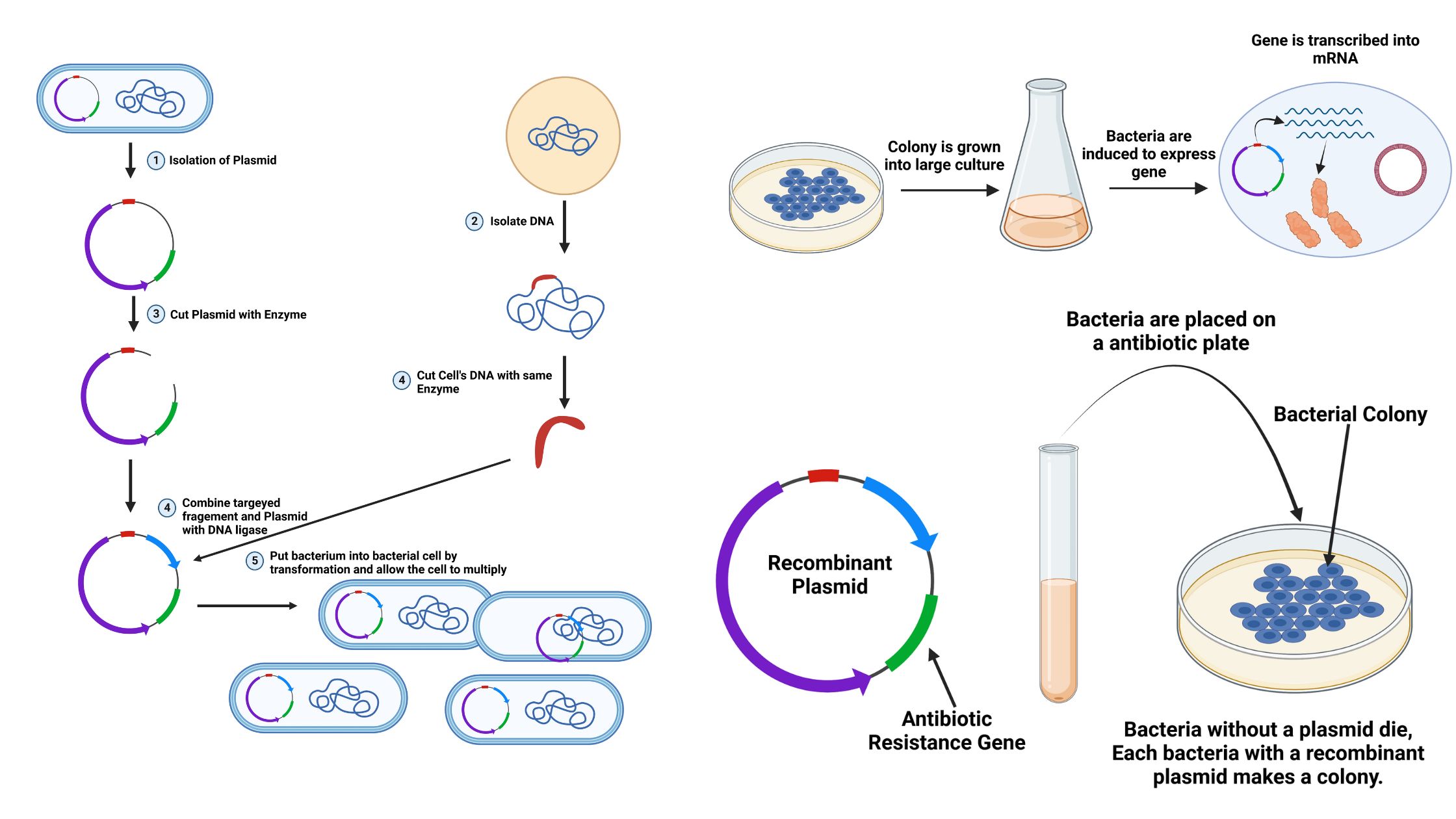
