Latest Notes
- Insect morphology (Morphology of Pest)
 by Sourav BioTaxonomy of Pests The taxonomy of pests plays a crucial … Read more
by Sourav BioTaxonomy of Pests The taxonomy of pests plays a crucial … Read more - Mesophiles – Habitat, Adaptations, Roles, Examples
 by Sourav BioWhat are Mesophiles? Habitat of Mesophiles Mesophiles are microorganisms that … Read more
by Sourav BioWhat are Mesophiles? Habitat of Mesophiles Mesophiles are microorganisms that … Read more - Ion exchange mechanism in Ion Exchange Chromatography
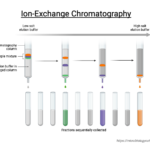 by Sourav BioIon exchange chromatography (IEC) is a chromatographic technique that allows … Read more
by Sourav BioIon exchange chromatography (IEC) is a chromatographic technique that allows … Read more - Ion Exchange Chromatography – Definition, Principle, Protocol, Applications, Examples
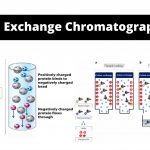 by Sourav Bioomatography) is a method that permits the separation of polar molecules and ions in accordance with their affinity to the ion exchangers.
by Sourav Bioomatography) is a method that permits the separation of polar molecules and ions in accordance with their affinity to the ion exchangers. - Sampling of Microorganisms From Soil
 by Sourav BioExploring the microscopic world within soil requires precise techniques for … Read more
by Sourav BioExploring the microscopic world within soil requires precise techniques for … Read more - Sampling of Bacteria From Water
 by Sourav BioWhen examining water samples for bacterial content, direct microscopic observation … Read more
by Sourav BioWhen examining water samples for bacterial content, direct microscopic observation … Read more - Sampling of Bacteria From Air
 by Sourav BioThe process of collecting bacteria from the air for analysis … Read more
by Sourav BioThe process of collecting bacteria from the air for analysis … Read more - Determination of Phosphorus In Milk
 by Sourav BioPhosphorus is an essential mineral found in many foods, including … Read more
by Sourav BioPhosphorus is an essential mineral found in many foods, including … Read more - Determination of Magnesium In Milk
 by Sourav BioMagnesium is an essential mineral found in many foods, including … Read more
by Sourav BioMagnesium is an essential mineral found in many foods, including … Read more - Determination of Calcium In Milk
 by Sourav BioMilk is widely recognized as a significant source of calcium, … Read more
by Sourav BioMilk is widely recognized as a significant source of calcium, … Read more - Determination of Lactose In Milk by Lane-Eynon Method
 by Sourav BioWhat is Lane-Eynon Method? Principle of Lane-Eynon Method The Lane-Eynon … Read more
by Sourav BioWhat is Lane-Eynon Method? Principle of Lane-Eynon Method The Lane-Eynon … Read more - Raw Materials for Production Media
 by Sourav BioIndustrial fermentation processes leverage a wide array of raw materials, … Read more
by Sourav BioIndustrial fermentation processes leverage a wide array of raw materials, … Read more - Production Media – Definition, Characteristics, Examples, Uses
 by Sourav BioWhat is Production Media? Production media, often associated with the … Read more
by Sourav BioWhat is Production Media? Production media, often associated with the … Read more - What is the Difference Between Holobasidium and Phragmobasidium?
 by Sourav BioWhat is Holobasidium? What is Basidium? What is Phragmobasidium? Difference … Read more
by Sourav BioWhat is Holobasidium? What is Basidium? What is Phragmobasidium? Difference … Read more - What is the Difference Between Cloaca and Anus?
 by Sourav BioWhat is Cloaca? Characteristics Features of Cloaca The cloaca is … Read more
by Sourav BioWhat is Cloaca? Characteristics Features of Cloaca The cloaca is … Read more - Basidiomycetes – Life cycle, Characteristics, Significance, Mycelium and Examples
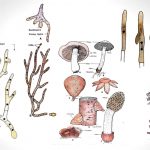 by MN EditorsBasidiomycetes are harmful as well as useful. Their attack foods and ornamental plants, cause many different diseases including seedling diseases, wood rots, root and stem rots, seed diseases (smuts), and rusts, on the other hand, it used as humans foods.
by MN EditorsBasidiomycetes are harmful as well as useful. Their attack foods and ornamental plants, cause many different diseases including seedling diseases, wood rots, root and stem rots, seed diseases (smuts), and rusts, on the other hand, it used as humans foods. - Deuteromycetes – Reproduction, Characteristics, Classification and Examples
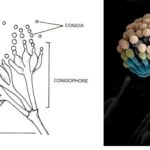 by Sourav BioKey Points on Deuteromycetes Here are the key points summarizing … Read more
by Sourav BioKey Points on Deuteromycetes Here are the key points summarizing … Read more - What is the Difference Between Basidiomycetes and Deuteromycetes
 by Sourav BioWhat is Basidiomycetes? Basidiomycetes, belonging to the Basidiomycota division, represent … Read more
by Sourav BioWhat is Basidiomycetes? Basidiomycetes, belonging to the Basidiomycota division, represent … Read more - Amoebiasis, Entamoeba Histolytica, Life cycle, Diagnosis
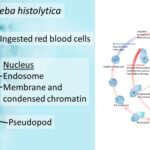 by Sourav BioWhat is Entamoeba Histolytica? Definition of Entamoeba Histolytica Entamoeba histolytica … Read more
by Sourav BioWhat is Entamoeba Histolytica? Definition of Entamoeba Histolytica Entamoeba histolytica … Read more - Secondary Consumers – Definition, Types, Functions, Examples
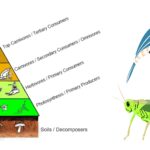 by Sourav BioWhat are Secondary Consumers? Definition of Secondary Consumers Secondary consumers … Read more
by Sourav BioWhat are Secondary Consumers? Definition of Secondary Consumers Secondary consumers … Read more
