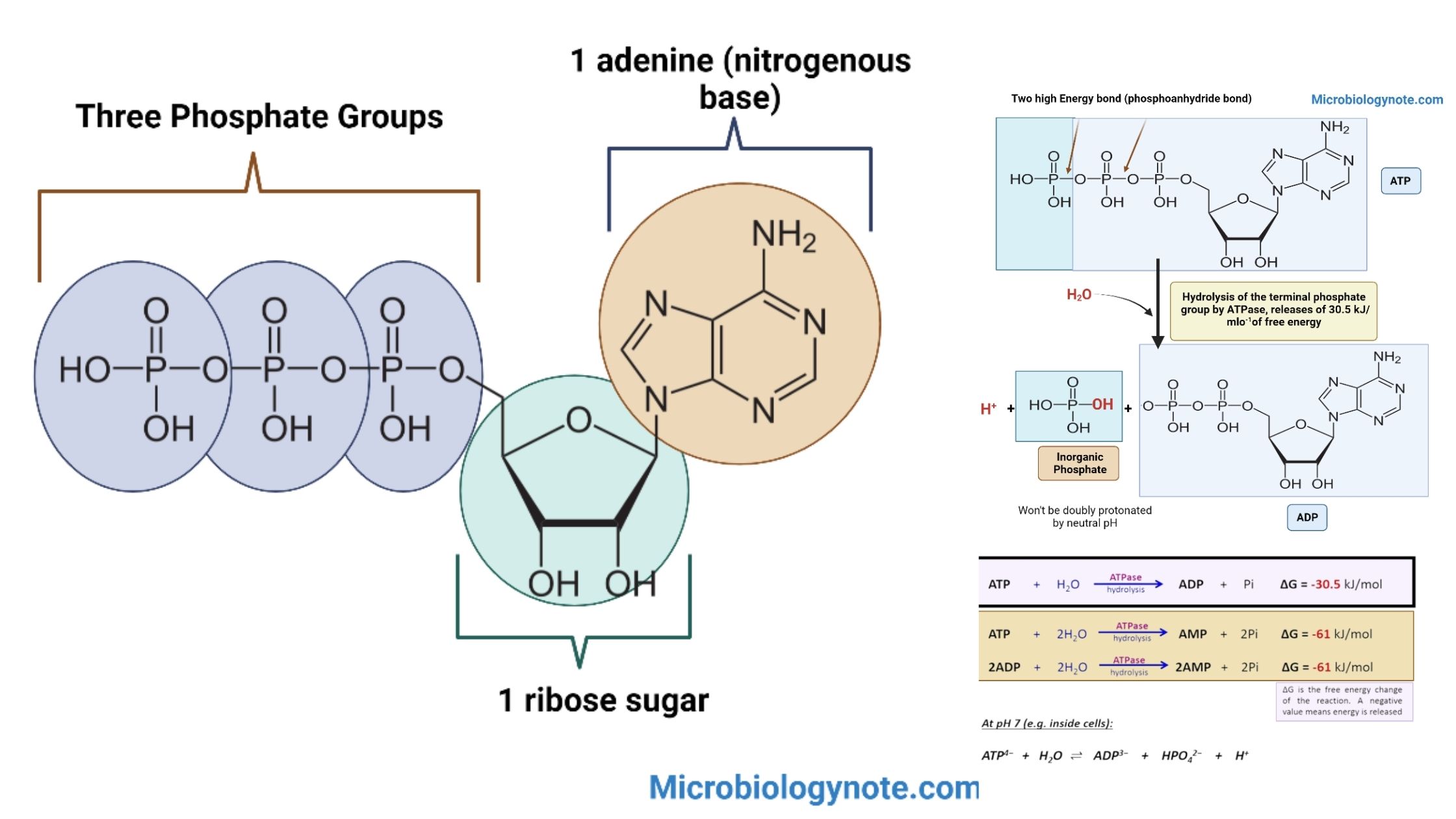
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) Structure, Synthesis, Functions
Because the body is complex, energy is required to ensure proper functioning. Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, is the energy source for use and storage at cellular level. ATP’s structure is a nucleoside triophosphate. It consists of a ribose glucose, a nitrogenous base (adenine) and three serially bonded phosphate group. ATP is often referred to by the term “energy currency” because it can be readily releasable in the bond between the third and second phosphate groups. Hydrolysis, which is the process of reducing ATP to energy, serves a wide range of cell functions including signaling and DNA/RNA synthesis. ATP synthesis uses energy from many catabolic mechanisms including cell respiration, betaoxidation, ketosis, and cellular metabolism.