Table of Contents
What is Western Blotting?
In molecular biology Western blotting is a rapid and sensitive assay for detection and characterization of proteins. This technique exploits the inherent specificity of antigen-antibody interaction to identify specific antigens by polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies.
- Western blotting is also known as protein immunoblot because an antibody is used to specifically detect its antigen.
- The western blotting is completed in three steps such as separation of protein by size, transfer of protein to a solid support, and marking target protein using a primary and secondary antibody to visualize.
- At first the proteins of a given sample are separated by using SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE).
- These separated proteins are transferred or blotted onto a matrix generally known as nitrocellulose or PVDF membrane.
- After that the secondary antibodies are added to it which will bind with the specific primary antibodies. Now these secondary antibodies are visualized by using different methods such as staining, immunofluorescence, and radioactivity, allowing indirect detection of the specific target protein.
Aim
To learn the technique of Western Blotting for the detection of a specific protein.
Western Blotting Principle – How does western blot work?
The western blotting technique is mainly used to identify a specific protein in a complex mixture along with the determination of its molecular weight. At first, the protein samples are electrophoresed on SDS-PAGE. During this time the proteins will migrate through the gel and they will be separated according to their size and charge.
These separated proteins are electrotransferred onto nitrocellulose/PVDF membrane for further analysis. To confirm the electrotransferred proteins or antigen are blotted on the membrane it is incubated with a primary antibody which is specific for the protein of interest.
After that, the membrane is incubated with the secondary antibody which is specific for the first antibody. The secondary antibodies are covalently attached to an enzyme, e.g. alkaline phosphatase or horseradish peroxidase. These enzymes form a coloured precipitate upon reacting with a chromogenic substrate.
As a result, a visible band can be seen on the membrane where the primary antibody is bound to the protein.
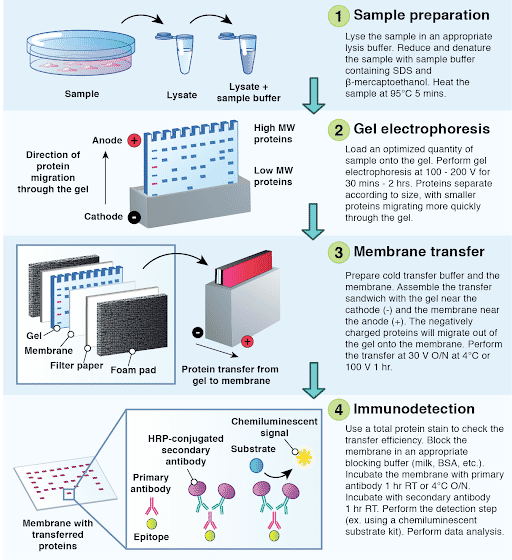
The Western blotting technique, also known as immunoblotting, is a widely used laboratory method for detecting and identifying specific proteins in a complex mixture. It involves a series of steps that allow the separation, transfer, and detection of proteins.
The first step in Western blotting is the separation of proteins based on their size using a technique called electrophoresis. A mixture of proteins is loaded onto a gel matrix, typically made of polyacrylamide, and an electric current is applied. Proteins migrate through the gel at different rates depending on their charge, size, and structure. As a result, the proteins separate into distinct bands along the gel based on their molecular weight.
Once the electrophoresis is complete, the proteins need to be transferred from the gel to a solid support, usually a membrane made of nitrocellulose or polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF). This process is known as blotting. The gel and membrane are stacked together and placed in a transfer apparatus. An electric field is applied, causing the proteins to migrate out of the gel and onto the membrane. The proteins retain their relative positions on the membrane, forming bands that correspond to the separated proteins.
After the transfer, the membrane is ready for protein detection. The target protein of interest is visualized using specific antibodies. The first step is to incubate the membrane with a primary antibody that recognizes and binds to the target protein. This primary antibody is specific to the protein of interest and can be either monoclonal or polyclonal. The unbound primary antibody is then washed away.
To visualize the bound primary antibody, a secondary antibody is used. The secondary antibody is conjugated with an enzyme that can produce a detectable signal. This enzyme-linked secondary antibody is incubated with the membrane, allowing it to bind to the primary antibody that is already bound to the target protein.
Finally, the presence of the target protein is detected by adding a substrate for the enzyme. The substrate undergoes a reaction with the enzyme, resulting in the production of a colored or luminescent product at the site of the target protein. This generates a visible band or signal on the membrane, indicating the presence of the protein of interest.
