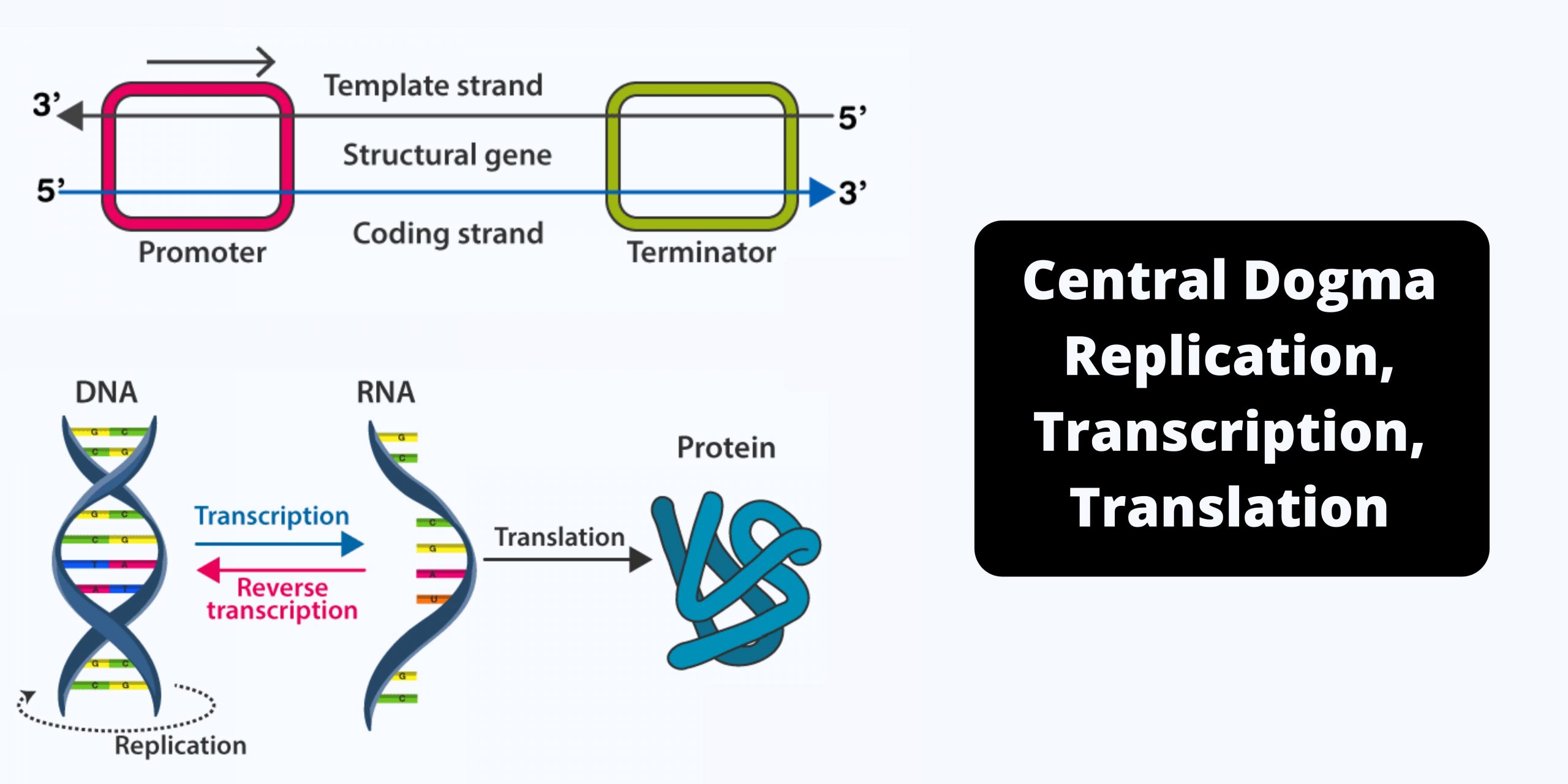
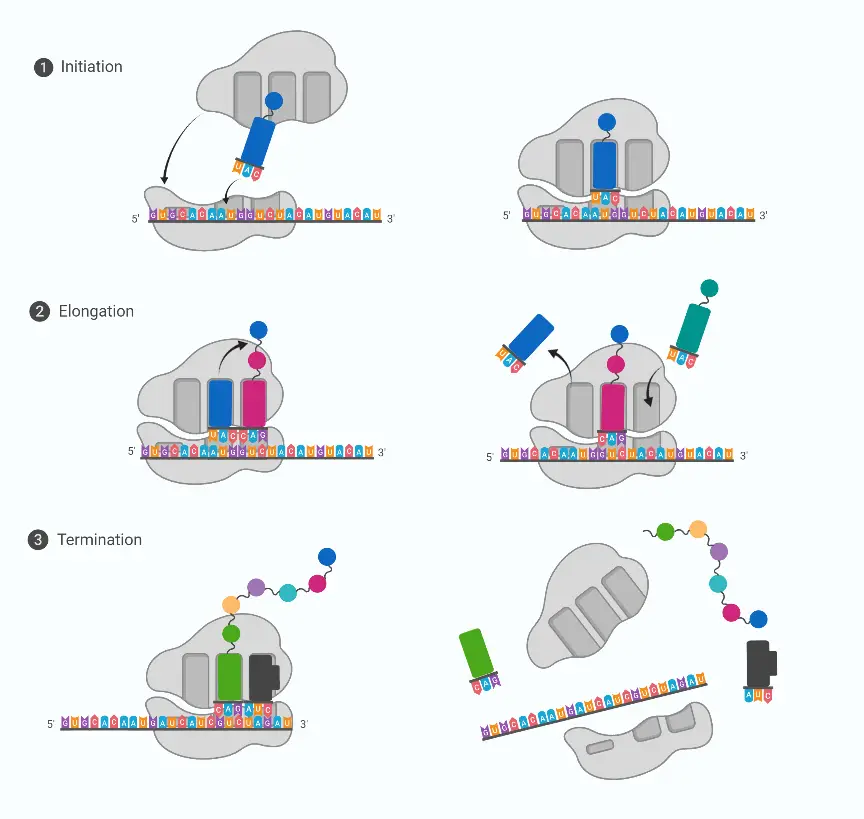
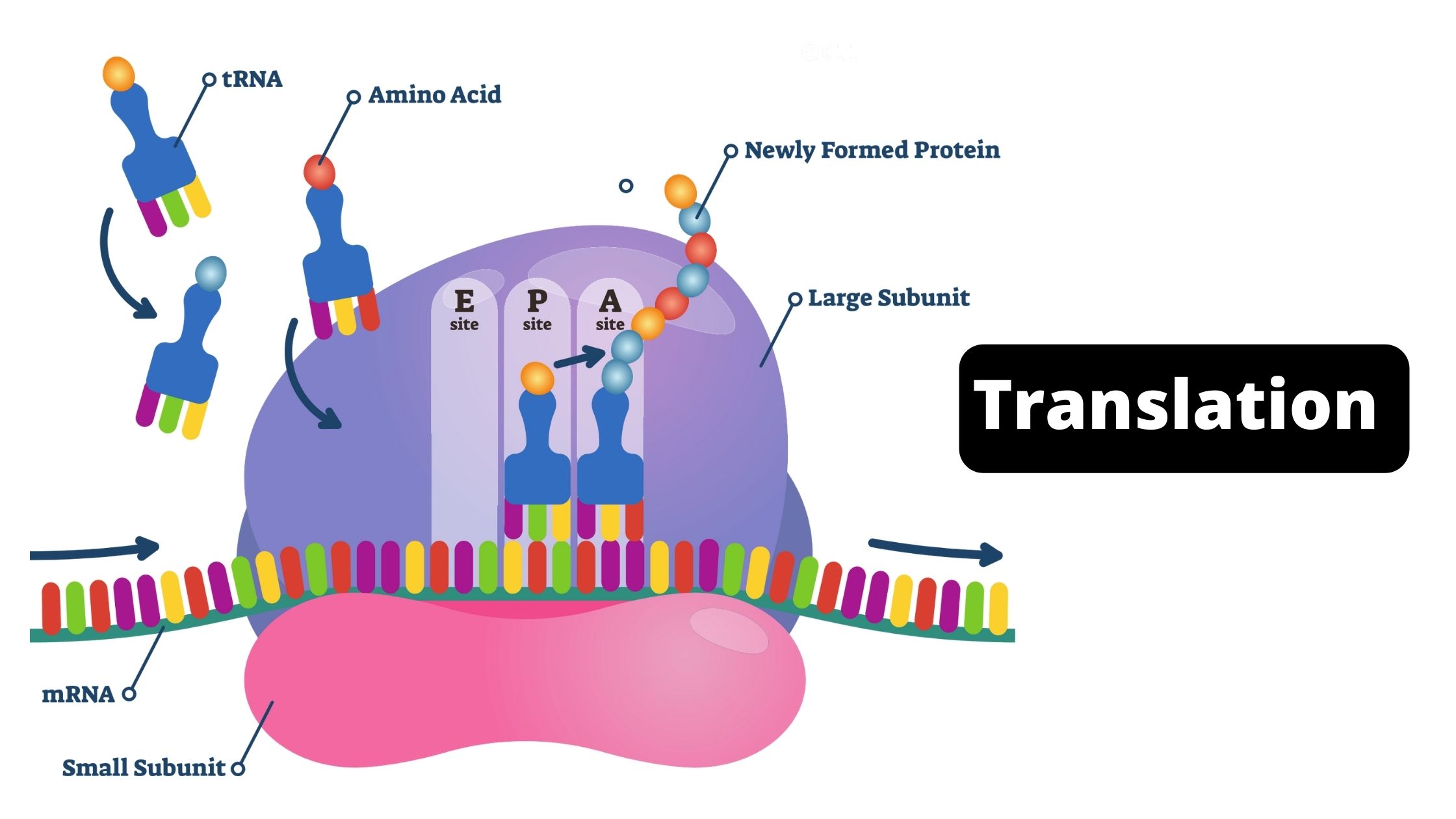