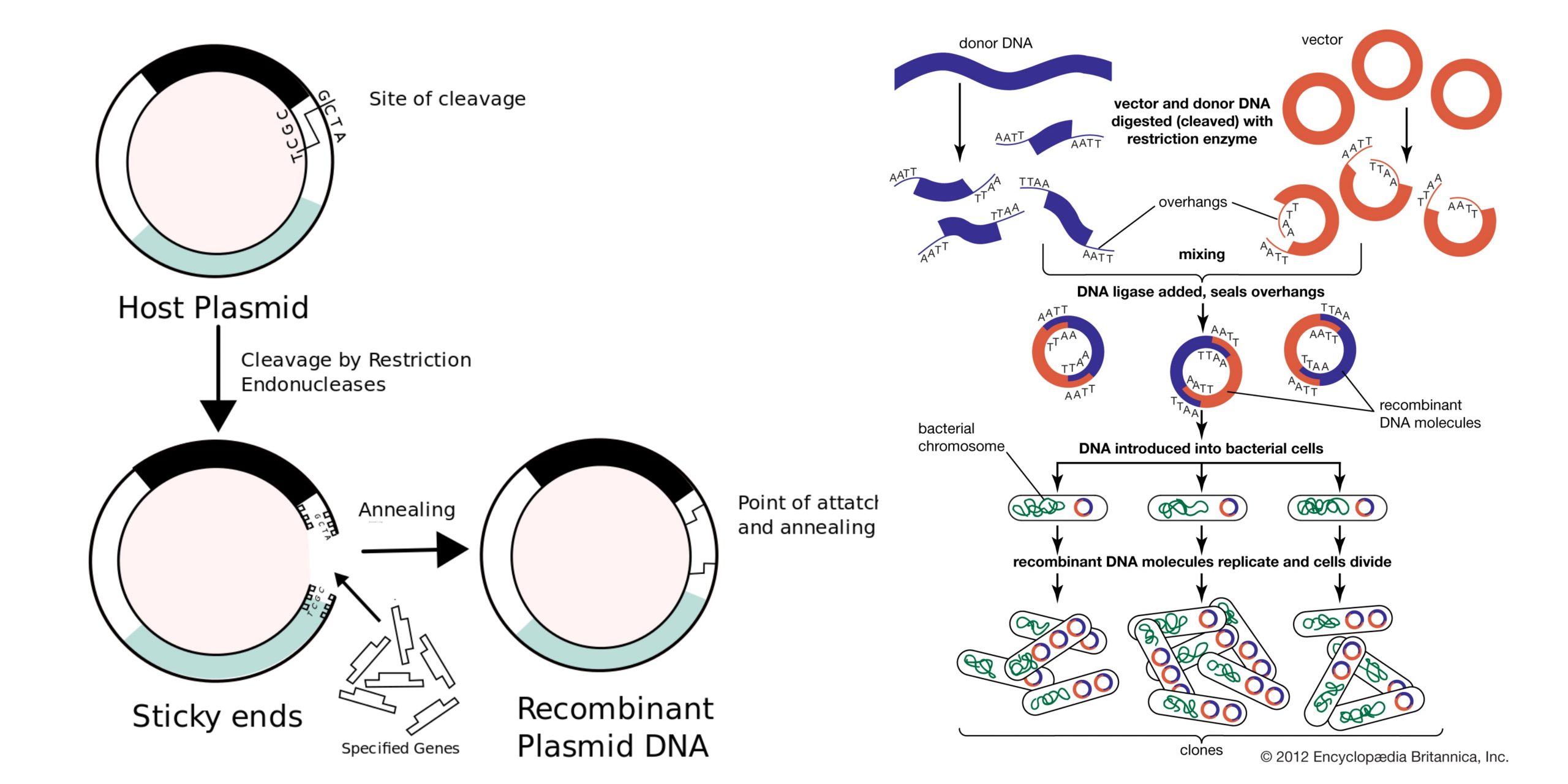
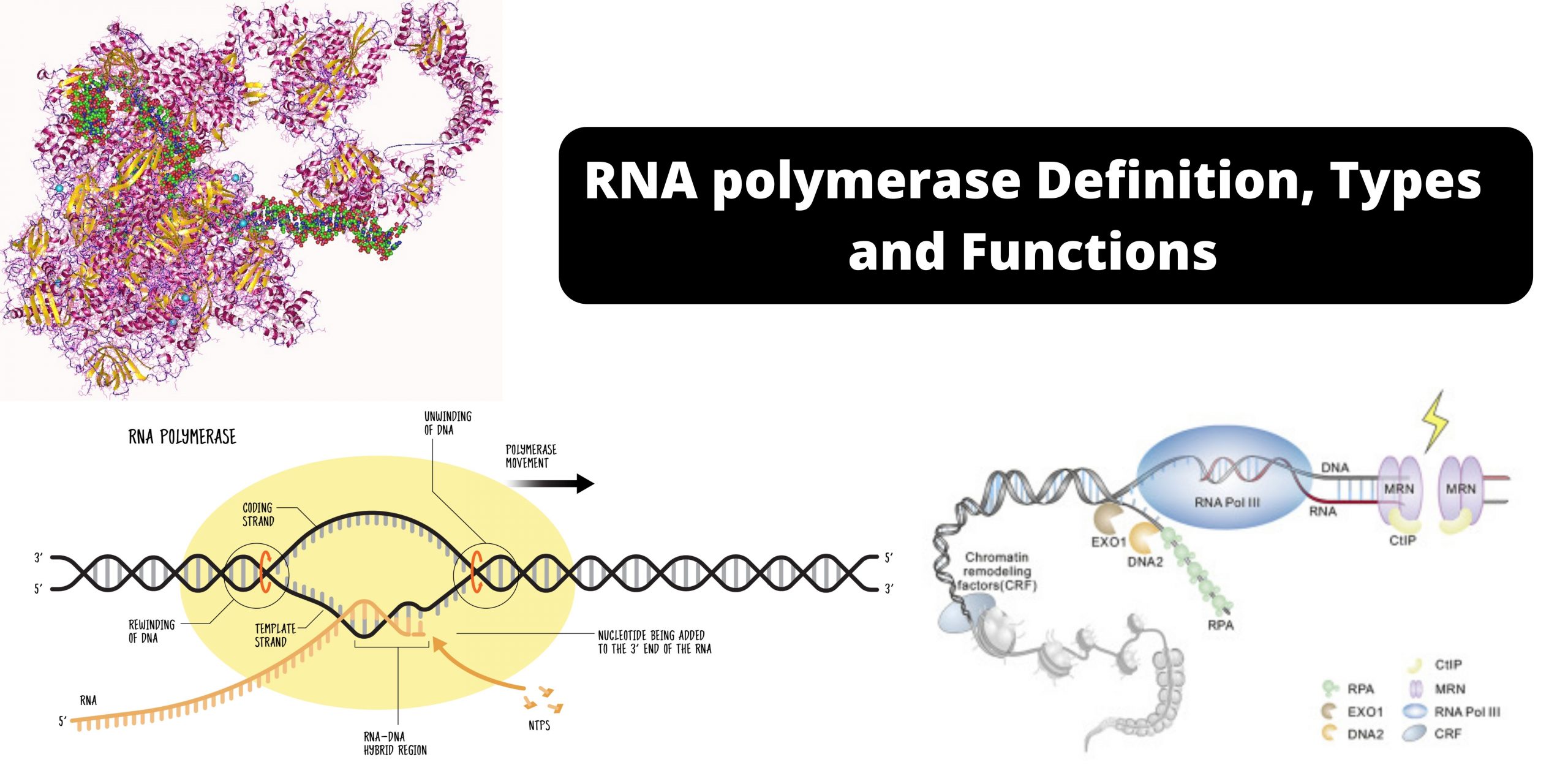
