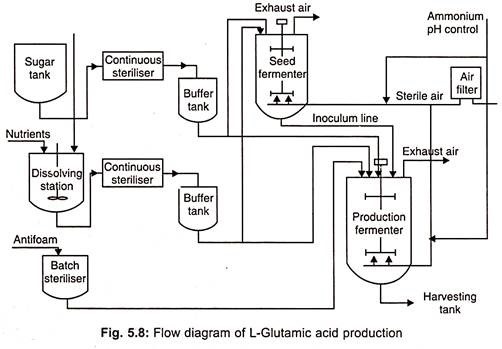
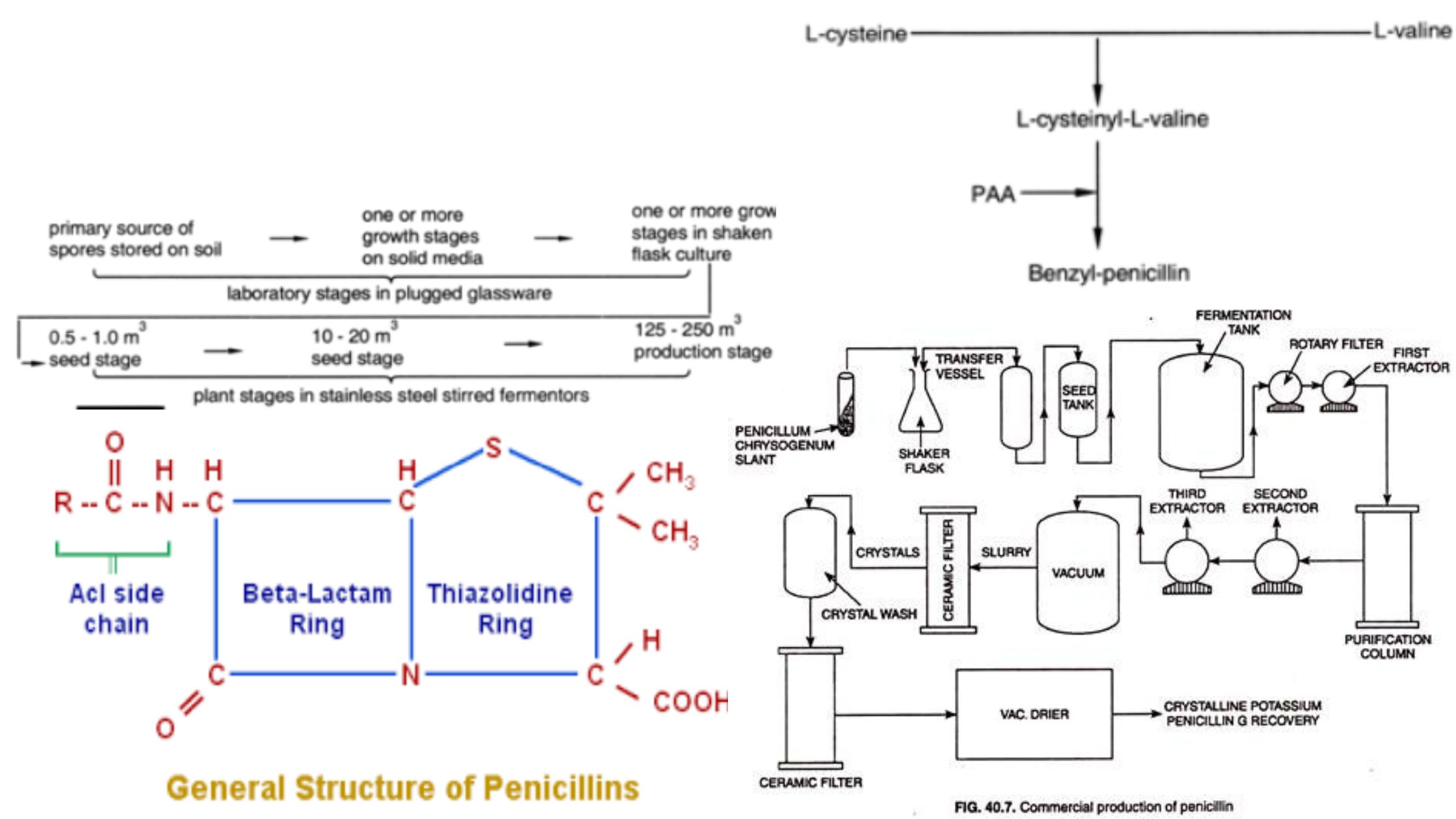
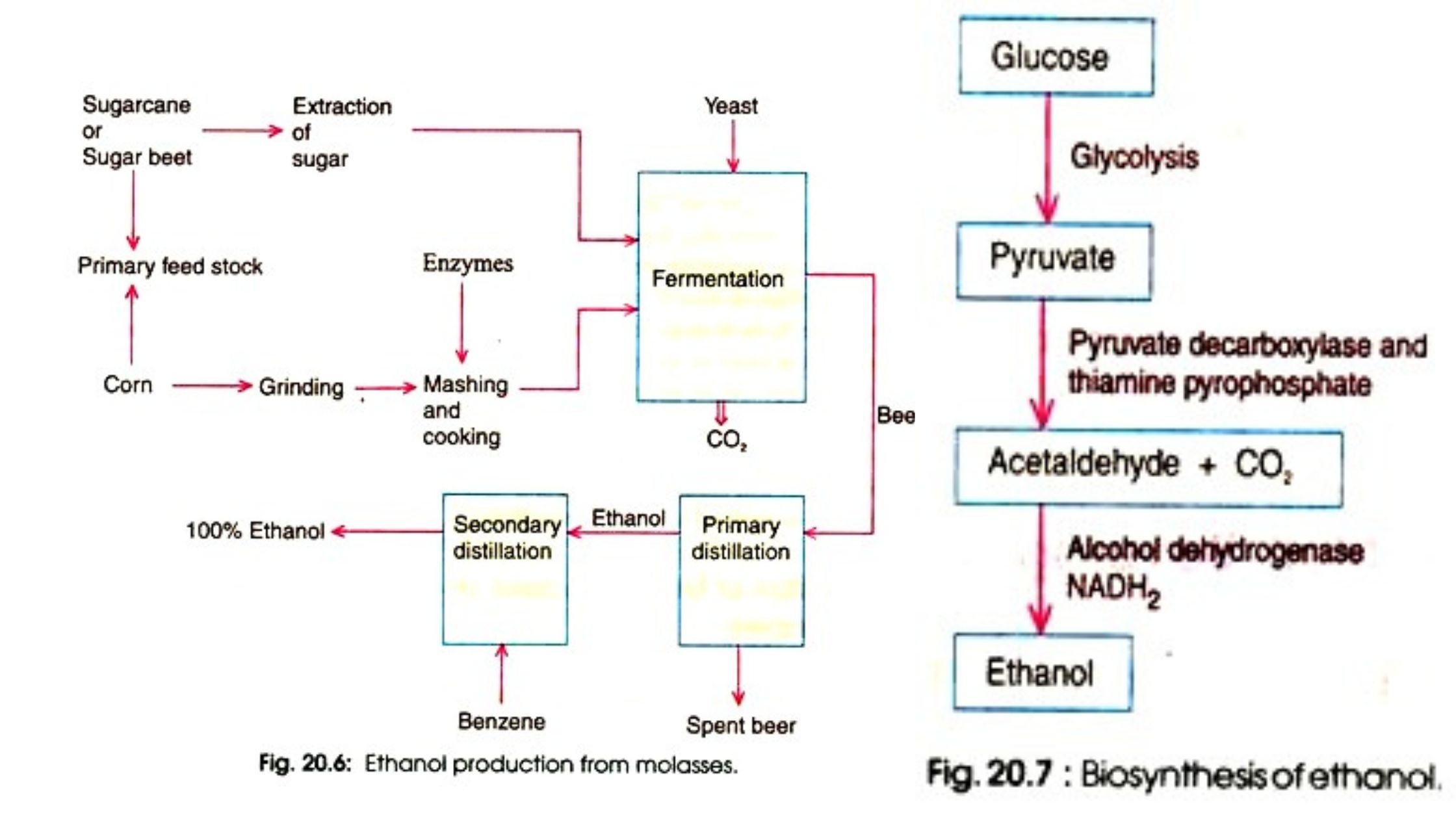
