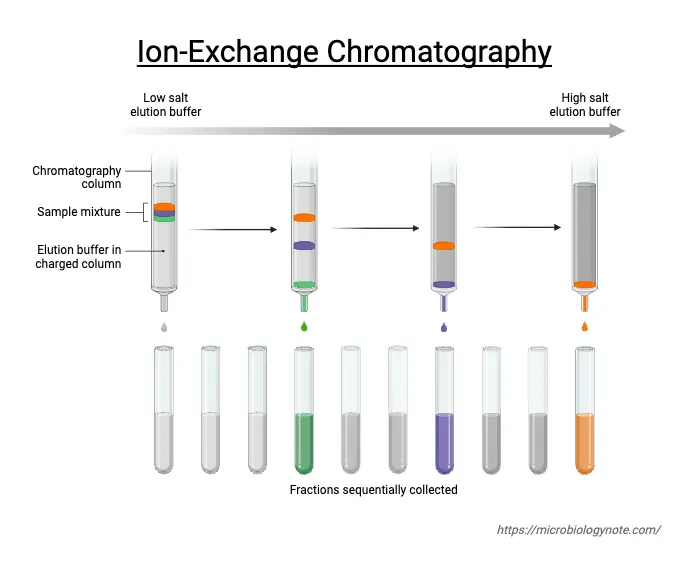
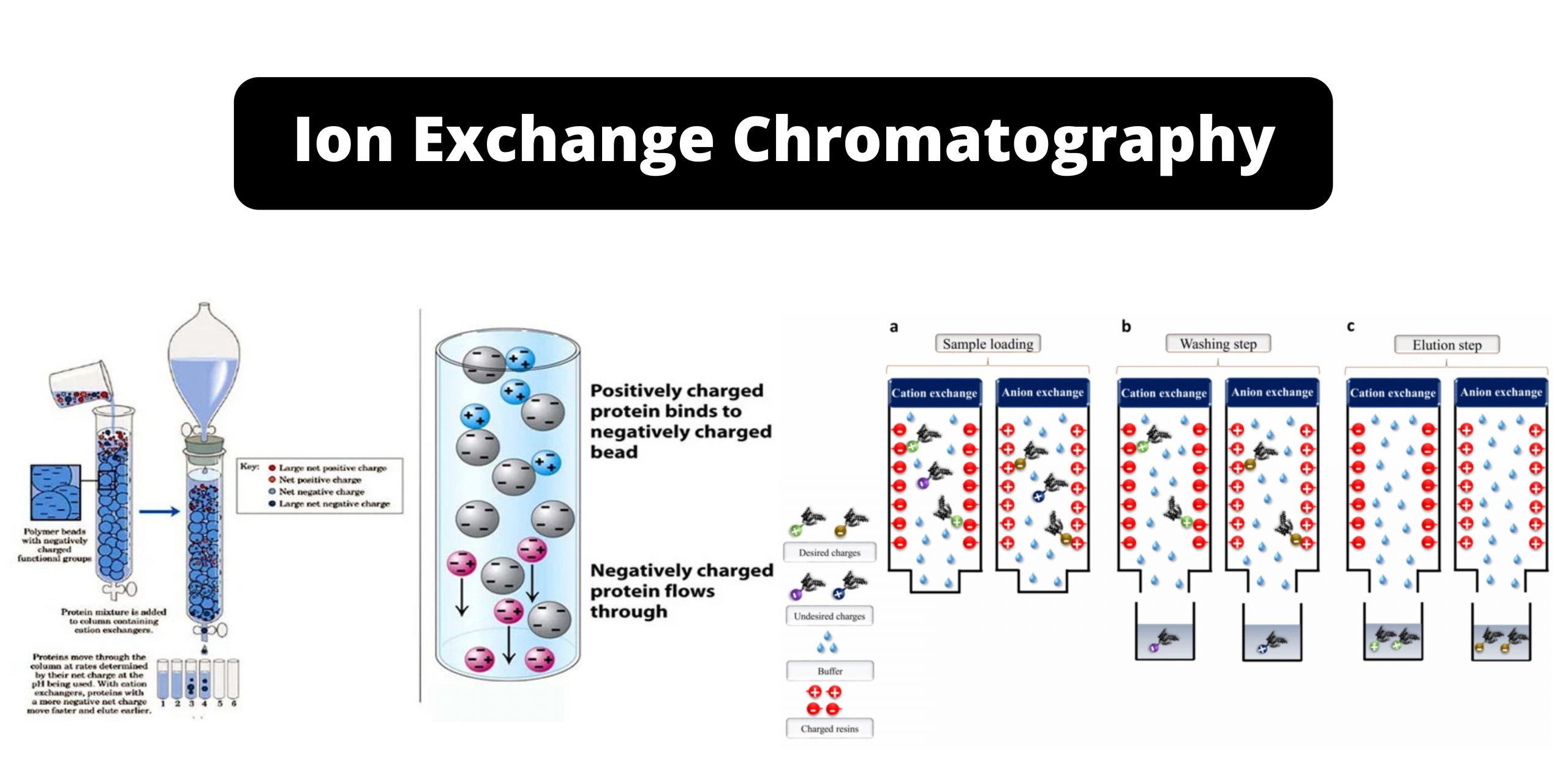
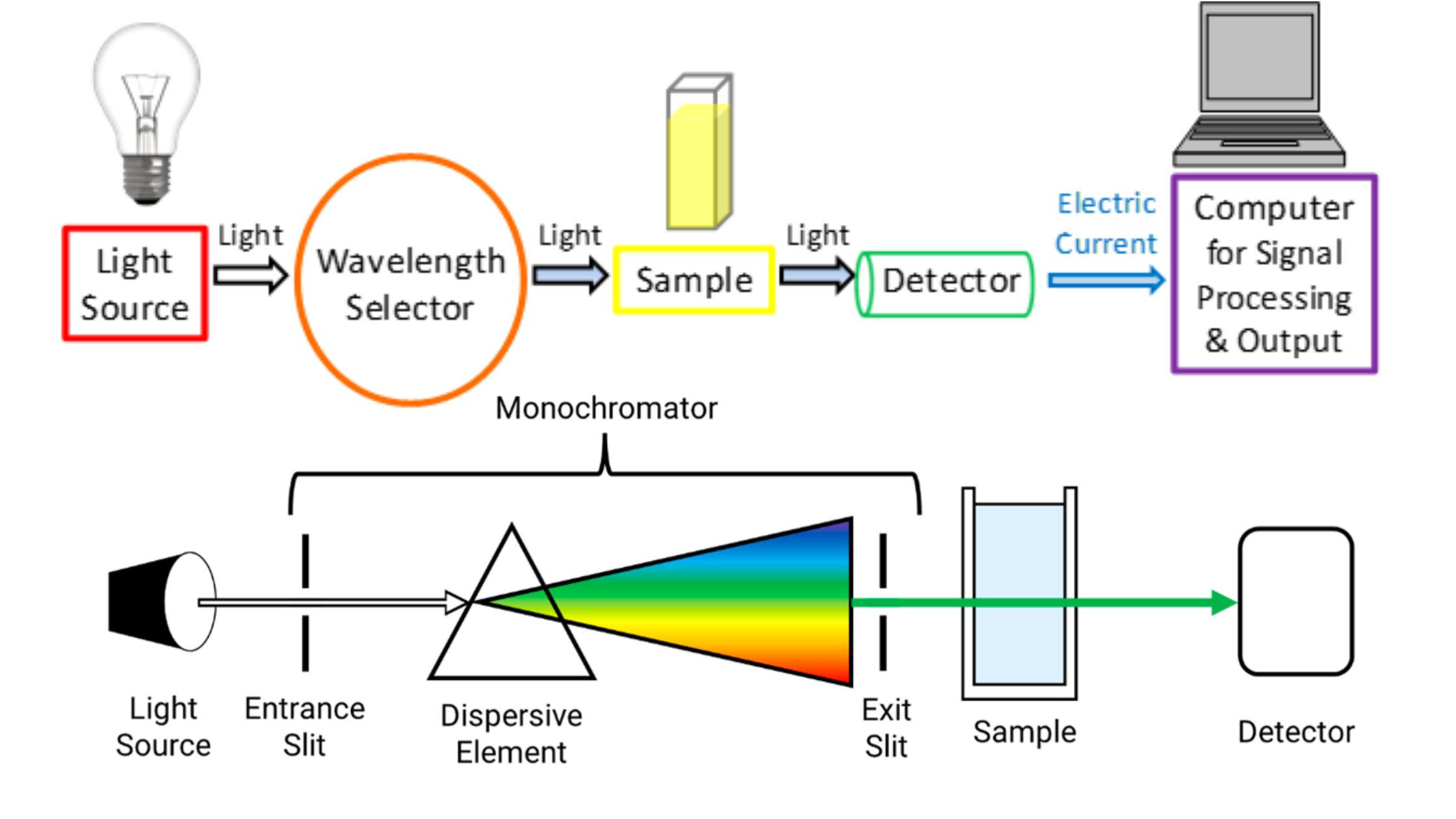
