Table of Contents
What is a water distiller?
- A water distiller is a specialized piece of equipment that plays a crucial role in producing pure and contaminant-free water. It operates by mimicking the natural filtration process that occurs on Earth, transforming water into vapor and then condensing it back into a liquid state.
- The primary purpose of a water distiller is to remove impurities from water, ensuring that the end result is of unmatched purity. When water is heated and transformed into steam during the distillation process, certain impurities such as germs, heavy metals, and arsenic cannot undergo the transformation and remain in the boiling chamber. These impurities are left behind while the water changes its state from a liquid to a gaseous form.
- Once the water has evaporated, the distiller cools it down, causing it to condense and return to a liquid state. This condensed water is pure and free from minerals, making it suitable for drinking. Distilled water finds applications in various settings, including fermentation processes, the medical industry, clinics, and organic chemistry labs. Additionally, equipment such as autoclaves and batteries often require distilled water for optimal performance.
- It’s important to note that there are notable differences between deionized water and distilled water in terms of the pollutants they remove, although the terms are sometimes used interchangeably. A water distiller system has the capability to filter out non-volatile organic molecules, a wide range of chemicals, and most minerals, along with charged ions. A properly maintained and clean distiller can eliminate over 95% of minerals like salt, sulfate, nitrate, and even arsenic. Moreover, biological pollutants such as bacteria, viruses, and cysts are also effectively removed through the distillation process.
- However, it is worth mentioning that due to the high operating costs and the relatively slow production of treated water, water distillers are often used to produce smaller quantities of water primarily for drinking and cooking purposes. In situations where larger amounts of treated water are required, a reverse osmosis system (RO) is typically a more suitable choice.
- In summary, a water distiller is a valuable piece of equipment that ensures the production of pure, mineral-free water. By replicating the natural filtration process, it effectively removes impurities, including germs, heavy metals, and chemicals, while also eliminating a wide range of minerals and biological pollutants. While water distillers are best suited for smaller-scale water production, they are indispensable in various industries and applications where the highest level of water purity is required.
Definition Water distiller
A water distiller is a device that purifies water by heating it to produce steam, then cooling and condensing the steam to remove impurities. This process helps remove contaminants such as bacteria, viruses, heavy metals, and minerals, resulting in purified and distilled water.
Principle of Water Distiller – How Does a Water Distiller Work?
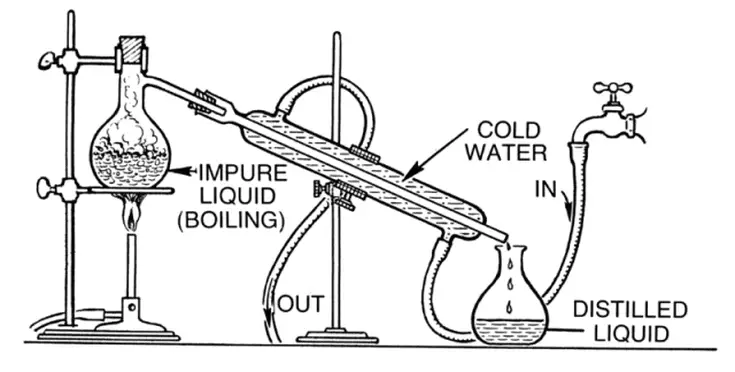
The principle of a water distiller revolves around the processes of evaporation and condensation. The distillation process begins by adding thermal energy to water, which is still in its liquid state. This energy causes the water molecules to gain enough kinetic energy to break free from the molecules of other substances that may be diluted or mixed with it.
As the water is heated, it undergoes evaporation and transforms into vapor. This vapor, containing only the water molecules, is then directed towards a condenser. The condenser is designed to cool down the water vapor, causing it to lose thermal energy and return to its liquid state.
During the condensation process, the water vapor converts back into liquid form, resulting in distilled water. The condensed water droplets are collected and stored in a separate tank or container. This distilled water possesses exceptional purity as it is free from the impurities that were present in the original water source.