Western blotting offers several advantages in protein analysis. It allows for the detection of specific proteins within a complex mixture and provides information about their molecular weight. It also enables the quantification of protein expression levels by comparing the intensity or density of the protein bands on the membrane. This technique is widely used in various fields of research, including molecular biology, biochemistry, immunology, and medical diagnostics.
Western Blot test Steps/Western blot protocol
The entire procedure can be divided into the following steps:
SDS-PAGE
- In biochemistry, genetics and molecular biology, the SDS-PAGE or sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis are used to separate proteins according to their molecular weight. The electrophoretic mobility of proteins depends upon their size.
- The main purpose of SDS-PAGE is to separate the proteins based on their size.
- As proteins are amphoteric compounds, their net charge can therefore be determined by the pH of the medium in which they are suspended.
- Therefore, at a given pH and under non-denaturing conditions, the electrophoretic separation of proteins is determined by both size and charge of molecules. As proteins are high molecular weight molecules, it needs porous gels to get separated.
- Polyacrylamide gels are those which provide a means of separating proteins by size as they are porous.
Western blotting
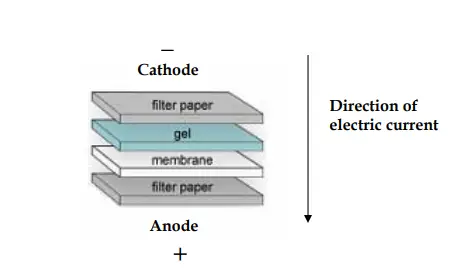
- The resolved proteins are transferred from the polyacrylamide gel to the nitrocellulose/PVDF membrane in presence of a specific buffer termed transfer buffer.
- During the transfer procedure, the gel and membrane are placed between two filter papers like a sandwiched, while the gel will be at the top of the membrane.
- This set is placed between two sponge pads and then placed in a plastic cassette.
- The entire set is then placed inside a gel tank filled with cold transfer buffer.
- The resolved proteins are transferred to the corresponding positions on the membrane after the electrotransfer. The protein of interest is immunodetected on the membrane.
Immunodetection
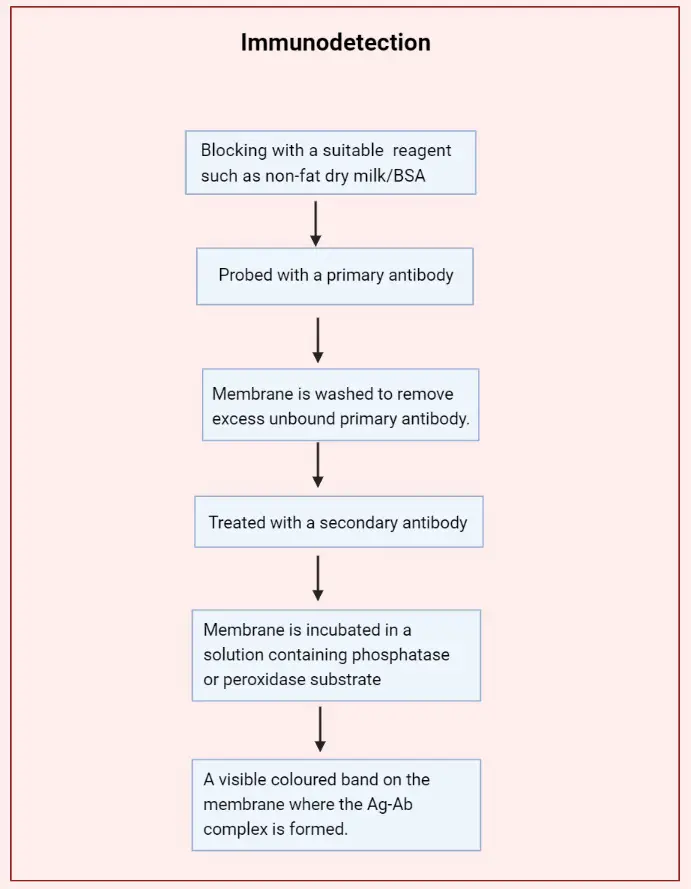
- In Immunodetection or Immunoblotting, the proteins which are bound to the membrane after the completion of electrotransfer, are detected immunologically.
- A suitable blocking reagent such as non-fat dry milk/BSA is used to block the unoccupied sites on the membrane.