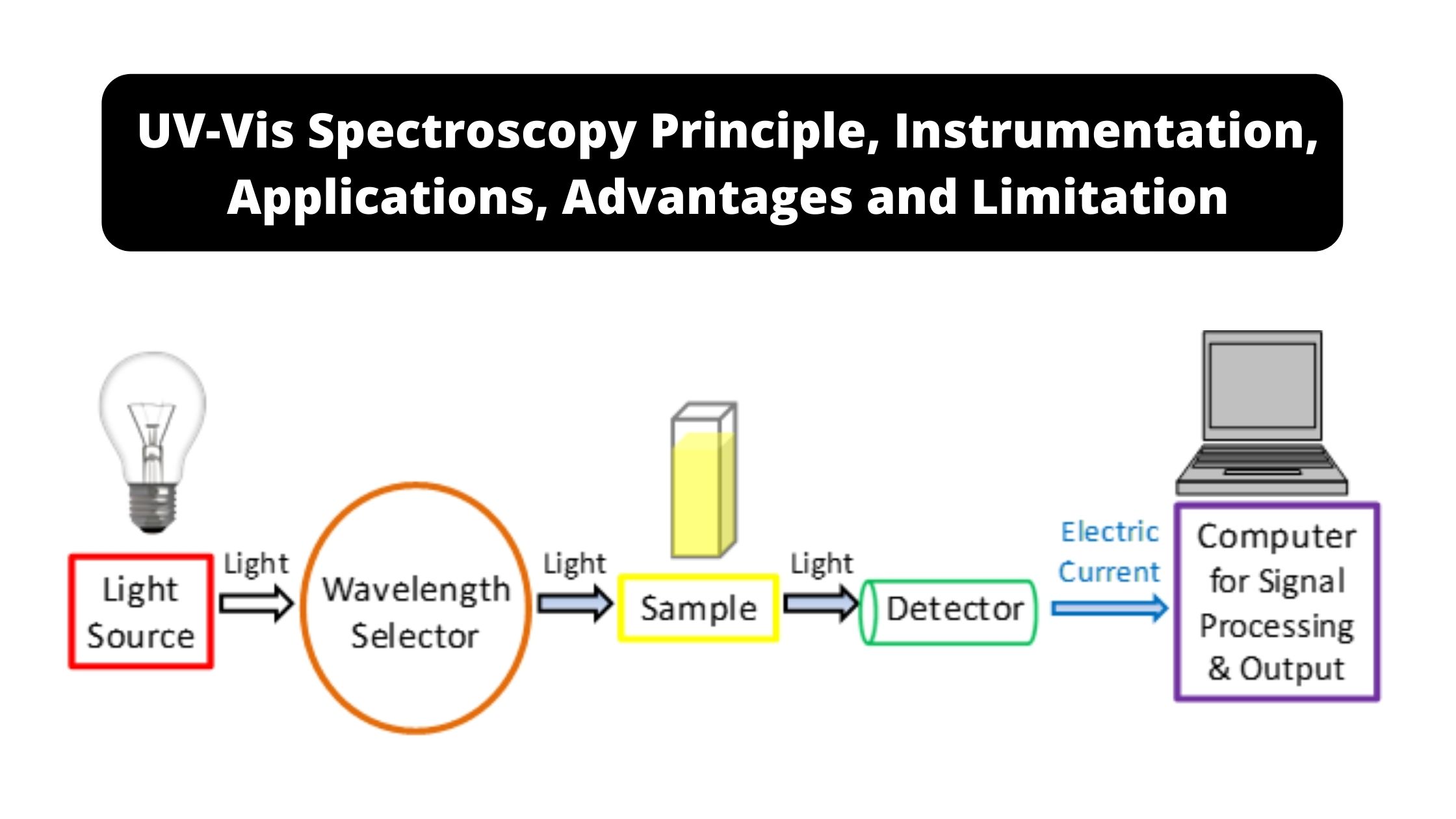
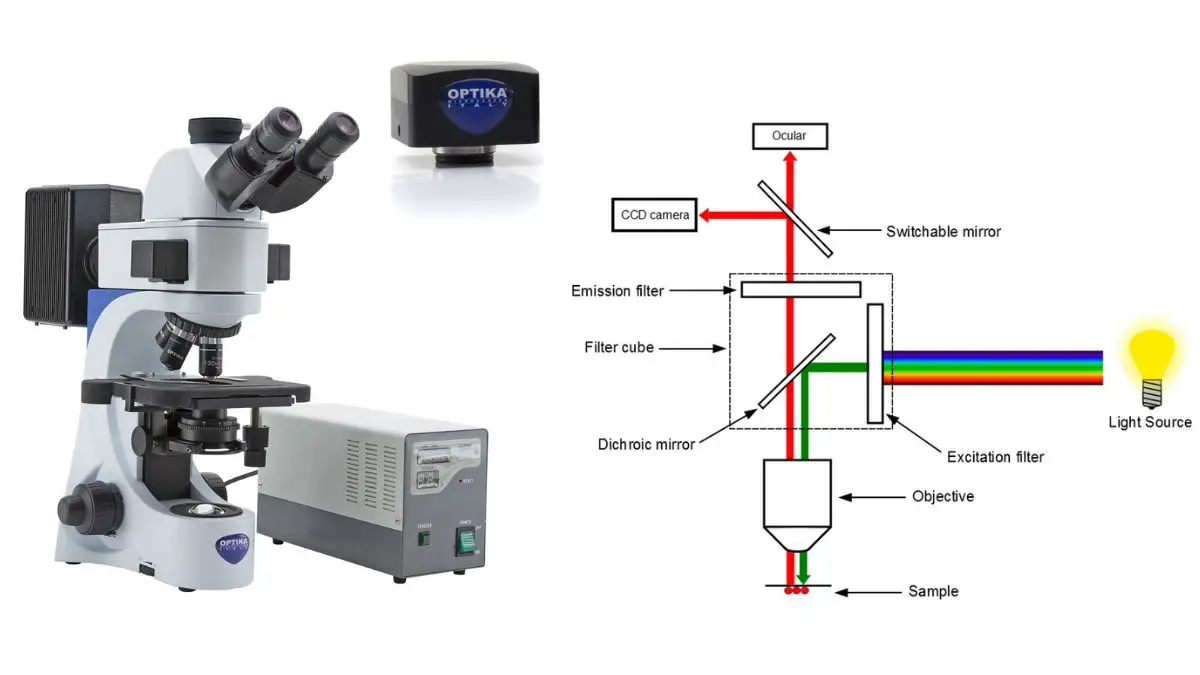
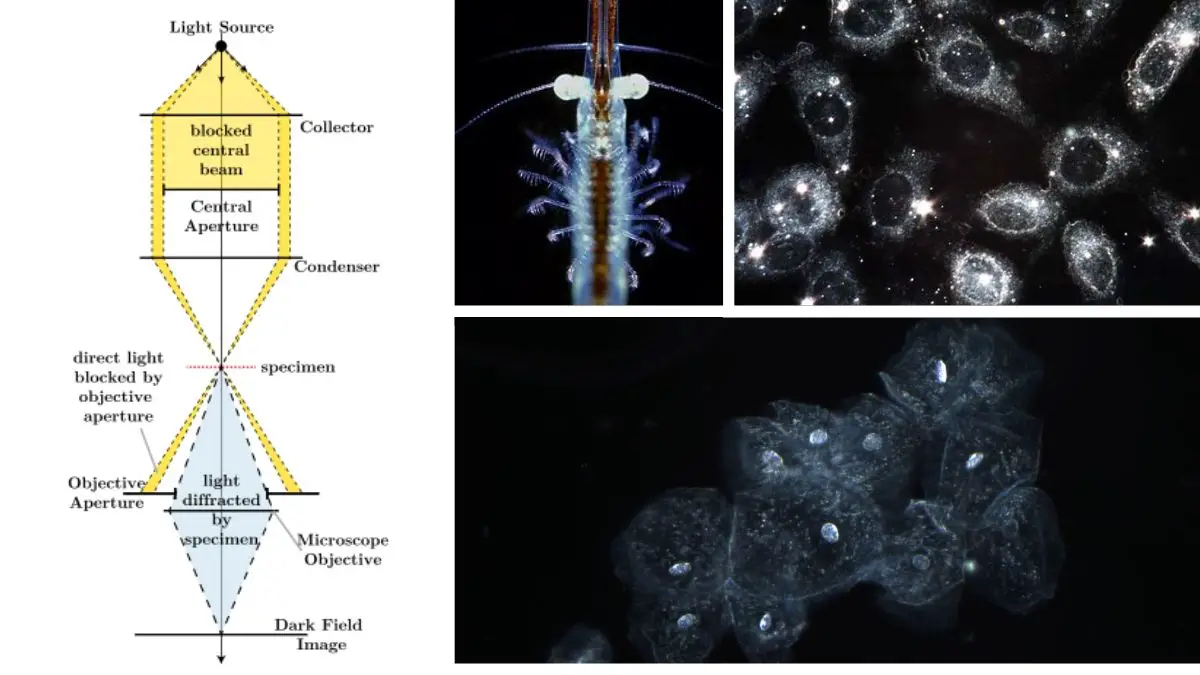
