Table of Contents
What is Stokes Disc Diffusion Method?
- The Stokes Disc Diffusion Method, a technique utilized for Antibiotic Sensitivity Testing (AST), presents a distinctive approach compared to the more standardized Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion method. This method is particularly employed in laboratories facing challenges related to the guaranteed amount of antimicrobial in a disc, difficulties in obtaining and storing discs accurately, or when the specific conditions essential for the Kirby-Bauer technique cannot be met.
- In contrast to the Kirby-Bauer technique, the Stokes method incorporates both control and test strains on the same plate, offering a nuanced comparative analysis. Despite its lower level of standardization, the Stokes disc diffusion technique remains prevalent in laboratories, especially in the United Kingdom, where it is employed to assess antibiotic susceptibility. This preference arises from situations where the precise amount of antimicrobial in a disc cannot be ensured, possibly due to challenges in disc acquisition and storage or when strict Kirby-Bauer conditions are unattainable.
- The method enables a direct comparison between individual isolates and a sensitive control of the same or similar species. The control and test organisms, positioned adjacent on the same plate, undergo identical technical conditions, including medium, incubation time, atmosphere, temperature, and disc content. This proximity allows for the direct measurement of the difference between respective zone sizes, enhancing the precision of the analysis.
- In the Stokes disc diffusion method, a set of standard strains serves as control strains, varying depending on the organism under examination. For instance, E. coli NCTC 10414 functions as a control strain for testing coliform bacilli from the urinary tract, while Pseudomonas aeruginosa NCTC 10662 serves against aminoglycosides. The utilization of control strains in this method ensures a standardized reference for comparison, contributing to the reliability and reproducibility of the results.
- Antibiotic Sensitivity Testing, achieved through methods such as the Stokes disc diffusion technique, is fundamental in determining the least amount of an antimicrobial chemotherapeutic agent required to inhibit microbial growth in vitro. The approach involves a comprehensive set of methods, including the disk diffusion method (Kirby Bauer and Stokes methods), minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) methods like broth dilution and agar dilution, and the E-test.
Principle of Stokes Disc Diffusion Method
The principle of the Stokes Disc Diffusion Method revolves around the strategic placement of discs between standard and test inocula on a culture plate. This method is designed to evaluate the susceptibility of microorganisms to antibiotics by observing the formation and measurement of Zone of Inhibition (ZOI) around each disc.
To begin, the procedure involves the application of discs that contain specific antibiotics. These discs are strategically positioned between the standard inoculum, representing a known strain, and the test inoculum, which consists of the microorganisms under investigation. By arranging the discs in this manner, the resulting Zone of Inhibition encompasses both standard and test bacteria.
The central process underlying this method is the diffusion of antibiotics from the discs into the surrounding agar medium. As antibiotics disperse, they encounter the bacterial populations present in the standard and test inocula. The susceptibility of these microorganisms to the antibiotics is reflected in the observed Zone of Inhibition, which represents the area where bacterial growth is inhibited due to the presence of the antimicrobial agent.
Measurement of the Zone of Inhibition provides quantitative data that allows for the determination of antibiotic susceptibility. A larger zone typically indicates greater susceptibility, as it suggests a more effective inhibition of bacterial growth. Conversely, a smaller or absent zone may suggest resistance to the antibiotic.
The use of this method allows for a direct comparison between the responses of standard and test strains to the same antibiotic. By placing them in close proximity on the same plate, the technical conditions, such as medium composition, incubation time, atmosphere, and temperature, are kept uniform. This standardization ensures a reliable assessment of the differences in zone sizes between the two populations.
In summary, the principle of the Stokes Disc Diffusion Method hinges on the spatial arrangement of discs between standard and test inocula to assess antibiotic susceptibility. The observed Zone of Inhibition, resulting from the diffusion of antibiotics, serves as a measurable indicator of the efficacy of the antimicrobial agents against the microbial populations under examination. This method, by emphasizing direct comparisons and standardized conditions, provides valuable insights into the relative susceptibility of microorganisms to specific antibiotics.