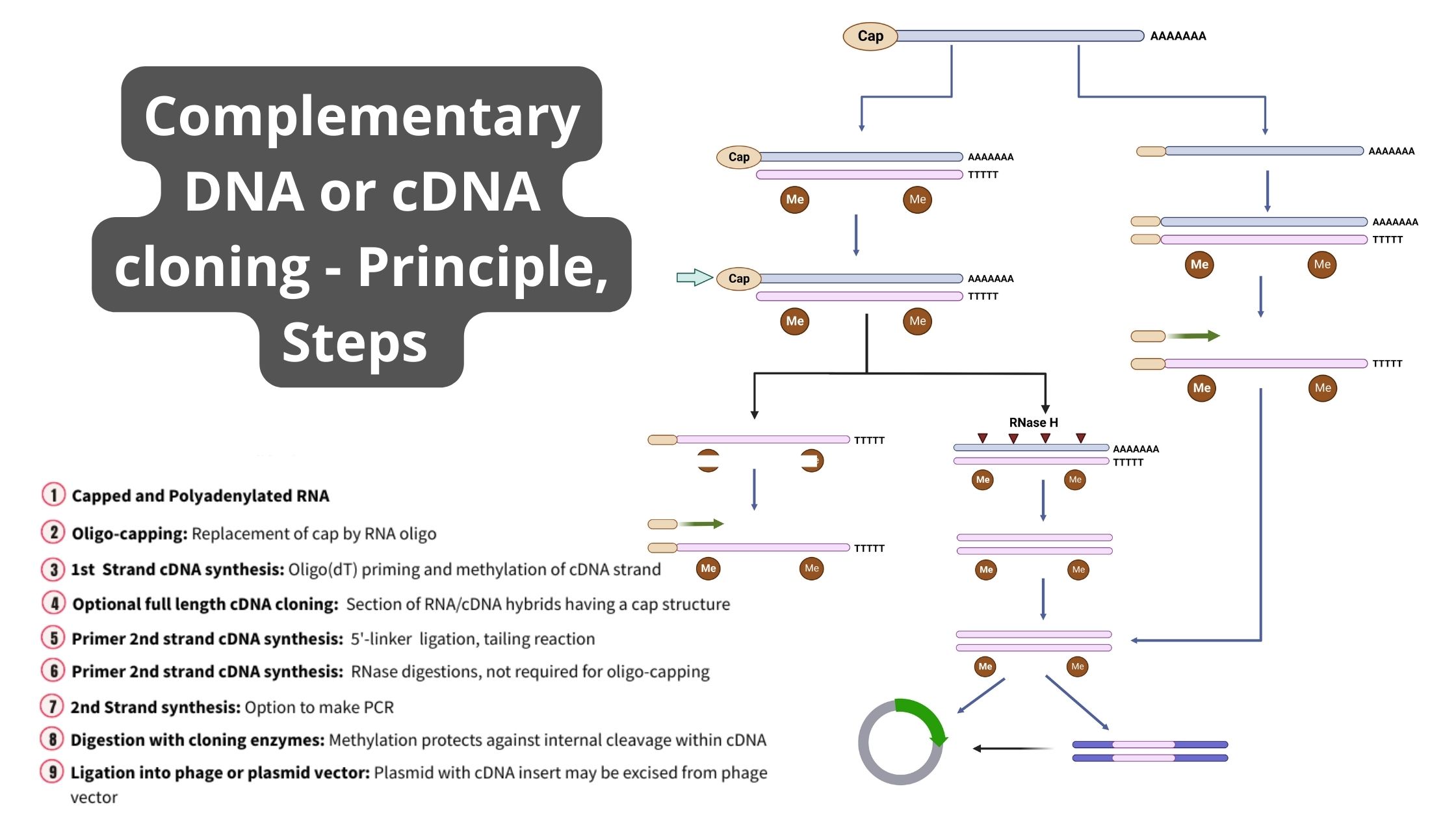
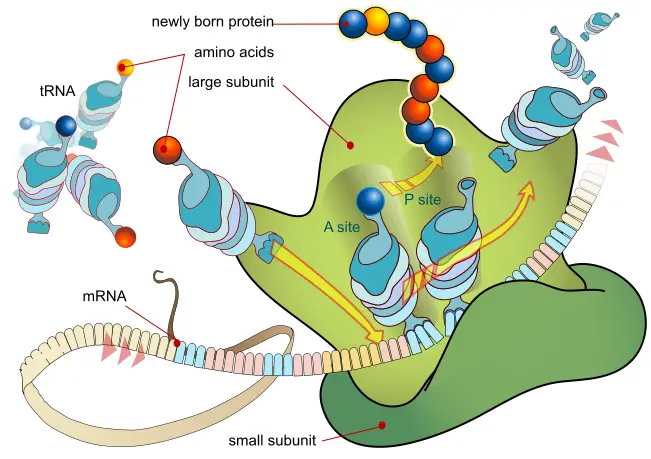
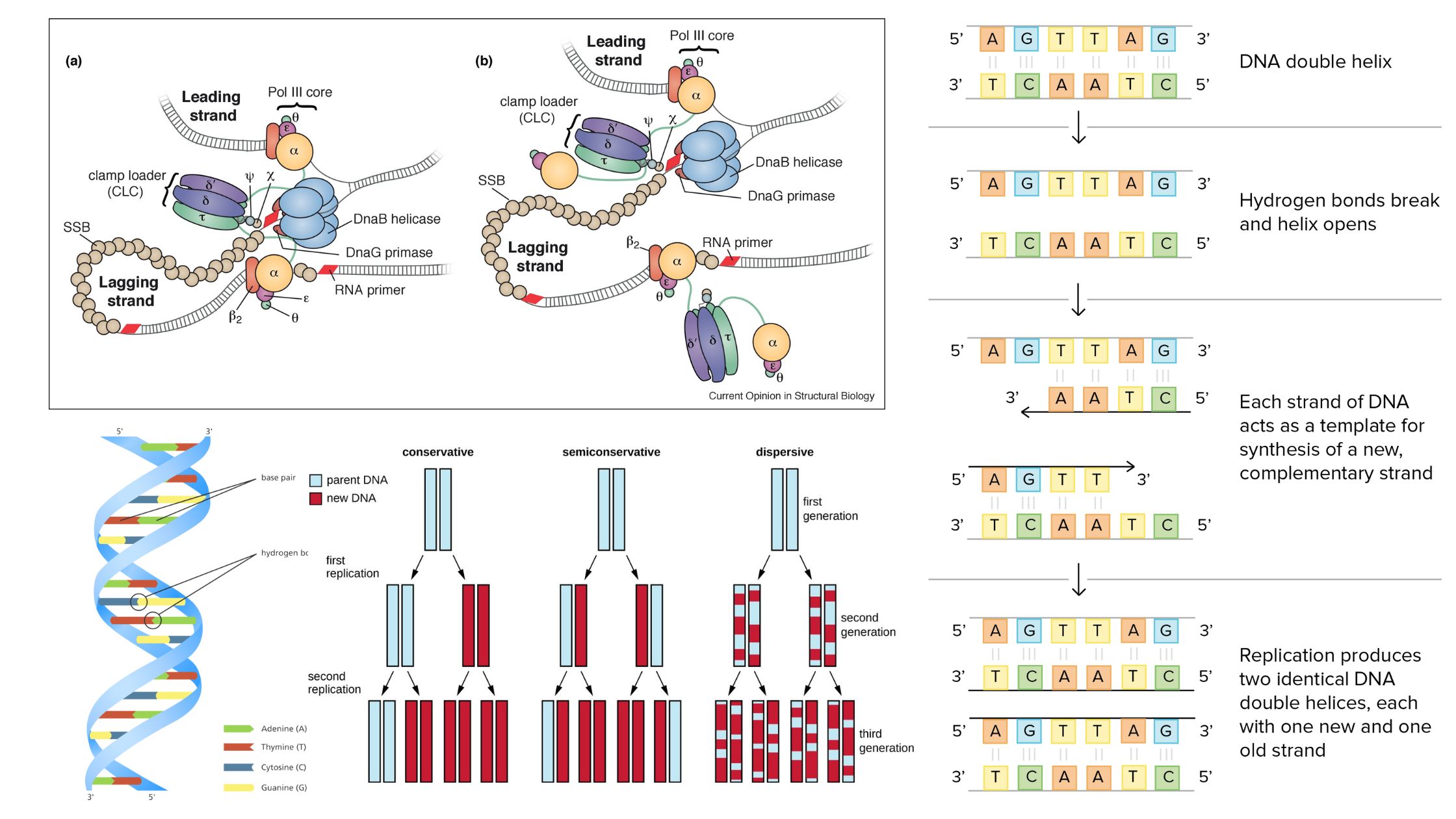
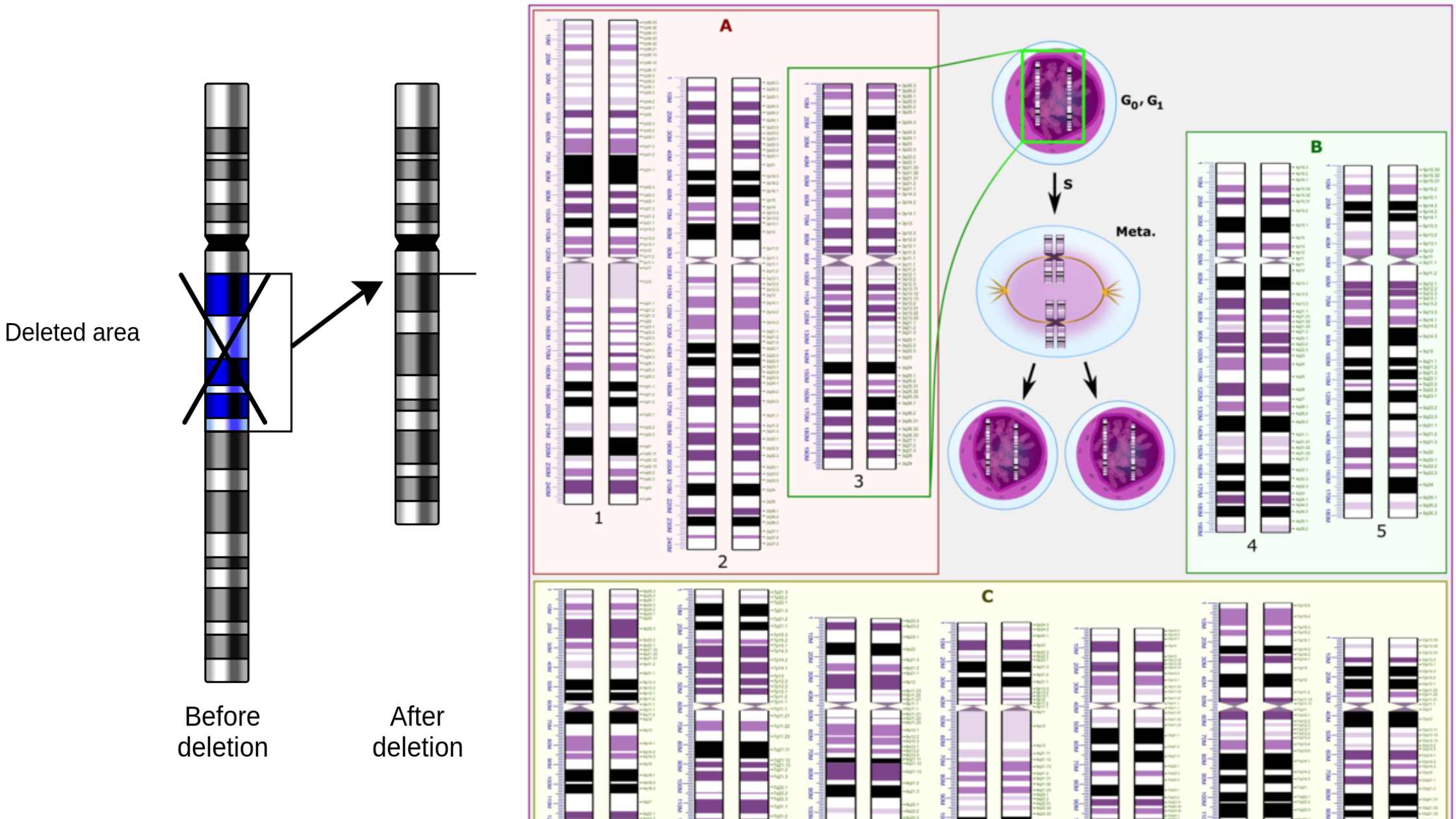