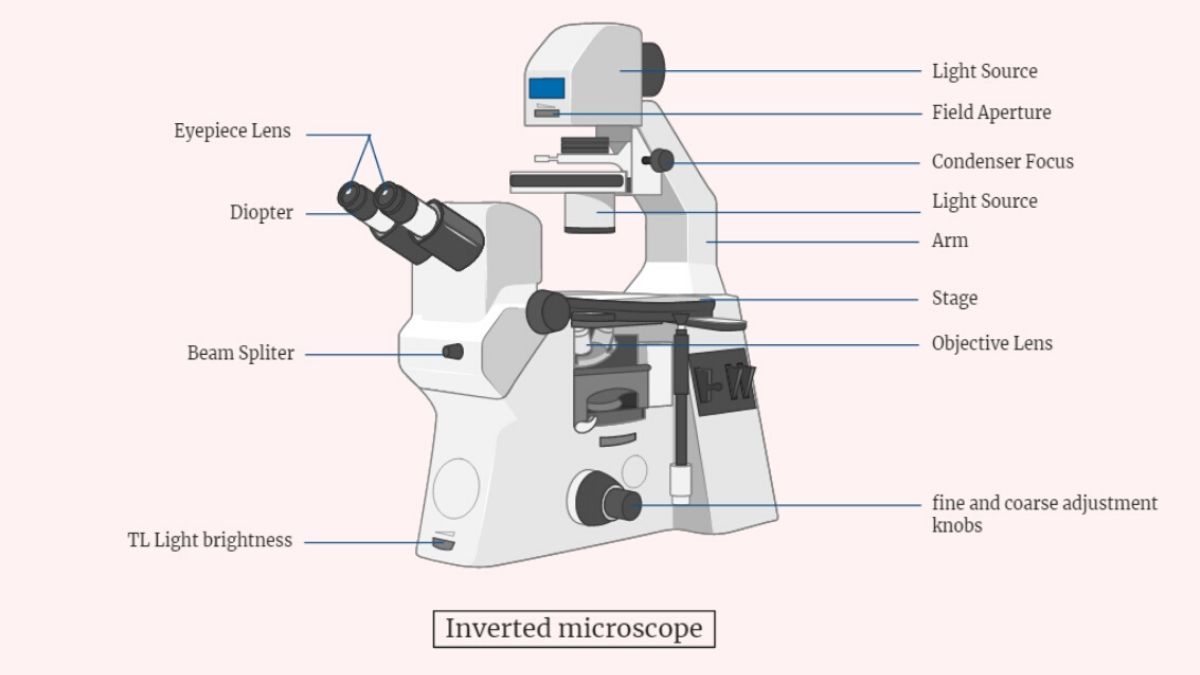
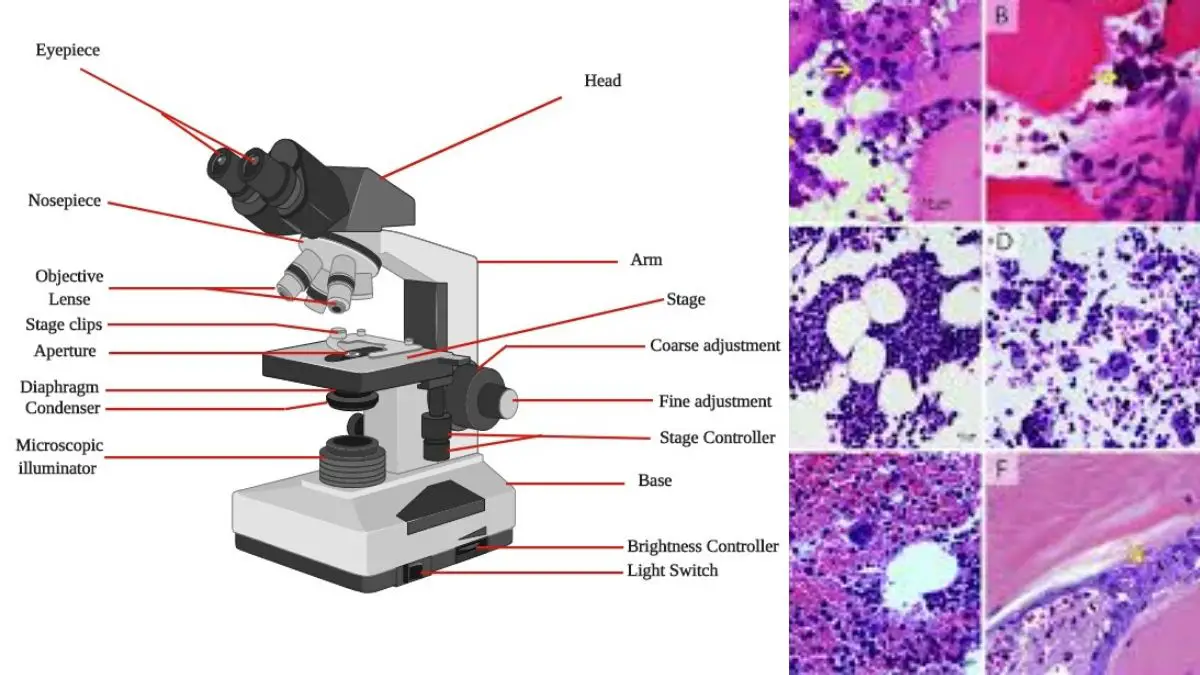
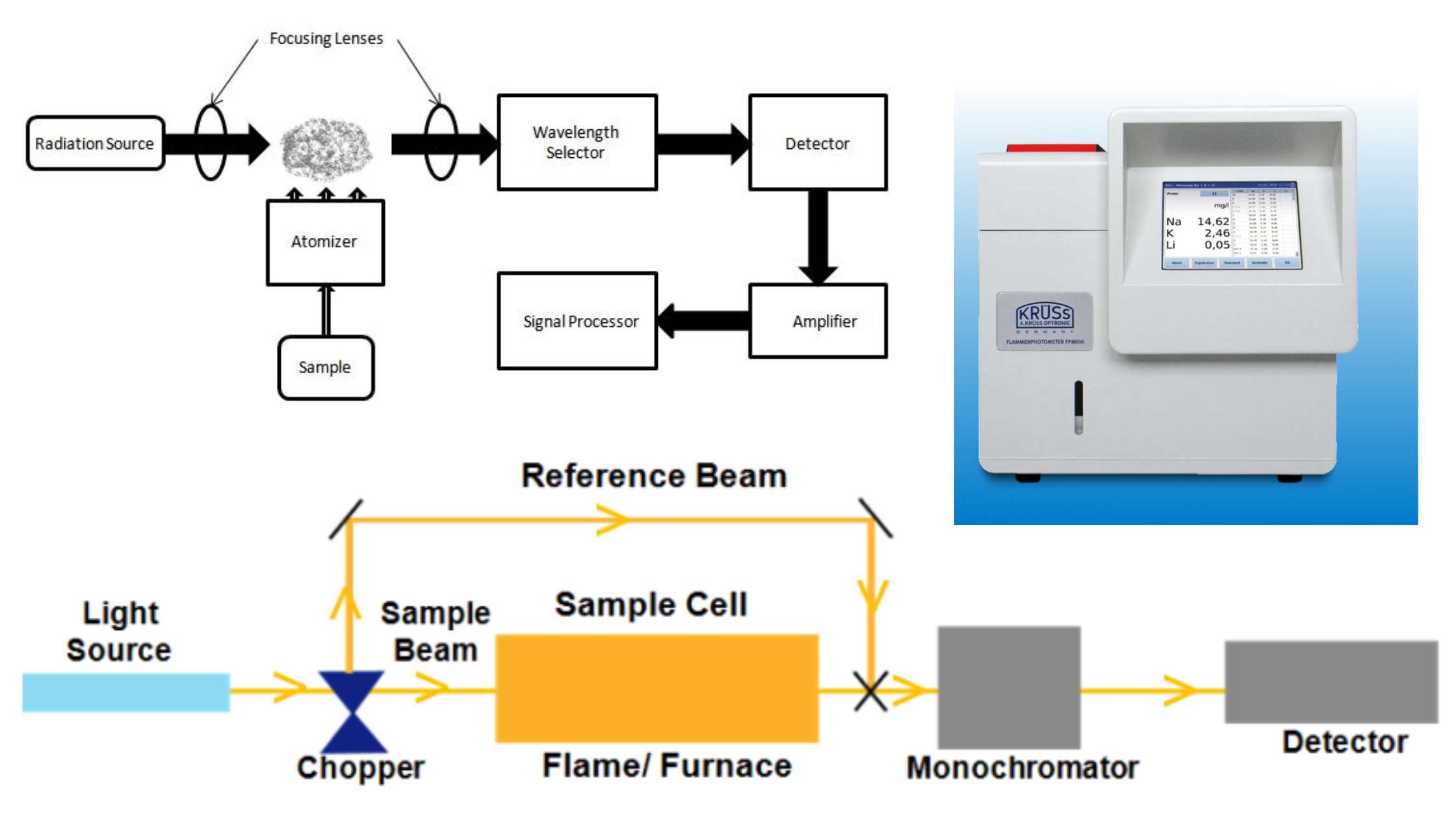
