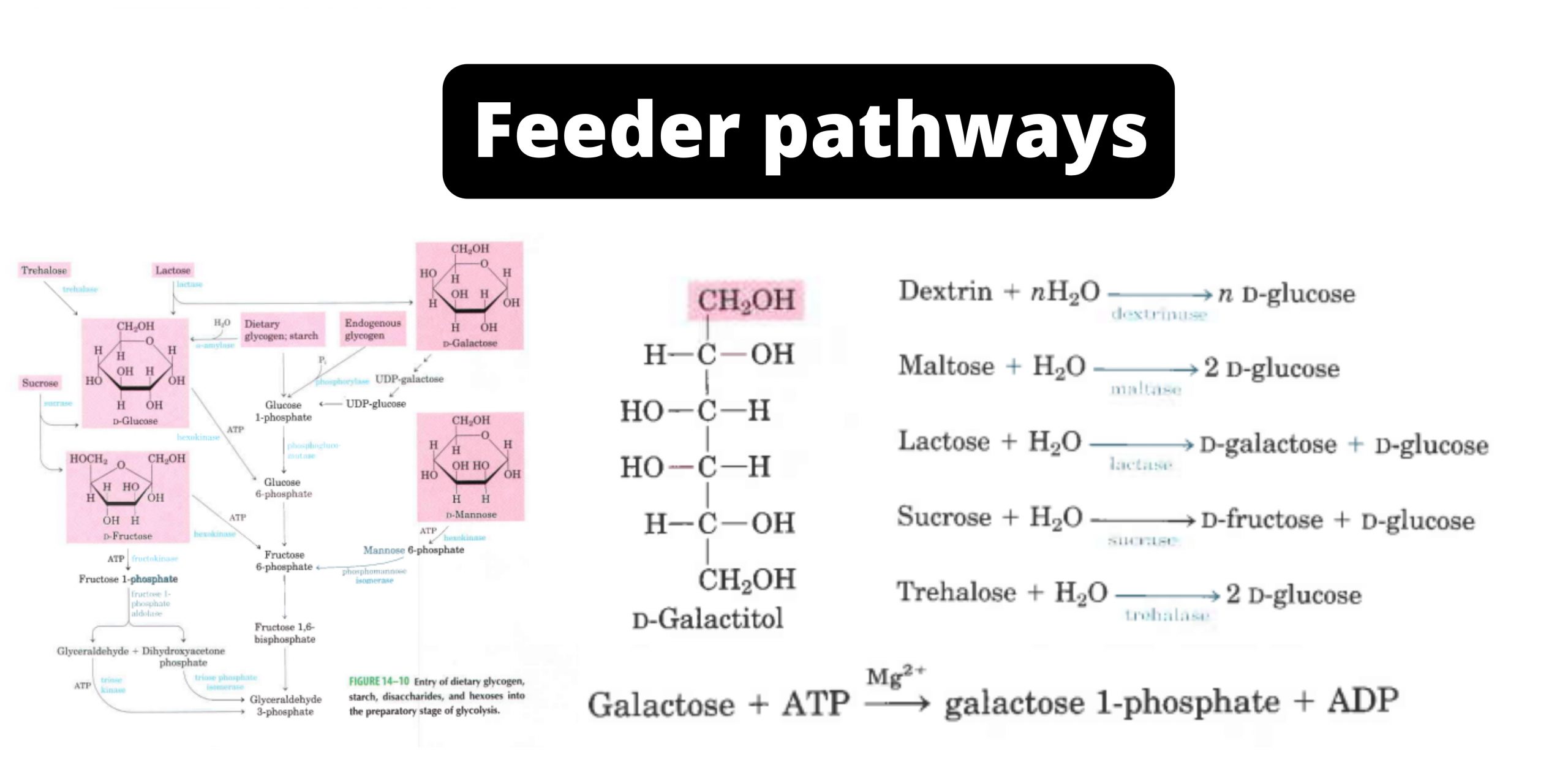
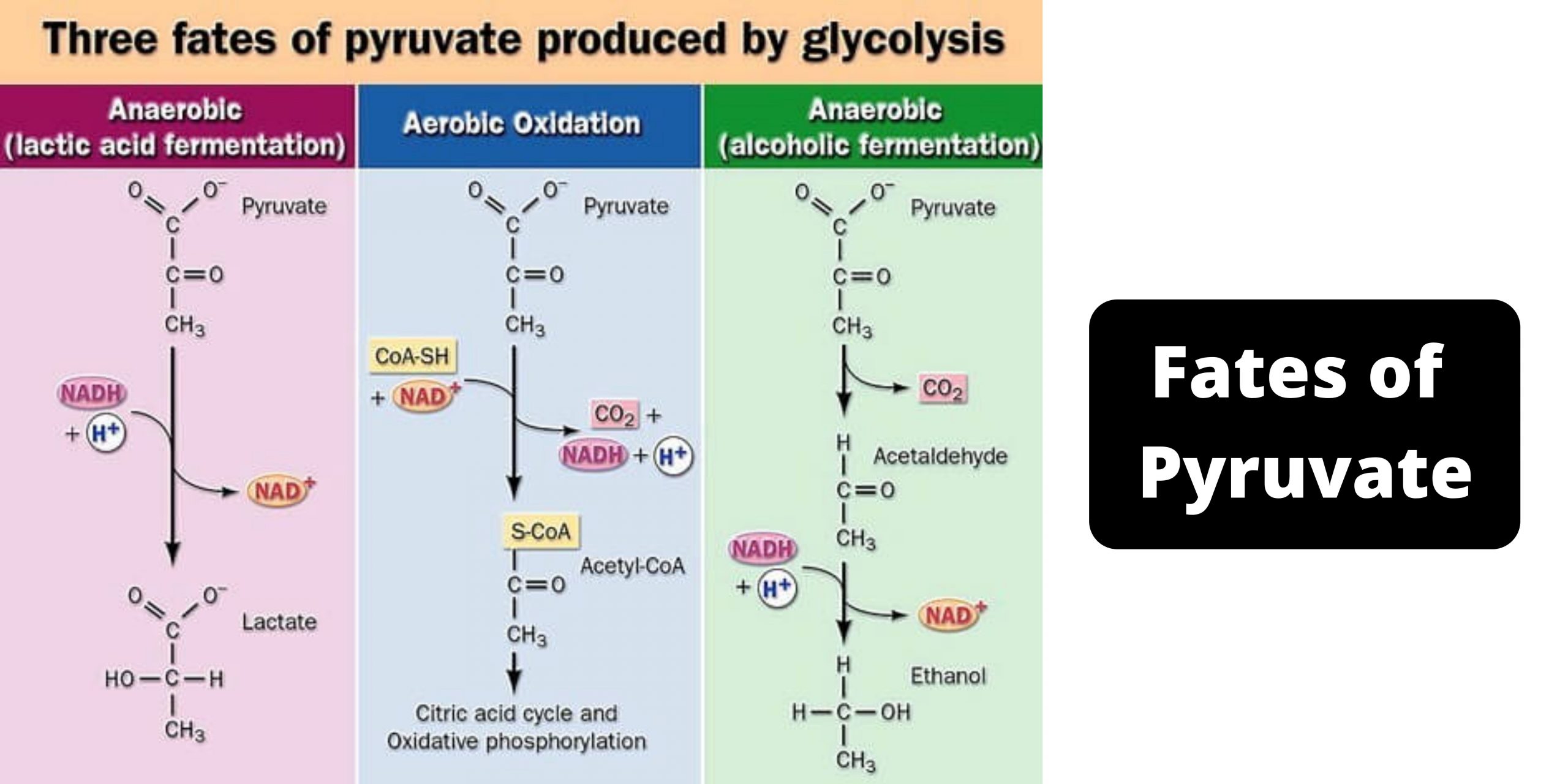
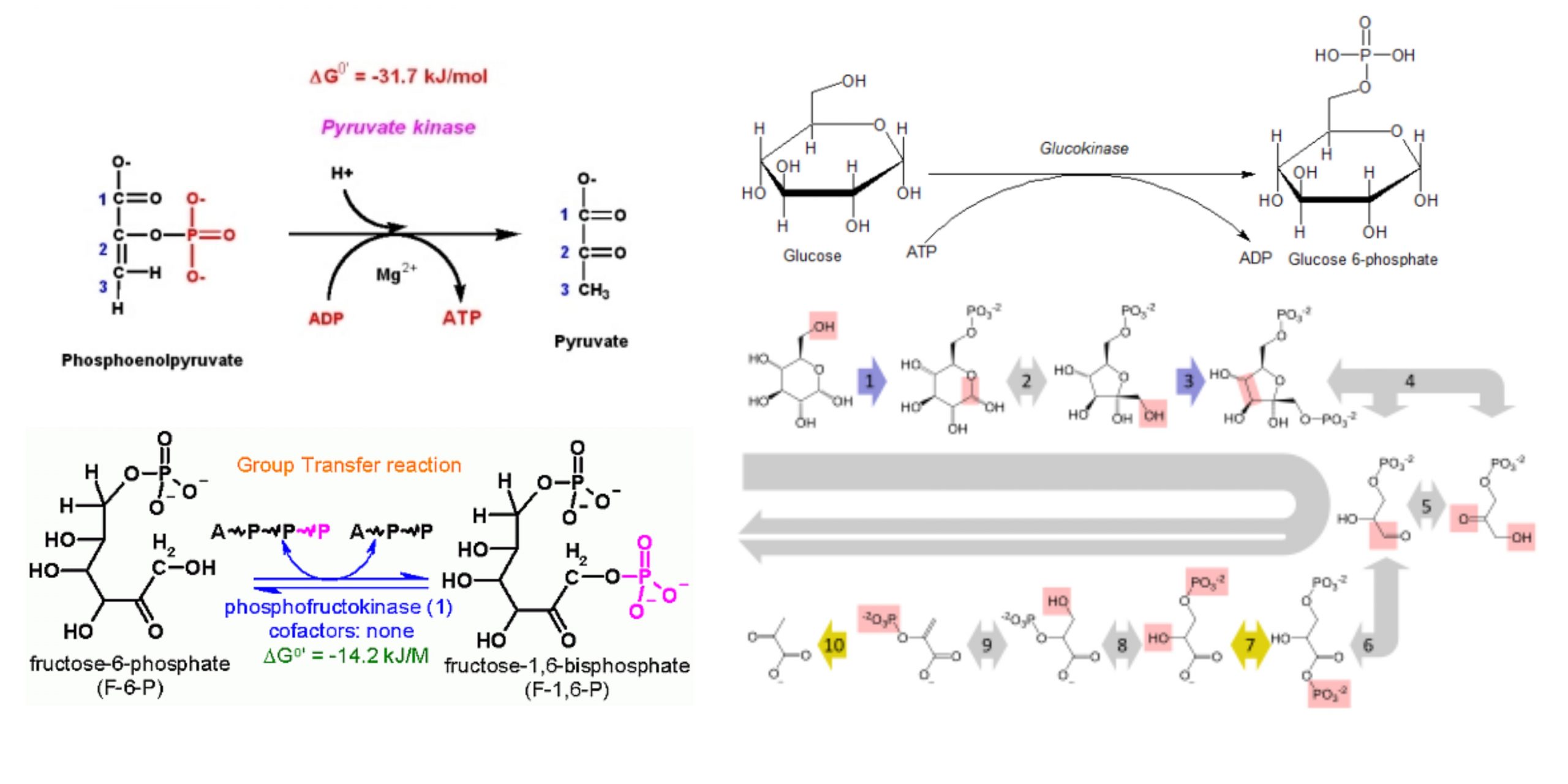