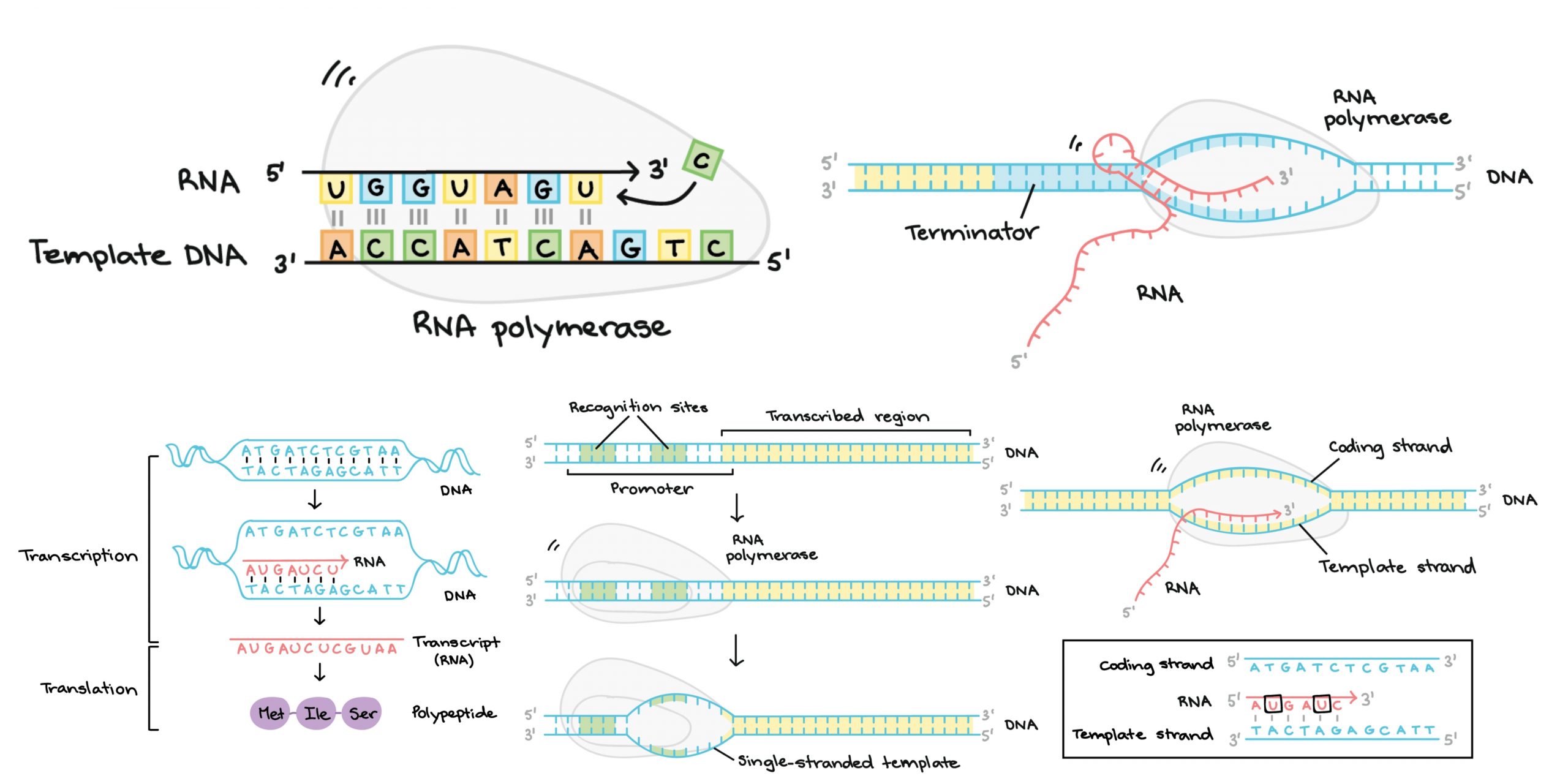