The principle of a water distiller is based on the fact that impurities, such as bacteria, viruses, minerals, heavy metals, and other contaminants, do not undergo the transformation into vapor. These impurities are left behind in the boiling chamber or discarded during the distillation process. As a result, the distilled water produced by a water distiller exhibits pristine qualities and is essentially free of impurities, making it suitable for various applications that require pure water.
Parts of a Water Distiller
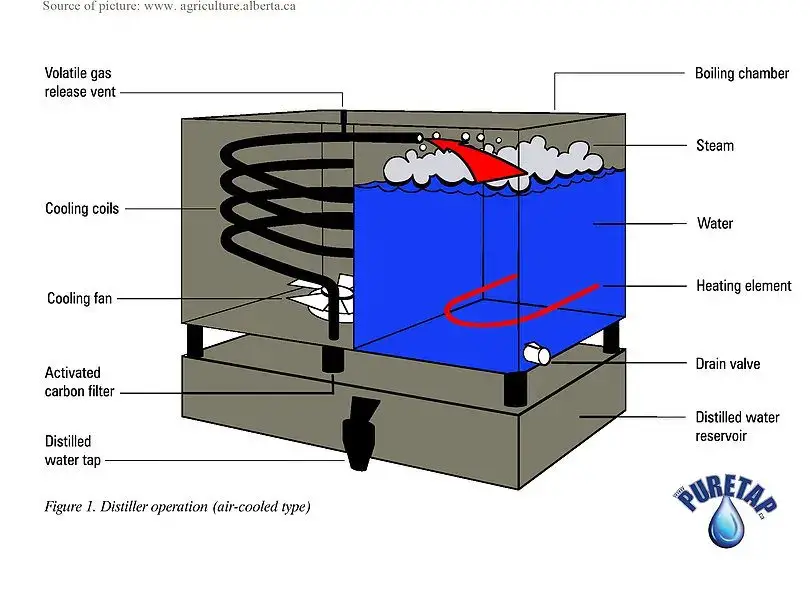
A water distiller is composed of several essential parts that work together to produce purified water. These parts include:
- Vapour generator/Boiling tank: This is the container designed to store the water to be distilled. In small-volume distillers, glass is typically used, while larger-volume machines are made of stainless steel with copper, tin, or titanium coverings.
- Water Level Gauge: It allows for the regulation of the water quantity in the vapour generator. The gauge enables the recovery of evaporated liquid when the water level in the boiling tank drops.
- Control valve: This device mechanically or electromechanically controls the flow of water towards the vapour generator tank.
- Immersion resistors: These resistors generate heat when an electrical current passes through them. They are sealed off by a ceramic cover and protected from the external environment by a metal plate.
- Refrigerator water outlet: This is a line used for the condensation of water vapor, providing cooling during the distillation process.
- Condenser: The condenser cools the vapor and returns it to its liquid phase by losing thermal energy. Forced convection, involving the circulation of low-temperature fluids such as water or air around the vapor flow line, accelerates this process.
- Filter: Activated carbon filters are often present in water distillers near the condenser or collector exit. They remove any flavors or particles that may be present as the vapor is condensed.
- Distilled water container: This container is where the liquid that has undergone distillation is collected. It is important to store distilled water in designated plastic containers to prevent ionic contamination. Containers made of materials like polytetrafluoroethylene, polyethylene, or polypropylene are commonly used.
Additionally, other common parts of a water distiller include:
- Boiler or heating element: Located at the bottom of the distiller, it generates heat to bring the water to boiling point.
- Boiling chamber: Positioned above the boiler or heating element, it holds the water to be heated and distilled.
- Collection chamber or bottle: Positioned above the condenser, it collects the purified water after condensation.
- Pre-filter: Some distillers have a pre-filter that removes larger particles and contaminants from the water before distillation.
- Carbon filter: Some distillers incorporate a carbon filter to remove chlorine, pesticides, and other chemicals from the water before the distillation process begins.
By working in harmony, these components enable the water distiller to produce purified, distilled water by utilizing the principles of evaporation and condensation.