- Then the membrane is probed with a primary antibody specific to the protein of interest. The primary antibody binds to the protein or antigen and an antigen (Ag)-antibody (Ab) complex is formed on the membrane.
- The membrane is washed to remove excess unbound primary antibody.
- It is then treated with an enzyme-labeled (Alkaline phosphatase/Horseradish peroxidase) secondary antibody which attaches to the primary antibody of the Ag-Ab complex.
- Finally, the membrane is incubated in a solution containing phosphatase or peroxidase substrate which results in a visible coloured band on the membrane where the Ag-Ab complex is formed.
- As a result the molecular weight of the protein of interest can be determined.
Materials Required for Western Blot
- Acrylamide-Bisacrylamide Solution 30% (29:1)
- 2.5X Tris-SDS Buffer (pH 8.8)
- 5X Tris-SDS Buffer (pH 6.8)
- Prestained Protein Ladder
- 5X Tris-Glycine-SDS Gel Running Buffer
- 5X Sample Loading Buffer
- Staining solution
- Destaining solution
- Ammonium persulphate (APS)
- Tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED)
- Agarose
- Protein Sample
- Transfer Buffer
- Blocking Agent
- Diluent Buffer
- Assay Buffer
- Wash Buffer
- Primary antibody
- Secondary antibody
- TMB/H2O2
- Nitrocellulose membrane with filter paper
- Glass wares: Conical flask, Measuring cylinder, Beaker, Petri dish, staining tray
- Reagents: Methanol, Distilled water
- Other: Protein Electrophoresis apparatus, Blotting Apparatus, Power pack, Gel rocker, Micropipettes, Tips, Microwave/Burner/Hotplate
Preparation of buffer and solution
- Preparation of 10% APS Solution: Dissolve 0.15 g of Ammonium persulphate in distilled water to make a final volume of 1.5 ml. Store at 2-8o C. Use within 3 months.
- Preparation of 1X Tris-Glycine-SDS Gel Running Buffer: To prepare 500 ml of 1X Tris-Glycine-SDS Gel Running buffer, take 100 ml of 5X Tris-Glycine-SDS Gel Running Buffer and add 400 ml sterile distilled water*. Store at 2-8o C. Mix well before use. The 1X Tris-Glycine-SDS Gel Running Buffer can be reused 4-5 times.
- Preparation of 1X Assay Buffer: To prepare 50 ml of 1X Assay Buffer, take 5 ml of 10X Assay Buffer and add 45 ml of sterile distilled water*
- Preparation of 1X Transfer Buffer: To prepare 1000 ml of 1X Transfer Buffer, take 100 ml of 10X Transfer Buffer, add 200 ml of methanol and 700 ml of sterile distilled water*. Store at 2-8o C. Mix well before use.
- Preparation of Blocking Buffer: To prepare 20 ml of Blocking Buffer, take 0.2 g of Blocking Agent and add 20 ml of Diluent Buffer.
- Preparation of 1X Wash Buffer: To prepare 1000 ml of 1X Wash Buffer, take 100 ml of 10X Wash Buffer and add 900 ml of sterile distilled water*.
Western Blot Protocol
Day 1: SDS- PAGE
- Assemble the electrophoresis unit such that the glass plates are clamped to the unit along with the spacers placed in-between them at two vertical edges.
- Prepare 1% agarose (0.05g in 5ml of distilled water). Boil to dissolve the agarose and pour a thin horizontal layer at the lower edge of the plates to seal the assembly. Let it solidify by allowing it to cool down for 5-10 minutes
- Preparation of 12% Separating Gel- To prepare separating gel, add the components as follows:
| 30% Acrylamide-bisacrylamide Solution | 6ml |
| Distilled water* | 3ml |
| 2.5X Tris-SDS Buffer (pH 8.8) | 6ml |
| 10% APS Solution | 125 μl |
| TEMED | 18 μl |
Pour the gel in-between the plates and allow it to solidify for an hour. Immediately after the gel is poured, add distilled water to level the gel.
- After an hour pour off the water by inverting the casting assembly.
- Preparation of 5% Stacking Gel- To prepare stacking gel, add the components as follows:
| 30% Acrylamide-bisacrylamide Solution | 1.3 ml |
| Distilled water* | 5.1 ml |
| 5X Tris-SDS Buffer (pH 8.8) | 1.6ml |
| 10% APS Solution | 75 μl |
| TEMED | 10 μl |
After addition of TEMED gently mix all the components by swirling the beaker. Pour the stacking gel on top of the separating gel and immediately place the comb avoiding air bubbles. Allow it to solidify for 30 minutes.