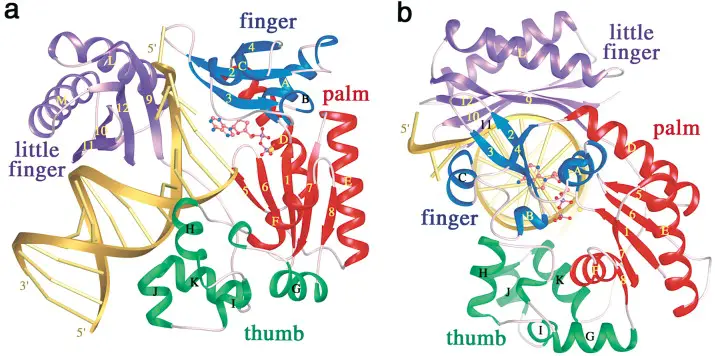
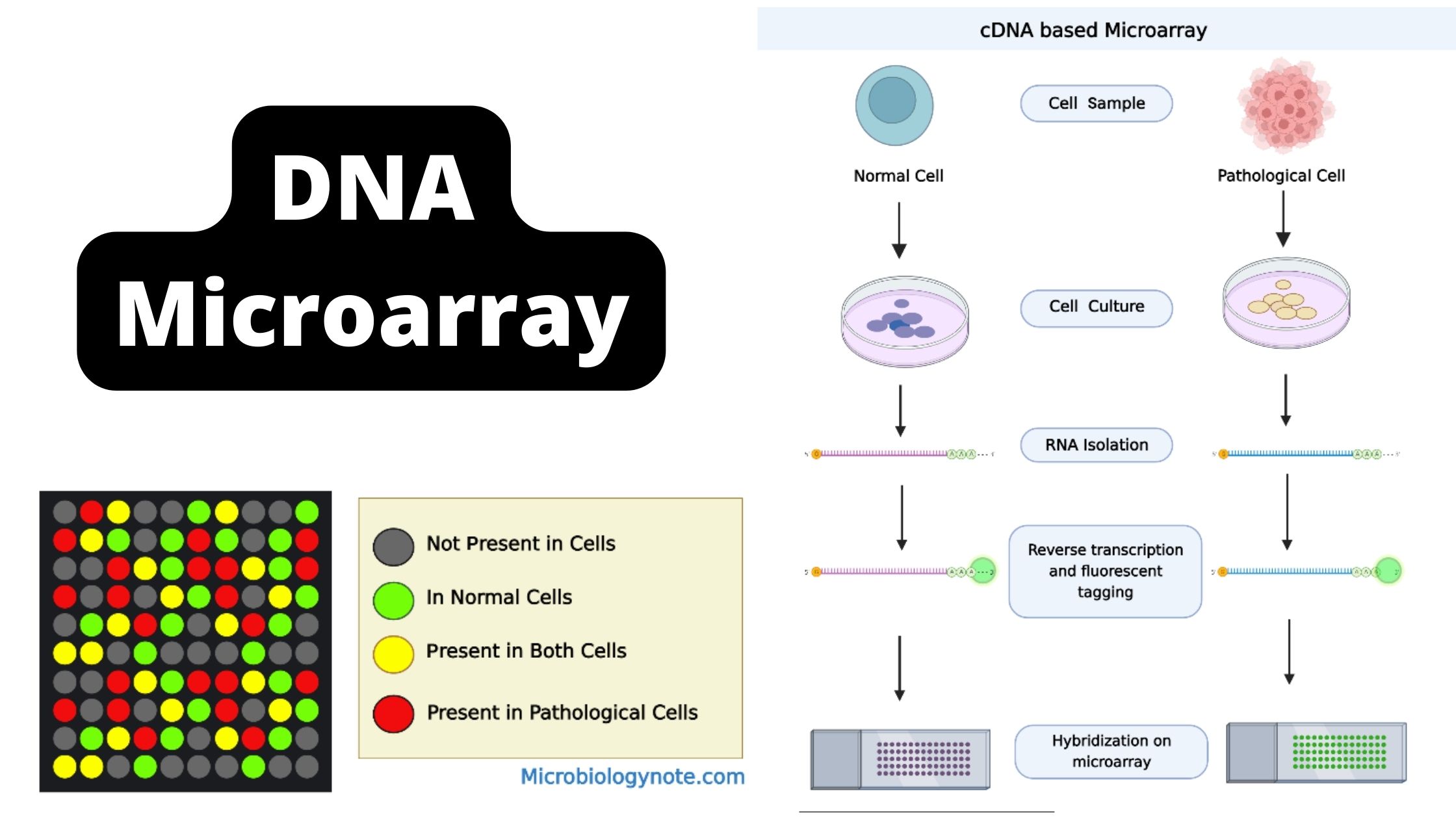
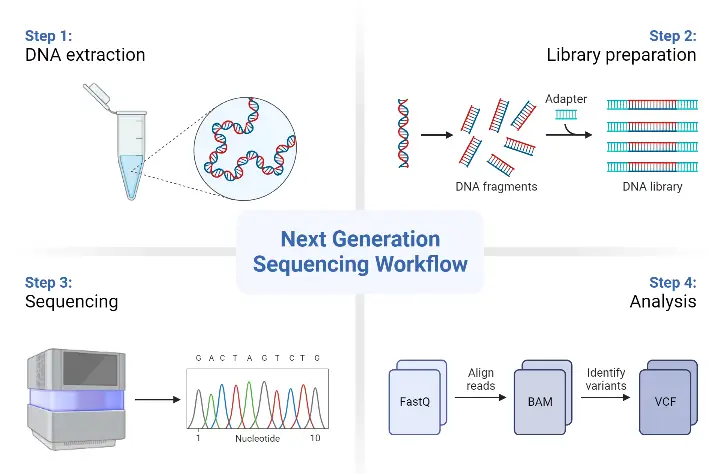