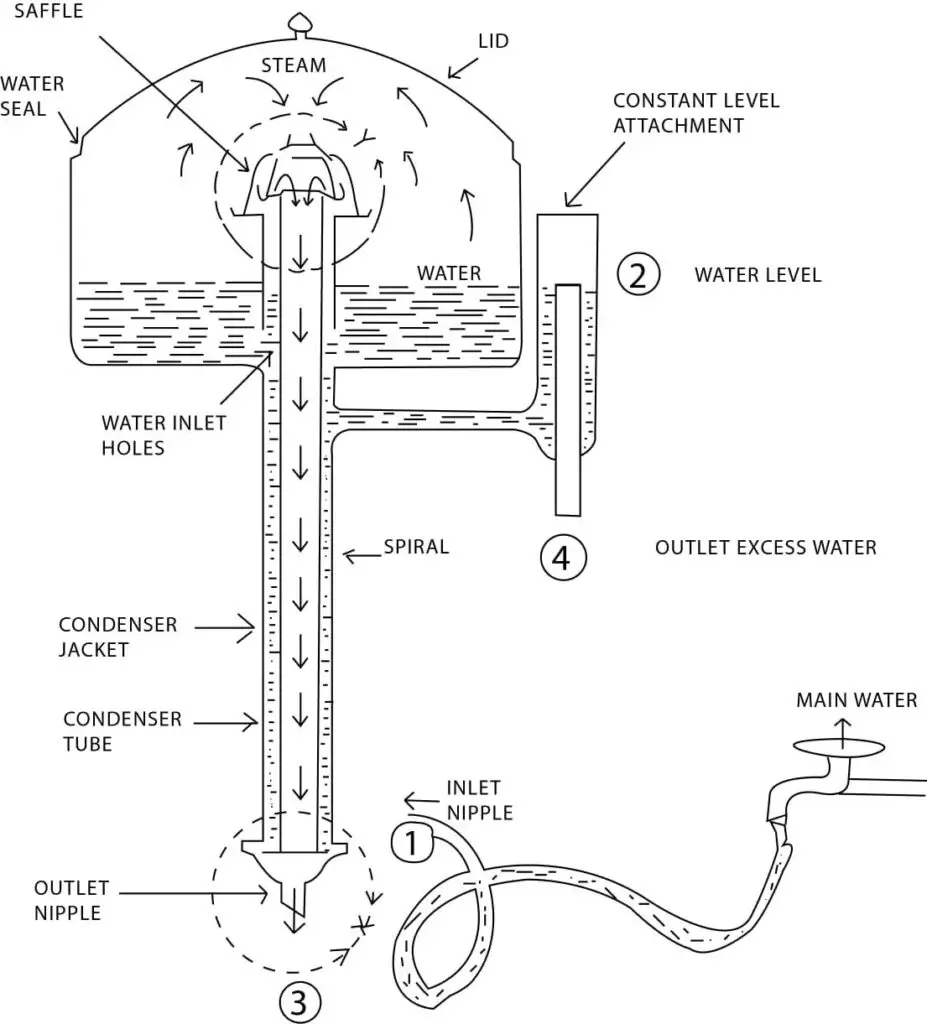
Types of Water Distillers
Water distillers can be classified into different types based on their configuration and usage. Let’s explore these types:
- Manual Distiller System: This type of distiller system requires manual operation. It can produce around 1 gallon of water at a time. Once the first gallon is produced, the system needs to be physically refilled to produce subsequent gallons of water. The capacity of a manual distiller is determined by the amount of water it can generate in an hour. Typically, 1-gallon-sized glass or plastic jars are used in manual distillation systems.
- Automatic Distiller System: Automatic distillers are designed to connect to a water source continuously, ensuring a constant supply of pure water. These systems are controlled by electronics or float valves, which stop the production of water when the holding tanks reach a specific level. The capacity of an automatic distiller system is determined by its daily output capacity. These systems can store 3 to 25 liters of water in a stainless-steel reservoir.
Types based on usage:
- Plumbing Distillers: Plumbing distillers are integrated into the plumbing system. They provide a convenient and cost-effective option for water distillation. However, they require regular maintenance, such as emptying sediments that may collect in the boiling chamber.