Note: Acrylamide is a potential neurotoxin and should be treated with great care. Always wear an face mask and use gloves.
- Pour 1X Tris-Glycine-SDS Gel Running Buffer in the unit such that the buffer connects the two electrodes, and hence completes the flow of current. Remove the comb from the Stacking Gel carefully.
- Sample Preparation: Take required amount of protein sample in a tube and boil the tube containing protein sample at 100o C in a boiling water bath. Do not boil the tube containing Prestained Protein Ladder.
- Load samples in alternative wells as follows: Lane 1: Prestained Protein Ladder – 5 μl; Lane 3: Protein Sample – 20 μl; Lane 5: Protein Sample – 20 μl
- Connect the power cord to the electrophoretic power supply according to the conventions: Red-Anode and Black- Cathode. Electrophorese at 120 volts and 90 mA until dye front reaches 0.5 cm above the sealing gel.
- Carefully remove the gel from in-between the plates using spatula into the plastic tray containing distilled water. Wash the gel for 1 minute. Discard the water & proceed for blotting and staining destaining procedure.
- To the gel pieces of lane no. 1 and 3 add 20 ml of water and proceed for staining destaining procedure.
- Cut the Gel along lane no. 4. Transfer lane no. 5 i.e. protein sample in 10 ml of cold Transfer buffer. Incubate at Room Temperature for 10 minutes and proceed with electroblotting.
Staining and Destaining of Gel
- After removing water, add 50 ml of Staining Solution in the tray containing gel, till the bands are visible. Sometimes the gel may have to be kept overnight in the staining solution for visualization of the bands.
- Remove gel from the Staining Solution. The Staining Solution can be re-used 2-3 times.
- Wash the gel by rinsing with distilled water till a considerable amount of stain leaches out from the gel. Keep changing the distilled water for 3-4 times.
- Add 50 ml of Destaining Solution to the gel. Destaining should be carried out with constant moderate shaking.
- Continue destaining till clear, distinct bands are observed.
- Remove gel from the Destaining Solution. The Destaining Solution can be re-used 2-3 times.
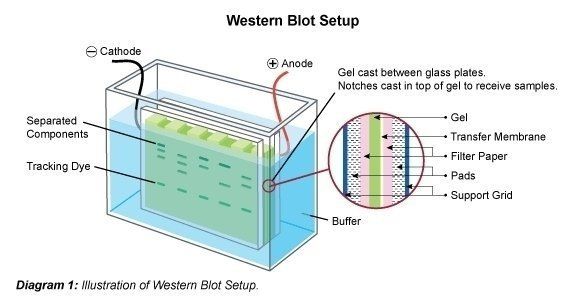
Electroblotting
- Assemble the gel with nitrocellulose membrane and filter papers.This blotting sandwich is placed within the blotting cassette. Try to avoid air bubble between gel and nitrocellulose membrane by rolling a glass tube on the membrane.
Note: Take out the transparent sheets carefully while using the nitrocellulose membrane.
- Insert this cassette into the gel transfer apparatus filled with cold transfer buffer and then connect the transfer unit to power supply as per conventions.
- Electrophoreses the sample at 150V, 300 mA for 2 hours for blotting.
- Remove the nitrocellulose membrane after electrophoresis from the blotting cassette and place the membrane (with protein side up) in 20 ml of 1X Blocking Buffer taken in petri dish.
- Keep it overnight at 40C.
Day 2: Immunodetection:
- Discard off the blocking buffer.
- Wash the membrane with 20 ml of 1X Wash Buffer for 5 minutes. Repeat the wash once.
- Immerse the membrane in 20 ml of 1X Assay Buffer. Add 4 μl of primary antibody solution and mix gently for an hour on a gel rocker. After that discard the primary antibody solution.
- Wash the blot with 20 ml of 1X Wash Buffer for 5 minutes. Repeat the wash once. Discard the buffer each time.
- Immerse the blot in 20 ml of 1X Assay Buffer. Add 2 μl of HRP labeled secondary antibody. Mix gently for an hour. Discard the HRP labeled antibody solution.
- Do a quick washing of the blot with 20 ml of 1X Wash Buffer. Wash the blot with 20 ml of 1X Wash Buffer for 10 minutes. Repeat the wash. Discard the buffer each time.