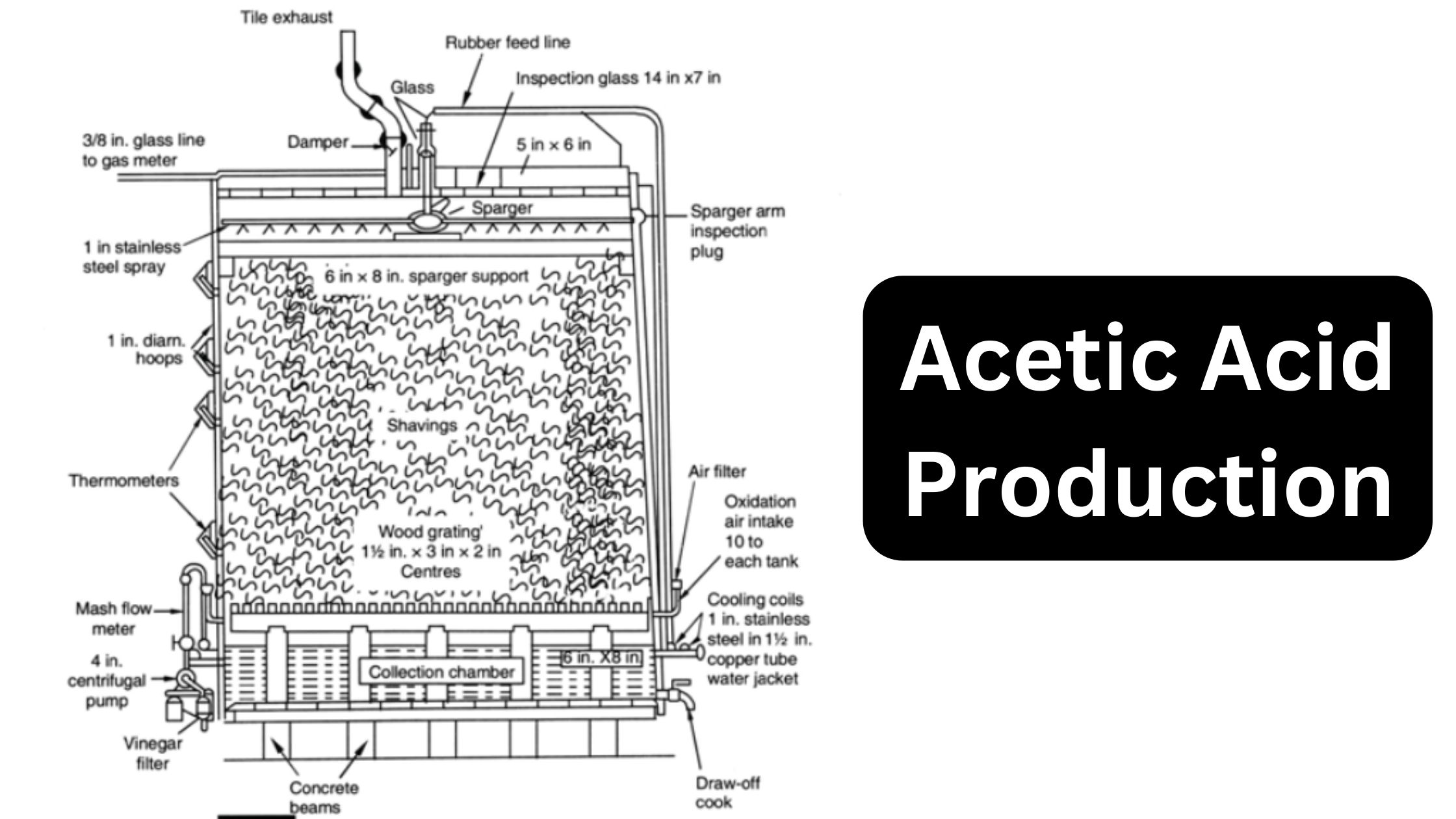
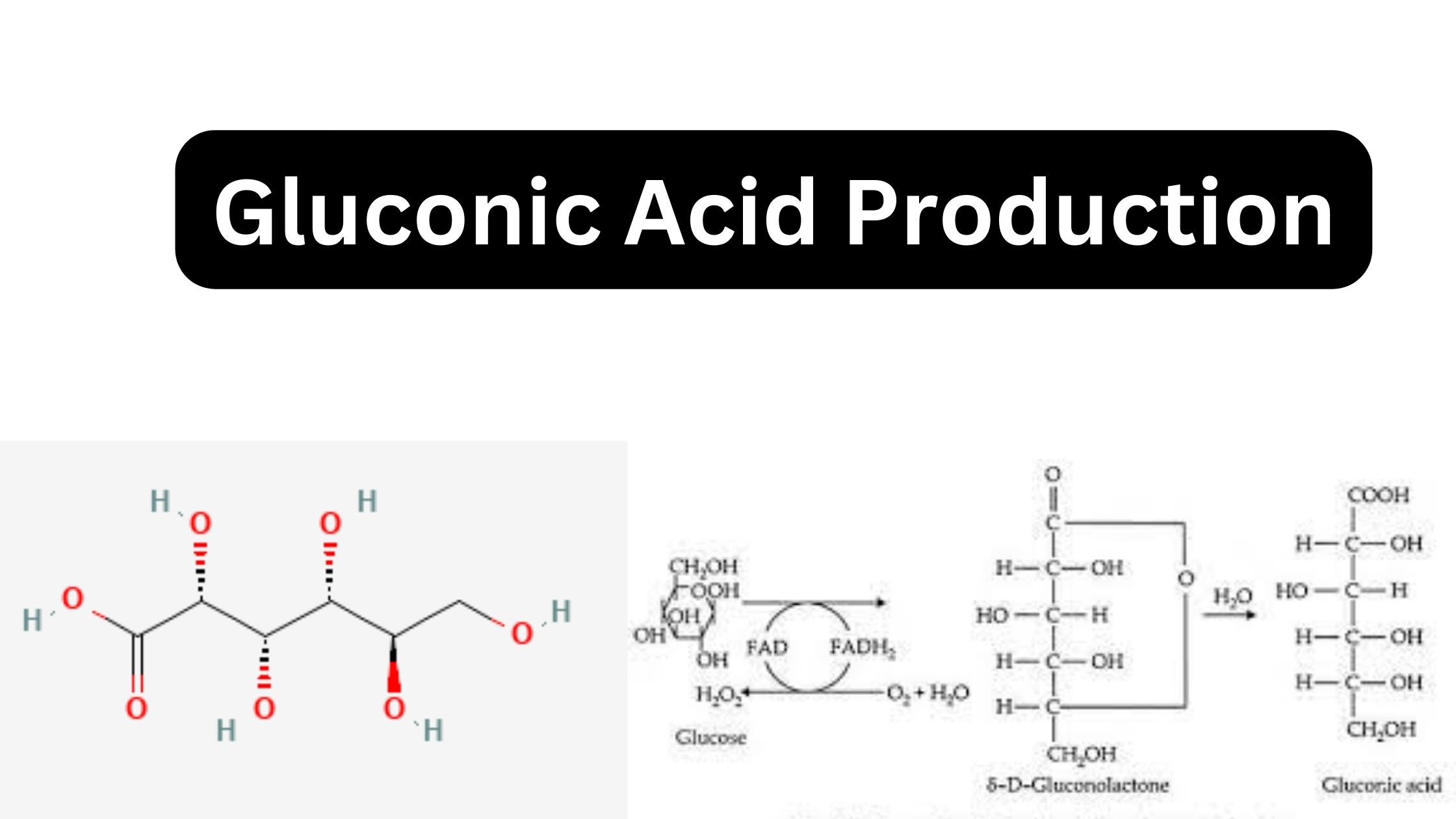
