Table of Contents
Microvilli Definition
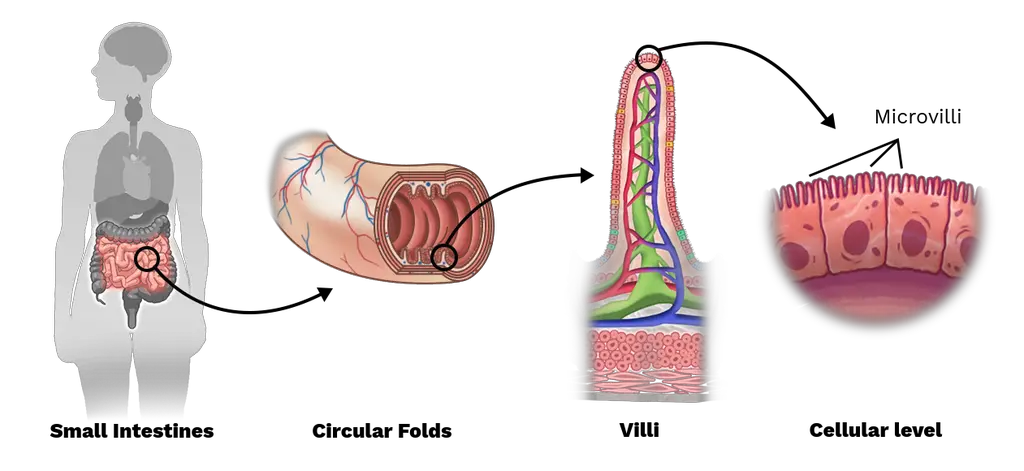
Epithelial cells’ outermost layers feature microvilli, which are little, finger-like projections that originate from villi.
- Although microvilli are characteristic of epithelial cells, they are not present on the surface of all epithelial cells.
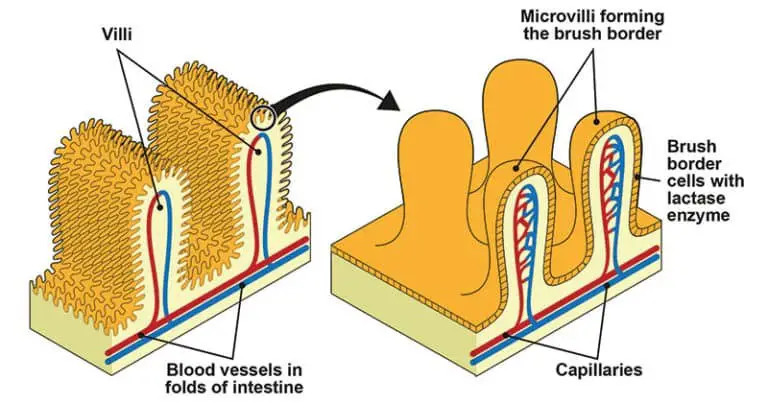
- Microvilli, so named for the brushlike border they present, are most commonly located in the small intestine.
- Microfilaments, specifically actin filaments, and cytoplasm come together to form microvilli, which are extensions of villi. Microvilli rely heavily on the support and structural integrity provided by actin filaments, which also enhance the surface area of the epithelial cells at the sites where they are located.
- Microvilli do more than just enhance surface area; they also help white blood cells and fertilized eggs stick together.
- The actin cytoskeleton is essential for the proper functioning of microvilli.
- They are present on the vast majority of cellular types.
- A growing body of evidence suggests that the dynamic lymphocyte microvilli, with their highly curved membranes, play a crucial role in signal transduction leading to immunological responses, as depicted in the microvilli diagram.
- Lymphocytes, cells of the immune system, often include membrane projections called microvilli.
- Many different types of cells, such as dendritic cells and neurons, as well as intestinal epithelial cells, all have microvilli on their outer surfaces. Parallel bundles of 10-30 F-actin filaments are responsible for their stability, much like the actin network that forms filopodia.
- In contrast, filopodia typically originate from lamellipodial and lamellar actin networks, rather than microvilli actin networks. Both T cells and B cells, which are both types of lymphocytes, had microvilli on their surfaces.
Locations of Microvilli
- Brush borders, composed of microvilli by the thousands, can be observed on the apical surface of some epithelial cells, most notably those lining the small intestine. (Don’t mix microscopic villi with the multicellular villi that line the intestinal tract.
- There are several microvilli on each of these cells. Microvilli are found on the egg’s plasma surface, where they help sperm cells that have broken through the egg’s extracellular covering to stay put.
- Microtubules that are stretched out into long clusters surround sperm, drawing them in and holding them in place so that fusion can take place. These are massive items that provide more absorbent surface area.
- Microvilli are a crucial part of the white blood cell’s surface because they aid in the cell’s movement.
Structure of Microvilli
- In microvilli, the plasma membrane encloses the cytoplasm and the microfilaments that move it. These microvilli are extensions of cells, although they contain almost no organelles.
- Inside the center of each microvillus is a dense bundle of cross-linked actin filaments. Formed by the cross-linking of 20-30 bundles of actin filaments by the bundling proteins fimbrin (or plastin-1), villin, and espin, the microvilli’s core is a specialized structure.