- Immerse the washed blot in 3 ml of TMB/H2O2 (substrate) solution, mix gently for 5-10 minutes, within this time coloured band will appear.
- Remove the blot; wash with distilled water, discard and dry.
- Compare the SDS-Polyacrylamide gel with the developed membrane.
Western Blot Results
- On staining SDS-Polyacrylamide gel, different proteins will appear as dark blue bands against a light blue backgroud.
- On immunodetection, a single blue band will be observed on NC membrane.
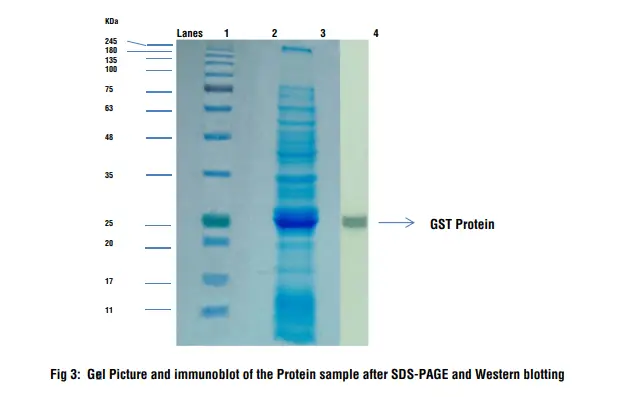
- Lane 1: Prestained Protein Ladder
- Lane 3: Protein Sample
- Lane 4: Immunodetection on the blotted membrane
Interpretation:
After staining and destaining of the gel several bands appear in the sample which is a crude bacterial cell lysate. After performing the Western blotting procedure a thick band can be seen on the nitrocellulose membrane which corresponds to the GST protein which is detected by anti-GST antibody. The molecular weight of GST protein is 26 kD and the position of the band corresponds to the protein size.
Advantages and Disadvantages of western blotting
Advantages of western blotting
- Sensitivity: Western blotting is highly sensitive and can detect small amounts of proteins, making it suitable for analyzing low-abundance proteins and detecting subtle changes in protein expression levels.
- Specificity: The combination of gel electrophoresis and specific antibody-antigen interactions allows for the selective detection of target proteins, even in complex mixtures of proteins.
- Versatility: Western blotting can be used for various applications, including protein expression analysis, protein-protein interactions, and post-translational modifications analysis.
- Quantification: Western blotting can provide semi-quantitative or quantitative data about protein expression levels by comparing the signal intensity of target proteins to internal controls or reference standards.
- Long-term storage: Western blots can be stored and re-probed multiple times, allowing for future analysis or validation of results.
Disadvantages of western blotting
- False or subjective results: Western blots can produce false-positive or false-negative results due to non-specific antibody binding or incomplete transfer of proteins, respectively. Interpretation of the results relies on the expertise and subjective judgment of the technician.
- High cost: Western blotting can be expensive due to the cost of antibodies, specialized equipment (such as imaging systems), and skilled personnel required for the procedure.
- Technical demand: Western blotting requires precise and meticulous execution of each step, including gel electrophoresis, membrane transfer, antibody incubation, and detection. Minor errors or variations in protocols can affect the reliability and reproducibility of results.
- Time-consuming: Western blotting is a time-consuming technique, involving several steps, including gel electrophoresis, transfer, blocking, antibody incubation, and detection. The entire process can take several hours to complete.
- Limited multiplexing: Western blotting typically allows the detection of one or a few target proteins per assay, limiting its ability to simultaneously analyze multiple proteins in a single experiment.
Advantages of western blotting over ELISA
Advantages of Western blotting over ELISA:
- Protein Confirmation: Western blotting directly detects and confirms the presence of specific proteins in a sample. It allows for the analysis of protein size, post-translational modifications, and protein-protein interactions, providing more comprehensive information about the target protein compared to ELISA, which primarily detects protein concentration.
- Sensitivity: Western blotting is known for its high sensitivity, capable of detecting low-abundance proteins in a sample. It can detect protein levels as low as picograms or even femtograms, making it suitable for analyzing samples with limited amounts of protein.
- Specificity: Western blotting utilizes the specificity of antibodies to detect and bind to target proteins. This specificity allows for the selective detection of the protein of interest, even in complex mixtures. ELISA, on the other hand, relies on the specificity of antibodies but primarily measures the concentration of the protein.