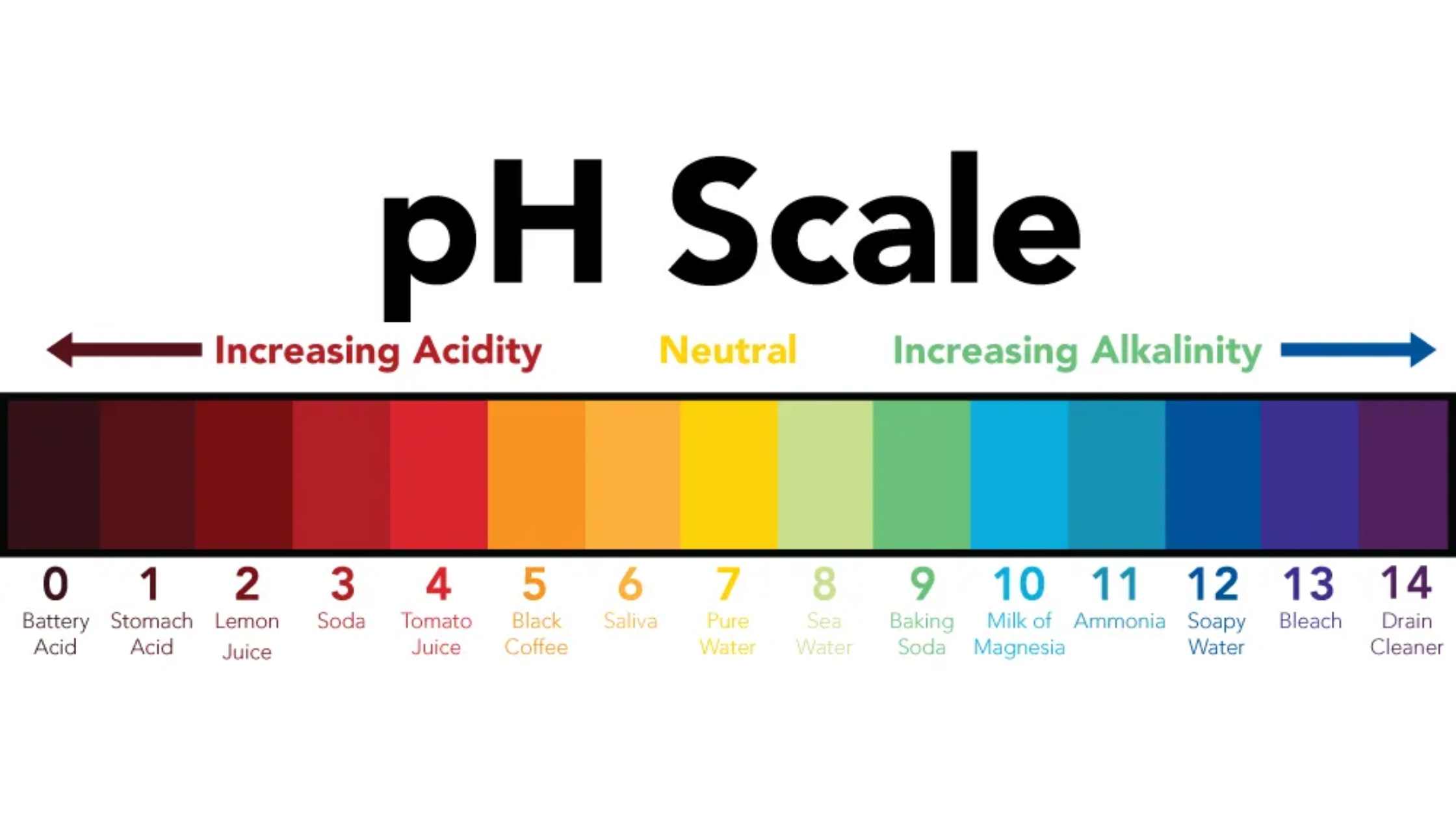
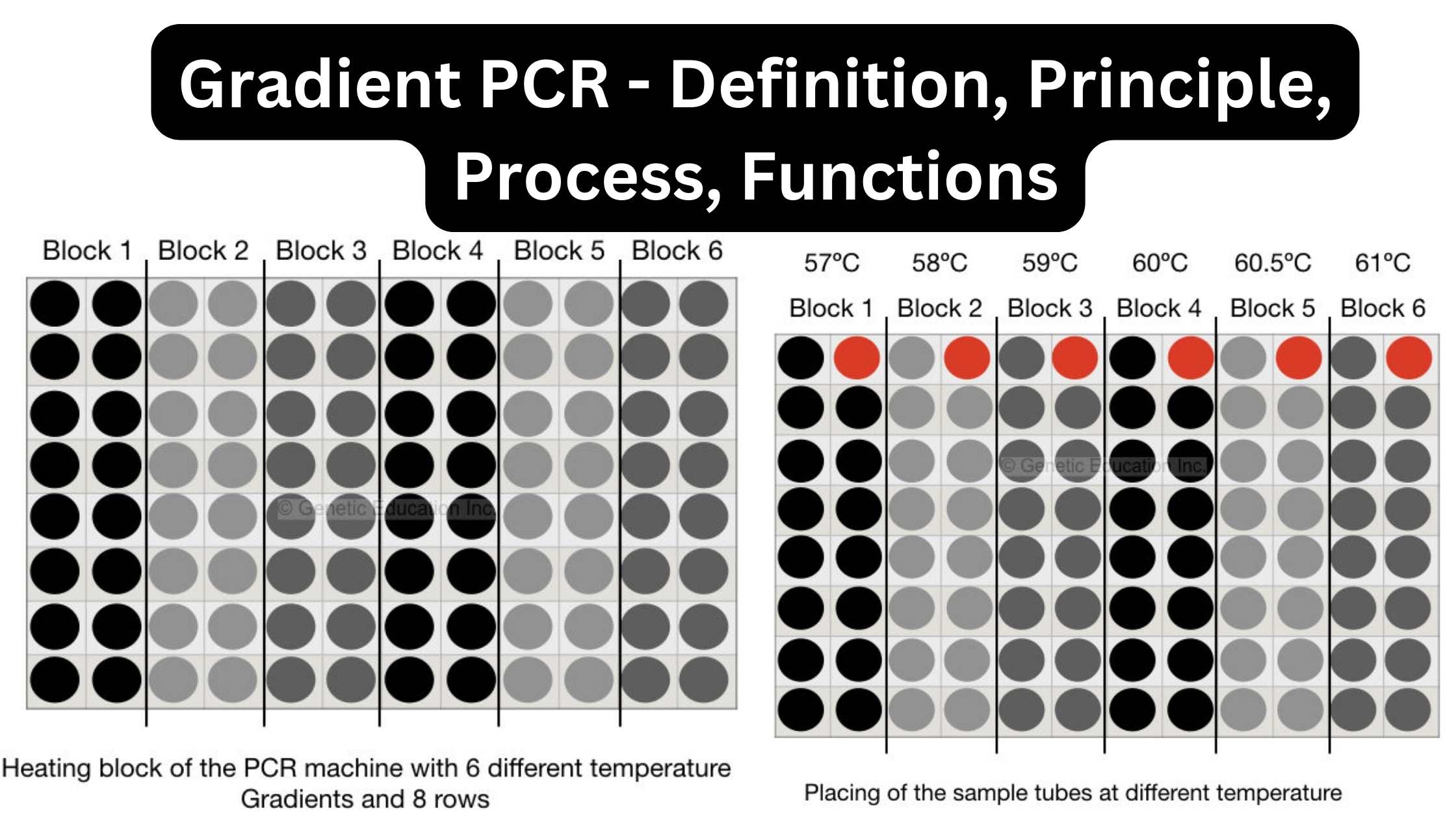
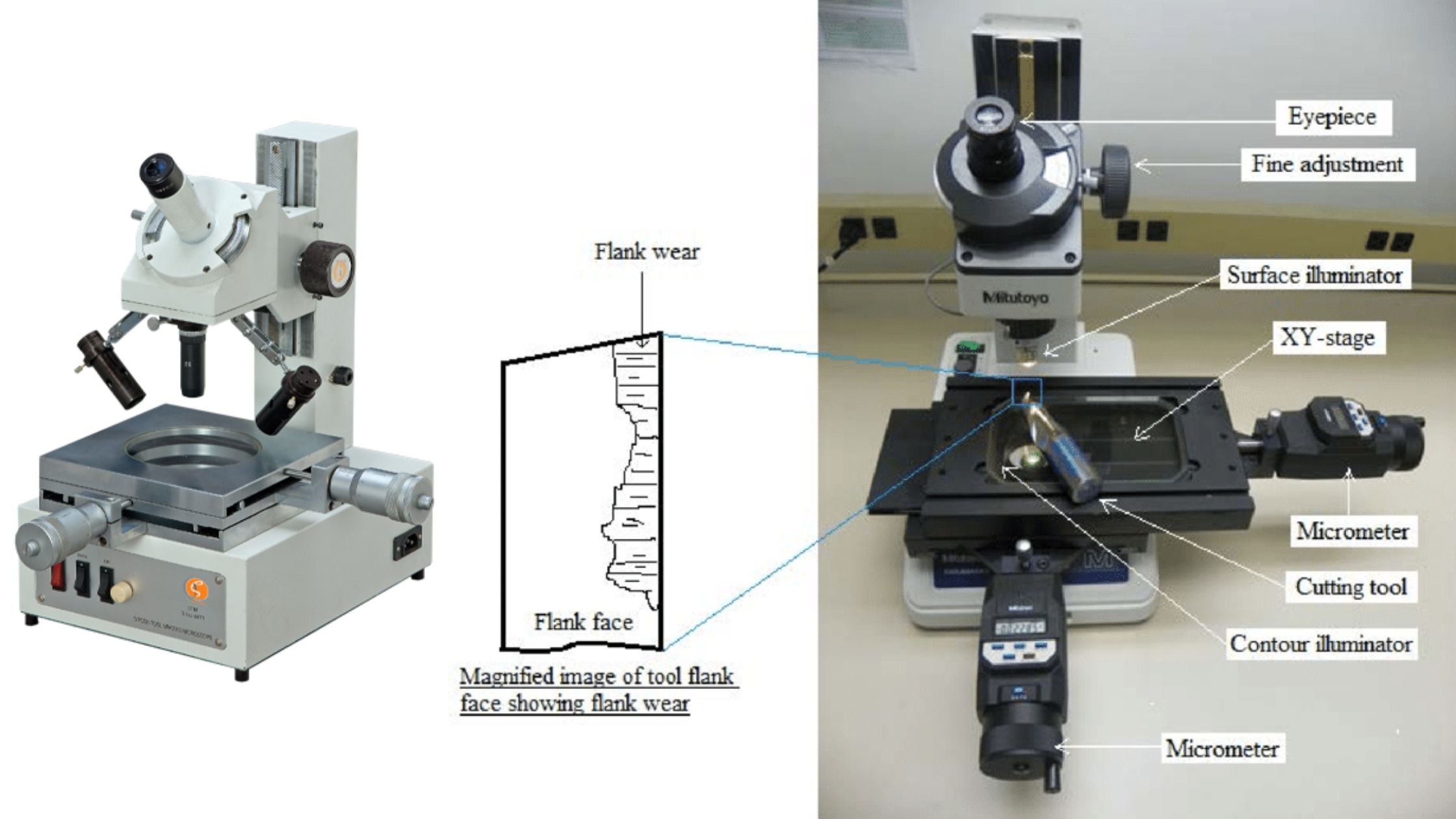
