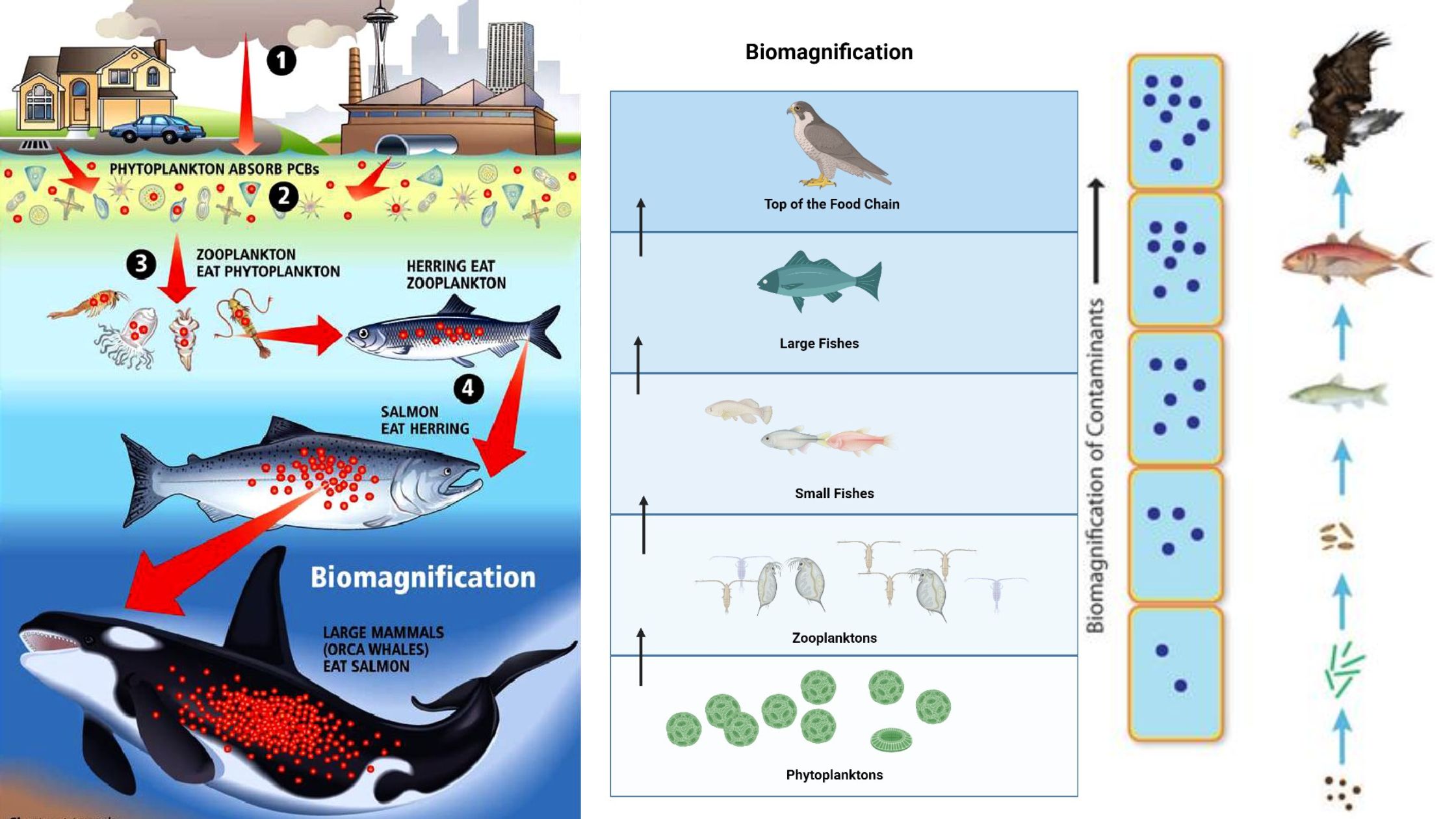
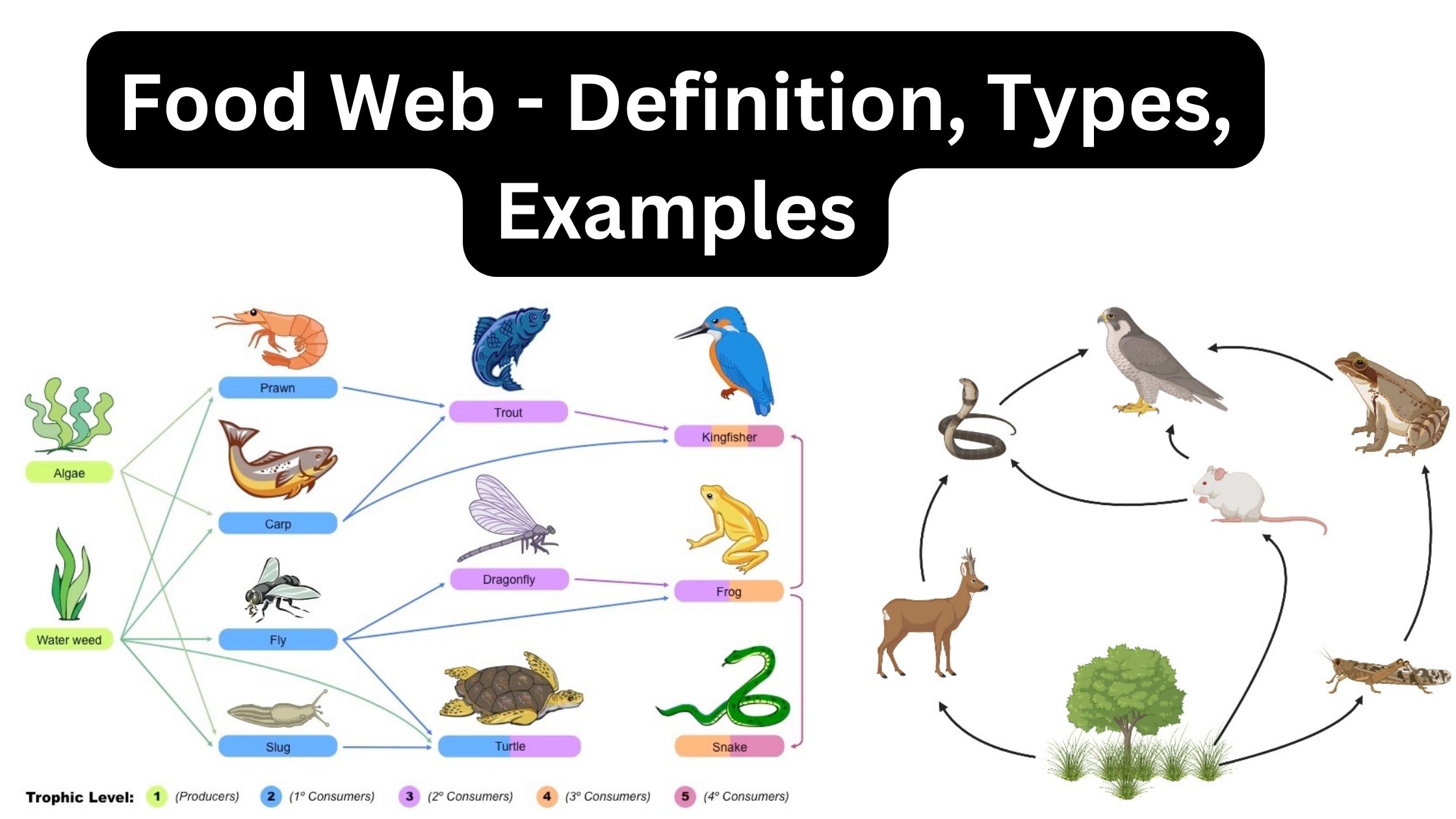
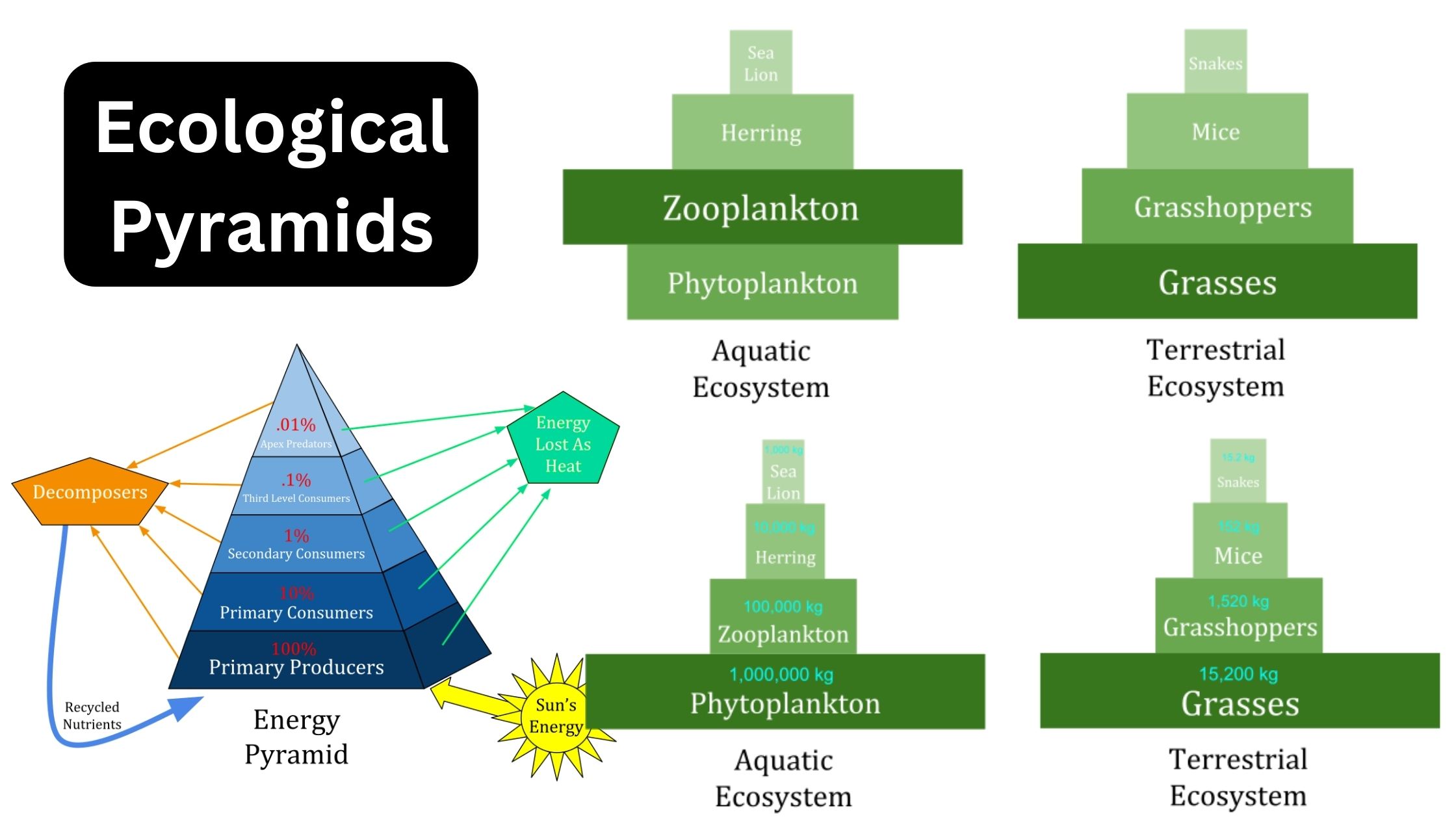