- Protein Separation and Characterization: Western blotting combines protein separation by gel electrophoresis with antibody detection, enabling the analysis of protein size and isoforms. This feature is particularly useful for studying protein isoforms, protein cleavage products, or protein modifications, which may have distinct biological functions.
- Flexibility in Sample Types: Western blotting is applicable to various sample types, including cell lysates, tissue extracts, biological fluids, and purified proteins. This versatility allows for the analysis of proteins in different biological contexts and sample matrices.
- Multiple Antibody Detection: Western blotting allows for the detection of multiple target proteins simultaneously by using different primary antibodies raised against different proteins, followed by species-specific secondary antibodies conjugated to different labels. This capability is useful for studying protein interactions, signaling pathways, or protein expression patterns.
- Long-term Storage and Reprobing: Western blot membranes can be stored for future analysis or re-probed with different antibodies to detect additional proteins of interest. This feature offers cost and time savings, as a single blot can be used for multiple experiments.
While ELISA has its advantages, such as high-throughput capacity and quantitative measurement of protein concentration, Western blotting provides unique advantages for protein characterization, sensitivity, and flexibility in sample types. The choice between the two techniques depends on the specific research goals and the nature of the protein analysis required.
Application of western blotting
The Western blotting technique finds numerous applications in various fields, including research, diagnostics, and disease detection. Some of the key applications of Western blotting are:
- Identification of specific proteins: Western blotting allows the identification of a particular protein within a complex mixture of proteins. By separating known antigens of well-defined molecular weight through SDS-PAGE and transferring them onto a nitrocellulose membrane, the bands of these antigens can be probed with a sample suspected to contain antibodies specific to those antigens. The reaction between the antibody and the protein band is then detected using radiolabeled or enzyme-linked secondary antibodies.
- Estimation of protein size and amount: Western blotting enables the estimation of the size and quantity of proteins present in a given mixture. By comparing the migration of protein bands on the membrane with known molecular weight markers, the size of the protein of interest can be determined. Additionally, by comparing the intensity or density of the protein bands, the relative amount of protein present in the sample can be estimated.
- Diagnosis of diseases: Western blotting plays a crucial role in the diagnosis of various diseases. It is commonly used as a confirmatory test for HIV, where it detects the presence of antibodies that react with viral proteins. This helps determine whether a patient is HIV-positive or not. Additionally, Western blotting is utilized in the diagnosis of neurocysticercosis and tubercular meningitis by demonstrating the presence of specific antibodies in the serum.
- Detection of defective proteins: Western blotting can be employed to detect and analyze defective or abnormal proteins. By comparing the protein bands of a healthy sample with those of a diseased sample, differences in protein expression or post-translational modifications can be observed. This information is valuable for understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying various diseases.
- Disease-specific applications: Western blotting has specific applications in the diagnosis of certain diseases. It is used as the definitive test for variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (vCJD) and Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE or “mad cow disease”). Additionally, it is utilized in the diagnosis of tularemia, Hepatitis B infection, and HSV-2 (Herpes Type 2) infection as a confirmatory test.
In summary, Western blotting is a versatile technique that enables the identification, quantification, and characterization of proteins. Its applications range from basic research to clinical diagnostics, contributing to our understanding of diseases and aiding in their detection and management.
Elisa vs Western blot
| Characteristics | ELISA | Western Blot |
|---|---|---|
| Principle | Based on antibody-antigen interaction | Based on antibody-antigen interaction followed by protein separation |
| Detection | Colorimetric or fluorescent signal | Colorimetric, chemiluminescent, or fluorescent signal |
| Sensitivity | Moderate to high sensitivity | High sensitivity |
| Specificity | High specificity | High specificity |
| Sample requirement | Small amount of sample required | Larger amount of sample required |
| Time | Quick turnaround time (few hours) | Longer turnaround time (few hours to overnight) |
| Multiplexing | Can measure multiple analytes simultaneously | Limited multiplexing capabilities |
| Quantitation | Quantitative measurement possible | Semi-quantitative measurement possible |
| Automation | Highly automated process | Some steps require manual handling |
| Cost | Relatively low cost per test | Relatively higher cost per test |
Western blot troubleshooting
Western blotting is a widely used technique for detecting and analyzing specific proteins in a sample. However, it can sometimes encounter various issues and troubleshooting steps are necessary to identify and resolve these problems. Here are some common observations during western blotting and their possible sources and suggestions for troubleshooting:
Observation: No Bands Observed
Possible Source:
- Insufficient antibody: The antibody used may have low affinity to the protein of interest. Increase the antibody concentration 2-4 fold higher than the recommended starting concentration.