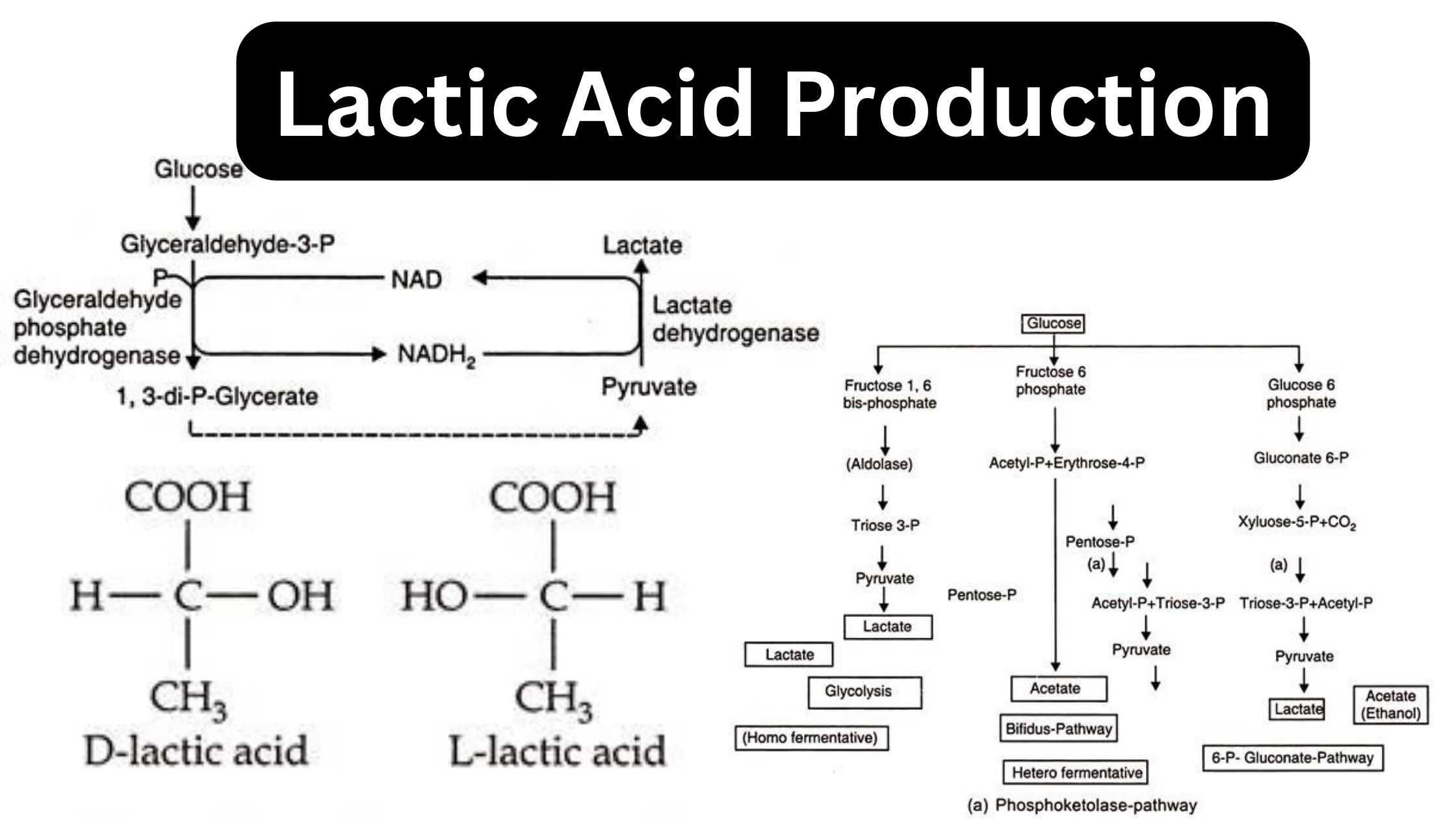
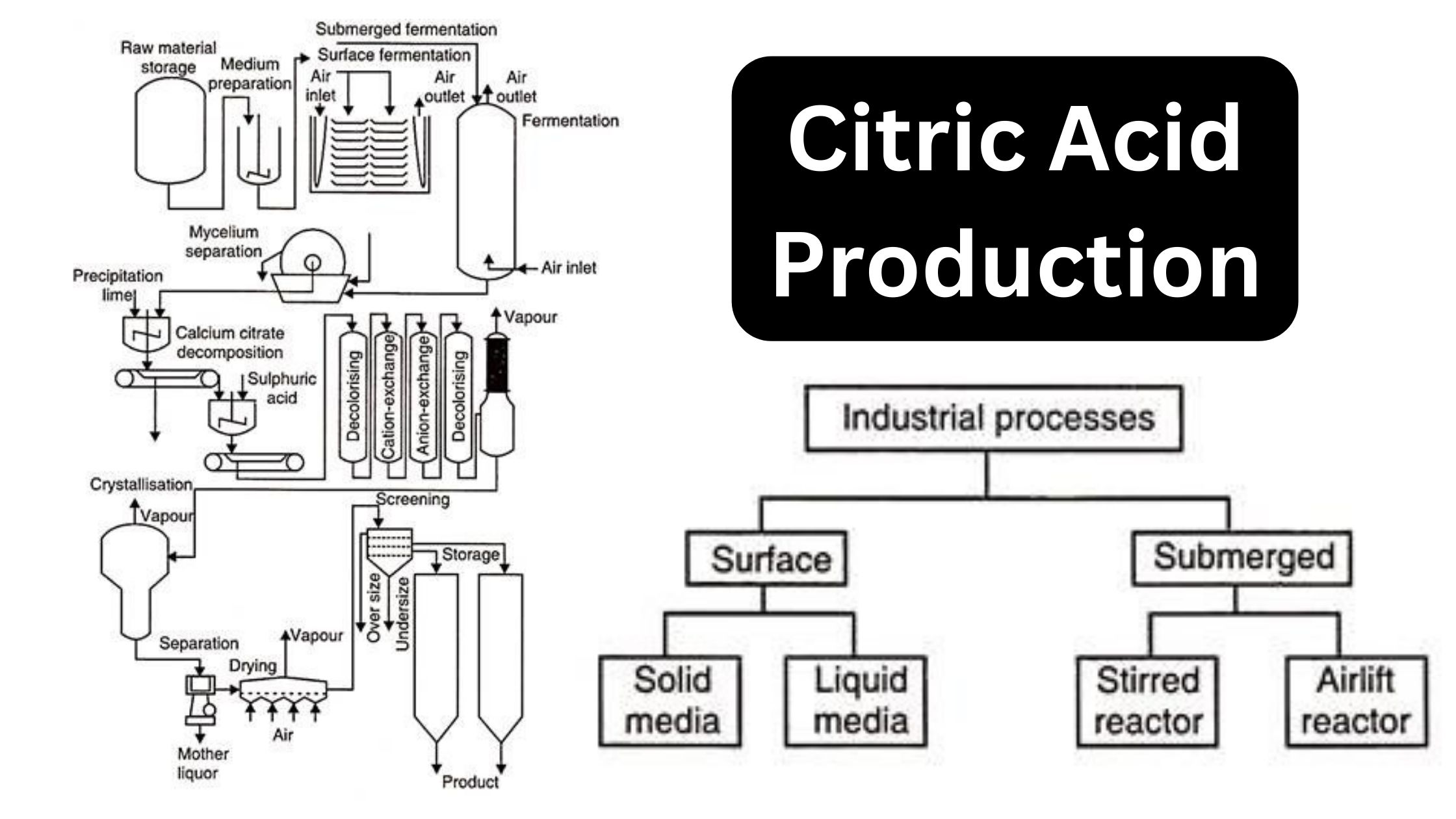
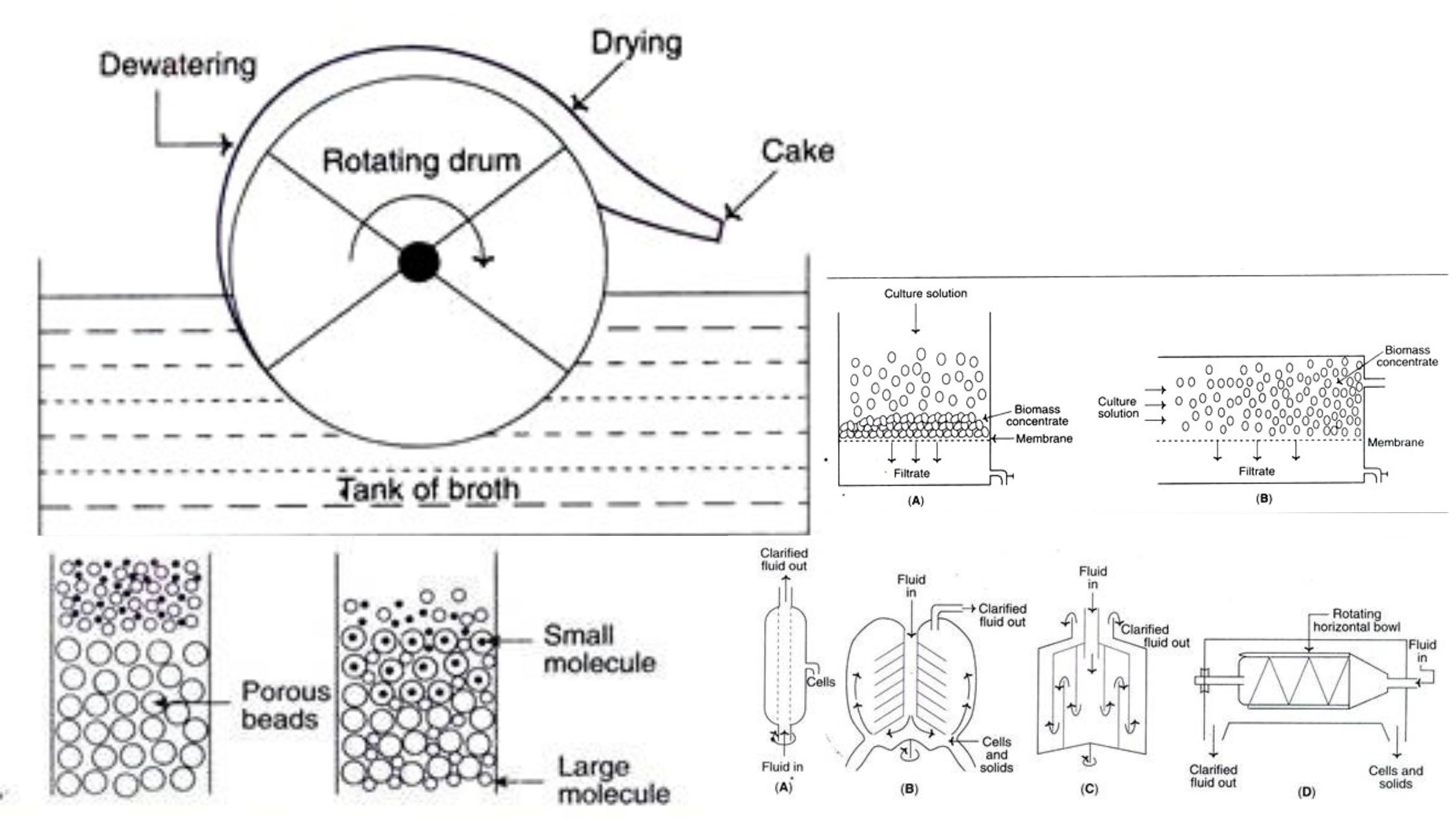