Purposes of Stokes Disc Diffusion Method
The Stokes Disc Diffusion Method is a laboratory technique used for several purposes, including:
- Determining antimicrobial susceptibility: The primary purpose of the Stokes Disc Diffusion Method is to determine the antimicrobial susceptibility of a microorganism to various antibiotics or other antimicrobial agents. The test helps to identify which antibiotics or agents are effective in treating an infection caused by the microbe.
- Quality control of antibiotics: The Stokes Disc Diffusion Method is also used to ensure the quality and potency of antibiotics. The test is performed on antibiotic products to determine their efficacy against specific microorganisms.
- Surveillance of antibiotic resistance: The test is used to monitor the emergence of antibiotic resistance in microbial populations. The results of the test can help to identify trends in antibiotic resistance and guide appropriate treatment strategies.
- Research: The Stokes Disc Diffusion Method is used in research studies to investigate the mechanisms of antibiotic resistance and to evaluate the effectiveness of new antimicrobial agents.
Overall, the Stokes Disc Diffusion Method is a valuable tool for determining the susceptibility or resistance of microorganisms to various antimicrobial agents. This information can be used to guide appropriate treatment strategies and to monitor the emergence of antibiotic resistance.
Types of Stokes Disc Diffusion Method
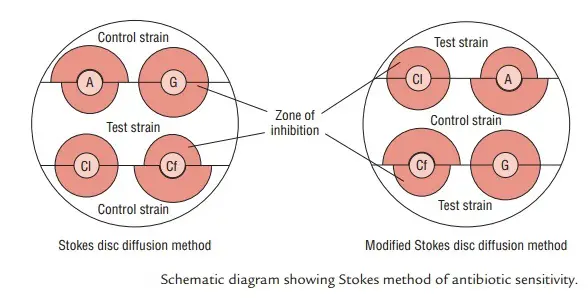
The Stokes Disc Diffusion Method is bifurcated into two distinct types, namely the conventional Stokes disc diffusion method and the Modified Stokes disc diffusion method. Each type is characterized by specific procedural nuances that influence the distribution of test and control organisms on the culture plate.
- Conventional Stokes Disc Diffusion Method: In the conventional approach, the test organism is strategically inoculated onto the central one-third of the culture plate. Concurrently, control organisms are placed on the upper and lower thirds of the plate. This distribution allows for a systematic evaluation of antibiotic susceptibility by observing the Zone of Inhibition (ZOI) formation around the discs. The central placement of the test organism ensures that its response to the antibiotic is directly comparable to the responses of the control strains located on either side.
- Modified Stokes Disc Diffusion Method: In the modified version of the Stokes disc diffusion method, there is a reversal in the placement of test and control organisms on the culture plate. Here, the test bacterium is inoculated over the upper and lower thirds of the plate, while the control organism is placed on the central one-third. This alteration in the spatial arrangement is a key distinction from the conventional method. The modified approach still achieves a comprehensive evaluation of antibiotic susceptibility, but the distribution of organisms on the plate is adjusted.
Other types of Stokes Disc Diffusion Method
- Kirby-Bauer Method: This is the most commonly used method of Stokes Disc Diffusion. In this method, paper discs impregnated with specific antibiotics or other antimicrobial agents are placed on a culture plate containing the test organism. The diameter of the zone of inhibition (clear zone around the disc where no growth of the organism occurs) is measured and compared to a standardized chart to determine the susceptibility or resistance of the microbe to the tested agent.
- E-test Method: This method uses a plastic strip impregnated with a gradient of antibiotic concentrations. The strip is placed on the agar surface inoculated with the test organism, and the lowest concentration of the antibiotic at which there is no growth of the organism is recorded as the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC).
- M.I.C.Evaluator Strips: Similar to the E-test method, M.I.C.Evaluator strips contain a gradient of antibiotic concentrations on a plastic strip, but in this case, the strip is placed in a liquid culture rather than on an agar surface. The lowest concentration of the antibiotic at which there is no visible growth of the organism is recorded as the MIC.
- Broth Dilution Method: In this method, the antimicrobial agent is diluted in liquid culture medium, and the test organism is inoculated into the medium at a specific concentration. The tubes are incubated, and the lowest concentration of the antimicrobial agent that inhibits growth of the organism is recorded as the MIC.
These different methods of the Stokes Disc Diffusion Method can be used to determine the susceptibility or resistance of a microorganism to various antimicrobial agents, which can guide appropriate treatment strategies.