- Insufficient protein: Increase the amount of total protein loaded on the gel.
- Poor transfer: Ensure that the PVDF or nitrocellulose membrane is wetted properly in methanol or transfer buffer, respectively. Make sure there is good contact between the membrane and gel.
- Incomplete transfer: Optimize transfer time, as high molecular weight proteins may require more time for transfer. Stain the membrane with Ponceau S, Amido Black, or India Ink to ensure transfer completeness. Use prestained molecular weight markers.
- Over transfer: Reduce voltage or time of transfer for low molecular weight proteins (<10 kDa).
- Isoelectric point is >9: Use an alternative buffer system with a higher pH, such as CAPS (pH 10.5).
- Incorrect secondary antibody used: Confirm the host species and Ig type of the primary antibody.
- Old antibody: If the antibody is expired or past the manufacturer warranty, purchase a fresh antibody.
- Incorrect storage of antibodies: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended storage instructions and avoid freeze/thaw cycles.
- Sodium Azide contamination: Ensure that the buffers used do not contain Sodium Azide, as it can quench the HRP signal.
- Insufficient incubation time with the primary antibody: Extend the incubation time to overnight at 4°C.
Observation: Faint Bands (Weak Signal)
Possible Source:
- Low protein-antibody binding: Reduce the number of washes to a minimum. Decrease the NaCl concentration in the blotting buffer and antibody solution.
- Insufficient antibody: Increase the antibody concentration 2-4 fold higher than the recommended starting concentration.
- Insufficient protein: Increase the amount of total protein loaded on the gel.
- Inactive conjugate: Mix enzyme and substrate in a tube. If color does not develop or is weak, make fresh or purchase new reagents. Consider switching to ECL.
- Weak/Old ECL: Purchase new ECL reagents.
- Non-fat dry milk may mask some antigen: Decrease the milk percentage in the blocking and antibody solutions or substitute with 3% BSA.
Observation: Extra Bands
Possible Source:
- Non-specific binding of primary antibody: Reduce the primary antibody concentration. Reduce the amount of total protein loaded on the gel. Use monospecific or antigen affinity-purified antibodies.
- Non-specific binding of secondary antibody: Run a control with the secondary antibody alone (omit primary antibody). If bands develop, choose an alternative secondary antibody. Use monospecific or antigen affinity-purified antibodies.
- Non-specific binding of primary or secondary antibodies: Add 0.1-0.5% Tween 20 to the primary or secondary antibody solution. Use 2% non-fat dry milk in the blotting buffer as a starting point to dilute primary and secondary antibodies. Increase the number of washes. Increase NaCl concentration in the blotting buffer. Increase Tween 20 concentration in the wash buffer.
- Aggregation of analyte: Increase the amount of DTT to ensure complete reduction of disulfide bonds. Perform a brief centrifugation.
- Degradation of analyte: Minimize freeze/thaw cycles of the sample. Add protease inhibitors to the sample before storage. Make fresh samples.
- Contamination of reagents: Check buffers for particulate or bacterial contamination. Make fresh reagents.
Observation: High Background
Possible Source:
- Non-specific binding of primary antibody: Use monospecific or antigen affinity-purified antibodies. Block in 5% milk. Adjust the milk or NaCl concentrations of the primary antibody solution. Decrease the antibody concentration.
- Non-specific binding of secondary antibody: Run a control with the secondary antibody alone. If bands develop, choose an alternative secondary antibody.
- Insufficient blocking: Start with 5% dry milk with 0.1-0.5% Tween 20, 0.15-0.5M NaCl in 25mM Tris (pH 7.4). Adjust the blocking conditions as needed.
- Non-fat dry milk may contain target antigen: Substitute with 3% BSA.
- Non-fat dry milk contains endogenous biotin and is incompatible with avidin/streptavidin: Substitute with 3% BSA.
- Some IgY antibodies may recognize milk protein: Substitute with 3% BSA.
- Insufficient wash: Increase the number of washes. Increase Tween 20 concentration in the wash buffer.
- Non-specific binding of primary antibody: Increase NaCl concentration in the primary antibody solution and blotting buffer.
Observation: Diffuse Bands
Possible Source: Excessive protein on the gel: Reduce the amount of protein loaded.
