Advertisements
Table of Contents
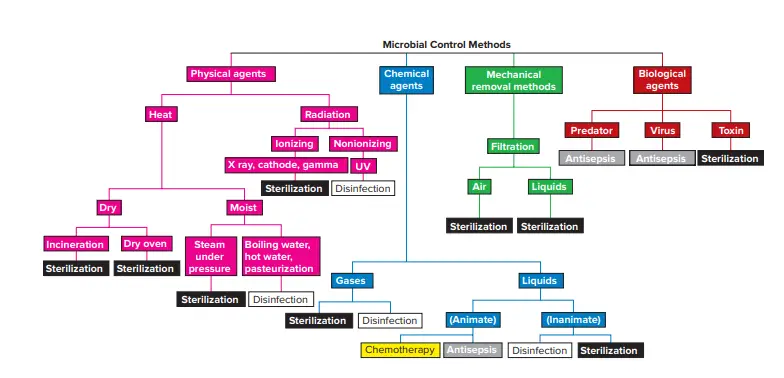
Microbial Control Methods
- The Microbial Control Method refers to those methods which are used to prevent or inhibit the growth of microbes.
- Microbes are ubiquitous in nature and they can be found with undesirable consequences, such as food spoilage and disease. Therefore, it is necessary to kill a wide variety of microorganisms or inhibit their growth to minimize their destructive effects
- The goal of these methods are: to destroy pathogens and prevent their transmission and; to reduce or eliminate microorganisms responsible for the contamination of water, food, and other substances.
- The agents which are used to control the growth of microorganisms are known as a biocide.
Types of Microbial Control Methods
There are present four distinct methods which are used to control the growth of microbes such as;
- Physical agents or Physical Method: It involves the use of heat and radiation to control the growth of microorganisms.
- Chemical agents or Chemical Method: It involves the use of different chemical agents (alcohol, phenol, etc) that can be gaseous or liquid to control the growth of microorganisms.
- Mechanical removal methods: It involves the use of the filtration method to control the growth of microorganisms. In this method, the microorganisms are removed rather than killing them
- Biological agents: It involves the use of different biological agents such as virus, predator, etc. to control the growth of microorganisms.
Different terms used in Microbial Control Methods
The following terms are used to describe the processes and chemical agents employed in controlling microorganisms.
Advertisements
- Sterilization
- Disinfection (for inanimate objects)
- Antiseptics (for tissue or living object)
- Sanitization
- Germicide (Microbicide)
- Bactericide
- Bacteriostasis
- Antimicrobial Agent
What is Sterilization?
- Sterilization is the process by which all living cells, spores, and acellular entities (e.g., viruses, viroids, and prions) are either destroyed or removed from an object or habitat.
- The Latin word sterilis menas unable to produce offspring.
- A sterile object is totally free of viable microorganisms, spores, and other infectious agents.
- Any substance that has been subjected to this process is known as sterile.
- When the sterilization process is achieved by a chemical agent, the chemical is called a sterilant.
What is Disinfection?
- Disinfection refers to the use of a chemical agent that destroys or removes all pathogenic organisms or organisms capable of giving rise to infection.
- If the chemical agents are used for the disinfection, they are called Disinfectants.
- Disinfectants are normally used only on inanimate objects because they can be toxic to human and other animal tissue when used in higher concentrations.
- A disinfectant does not necessarily sterilize an object because viable spores and a few microorganisms may remain.
- This process destroys vegetative pathogens but not bacterial endospores.
- Disinfection processes also remove the harmful products of microorganisms (toxins) from materials.
- Examples of disinfection are (a) applying a solution of 5% bleach to examining table, (b) boiling food utensils used by a sick person, and (c) immersing thermometers in an isopropyl alcohol solution between use.
What is Antiseptics ?
- Antiseptics are chemical agents applied to tissue to prevent infection by killing or inhibiting pathogen growth; they also reduce the total microbial population.
- They must not cause too much harm to the host, antiseptics are generally not as toxic as disinfectants.
- Antisepsis (Greek anti, against; sepsis, putrefaction) is the destruction or inhibition of microorganisms on living tissue; it is the prevention of infection or sepsis.
- Antiseptics are applied directly to the exposed body surfaces (e.g., skin and mucous membranes), wounds, and surgical incisions to destroy or inhibit vegetative pathogens.
- Examples of antisepsis include (a) preparing the skin before surgical incisions with iodine compounds, (b) swabbing an open root canal with hydrogen peroxide, and © ordinary hand washing with a germicidal soap.
What is Sanitization?
- Sanitization is any cleansing technique that mechanically removes microorganisms (along with food debris) to reduce the level of contaminants.
- The components which are used for Sanitization are known as sanitizer.
- Sanitizers are commonly applied to inanimate objects and are generally employed in the daily care of equipment and utensils in dairies and food plants and for glasses, dishes, and utensils in restaurants.
- Air sanitization is done by using ultraviolet lamps, which reduces airborne microbes in hospital rooms, veterinary clinics, and laboratory installations.
- Sanitizer kills 99.9 percent of the growing bacteria.
- Examples of sanitizer are soap or detergent.
What is Germicide (Microbicide)?
- An agent that kills the growing forms but not necessarily the resistant spore forms of germs is known as Germicide.
- Germicide is almost the same thing as a disinfectant, but germicides are commonly used for all kinds of germs (microbes) for any application.
- The term germicide includes both antiseptics and disinfectants.
What is Bactericide?
- An agent that kills bacteria (adjective, bactericidal) is known as Bactericide.
- Similarly, the terms fungicide, virucide, and sporicide refer to agents that kill fungi, viruses. and spores, respectively.
- Examples of bactericides are disinfectants, antiseptics and antibiotics.
What is Bacteriostasis?
- Bacteriostasis is defined as a condition in which the growth of bacteria is prevented (adjective, bacteriostatic).
- Similarly, fungistatic describes an agent that stops the growth of fungi. Examples of fungistatic are Sodium benzoate and potassium sorbate.
- Agents that have in common the ability to inhibit growth of microorganisms are collectively designated microbiostatic agents.
- Examples of Bacteriostasis are; tetracyclines, macrolides, clindamycin, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, linezolid, and chloramphenicol.
What is Antimicrobial Agent?
- Those agents that interfere with the growth and metabolism of microbes are known as Antimicrobial agents.
- In common usage the term denotes inhibition of growth, and with reference to specific groups of organisms such terms as antibacterial or antifungal are frequently employed.
- Some antimicrobial agents are used to treat infections, and they are called chemotherapeutic agents.
- Examples of antimicrobial agents are penicillin G, procaine penicillin, benzathine penicillin, and penicillin V.