- Household Distillers: Household distillers are designed for domestic use. They are typically compact and can be placed on a kitchen counter or in the workplace. One common type is the single-effect distiller, which allows users to add the desired amount of water to be distilled, collect it, and filter it for consumption.
- Commercial Distillers: Commercial distillers are used in large-scale applications where a higher volume of distilled water is needed. They often utilize multiple-effect distillation technology, allowing for a daily output range of 75 gallons to millions of gallons. Commercial distillers may have different boiling chambers to produce a larger quantity of distilled water.
These different types of water distillers cater to various needs, ranging from small-scale domestic use to large-scale commercial applications. Whether manual or automatic, plumbing or household, water distillers offer a reliable method for producing purified and distilled water.
Operating Procedure of Water Distiller
The operating procedure of a water distiller typically involves the following steps:
- Powering On: The water distiller is plugged into a power source and turned on. It is important to ensure that the distiller is properly connected to a reliable power supply.
- Adding Water: Water is poured into the boiling chamber of the distiller. The amount of water added should be appropriate for the capacity of the distiller and within its specified limits.
- Boiling Process: The heating element inside the distiller raises the temperature of the water in the boiling chamber. As the water reaches its boiling point, it starts to evaporate and turn into steam. This process helps separate the water molecules from impurities present in the water.
- Separation of Impurities: As the water boils and turns into steam, impurities such as bacteria, fluorides, and other harmful substances remain behind in the boiling chamber. These impurities cannot transform into steam and are left behind in the distillation process.
- Condensation: The steam rises from the boiling chamber and enters the cooling system, which typically consists of a stainless-steel condenser. The condenser cools the steam, causing it to condense back into liquid form.
- Filtration: Some water distillers are equipped with an activated carbon filter. This filter helps remove any remaining impurities or contaminants present in the condensed water droplets. Activated carbon has adsorptive properties that attract and trap pollutants, improving the overall quality of the distilled water.
- Collection: The purified and distilled water droplets, free from impurities, pass through the filter and are collected in a designated container or collection chamber. It is important to use appropriate storage containers made of materials suitable for storing distilled water, such as glass or designated plastic containers.
Applications of Water Distiller
Water distillers have a wide range of applications due to the purity and cleanliness of the distilled water they produce. Here are some common applications of water distillers:
- Battery Maintenance: Distilled water is essential for maintaining lead-acid batteries found in vehicles, such as cars and motorcycles. It helps promote electrical flow and prevent mineral build-up, ensuring optimal battery performance and longevity.
- Medical Applications: Distilled water is widely used in medical settings. It is a key component in medical devices like Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) machines used for sleep apnea treatment. Distilled water in the humidification chamber helps prevent mineral accumulation and bacterial growth.
- Nasal Irrigation: Distilled water is used with Neti pots for nasal irrigation, providing relief from sinus congestion. The sterile nature of distilled water ensures a clean and safe environment for flushing nasal passages.
- Household Use: Distilled water is utilized in various household applications. It is ideal for ironing clothes as it prevents mineral deposits and scale build-up that can damage the iron. Distilled water is also used in aquariums to maintain a healthy aquatic environment and prevent mineral imbalances.
- Cleaning Tasks: Distilled water is beneficial for cleaning tasks where mineral-free water is preferred. It helps prevent streaks, spots, and residue when cleaning windows, mirrors, and other surfaces that require a streak-free finish.
- Scientific and Laboratory Applications: Distilled water is commonly used in scientific experiments, research, and laboratory procedures. Its purity ensures accurate and reliable results, particularly in chemistry, biology, and other scientific disciplines.
- Hydroponics: In hydroponic systems, where plants are grown without soil, distilled water is often used. It provides a clean and nutrient-free base, allowing for precise control over the nutrient composition delivered to the plants.
Advantages of Water Distiller
- Superior Contaminant Removal: Water distillers are highly effective at removing harmful contaminants from impure water. They can eliminate up to 99% of impurities, including fluoride, lead, bacteria, viruses, and various chemicals. This ensures that the water produced is of high purity and safe for consumption.