Requirements for the Test
- MHA Plate: The Mueller-Hinton Agar (MHA) plate serves as the foundational substrate for the entire procedure. MHA, with its standardized composition, provides an ideal medium for the growth and diffusion of microorganisms and antimicrobial agents. Its consistent formulation is vital for maintaining uniform testing conditions.
- Antimicrobial Discs: Specialized discs containing specific concentrations of antimicrobial agents are a core component. These discs act as carriers for the antibiotics and are responsible for inducing the formation of Zones of Inhibition (ZOI) when placed on the MHA plate. The selection of appropriate antimicrobial discs is critical for accurate susceptibility assessment.
- Sterile Cotton Swabs: Sterile cotton swabs are indispensable for the uniform distribution of microbial inocula on the MHA plate. They facilitate the even spread of bacterial cultures, ensuring consistency and reproducibility in the testing process.
- Sterile Forceps: Sterile forceps are employed to handle antimicrobial discs and prevent contamination. Their sterile nature is paramount in maintaining the integrity of the experiment and preventing unintended influences on the test results.
- Control Strains: Depending on the specific bacterium under examination, control strains such as S. aureus NCTC 6571, E. coli NCTC 10414, or P. aeruginosa NCTC 10662 are utilized. These strains serve as reference points, enabling a standardized comparison between test and control organisms. Their known susceptibilities contribute to the reliability of the results.
- Bunsen Burner: The Bunsen burner is employed to create a sterile working environment. It ensures that all equipment, such as inoculating loops and forceps, is free from contaminants, thus preventing interference with the experimental setup.
- Inoculating Loop: The inoculating loop is used to transfer and streak microbial cultures onto the MHA plate. Its sterile application guarantees the accurate placement of test and control organisms, a critical factor in the reliability of the results.
- 0.5 McFarland Standard or McFarland Densitometer: The McFarland Standard, or a McFarland Densitometer, is employed to standardize the density of microbial suspensions. This standardization is crucial for achieving consistent and reproducible results, as it ensures uniformity in the quantity of microbial cells introduced onto the MHA plate.
- Incubator: An incubator provides the controlled environment necessary for bacterial growth and the expression of susceptibility. The specified conditions of temperature, atmosphere, and incubation time are critical variables that influence the outcome of the test.
- Wickerham Card: The Wickerham Card is likely utilized for the interpretation of results, contributing to the standardization and documentation of the experimental outcomes.
Procedure of Stokes Disc Diffusion Method – How do you perform disc diffusion method?
- Isolation of Colonies:
- Select 3-5 well-isolated colonies of the same morphological type from both test and control strains on an agar plate.
- Broth Culture Preparation:
- Transfer the selected colonies into a tube containing 4 to 5 ml of a tryptic soy broth.
- Incubate the broth culture at 37°C until it achieves the turbidity of the 0.5 McFarland standard, typically taking 2 to 6 hours.
- Turbidity Adjustment:
- Adjust the turbidity of the actively growing broth culture to match the 0.5 McFarland standard using sterile saline or tryptic soy broth.
- This step ensures a standardized suspension containing approximately 1 to 2 x 10^8 CFU/ml for E. coli ATCC 25922.
- McFarland Densitometer or Visual Comparison:
- Utilize a McFarland densitometer for precise measurement or visually compare the inoculum tube against the 0.5 McFarland standard with a Wickerham card.
- Cotton Swab Inoculation:
- Dip sterile cotton swabs into each of the adjusted suspensions within 15 minutes of turbidity adjustment.
- Rotate the swabs, remove excess inoculum by pressing firmly on the tube’s inner wall.
- Preparation of Inoculation Plates:
- Dry Müeller-Hinton agar plates with the lid open, allowing free droplets of moisture on the surface.
- Divide the dried surface of the Müeller-Hinton agar plate into three halves.
- Control Strain Inoculation:
- Inoculate the upper and lower thirds of the plate evenly with control strains, leaving a central band uninoculated.
- Allow the inocula to dry for a few minutes.
- Test Strain Inoculation:
- In conventional Stokes disc diffusion method, apply the test organism in the central portion without touching either side.
- In modified Stokes disc diffusion method, reverse the order of steps 7 and 8.
