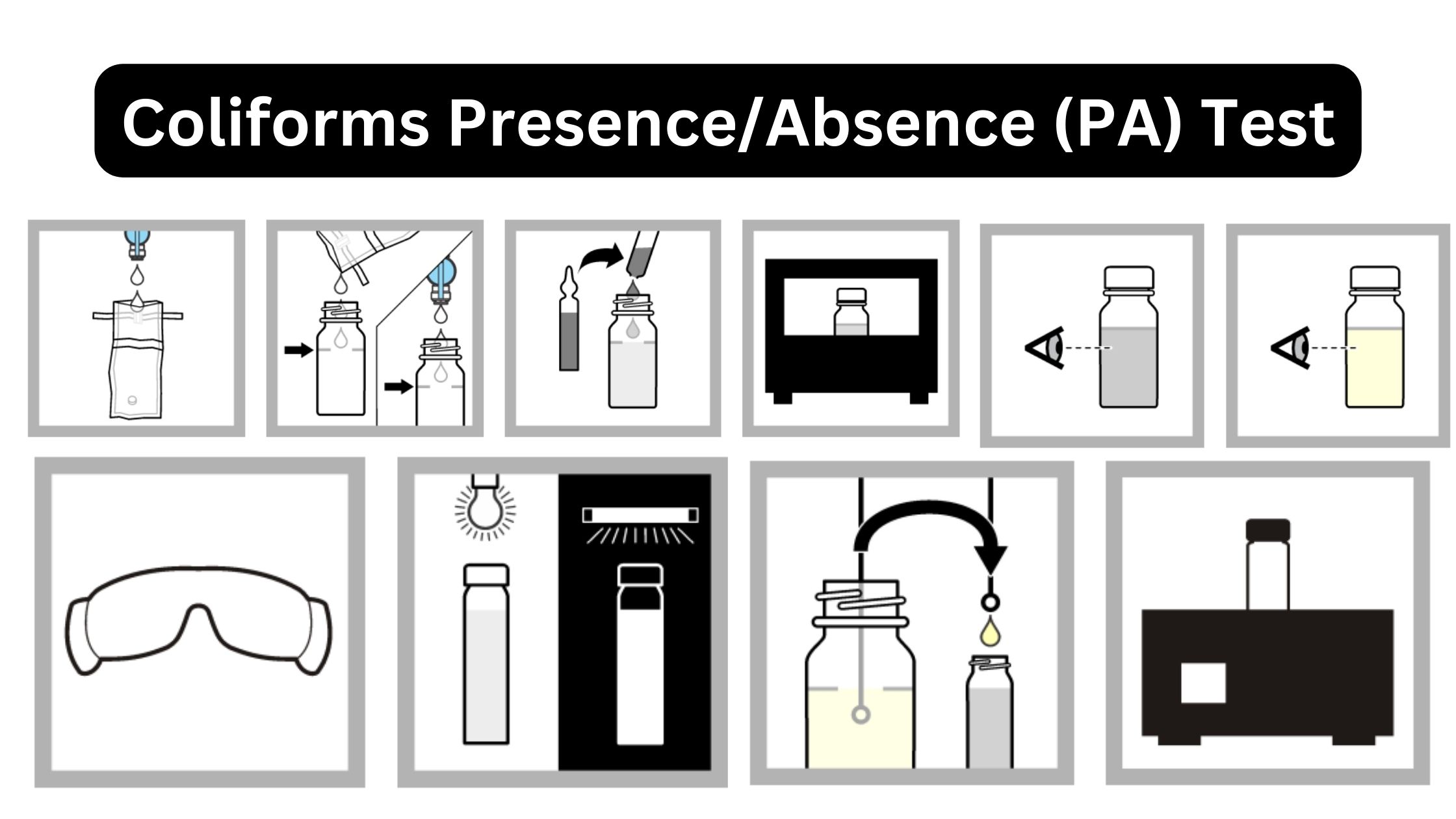
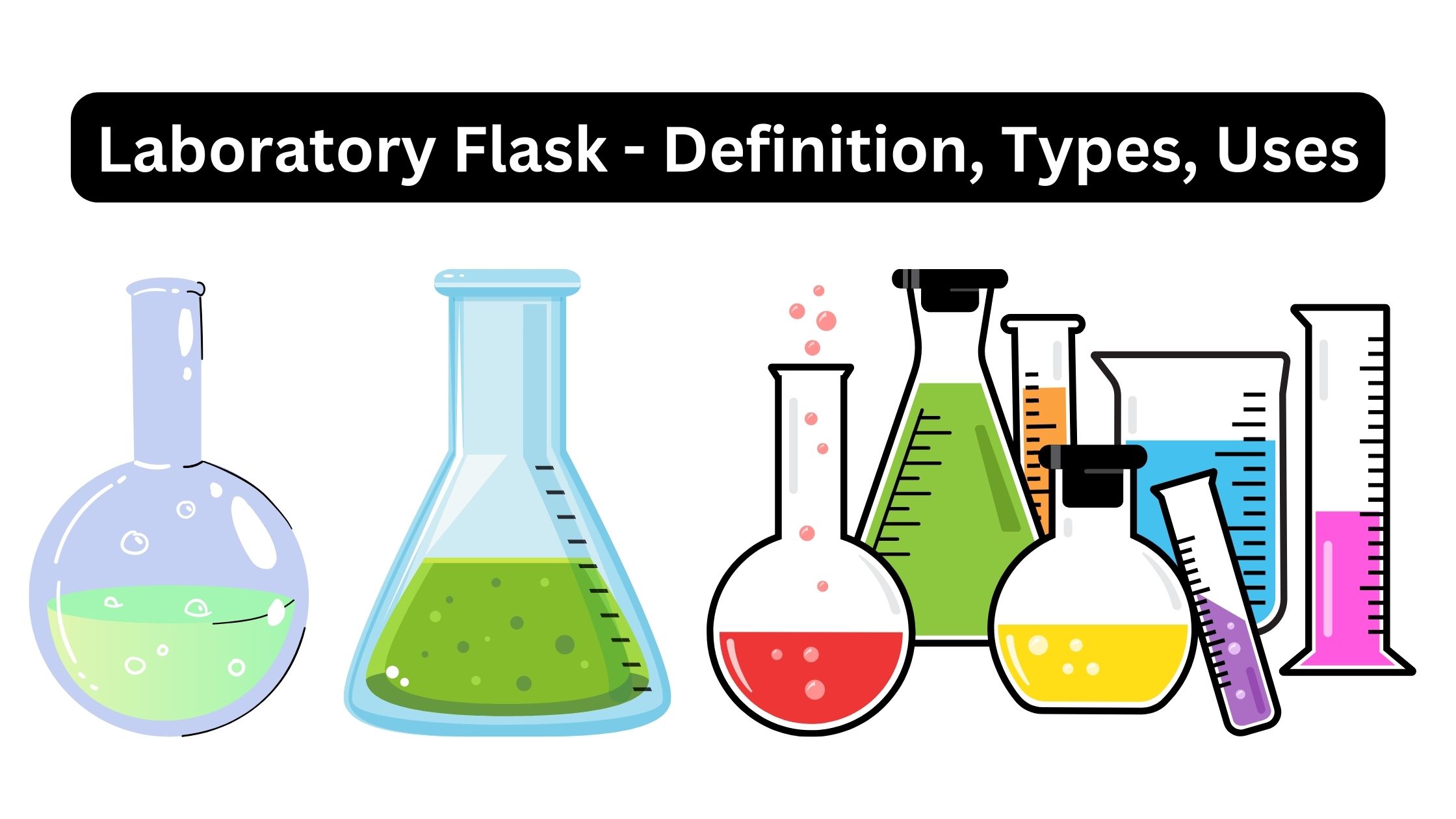
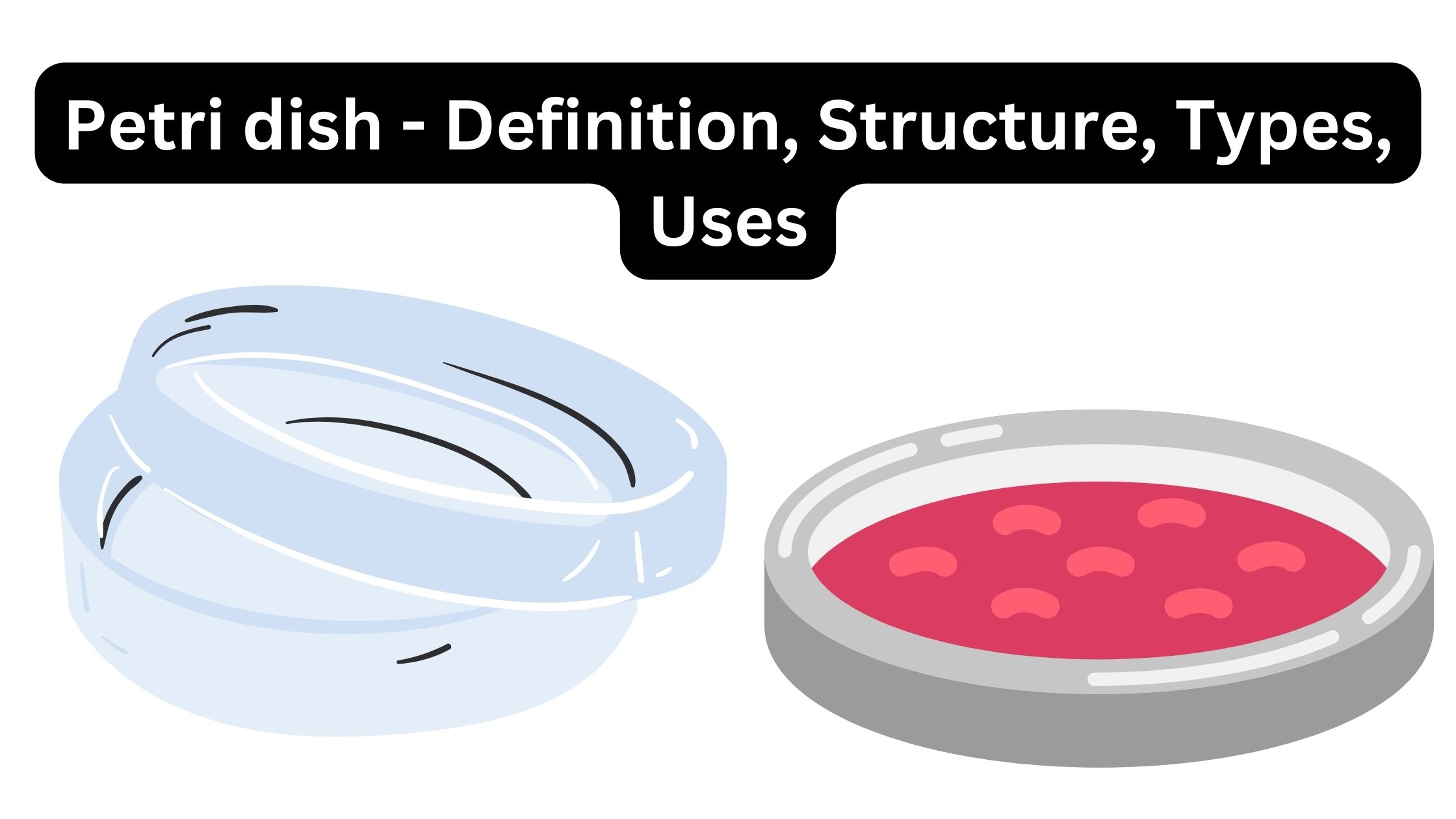