- Health Benefits: The purified water from a distiller can provide numerous health benefits. It can help improve the appearance of the skin by removing impurities that may contribute to skin issues. Additionally, consuming distilled water can promote mental clarity and enhance cognitive performance. It may also help alleviate headaches and promote overall well-being.
- Easy Installation and Use: Water distillers are generally easy to install and use. They typically require minimal setup and can be quickly integrated into your water supply system. Once installed, they operate automatically, requiring little effort or expertise to maintain.
- Portability: Many water distillers are compact and portable, allowing for convenient use in various settings. Whether you need purified water at home, in the office, or while traveling, portable distillers offer flexibility and ease of use.
- Environmental Friendliness: Water distillers are an environmentally friendly water purification option. They do not produce any harmful byproducts or waste materials during the purification process. Unlike other filtration methods that require the use of chemicals or generate plastic waste from filters, distillers rely on heat and condensation to produce clean water without any negative impact on the environment.
- Long Shelf Life: Distilled water has a long shelf life compared to other types of water. Since the distillation process removes impurities and microorganisms, the water remains clean and free from contaminants for an extended period. This makes it convenient for storage and ensures a steady supply of purified water.
Limitations of Water Distiller
- Dependence on Electricity: Water distillers require electricity to operate, as they rely on heat energy generated by the flow of electric current. This means that they are not suitable for areas with limited or unreliable electricity supply.
- Flavorless Water: The process of distillation removes all contaminants and minerals from the water, including those that contribute to its flavor. As a result, distilled water may taste flat and lack the pleasant taste that is often associated with naturally occurring minerals in water.
- Time-Consuming Process: Distillation is a time-consuming purification process. It can take several hours to produce a relatively small amount of purified water, which may not be ideal for situations where a large volume of water is needed in a short period.
- Energy Inefficiency: Water distillers can be energy-intensive, especially when producing large quantities of purified water. The continuous heating and cooling processes consume a significant amount of energy, which can lead to increased energy costs.
- Limited Capacity: Many water distillers have a limited capacity and can only produce a certain amount of purified water per day. This can be a limitation for larger households or for commercial or industrial applications where a higher volume of purified water is required.
- Cost: Water distillers can be expensive to purchase, particularly those designed for commercial or industrial use. Additionally, ongoing maintenance costs, such as filter replacements, can contribute to the overall cost of owning and operating a water distiller.
- Removal of Beneficial Minerals: While water distillers effectively remove impurities and contaminants from water, they also eliminate beneficial minerals that are naturally present in water, such as calcium and magnesium. This can result in purified water that lacks essential minerals, which may be desirable for some individuals.
- Incomplete Contaminant Removal: While water distillers are effective at removing many contaminants, they may not eliminate all types of contaminants. Certain chemicals, such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs), may not be effectively removed through the distillation process alone. Additional filtration methods may be required to address specific contaminants.
Precautions Should be taken When Operating a Water Distiller
- Reliable Electricity Supply: Ensure that a reliable and stable electricity supply is available to operate the water distiller effectively. Fluctuations or interruptions in power can disrupt the distillation process.
- Continuous Supervision: Regularly monitor the water distiller to ensure a consistent supply of cooling water, prevent the boiling flask from running dry, and avoid overfilling the receiver. Some distillers may offer automatic protection features, but it is still important to supervise the operation.
- Descaling and Cleaning: In areas with hard water, inorganic deposits can build up inside the boiling chamber over time. Regularly check for deposits and descale the boiling chamber as necessary according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Additionally, conduct regular cleaning processes to maintain the efficiency of the distiller.
- Glassware Inspection: Thoroughly inspect the glassware components of the water distiller for any cracks or damage. Cracked glassware should be replaced immediately to prevent leaks or breakages during operation.
- Leak-proof System: Regularly inspect the connections and seals of the water distiller to ensure a leak-proof system. Address any leaks promptly to prevent water wastage and ensure proper functioning.
- Proper Water Levels: Maintain the proper water levels in the distillation process. Make sure that a small amount of additional water spills out throughout both the boiling phase and the distillation-collection phase to prevent the boiler from draining completely.