- Disc Application:
- Apply antimicrobial discs with forceps on the line between test and control organisms.
- Press gently to ensure even contact with the medium. Maintain a minimum distance of 2 cm between discs.
- Incubation:
- Incubate the plates aerobically at 35-37°C for 18-24 hours.
Result Interpretation of Stokes Disc Diffusion Method
The interpretation of results in the Stokes Disc Diffusion Method is a critical phase that involves the measurement and comparison of inhibition zones formed around antimicrobial discs. To ensure accuracy, extremes in inoculum density are to be avoided, and undiluted overnight broth cultures or unstandardized inocula should never be used for streaking plates.
Result Interpretation:
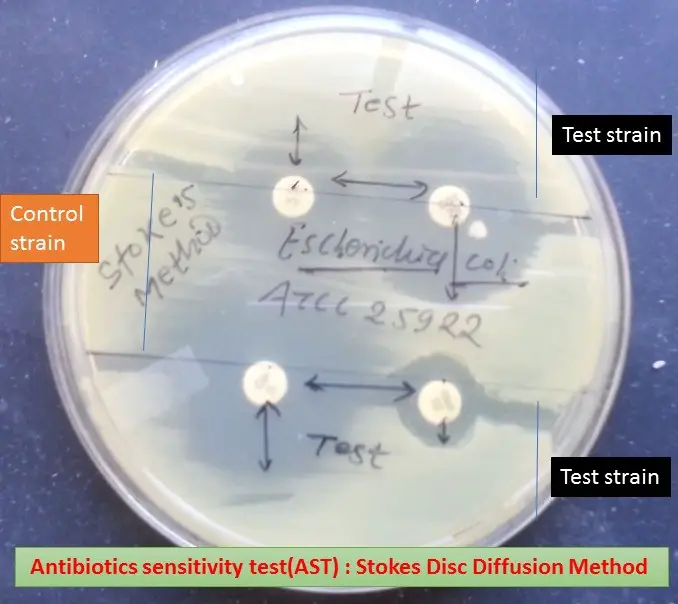
- Measurement of Inhibition Zones: The radius of the inhibition zone is measured from the edge of the antimicrobial disc to the edge of the zone.
- Sensitive (S): A strain is categorized as sensitive if the zone radius is wider than or equal to, or not more than 3mm smaller than the control. In other words, the test strain exhibits a zone size that is larger than or equal to the control strain. If the zone size of the test bacterium is smaller than that of the control, the difference between the two should not exceed 3 mm.
- Intermediate (I): A strain falls into the intermediate category if the zone radius is greater than 2 mm but smaller than the control by more than 3 mm.
- Resistant (R): A strain is considered resistant if there is no zone of inhibition or if the zone radius measures 2 mm or less.
Visual Representation
- The interpretation involves visually assessing the inhibition zones as illustrated in the provided image.
- The zones are measured meticulously to categorize strains as sensitive, intermediate, or resistant based on the defined criteria.
Antibiotic Susceptibility Result
| Zone Radius | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| ≥ Control or ≤ Control + 3mm | The test strain is sensitive to the antibiotic. |
| > 2mm but < Control – 3mm | The test strain shows intermediate susceptibility. |
| No zone or ≤ 2mm | The test strain is resistant to the antibiotic. |
Uses of Stokes Disc Diffusion Method
- Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing:
- The primary and fundamental use of the Stokes Disc Diffusion Method is in determining the susceptibility of bacterial isolates to various antibiotics. This method helps microbiologists and clinicians assess the effectiveness of specific antimicrobial agents against a given bacterial strain.
- Comparison of Control and Test Strains:
- The method allows for a direct comparison between control strains and test strains on the same plate. This simultaneous evaluation is crucial for understanding how different bacterial strains respond to the same set of experimental conditions, providing valuable insights into variations in antibiotic susceptibility.
- Quality Testing of Antimicrobial Discs:
- The method is employed for quality testing of antimicrobial discs. By incorporating both control and test strains in close proximity, any discrepancies in the quality of the discs, such as variations in the amount of antimicrobial agents, can be readily identified. This ensures a higher level of precision in the assessment of antibiotic susceptibility.