Raw Materials for Production Media
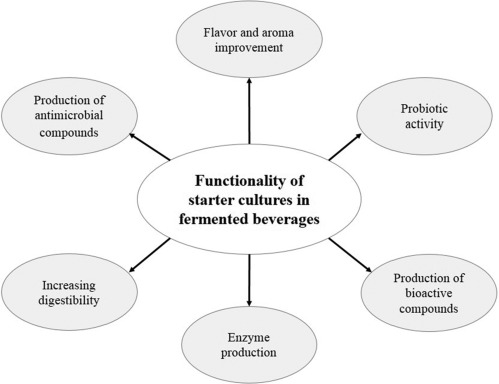
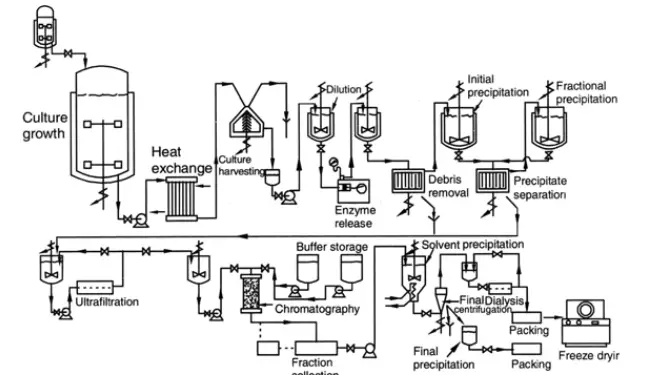