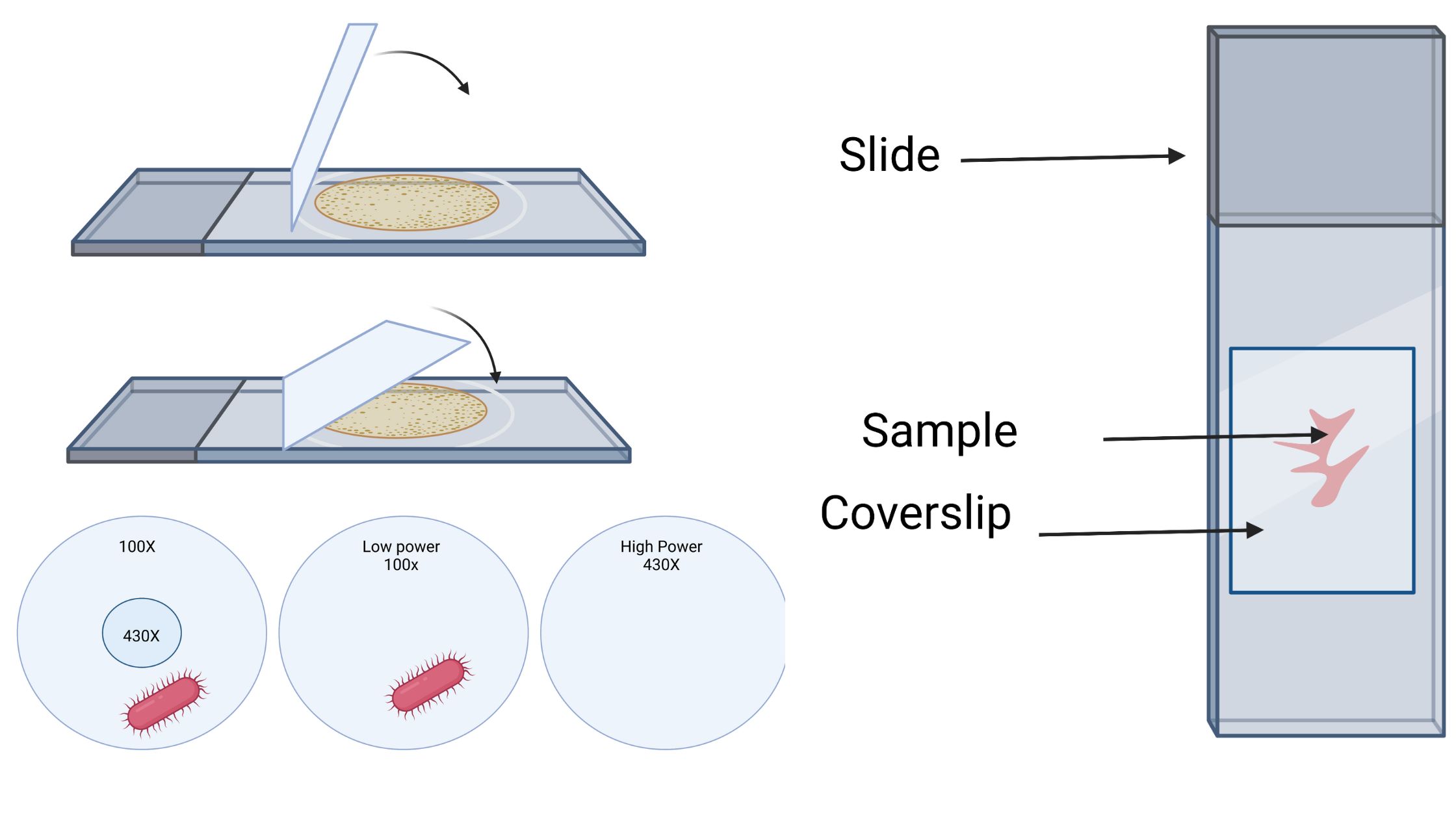
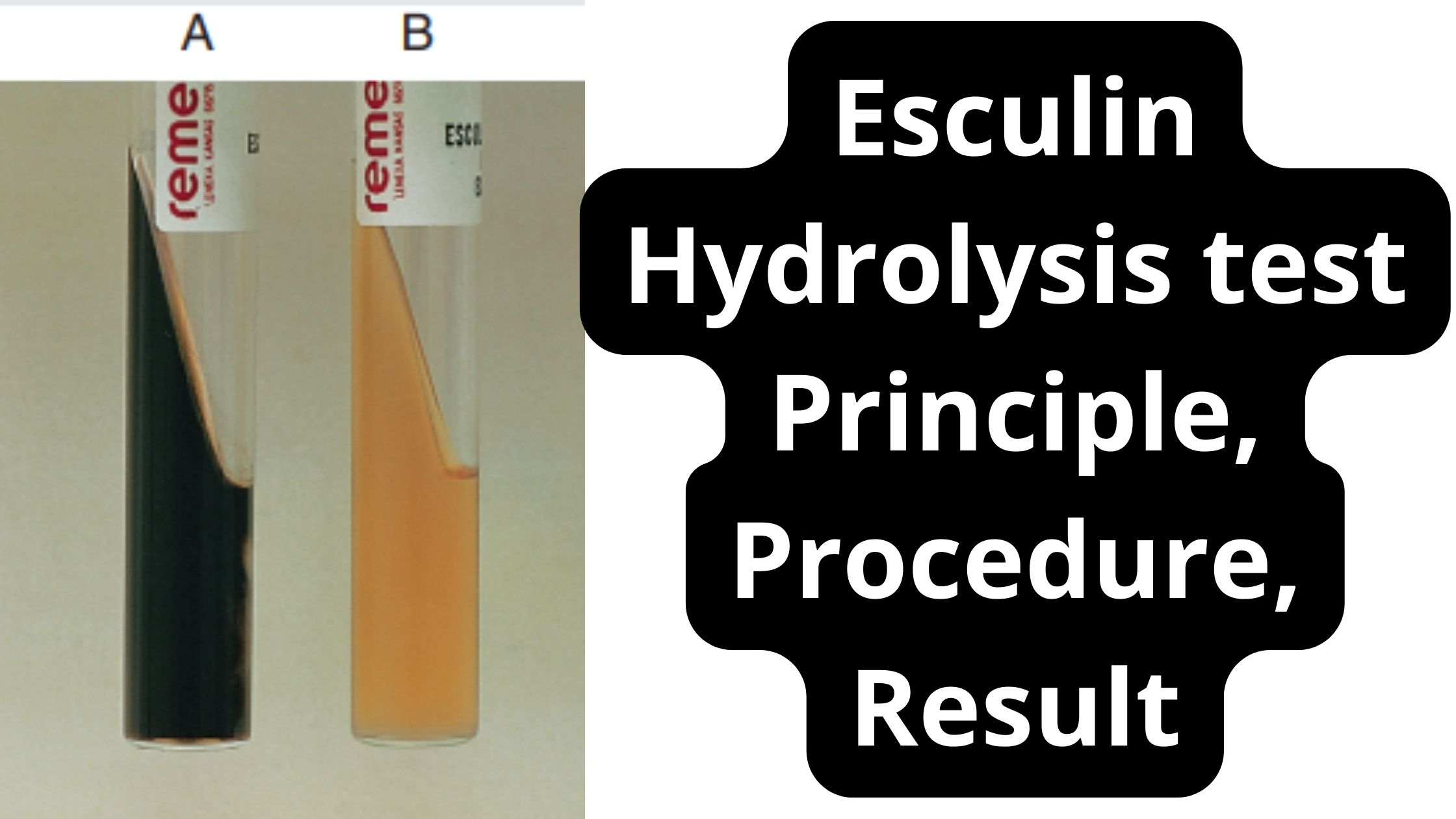