- Minimization of Environmental Variation Effects:
- The Stokes method minimizes errors introduced by variations in environmental conditions such as temperature and time. Since both control and test organisms are subjected to the same environment on the same plate, any impact of these external factors affects both strains simultaneously. This inherent standardization contributes to result consistency and reduces the likelihood of experimental errors.
- Detection of Inoculum Errors:
- The method facilitates the detection of errors related to inoculum density. Errors arising from using excessively heavy or light inocula are readily apparent, as the consequences of such variations are observed in both control and test strains. This feature enhances the method’s ability to identify and account for potential sources of experimental error.
- Efficient Testing of Multiple Antibiotics:
- Stokes Disc Diffusion Method allows the testing of strips with multiple antibiotics on a single plate. This efficiency is advantageous in scenarios where a comprehensive analysis of multiple antimicrobial agents is required. It streamlines the testing process, conserves resources, and facilitates a more comprehensive evaluation of antibiotic susceptibility.
Advantages of Stokes Disc Diffusion Method
- Simultaneous Evaluation of Control and Test Strains:
- One notable advantage is the ability to check both the control strain and test strain on the same plate. This simultaneous evaluation ensures a direct and immediate comparison, providing valuable insights into the relative responses of these strains to the applied antimicrobial agents.
- Enhanced Reliability in Disc Quality Testing:
- The method proves more reliable for the quality testing of discs. By incorporating both control and test strains in close proximity, any discrepancies in the quality of the discs, such as variations in the amount of antimicrobial agents, can be readily identified. This ensures a higher level of precision in the assessment of antibiotic susceptibility.
- Minimization of Environmental Variation Effects:
- The Stokes method minimizes errors introduced by variations in environmental conditions such as temperature and time. Since both control and test organisms are subjected to the same environment on the same plate, any impact of these external factors affects both strains simultaneously. This inherent standardization contributes to result consistency and reduces the likelihood of experimental errors.
- Detection of Inoculum Errors:
- The method facilitates the detection of errors related to inoculum density. Errors arising from using excessively heavy or light inocula are readily apparent, as the consequences of such variations are observed in both control and test strains. This feature enhances the method’s ability to identify and account for potential sources of experimental error.
- Testing of Multiple Antibiotics on a Single Plate:
- Stokes Disc Diffusion Method allows the testing of strips with multiple antibiotics on a single plate. This efficiency is advantageous in scenarios where a comprehensive analysis of multiple antimicrobial agents is required. It streamlines the testing process, conserves resources, and facilitates a more comprehensive evaluation of antibiotic susceptibility.
Disadvantages of Stokes Disc Diffusion Method
- Limited Standardization Compared to Kirby Bauer Technique:
- One notable disadvantage is the lower level of standardization in the Stokes disc diffusion technique when compared to the Kirby Bauer technique. The Kirby Bauer method is recognized for its highly standardized procedures, making it a preferred choice in many laboratories. In contrast, the Stokes method is employed when challenges exist in ensuring the precise amount of antimicrobial in a disc. This lack of standardization may result from difficulties in obtaining discs and storing them correctly.
- Challenges in Disc Acquisition and Storage:
- Difficulties in obtaining antimicrobial discs and maintaining their correct storage conditions pose challenges to the Stokes Disc Diffusion Method. The reliability of the method is contingent upon the quality and consistency of the discs used. Issues related to disc availability and storage can introduce variability and compromise the accuracy of the test results.
- Conditions Unsuitable for Kirby-Bauer Technique:
- The Stokes method becomes a preferred alternative when the specific conditions required for the Kirby-Bauer technique cannot be met. The method is employed in situations where the precise conditions necessary for the Kirby Bauer method, such as controlled disc storage and acquisition, are challenging to maintain.
- Limitation in the Number of Antibiotics Tested:
- Another limitation of the Stokes Disc Diffusion Method is the testing of a relatively low number of antibiotics on a single plate. This restriction can be a drawback when there is a need for a more extensive analysis of antimicrobial agents. Laboratories requiring a comprehensive evaluation of multiple antibiotics may find this method less suitable due to its inherent limitation in testing capacity.