- Addressing Overheating: If the overheating signal sounds, do not immediately restart the distiller. Take the time to identify the cause of the overheating before proceeding to prevent potential damage to the equipment. Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions or seek professional assistance if needed.
- Regular Maintenance: Implement a regular maintenance schedule for the water distiller, including cleaning, descaling, and inspection of components. This helps to ensure efficient and safe operation over time.
How to clean your water distiller?
To clean your water distiller, you can follow these steps:
- Turn off and unplug the distiller: Before starting the cleaning process, make sure the distiller is turned off and unplugged from the power outlet to ensure safety.
- Empty and rinse the reservoir: Empty any remaining water from the distiller’s reservoir and give it a thorough rinse to remove any debris or sediment.
- Prepare a cleaning solution: Create a mixture of equal parts water and vinegar or lemon juice. These natural cleaning agents help dissolve mineral deposits and disinfect the distiller.
- Fill the reservoir with the cleaning solution: Pour the prepared cleaning solution into the distiller’s reservoir. Make sure to fill it enough to cover the areas that need cleaning.
- Run the distiller: Turn on the distiller and let it run for about 20 minutes. This allows the cleaning solution to circulate and remove mineral deposits or any impurities that may have accumulated inside the distiller.
- Let it cool and drain: After 20 minutes, turn off the distiller and allow it to cool down for a few minutes. Then, drain the cleaning solution from the reservoir.
- Rinse the reservoir: Rinse the reservoir thoroughly with clean water to remove any residue or odor from the cleaning solution. Repeat this step as needed until the reservoir is free from any traces of the cleaning solution.
- Final rinse: Fill the reservoir with clean water and run the distiller for a few minutes to perform a final rinse. This ensures that any remaining cleaning solution is flushed out completely.
- Dry and reassemble: Once the distiller is cleaned and rinsed, dry all the components thoroughly before reassembling the distiller. This helps prevent the growth of mold or bacteria.
- Test run: Before using the distiller for drinking water or other purposes, refill the reservoir with clean water and run the distiller for a few minutes to ensure that all traces of the cleaning solution are eliminated.
Water Distiller Examples
Here is a list of top and best water distiller systems for laboratory use, along with a brief description of each:
- Millipore ELIX Essential Water Distiller: This distiller is designed for use in laboratories and produces high-purity water with a resistivity of up to 18.2 MΩ·cm. It has a compact design and is easy to use, with a user-friendly LCD display and automatic shut-off feature.
- Pure Water Mini-Classic CT Countertop Water Distiller: This countertop distiller produces high-purity water with a resistivity of up to 18.2 MΩ·cm. It has a compact design and is easy to use, with a user-friendly LCD display and automatic shut-off feature.
- H2O Labs Countertop Water Distiller: This countertop distiller produces high-purity water with a resistivity of up to 18.2 MΩ·cm. It has a compact design and is easy to use, with a user-friendly LCD display and automatic shut-off feature.
- Water Wise 4000 Countertop Water Distiller: This countertop distiller produces high-purity water with a resistivity of up to 18.2 MΩ·cm. It has a compact design and is easy to use, with a user-friendly LCD display and automatic shut-off feature.
- Pure Water Countertop Water Distiller: This countertop distiller produces high-purity water with a resistivity of up to 18.2 MΩ·cm. It has a compact design and is easy to use, with a user-friendly LCD display and automatic shut-off feature.
- AquaNui Classic Water Distiller: This water distiller produces high-purity water with a resistivity of up to 18.2 MΩ·cm. It has a compact design and is easy to use, with a user-friendly LCD display and automatic shut-off feature.
- WaterWise Water Distiller: This water distiller produces high-purity water with a resistivity of up to 18.2 MΩ·cm. It has a compact design and is easy to use, with a user-friendly LCD display and automatic shut-off feature.
- WaterWise Model 8800 Water Distiller: This water distiller produces high-purity water with a resistivity of up to 18.2 MΩ·cm. It has a compact design and is easy to use, with a user-friendly LCD display and automatic shut-off feature.
- Megahome Countertop Water Distiller: This countertop distiller produces high-purity water with a resistivity of up to 18.2 MΩ·cm. It has a compact design and is easy to use, with a user-friendly LCD display and automatic shut-off feature.