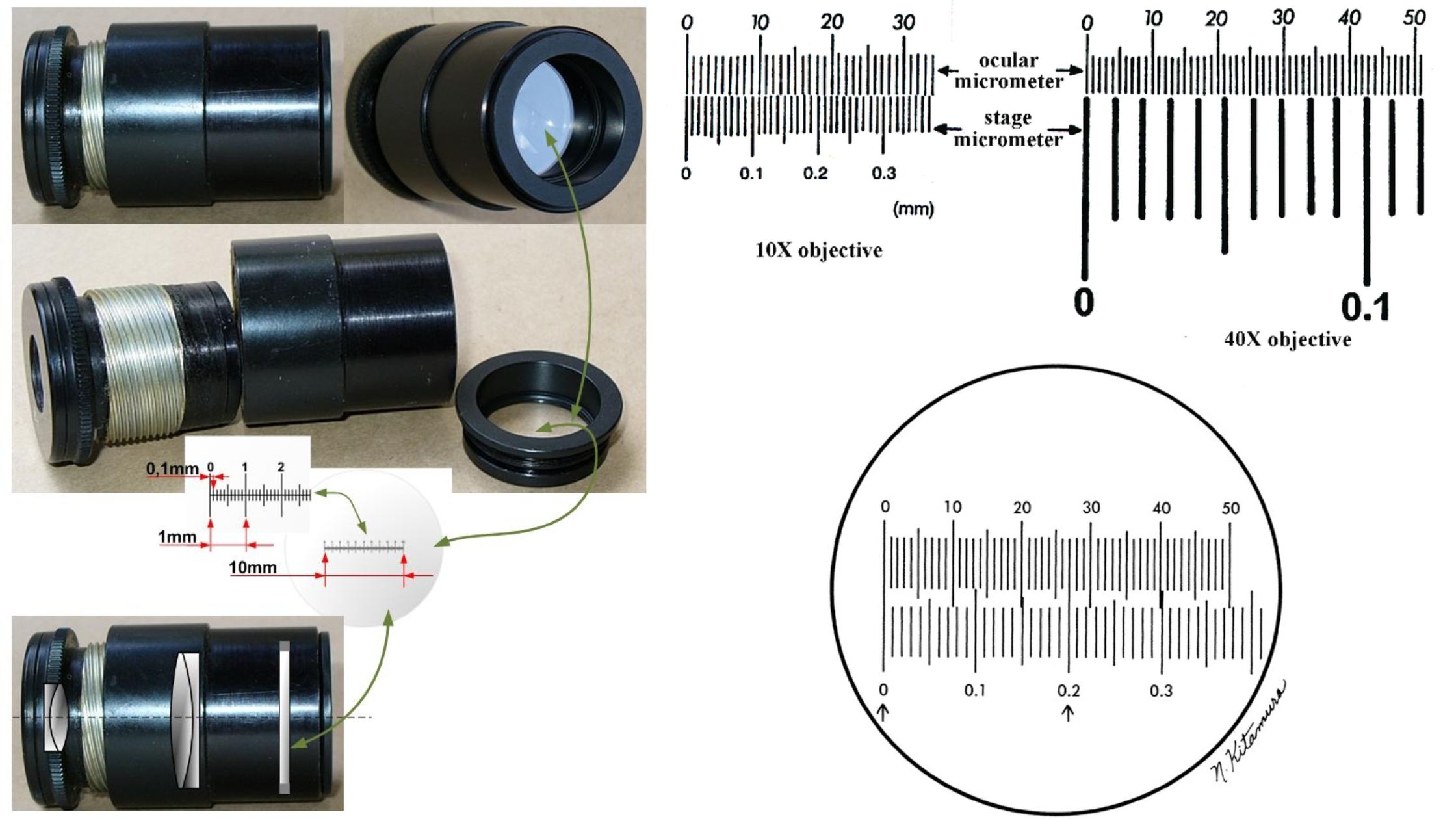
Ion exchange mechanism in Ion Exchange Chromatography
Ion exchange chromatography (IEC) is a chromatographic technique that allows for the separation of ions and polar molecules based on their charge. It utilizes a stationary phase composed of an insoluble matrix with covalently bonded charged groups. These charged groups can attract and bind ions of the opposite charge present in the mobile phase, which … Read more