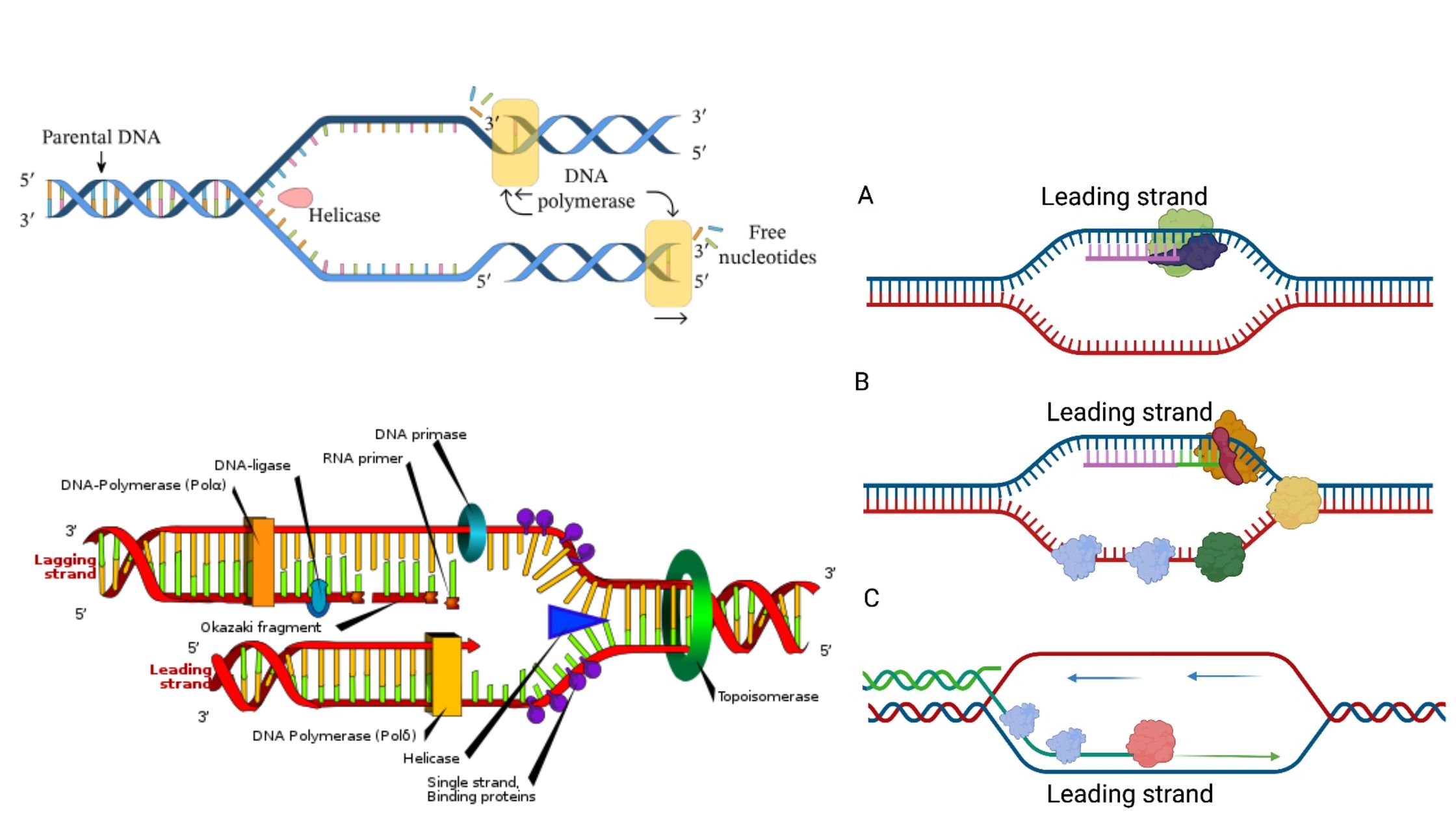
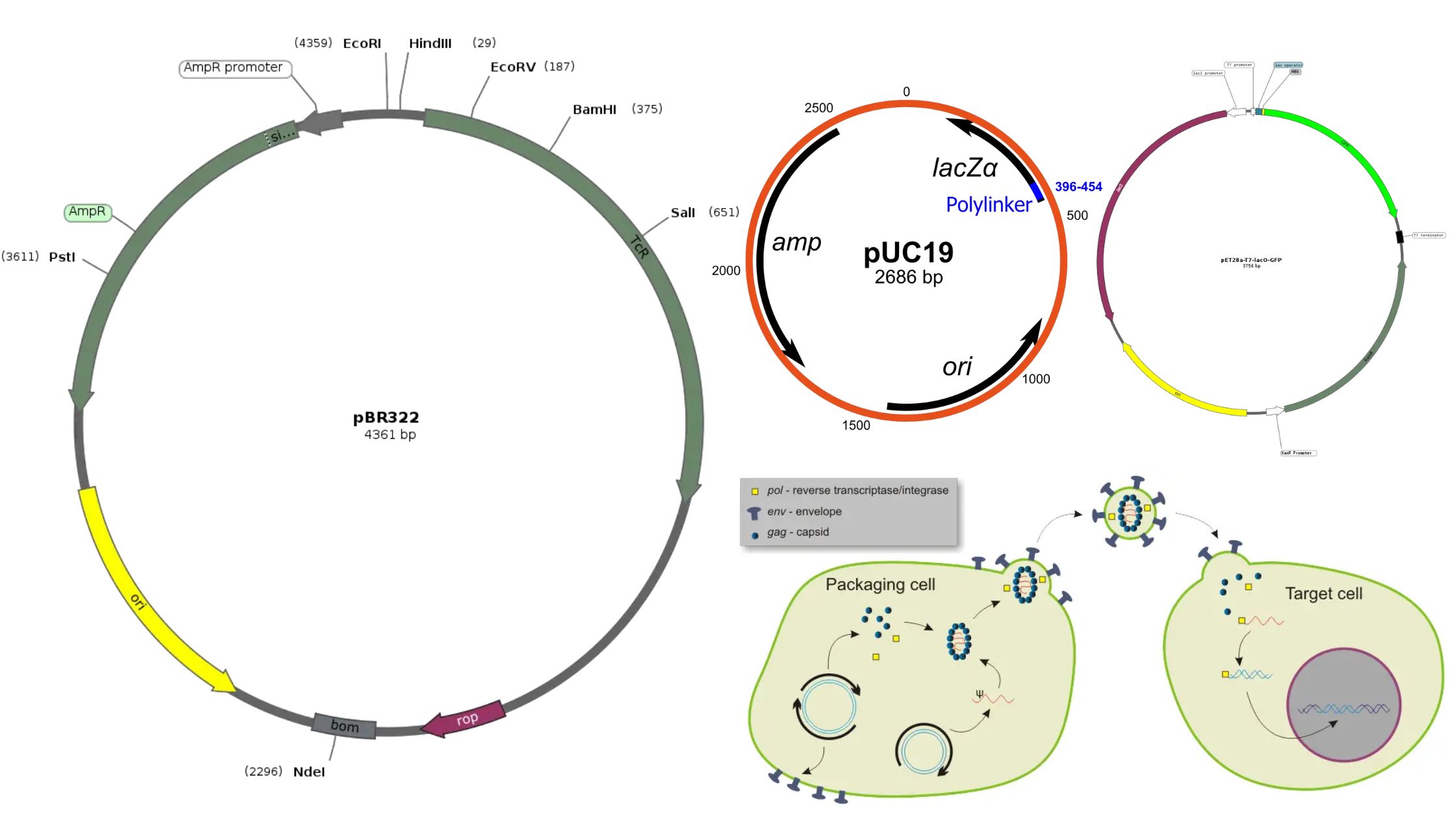
Central Dogma Theory of Molecular Biology and Genetic Code