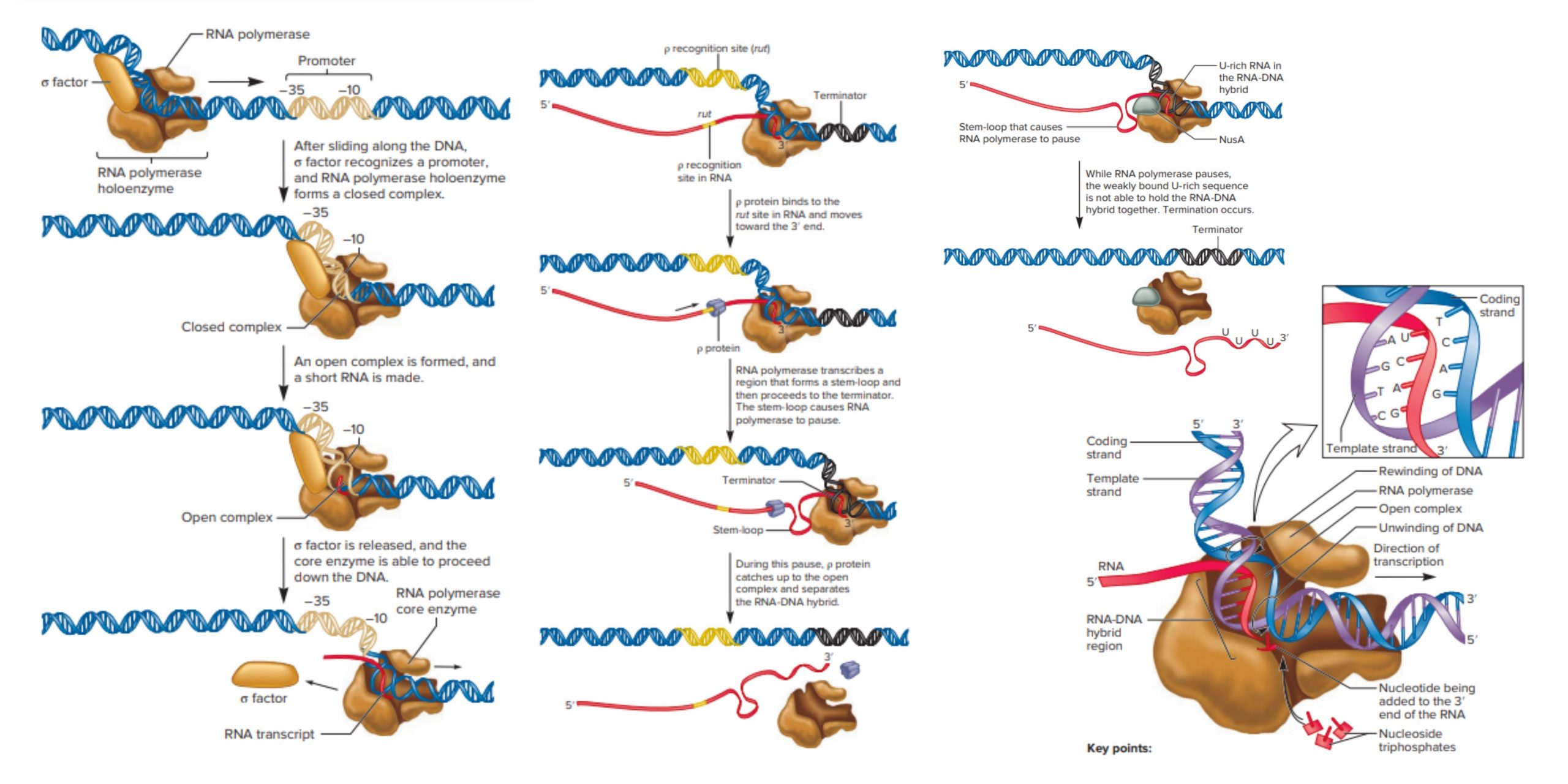
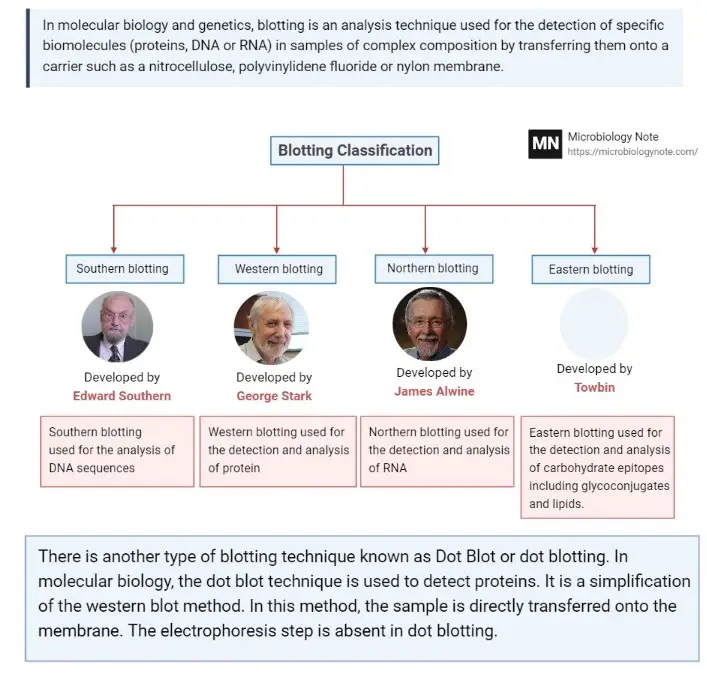
What are Telomeres and Telomerases?