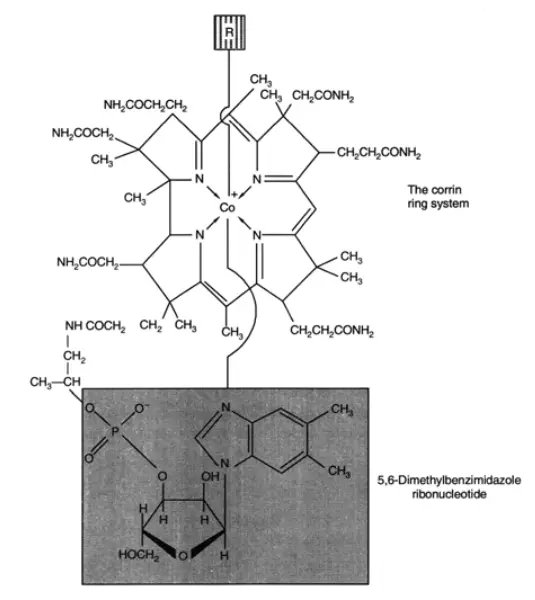
Industrial fermentation processes leverage a wide array of raw materials, with a significant emphasis on utilizing cost-effective and readily available sources. Among these, agricultural by-products stand out due to their abundance and potential for repurposing. The interest in these materials stems from several key factors: The concept of transforming ‘wastes into resources’ is not just … Read more