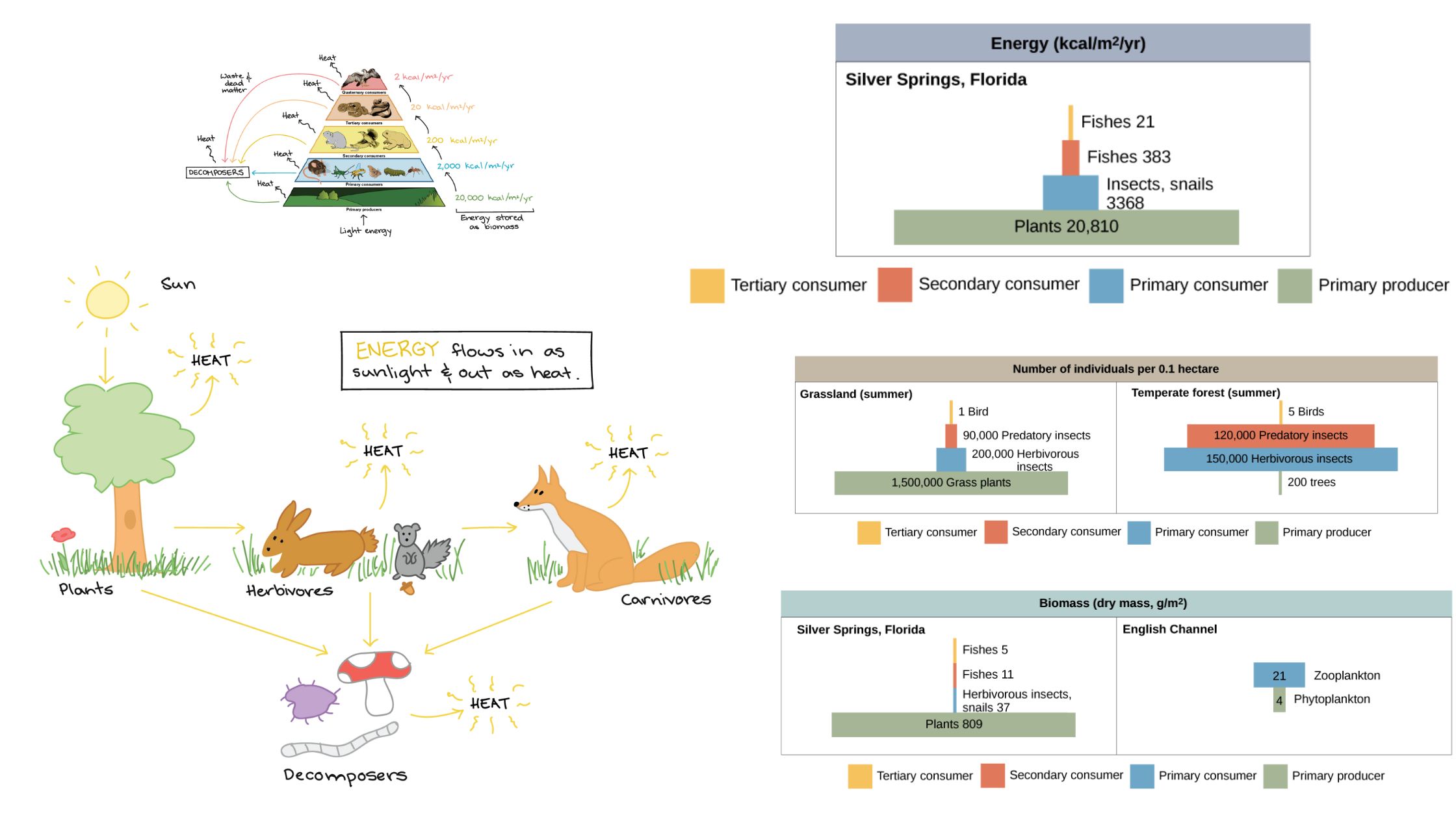
Rhizosphere – Definition, Microflora, Structure, Importance