Observation: White Bands (ECL method)
Possible Source: Excessive signal generated: Reduce antibody or protein concentration. Excessive antibody or protein can cause extremely high levels of localized signal, resulting in white bands when exposed to film.
Observation: Patchy uneven spots all over the blot
Possible Source:
- Contamination of reagents: Check buffers for particulate or bacterial contamination. Make fresh reagents.
- Not enough solution during incubation or washing: Ensure the membrane is fully immersed during washes and antibody incubations.
- Air bubble trapped in the membrane: Gently remove any air bubbles, especially during transfer.
- Uneven agitation during incubations: Ensure uniform agitation by placing on a rocker/shaker.
- Contaminated equipment: Make sure the electrophoresis unit is properly washed. Wash the membrane thoroughly to remove any protein or gel residues.
- HRP aggregation: Filter the conjugate to remove HRP aggregates.
- Long exposure: Reduce exposure time.
These troubleshooting suggestions can help identify and resolve common issues encountered during western blotting, enabling more accurate and reliable protein detection.
Western Blotting vs Southern Blotting
| Characteristics | Western Blotting | Southern Blotting |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Detects and analyzes specific proteins in a sample | Detects and analyzes specific DNA sequences in a sample |
| Target molecules | Proteins | DNA |
| Technique | Uses antibodies to detect and bind target proteins | Uses DNA probes to detect and bind target DNA sequences |
| Separation method | Protein separation by gel electrophoresis | DNA separation by gel electrophoresis |
| Transfer to membrane | Protein transfer from gel to PVDF or nitrocellulose membrane | DNA transfer from gel to nylon or nitrocellulose membrane |
| Hybridization | Antibodies bind to target proteins on the membrane | DNA probes bind to target DNA sequences on the membrane |
| Detection | Enzyme-conjugated secondary antibodies generate a signal | Radioactive or fluorescent probes generate a signal |
| Sensitivity | High sensitivity, can detect small amounts of proteins | Moderate sensitivity, can detect specific DNA sequences |
| Target specificity | Specific binding to target proteins | Specific binding to target DNA sequences |
| Application | Protein expression analysis, protein-protein interactions | DNA sequence analysis, DNA fragment identification |
FAQ
What is Western blotting?
Western blotting is a laboratory technique used to detect and analyze specific proteins in a biological sample.
What is the principle behind Western blotting?
Western blotting involves separating proteins by size using gel electrophoresis, transferring them to a membrane, and then using specific antibodies to detect the target proteins.
What are the steps involved in performing a Western blot?
The typical steps include sample preparation, protein separation by gel electrophoresis, transfer to a membrane, blocking to prevent non-specific binding, incubation with primary and secondary antibodies, and detection of protein bands.
What type of samples can be used for Western blotting?
Western blotting can be performed on a variety of samples, including cell lysates, tissue homogenates, serum, plasma, and purified protein samples.
What are the applications of Western blotting?
Western blotting is commonly used in molecular biology research to study protein expression, protein-protein interactions, and post-translational modifications. It is also used for clinical diagnosis and drug development.
How is protein size determined in Western blotting?
Protein size is determined by comparing the migration of protein standards (molecular weight markers) run alongside the sample proteins on the gel. The size can be estimated by comparing the migration distance of the protein bands.
What is the role of antibodies in Western blotting?
Antibodies are used to specifically bind to the target proteins of interest. Primary antibodies recognize the target protein, while secondary antibodies conjugated with a detection molecule provide a signal for visualization.
What are the detection methods used in Western blotting?
Various detection methods are used, including colorimetric (enzyme substrates), chemiluminescent (enzyme-catalyzed light emission), and fluorescent (fluorescently labeled antibodies) detection.
How can I troubleshoot common issues in Western blotting?
Common issues include non-specific binding, weak or no signal, high background, and band distortion. Troubleshooting strategies involve optimizing antibody concentration, blocking conditions, washing steps, and protein sample quality.
Can Western blotting provide quantitative results?
Western blotting is primarily a semi-quantitative technique. However, with appropriate calibration and densitometry analysis, it can provide relative quantification of protein expression levels.
References
- https://www.bosterbio.com/protocol-and-troubleshooting/western-blot-principle
- https://himedialabs.com/td/hti009.pdf
- http://www.ispybio.com/search/protocols/WesternBlotting.pdf
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Western_blot
- https://www.mybiosource.com/learn/westernblotting
- https://www.antibodies.com/western-blotting
