: Utilizing reference bacterial strains is a cornerstone of quality control, ensuring that the test reagents and procedures are functioning optimally. The following strains are typically employed:
- For General QC:
- Escherichia coli ATCC 25922: This strain should yield an indole-positive result.
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853: This strain should yield an indole-negative result.
- For QC with Ehrlich’s Reagent (Anaerobic Microorganisms):
- Porphyromonas asaccharolytica ATCC 25260: This strain should produce an indole-positive result.
- Bacteroides fragilis ATCC 25285: This strain should yield an indole-negative result.
- For General QC:
- Reagent Lot Verification: Every new lot of reagent should undergo quality control prior to its utilization in the test. This ensures that the reagent’s quality is consistent and meets the required standards.
In conclusion, rigorous quality control measures are paramount in ensuring the reliability and accuracy of the indole test. By adhering to these procedures, laboratories can ensure that their results are both consistent and reproducible, upholding the gold standard in microbiological diagnostics.
Limitations of Indole Test
The indole test, while invaluable in microbiological diagnostics, is not without its limitations. These constraints can impact the accuracy and reliability of the test results. Here’s a comprehensive overview of the limitations associated with the indole test:
- Diffusion Issues: Detectable indole can diffuse towards adjacent colonies within a 5 mm radius of a 2- to 3-mm colony, potentially leading to false-positive outcomes.
- Media Restrictions: Media containing dyes, such as EMB and MAC, are unsuitable for the indole test. Additionally, the growth medium must be enriched with an adequate quantity of tryptophan. Mueller-Hinton agar is not recommended for this test, as the acid hydrolysis of casein in this medium destroys tryptophan.
- Reagent Limitations for Anaerobes: Only the cinnamaldehyde reagent is suitable for spot testing anaerobic microorganisms. While it offers enhanced sensitivity, its stability is compromised compared to other reagents.
- Interference from Nitrate: Plates containing nitrate disks should be avoided, as nitrate can interfere with the spot indole test, potentially leading to false-negative results.
- Sensitivity Discrepancies: If the rapid indole test yields a negative result, it’s advisable to conduct the tube test. The latter is more sensitive, especially when xylene extraction is employed. Substitutes for xylene tend to be less sensitive.
- Requirements for Fastidious Organisms: For fastidious Gram-negative rods, such as C. hominis, it’s imperative to use a heavy inoculum and perform an extraction to obtain accurate results.
- Stability Concerns: The cinnamaldehyde reagent, while more sensitive, is less stable, which can impact the reliability of the test results over time.
In summary, while the indole test is a cornerstone in microbial characterization, it’s essential to be cognizant of its limitations. Ensuring adherence to recommended procedures, using appropriate media, and being aware of potential interferences can mitigate these limitations, ensuring accurate and reliable outcomes in microbiological diagnostics.
List of Indole positive And Negative Organisms
| Microorganism Name | Indole Positive | Indole Negative |
| Actinobacillus spp. | No | Yes |
| Aeromonas hydrophila | Yes | No |
| Aeromonas punctata | Yes | No |
| Aeromonas salmonicida | No | Yes |
| Alcaligenes sp. | No | Yes |
| Bacillus alvei | Yes | No |
| Bacillus sp. | No | Yes |
| Bordetella sp. | No | Yes |
| Edwardsiella sp | Yes | No |
| Enterobacter sp. | No | Yes |
| Enterococcus faecalis | Yes | No |
| Escherichia coli | Yes | No |
| Flavobacterium sp. | Yes | No |
| Haemophilus influenzae | Yes | No |
| Haemophilus sp. | No | Yes |
| Klebsiella oxytoca | Yes | No |
| Klebsiella sp. | No | Yes |
| Lactobacillus reuteri | Yes | No |
| Mannheimia haemolytica | No | Yes |
| Neisseria sp. | No | Yes |
| P. penneri | No | Yes |
| Pasteurella multocida | Yes | No |
| Pasteurella pneumotropica | Yes | No |
| Pasteurella ureae | No | Yes |
| Plesiomonas shigelloides | Yes | No |
| Proteus mirabilis | No | Yes |
| Proteus sp. (not P. mirabilis and P. penneri) | Yes | No |
| Pseudomonas sp. | No | Yes |
| Rhizobium sp. | No | Yes |
| Salmonella sp. | No | Yes |
| Serratia sp. | No | Yes |
| Vibrio sp | Yes | No |
| Yersinia sp. | No | Yes |
Indole-Positive Bacteria
Bacteria with a positive test for the ability to cleave indole from tryptophan are: Aeromonas hydrophila, Aeromonas punctata, Bacillus Alvei, Edwardsiella Sp., Escherichia coli, Flavobacterium sp., Haemophilus influenzae, Klebsiella Oxytoca Proteus sp. (not P. mirabilis and P. penneri), Plesiomonas shigelloides, Pasteurella multocida, Pasteurella pneumotropica, Enterococcus faecalis Vibrio sp. and Lactobacillus reuteri.
Indole-Negative Bacteria
Bacteria that produce negative results on the indole test are: Actinobacillus spp., Aeromonas salmonicida and Alcaligenes sp. Most Bacillus species., Bordetella sp., Enterobacter sp., the majority of Haemophilus sp. The most Klebsiella isp., Neisseria sp., Mannheimia haemolytica, Pasteurella ureae and Proteus mirabilis. P. penneri Pseudomonas Sp., Salmonella sp., Serratia sp., Yersinia sp., and Rhizobium sp.
Quiz
FAQ
What is the Indole Test?
The Indole Test is a biochemical test used to determine an organism’s ability to convert tryptophan into indole.
Why is the Indole Test important?
The test is crucial for differentiating members of the Enterobacteriaceae family and identifying certain bacterial species based on their metabolic capabilities.
How is a positive result for the Indole Test indicated?
A positive result is indicated by the formation of a pink-red coloration when the reagent is added.
What enzyme is responsible for the conversion of tryptophan to indole?
The enzyme tryptophanase is responsible for this conversion.
Can the Indole Test differentiate between E. coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae?
Yes, E. coli is typically indole positive, while Klebsiella pneumoniae is indole negative.
What reagents are commonly used in the Indole Test?
Kovac’s reagent is commonly used for aerobic organisms, while Ehrlich’s reagent is used for anaerobes and weak indole producers.
Is the spot indole test as sensitive as the conventional tube method?
No, the spot indole test is generally considered less sensitive than the conventional tube method.
Why is tryptophan essential for the Indole Test?
Tryptophan is the substrate that is metabolized to produce indole, making it essential for the test.
Can the Indole Test be used for anaerobic bacteria?
Yes, but it requires specific reagents like Ehrlich’s reagent and specific conditions to ensure accurate results.
Are there any limitations to the Indole Test?
Yes, the conventional method is time-consuming, and there are challenges in differentiating non-fermentative and anaerobic bacteria. Additionally, certain media and conditions can interfere with the results.