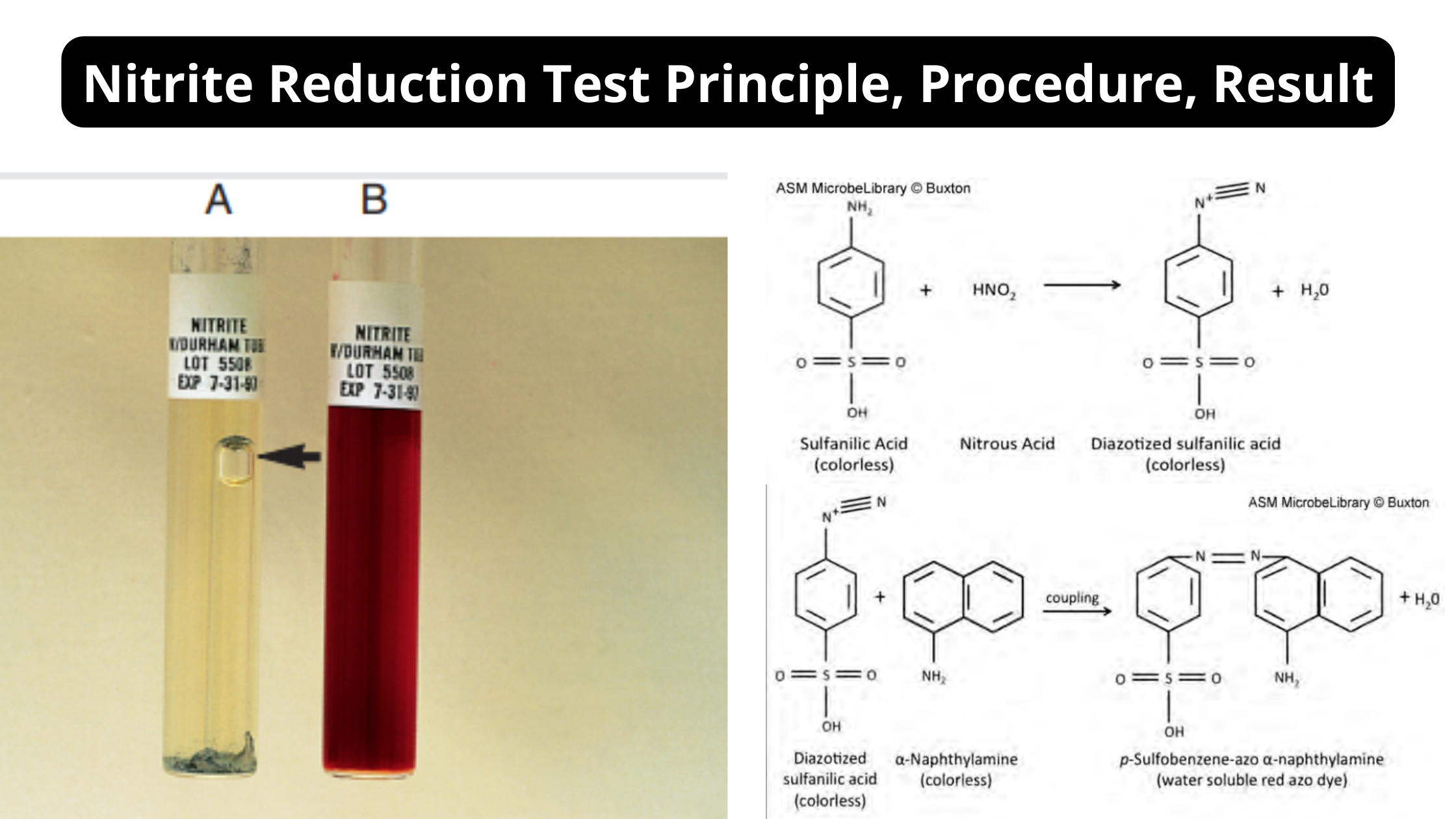
BOD Test – Biological Oxygen Demand Test
All aquatic organisms depend on the oxygen in the water (dissolved oxygen) for survival. As a food supply, aquatic microbes consume the organic matter discharged into the water. Plant decomposition and leaf fall are common sources of organic debris. Using the dissolved oxygen in the water, bacteria will decompose this organic stuff and form less … Read more