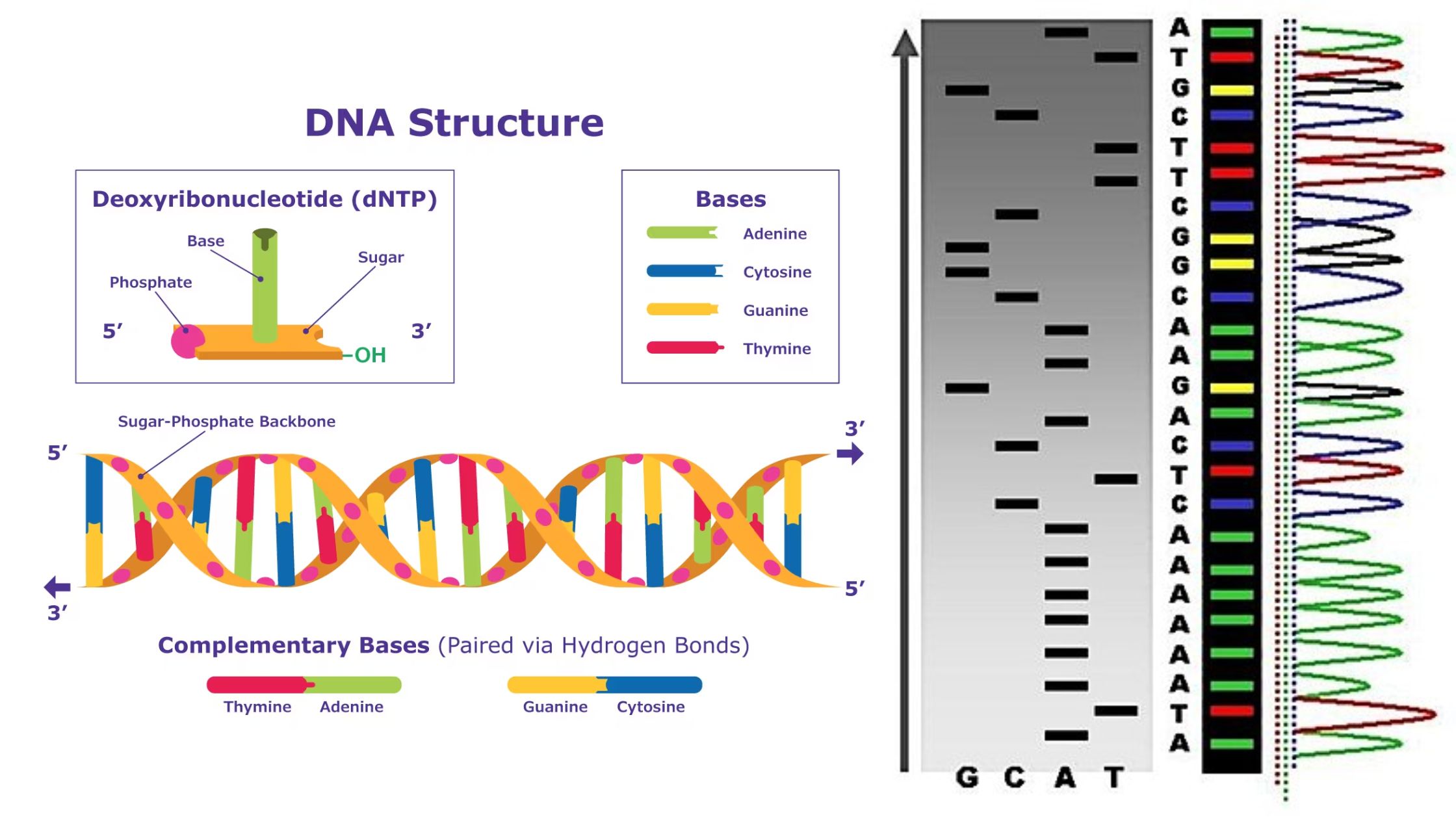
DNA is the full genetic information that determines the nature and function that an animal has. Proteins are made by the genetic code contained in DNA. Conversion of DNA encoded data to RNA is necessary to make proteins. So, in the majority of cells, genetic information is transferred from – DNA to RNA, and then to protein. The transfer of information is controlled by three different processes that help in the transfer of genetic information as well as its transformation into a different form: