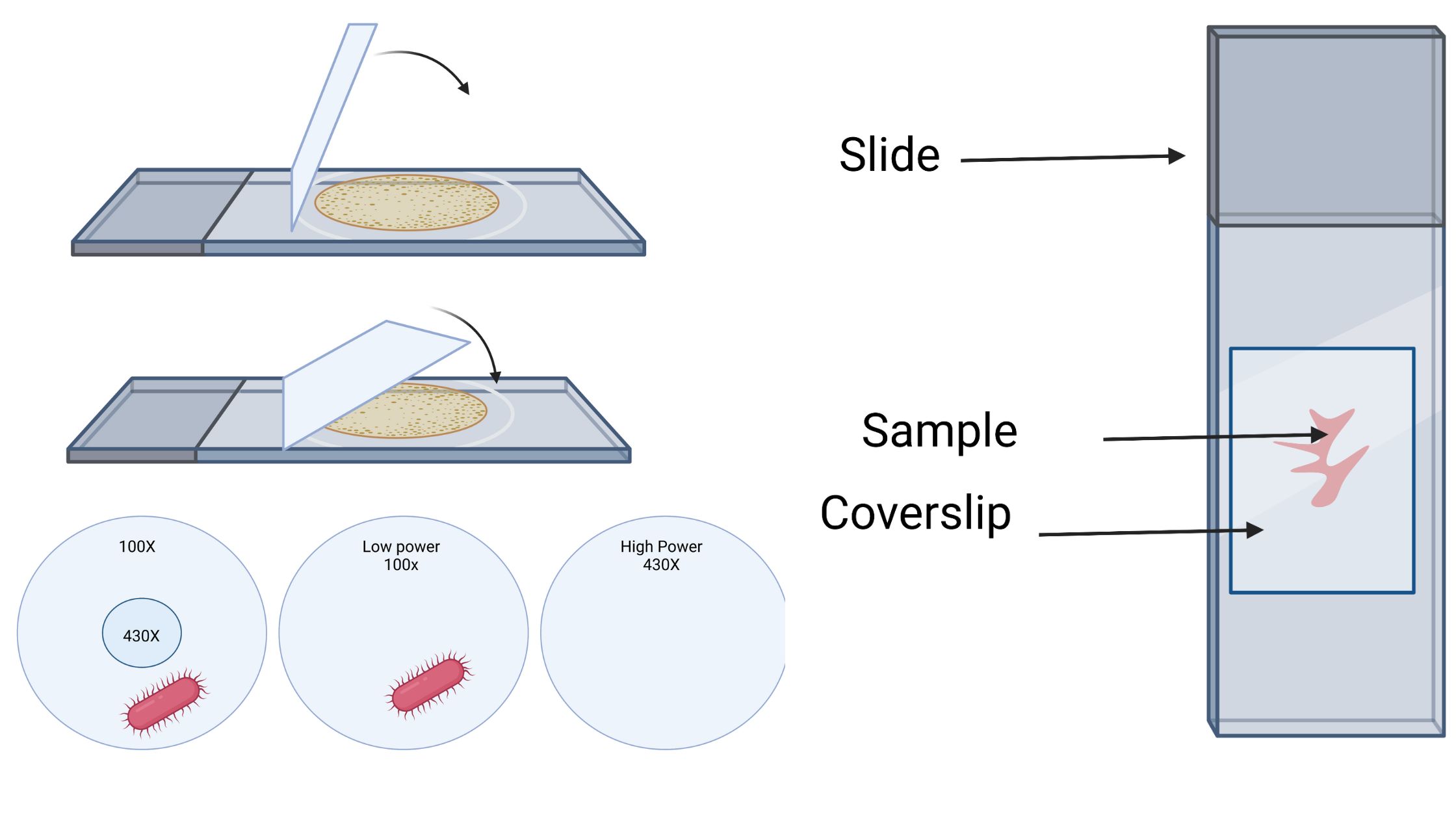
Microinjection – Definition, Types, Principle, Steps Applications
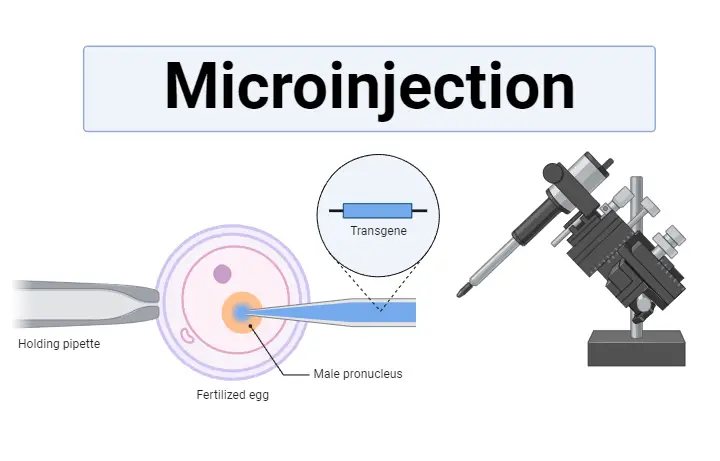
What is Microinjection? Definition of Microinjection Microinjection is a precise technique used to introduce DNA or other genetic materials directly into a cell using a micropipette or fine glass needle. It is widely employed in genetic engineering, genome editing, and various biomedical research areas. Principle of Microinjection Microinjection operates on the fundamental principle of directly … Read more