- Lateral arms composed of myosin 1a and the Ca2+ binding protein calmodulin join the structural core of the enterocyte microvillus to the plasma membrane along its length.
- Myosin 1a is an integral protein that binds to filamentous actin and also has a lipid binding domain. At the tip of the microvillus, actin filaments are capped, perhaps by capZ proteins, while their minus ends are anchored in the terminal web, which is made up of a diverse mix of proteins like as spectrin and myosin II.
- Intermicrovillous space refers to the area between microvilli on the surface of a cell. The distance between adjacent microvilli expands during contraction mediated by myosin II and tropomyosin and contracts again when the muscle relaxes.
Functions of microvilli
- Increasing surface area: More nutrients and fluids can be taken in and secreted with the help of microvilli since their increased surface area facilitates this process. Microvilli, which are found on the surface of absorptive cells in the small intestine, increase the area of these cells that can be used to absorb nutrients.
- Facilitating transport: Microvilli can also help move molecules across the cell membrane, another way they facilitate transport. Many different types of proteins found in these membranes serve as transporters or channels for molecules including ions, glucose, and amino acids.
- Sensing stimuli: Microvilli on hair cells, which are specialized cells in the inner ear that detect sound waves and head motions, are engaged in this sensing process. There are mechanosensitive proteins in these microvilli, and they are triggered by motion to generate electrical signals that are then sent to the brain.
- Cell adhesion: Adhesion of cells to one another is essential for tissue formation, and microvilli may play a part in this process. Epithelial cells in the kidney, for instance, are anchored to the basement membrane by microvilli on their surface.
- Absorb more nutrients: They help the body absorb more nutrients and substances by increasing the intestinal tract’s surface area and working in tandem with villi.
- Breakdown of complex nutrients: Enzymes help break down difficult-to-absorb nutrients into simpler substances in the microvillar membrane. Glycosidases, an enzyme family used in the digestion of carbohydrates, are abundant on the surface of enterocyte microvilli. Hence, microvilli not only expand the absorbent surface area of cells but also permit more digestive enzymes to be present there.
- Anchoring the sperm: Egg cells need them because they assist in sperm adhesion, making fertilization possible.
- Anchoring the WBC: Microvilli are a type of anchor found on the surface of white blood cells. They help white blood cells get where they need to go.
- Membrane and microfilament materials stores: To keep membrane and microfilament materials is the second sort of proposed use. Microvilli also have a role in motility. It’s possible that the microvilli on the cell surface sweep debris toward a resorptive part of the cell.
FAQ
What are microvilli?
Microvilli are small, finger-like projections that extend from the surface of cells in various organs of the body. They are typically 0.5 to 1 micrometer in diameter and several micrometers in length.
Where are microvilli found in the body?
Microvilli are found in many different tissues and organs, but they are most abundant in the small intestine, where they help with nutrient absorption.
What is the function of microvilli?
Microvilli serve several important functions, including increasing the surface area of cells, facilitating the transport of molecules, sensing stimuli, and aiding in cell adhesion.
How do microvilli increase the surface area of cells?
Microvilli extend from the surface of cells, creating a brush-like structure that increases the surface area available for absorption and secretion of nutrients and fluids.
What is the structure of microvilli?
Microvilli consist of a core of actin filaments surrounded by a plasma membrane. They may also contain various proteins, such as transporters, channels, and receptors.
Can microvilli regenerate?
Yes, microvilli have a high turnover rate and can regenerate quickly after being damaged or lost.
What happens if microvilli are damaged or lost?
Damage or loss of microvilli can lead to a variety of health problems, such as malabsorption of nutrients, diarrhea, and hearing loss.
What is microvillus inclusion disease?
Microvillus inclusion disease is a rare genetic disorder that affects the microvilli in the small intestine. It leads to severe diarrhea and malabsorption of nutrients, and is typically diagnosed in infancy.
Can microvilli be seen under a microscope?
Yes, microvilli can be visualized using an electron microscope, which can magnify them to a size that is visible to the human eye.
Are microvilli unique to humans?
No, microvilli are found in many different animal species, and are thought to have evolved as a way to increase the surface area of cells in order to improve nutrient absorption and other cellular functions.
References
- https://www.biologydiscussion.com/cell/cell-surface/3-types-of-cell-surface-projection-cell-biology/26375
- https://unacademy.com/content/neet-ug/study-material/biology/microvilli/
- http://histologyguide.com/EM-view/EM-093-microvilli/02-photo-1.html
- https://biology.kenyon.edu/edwards/project/greg/pd.htm
- https://study.com/academy/lesson/microvilli-definition-function.html
- http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/Biology/micvil.html
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/microvillus
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/biochemistry-genetics-and-molecular-biology/microvillus
- https://www.biologyonline.com/dictionary/microvillus
- https://rupress.org/jcb/article-pdf/12/3/623/1064187/623.pdf
- https://www.easybiologyclass.com/difference-between-cilia-and-microvilli-comparison-table/