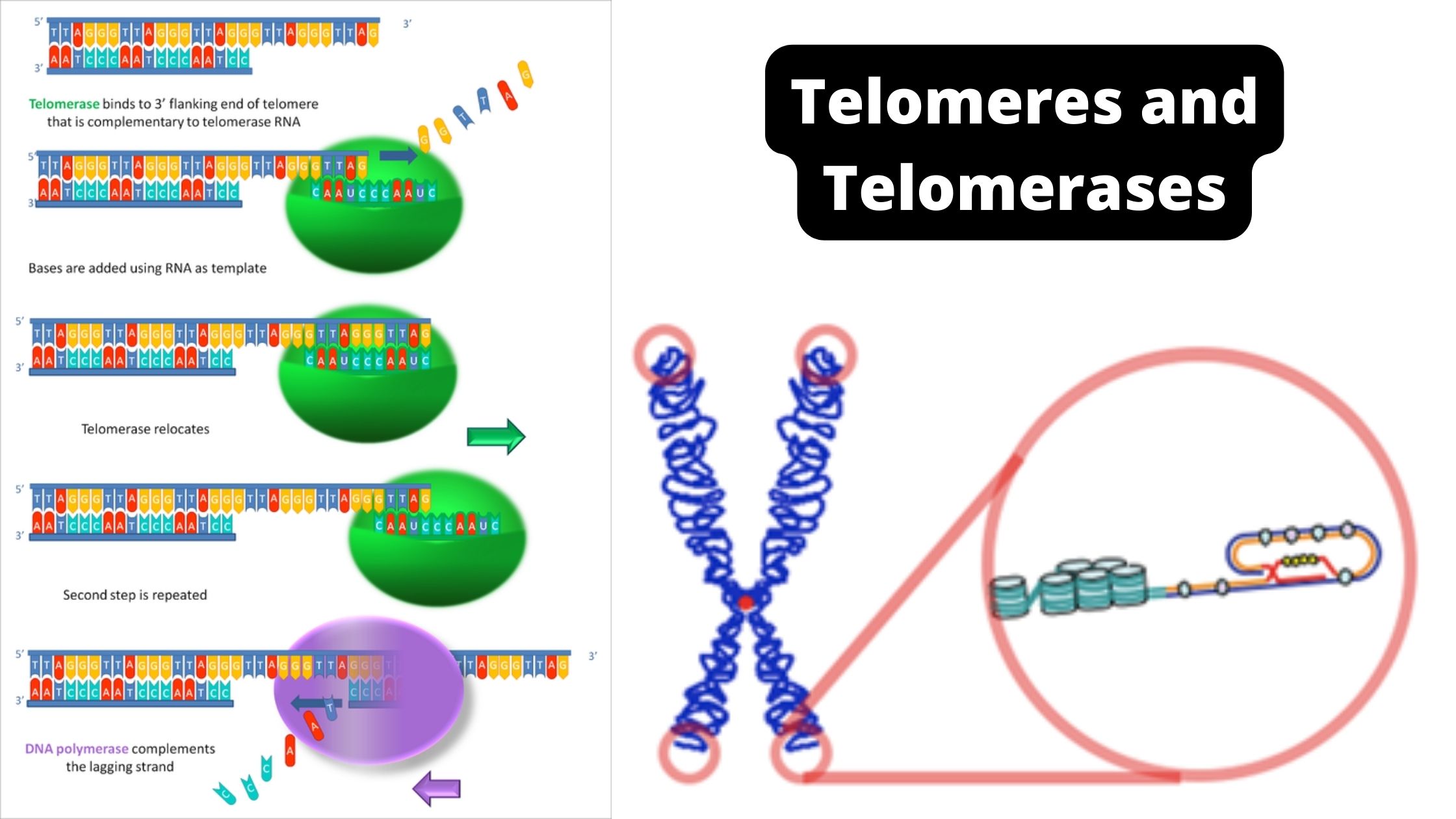
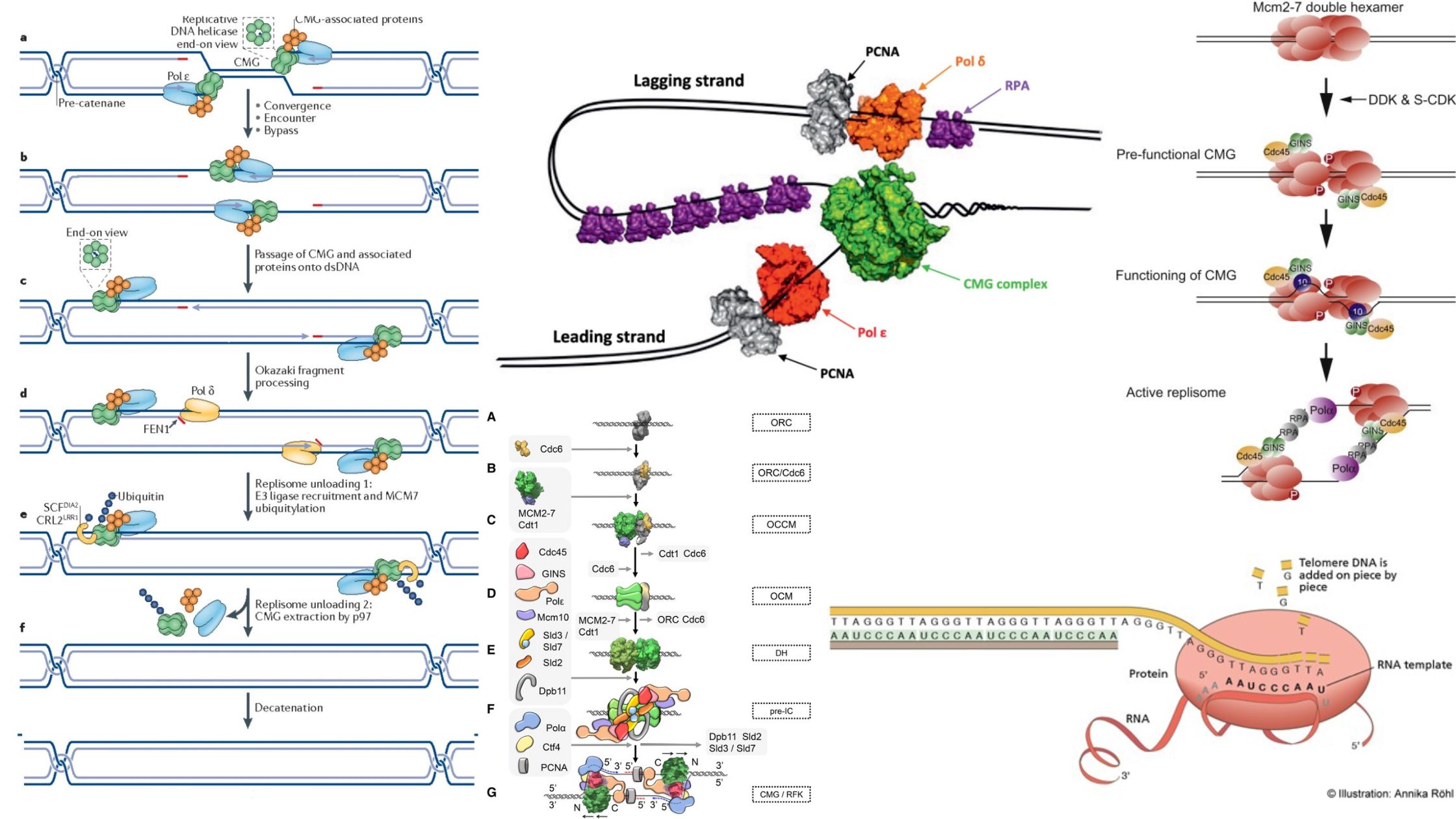
A ribonucleoprotein known as telomerase, terminal transferase adds a repeat sequence of telomeres to the 3′ end of chromosomes, the length of which varies depending on species. In most eukaryotic organisms, the chromosomal ends are capped by a repeating sequence known as a telomere. Telomeres prevent DNA damage and chromosomal fusion at the chromosome’s end. … Read more