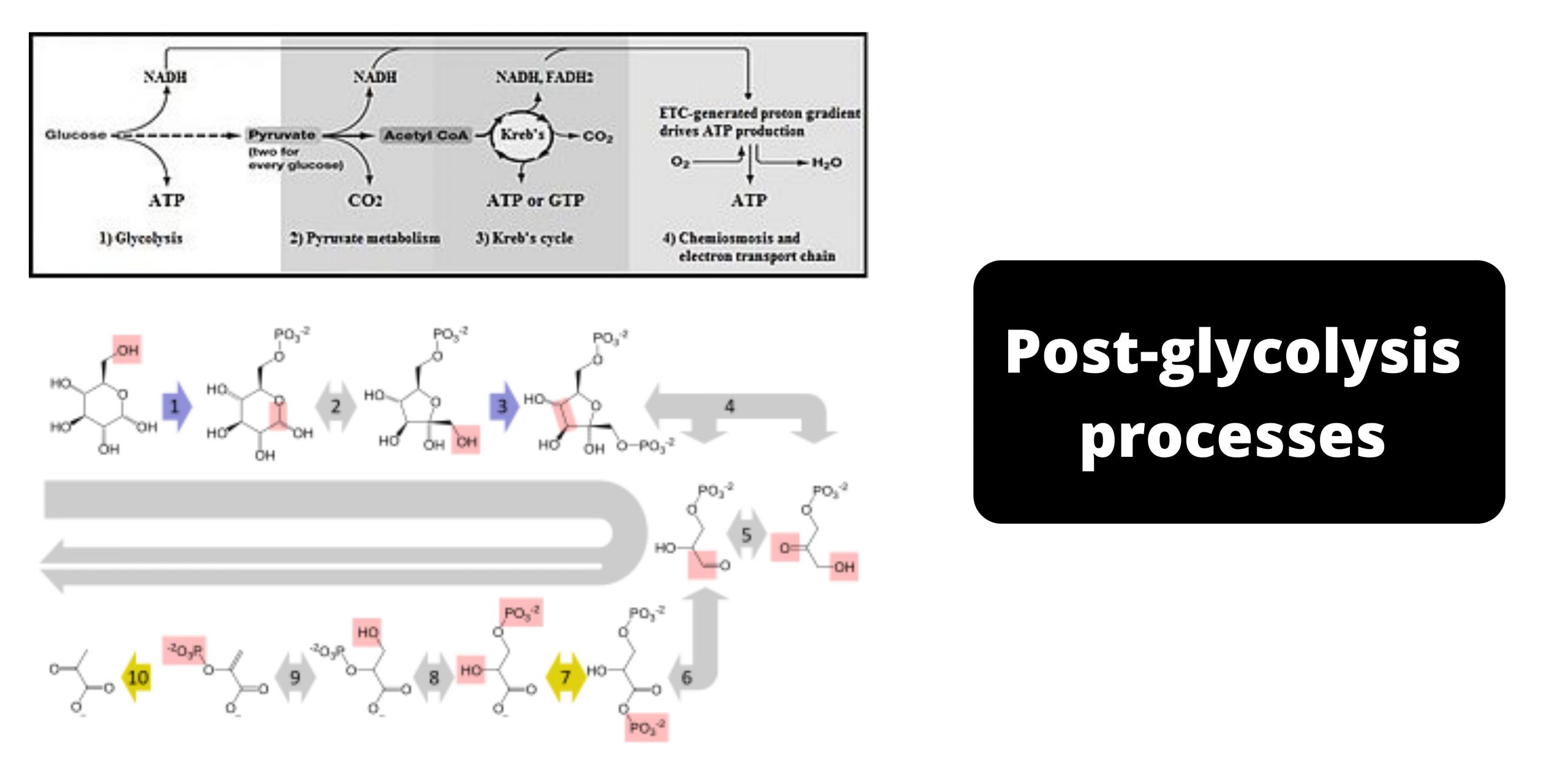
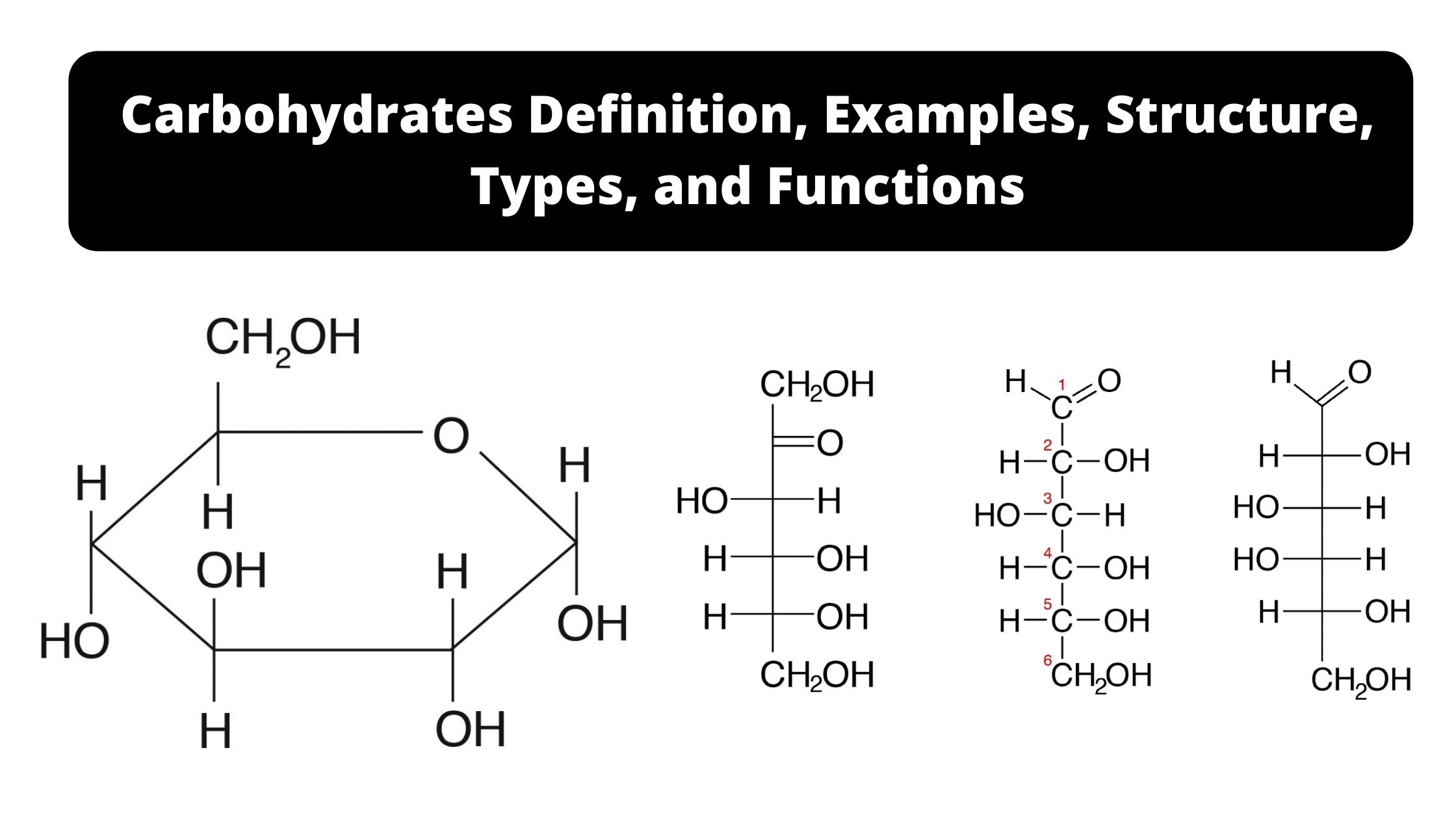
Feeder Pathways for Glycolysis