Keynotes on Stokes Disc Diffusion Method
- Disc Accommodation on Circular Plate:
- A distinctive aspect of the Stokes method is its accommodation of four discs on an 85 mm circular plate. This specification provides a clear delineation of space for the placement of antimicrobial discs, ensuring a systematic and organized layout for testing.
- Caution Against Inoculum Density Extremes:
- The method emphasizes the avoidance of extremes in inoculum density. Specifically, undiluted overnight broth cultures or other unstandardized inocula are cautioned against for streaking plates. This precautionary measure is vital to maintain the consistency and reliability of results by preventing variations introduced by irregular inoculum densities.
- Rotatory Plating Method for Inoculation:
- An alternative to the standard inoculation procedure involves the use of a rotatory plating method. In this variation, the control strain is applied on the outer periphery of the circular plate, while the test strain is applied in the central portion. This technique allows for the accommodation of six discs on an 85 mm circular plate, offering an expanded testing capacity within the same experimental setup.
FAQ
What is Stokes disc diffusion method?
The Stokes Disc Diffusion Method, also known as the disk diffusion method or the Kirby-Bauer method, is a laboratory technique used to determine the antimicrobial susceptibility of microorganisms to various antibiotics or other antimicrobial agents.
In this test, paper discs that have been impregnated with specific antibiotics or other antimicrobial agents are placed on a culture plate containing the test organism. As the antibiotics diffuse out of the discs into the surrounding agar, they inhibit the growth of the microbe in the immediate vicinity, creating a circular zone of inhibition around the disc. The diameter of this zone of inhibition is measured and compared to a standardized chart to determine the susceptibility or resistance of the microbe to the tested agent.
The Stokes Disc Diffusion Method is a rapid, simple, and inexpensive test that can be used to identify which antibiotics or agents are effective in treating an infection caused by a particular microbe. The results of the test can help clinicians select the appropriate antibiotic for a patient’s infection and can also help to monitor the emergence of antibiotic resistance in microbial populations.
What is the aim of Stokes method?
The Stokes Disc Diffusion Method, also known as the disk diffusion method or the Kirby-Bauer method, is a laboratory technique aimed at determining the antimicrobial susceptibility of microorganisms to various antibiotics or other antimicrobial agents.
The primary aim of the Stokes Disc Diffusion Method is to provide information about the effectiveness of different antibiotics or antimicrobial agents against a particular microbe. This information can help clinicians choose the appropriate antibiotic or treatment for an infection caused by the microbe. The test can also be used to monitor the emergence of antibiotic resistance in microbial populations and to evaluate the efficacy of new antimicrobial agents.
Overall, the Stokes Disc Diffusion Method is a valuable tool in the fight against infectious diseases, helping to guide appropriate treatment strategies and monitor the emergence of antimicrobial resistance.
Why is disk diffusion method used?
The disk diffusion method, also known as the Stokes Disc Diffusion Method or the Kirby-Bauer method, is a laboratory technique used to determine the antimicrobial susceptibility of microorganisms to various antibiotics or other antimicrobial agents.
The disk diffusion method is used for several reasons, including:
1. Identification of effective antibiotics: The primary reason for using the disk diffusion method is to identify which antibiotics or other antimicrobial agents are effective against a particular microbe. This information can help clinicians choose the appropriate treatment for a patient’s infection.
2. Monitoring the emergence of antimicrobial resistance: The disk diffusion method is also used to monitor the emergence of antimicrobial resistance in microbial populations. By testing the susceptibility of microorganisms to various antibiotics over time, trends in resistance can be identified, allowing for the development of appropriate treatment strategies.
3. Quality control of antibiotics: The disk diffusion method is used to ensure the quality and potency of antibiotics. The test is performed on antibiotic products to determine their efficacy against specific microorganisms.
4. Research: The disk diffusion method is used in research studies to investigate the mechanisms of antibiotic resistance and to evaluate the effectiveness of new antimicrobial agents.
Overall, the disk diffusion method is a simple, rapid, and inexpensive test that can provide valuable information about the antimicrobial susceptibility of microorganisms. This information can guide appropriate treatment strategies, monitor the emergence of antimicrobial resistance, and inform the development of new antimicrobial agents.
What is the name of the disc diffusion test?
The name of the test is the disc diffusion method, also known as the Stokes Disc Diffusion Method or the Kirby-Bauer method.