- Durastill Water Distiller: This water distiller produces high-purity water with a resistivity of up to 18.2 MΩ·cm. It has a compact design and is easy to use, with a user-friendly LCD display and automatic shut-off feature.
It is important to note that the purity and resistivity of the water produced by these distillers may vary depending on the specific model and the source water being used. It is always a good idea to thoroughly research and compare different models to find the one that best meets your needs and budget.
Alternatives to Water Distillers
There are several alternatives to water distillers for producing purified water, including:
- Reverse osmosis: Reverse osmosis is a process that uses a membrane to remove impurities from water. The water is forced through a semi-permeable membrane, which removes contaminants and leaves behind purified water.
- Carbon filtration: Carbon filters use activated carbon to remove impurities from water. The water passes through a bed of activated carbon, which absorbs contaminants and leaves behind purified water.
- Ultraviolet light: Ultraviolet light can be used to kill bacteria and other microorganisms in water. It is often used in combination with other purification methods, such as carbon filtration.
- Ozonation: Ozonation is a process that uses ozone gas to purify water. Ozone is a powerful oxidant that can kill bacteria and other microorganisms, as well as remove other contaminants from water.
- Chlorination: Chlorination is a process that uses chlorine to purify water. Chlorine is a powerful disinfectant that can kill bacteria and other microorganisms in water. However, it can also leave behind unwanted by-products and has a strong taste and odor.
It is important to note that each of these methods has its own pros and cons, and the most suitable method will depend on the specific needs and circumstances of the user.
FAQ
How long does it take to distill water?
The time it takes to distill water will depend on the size of the distiller and the amount of water being distilled. In general, a small countertop water distiller will take about 4-6 hours to distill one gallon of water. Larger, more industrial-sized distillers may be able to produce one gallon of distilled water in as little as one hour.
It’s important to note that the time it takes to distill water can also be affected by factors such as the purity of the water being distilled, the temperature of the water, and the humidity level in the environment. In general, it will take longer to distill water if the water is dirty or contaminated, or if the temperature or humidity is high.
To get a more accurate estimate of how long it will take to distill a specific amount of water, it’s best to consult the manufacturer’s instructions or guidelines for your particular water distiller.
What does a water distiller remove?
A water distiller removes impurities from water by using the process of distillation. Distillation involves heating water to its boiling point so that it turns into steam. As the steam rises, it leaves behind any impurities that are dissolved in the water, such as minerals, bacteria, and other contaminants.
The steam is then collected and cooled, resulting in pure, distilled water. Because the distillation process removes impurities from the water, it is an effective way to produce pure, clean drinking water.
However, it’s important to note that while distillation can remove many types of impurities, it may not be effective at removing certain contaminants, such as certain chemicals or heavy metals. To ensure that your water is as pure as possible, it may be necessary to use other methods in addition to distillation, such as carbon filtration or reverse osmosis.
Does boiling water distill it?
Boiling water can produce distilled water if the steam produced is collected and condensed back into a liquid. This is the process of distillation.
When water is heated to boiling, it produces steam, which is a mixture of water vapor and air. As the steam rises, it comes into contact with a cooled surface, such as a condenser coil or a cooled glass tube. As the steam cools, it condenses back into a liquid, and the resulting liquid is pure water with any impurities left behind.
To collect the distilled water, the condensation must be collected in a clean container. This container should not be made of a material that can leach contaminants into the water, such as plastic or metal. Glass or ceramic containers are best for collecting distilled water.
While boiling water can produce distilled water, it is not the most efficient method of distillation. It is also not suitable for producing large quantities of distilled water. For these purposes, a more sophisticated distillation system is typically used.
Can I distill water myself?
Yes, it is possible to distill water yourself at home using simple equipment and materials. Here is a basic outline of the process:
1. Collect the materials you will need: a large pot or kettle, a smaller pot or jar, a clean cloth or coffee filter, and some ice.