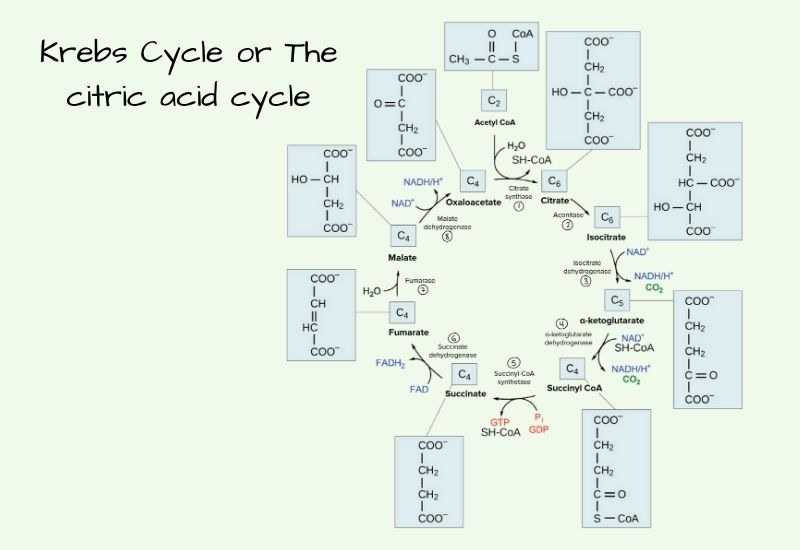
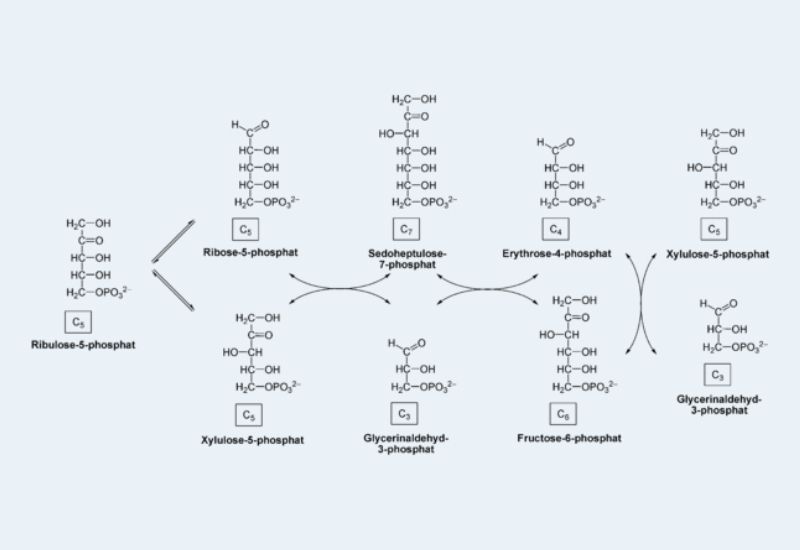
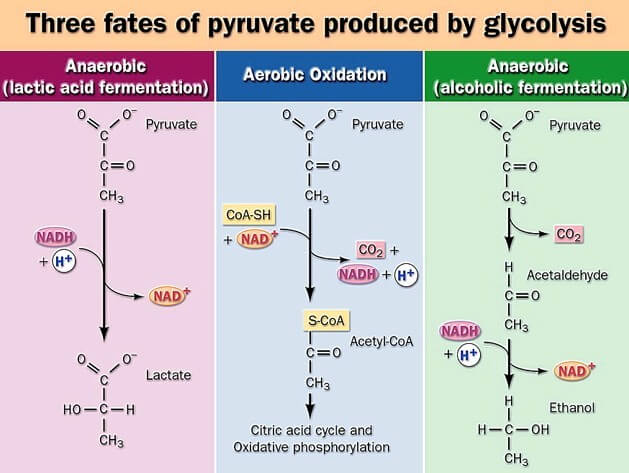
Numerous carbohydrates, including glucose, meet their catabolic end in $ycolysis after being transformed into glycolytic intermediates. Most significant are glycogen and starch, which are storage polysaccharides that are either in cell walls (endogenous) or in the diet. The disaccharides are maltose. Lactose, trehalose. and sucrose, and the monosaccharides fructose and mannose and galactose.