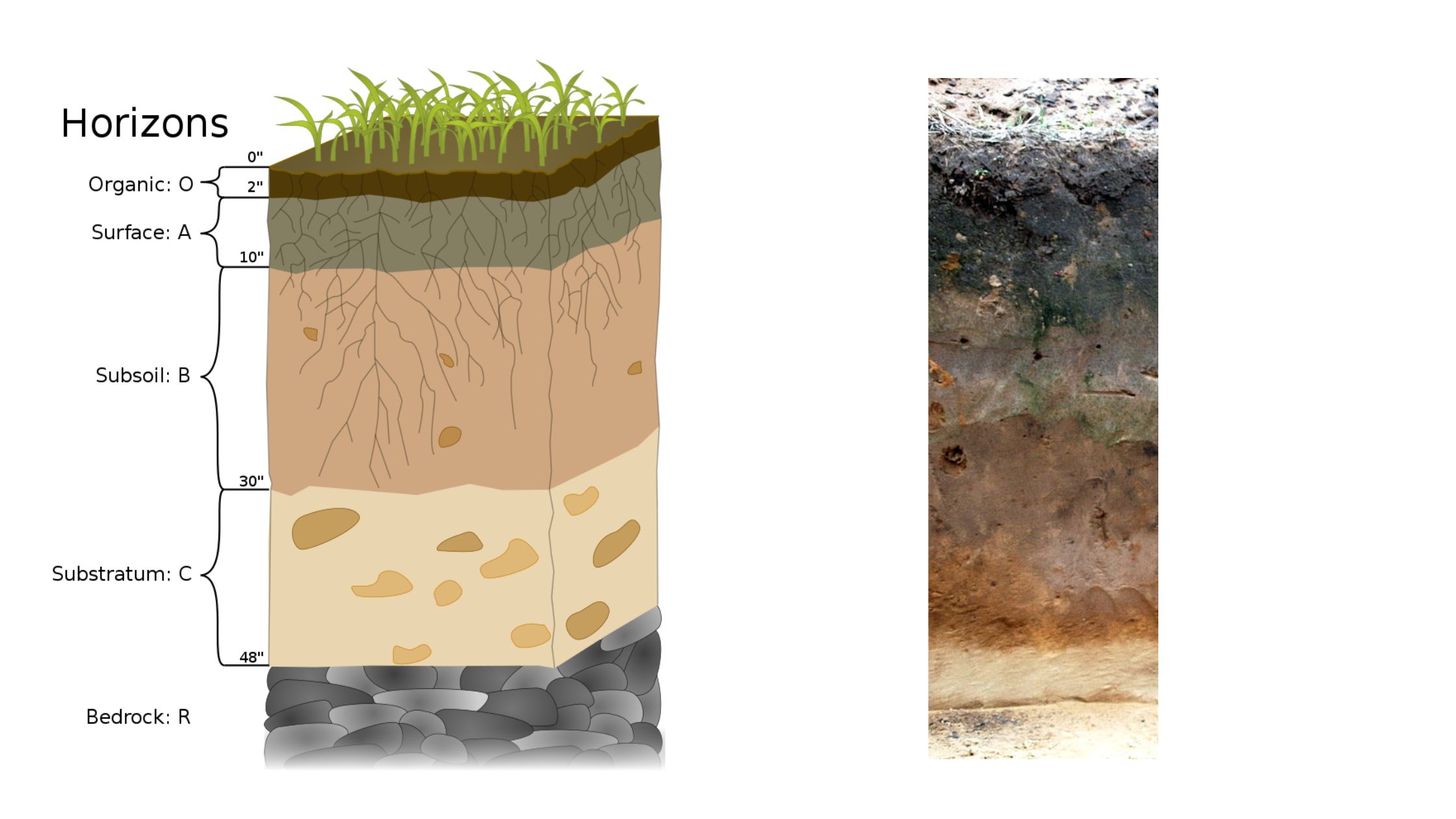
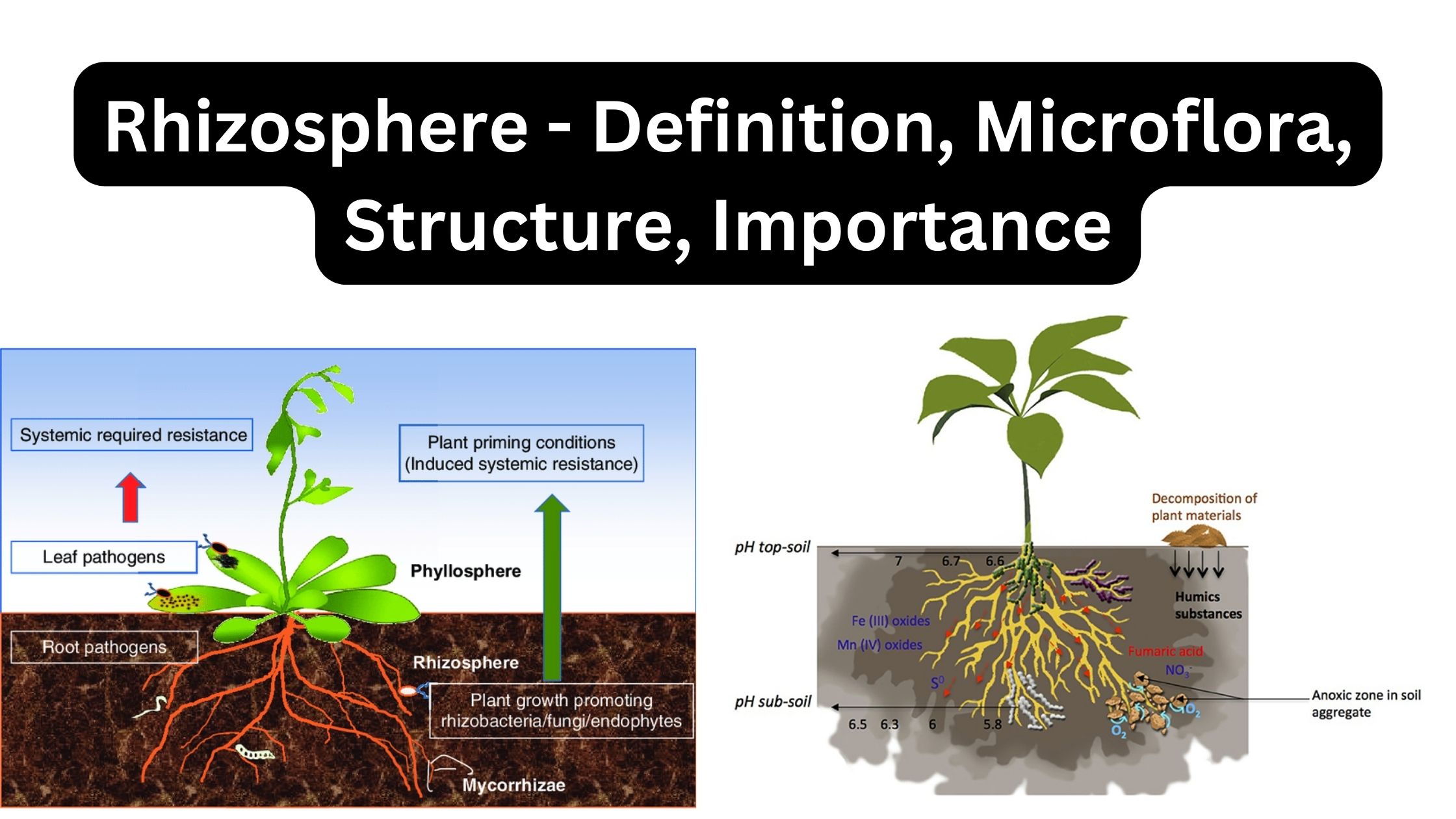
Rhizosphere Definition Rhizosphere effect Definition Structure of Rhizosphere Based on their proximity to the root system, the rhizosphere structure consists of three zones. Characteristics of Rhizosphere Effects of rhizosphere microbial populations on Plants Degradation of organic materials, disease suppression, and nutrient conversions within root zones are just a few of the many chemical changes that … Read more