2. Fill the large pot with water and bring it to a boil.
3. Place the smaller pot or jar on top of the large pot, making sure that it is not touching the water.
4. Cover the smaller pot or jar with the cloth or coffee filter and secure it in place with a rubber band.
5. As the water boils, steam will rise and collect on the cloth or coffee filter. As the steam cools, it will condense and drip into the smaller pot or jar.
6. To increase the efficiency of the process, you can place ice on top of the cloth or coffee filter. This will help to cool the steam and cause it to condense more quickly.
7. Continue boiling the water until you have collected as much distilled water as you need. Be sure to keep the water level in the large pot topped up so that it does not boil dry.
This is a simple, low-tech way to produce small quantities of distilled water at home. However, it is not the most efficient or effective method for producing large quantities of distilled water. For these purposes, a more sophisticated distillation system is typically used.
Is it safe to drink distilled water?
Distilled water is safe to drink. In fact, it is one of the purest forms of water available and is often used in laboratories and medical settings where high levels of purity are required.
During the distillation process, impurities such as minerals, bacteria, and other contaminants are removed from the water, leaving behind pure H2O. Distilled water does not contain any minerals or other contaminants, which makes it ideal for certain uses, such as preparing infant formula or filling lead-acid car batteries.
However, it is important to note that while distilled water is safe to drink, it can also be less beneficial to drink on a regular basis because it lacks the minerals and other substances found in most other types of water. Some experts recommend drinking mineral water or fortified water to help ensure that you are getting enough minerals in your diet.
In summary, distilled water is safe to drink, but it may not be the best choice for everyday consumption due to the lack of minerals and other substances found in most other types of water.
Is distilling water better than boiling?
Distillation is generally considered to be a more effective method of purifying water than boiling, because it removes a wider range of impurities and contaminants.
During the distillation process, water is heated to the point of vaporization, and the steam that is produced is collected and condensed back into a liquid. This process removes impurities such as minerals, bacteria, and other contaminants, leaving behind pure water.
Boiling water can also kill bacteria and other microorganisms, but it is not as effective at removing other contaminants such as minerals and chemicals. Boiling water is also less efficient at producing purified water, as it requires a lot of energy and time to bring the water to a boil and maintain it at that temperature.
In summary, distillation is generally considered to be a more effective and efficient method of purifying water than boiling, as it removes a wider range of impurities and contaminants. However, boiling can still be useful for killing bacteria and other microorganisms in water, and it can be a simple and effective way to produce small quantities of purified water at home.
Why can’t adults drink distilled water?
There is no inherent reason why adults cannot drink distilled water. Distilled water is safe to drink and is often used in medical settings and laboratories due to its high level of purity.
However, it is important to note that distilled water lacks minerals and other substances that are found in most other types of water. These minerals and substances, such as calcium and magnesium, can be important for maintaining good health and can be beneficial when consumed as part of a balanced diet.
While it is generally safe for adults to drink distilled water, it may not be the best choice for everyday consumption due to the lack of minerals and other substances. Some experts recommend drinking mineral water or fortified water to help ensure that you are getting enough minerals in your diet.
In summary, there is no inherent reason why adults cannot drink distilled water, but it may not be the best choice for everyday consumption due to the lack of minerals and other substances found in most other types of water.
References
- https://dashappliances.com/what-is-a-water-distiller/
- https://www.wqpmag.com/softening-conditioning/distiller-equipment-components/article/10956704/what-are-water-distillers-how-do-they-work
- https://www.pharmaceuticalsky.com/2021/08/sop-for-distilled-water-still.html
- https://slidetodoc.com/maintaining-a-water-distiller-o-principles-of-operation/
- https://www1.agric.gov.ab.ca/$department/deptdocs.nsf/all/agdex715/$file/716d62.pdf
- https://www.freshwatersystems.com/blogs/blog/what-is-a-water-distiller-and-how-does-it-work
- https://advancedwaterinc.com/water-distillation-work/
- https://puretap.ca/information-on-water-distillers/
- http://www.i4at.org/surv/distill.htm
- https://www.megahome-distillers.co.uk/what-does-a-water-distiller-do
- https://www.pharmaguideline.com/2007/02/distillation-basic-principle-and-mehodology-of-simple-distillaion.html
