Table of Contents
What is a Vortex Mixer?
- A vortex mixer is a common laboratory equipment for combining small amounts of liquid samples. It is a simple gadget that consists of an electric motor and a vertically oriented drive shaft attached to a cupped rubber piece that is slightly off-center. When the motor is turned on, the rubber piece oscillates fast in a circular motion.
- The operation of a vortex mixer is simple. When a test tube or other suitable container is forced into the rubber cup or touched to its edge, the motion of the rubber piece is conveyed to the liquid inside, forming a vortex. This vortex is a swirling motion of the liquid that allows for full mixing and blending of the sample.
- Most vortex mixers have two or four plates, allowing numerous samples to be mixed at the same time. They include variable speed settings ranging from 100 to 3,200 rpm, allowing customers to modify the mixing intensity based on their needs. Furthermore, many vortex mixers may be set to run constantly or only when downward pressure is applied to the rubber piece, giving you flexibility and control over the mixing process.
- Vortex mixers are ideal for a variety of scientific applications due to their compact and efficient construction. They are especially beneficial in microbiology and biological sciences, when sensitive samples or high throughput operations are involved. Unlike traditional stirrers, which can only mix one sample container at a time, vortex mixers can mix many samples at the same time. This capacity is useful when working with sealed flasks or combining reagents for biochemical investigations. Furthermore, vortex mixers can be used to suspend cells, enhancing their utility in cell culture activities.
- The availability of several inserts or attachments increases the adaptability of vortex mixers. These inserts allow for the agitation and mixing of samples of various sizes, ranging from small test tubes to big flasks or microplates. Vortex mixers provide versatility and simplicity in laboratory procedures by accommodating a variety of sample containers.
- In summary, a vortex mixer is a laboratory equipment used to blend small amounts of liquid samples. Its oscillating action forms a vortex in the sample container, allowing for effective mixing and homogenization. Vortex mixers have become significant equipment in microbiology, biological sciences, and other areas of scientific research due to its small design, variable speed settings, and capacity to handle numerous samples at the same time.
Definition of Vortex Mixer
A vortex mixer is a laboratory device that uses rapid circular oscillations to create a swirling motion, or vortex, in small volumes of liquid samples for efficient mixing and blending.
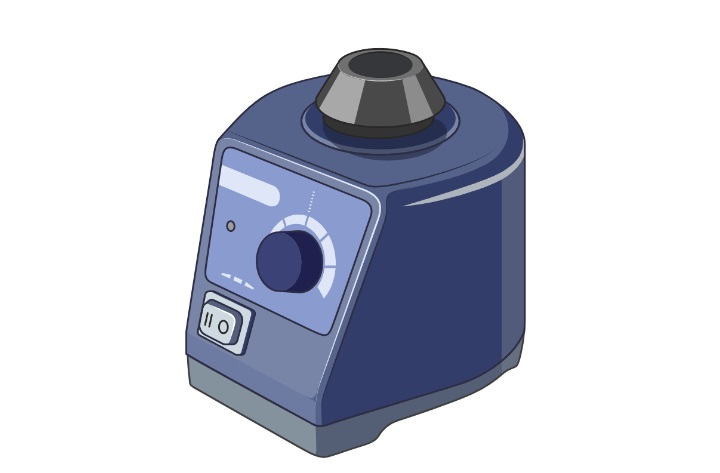

Principle of Vortex Mixer
The principle of a vortex mixer is based on the oscillation of a cupped rubber piece attached to a vertically oriented drive shaft. When the motor of the vortex mixer is activated, the rubber piece rapidly oscillates in a circular motion. This motion is transferred to the liquid sample when it is placed on the rubber piece, creating a vortex.
The off-center positioning of the rubber piece ensures that the circular motion generated by the motor is transmitted to the liquid in an effective manner. As the liquid interacts with the swirling motion, a vortex is formed. This vortex creates turbulent flow within the sample, resulting in thorough mixing and blending.
By utilizing the principle of rapid circular oscillations, the vortex mixer achieves powerful and efficient sample mixing. The motion of the rubber piece enables the creation of a dynamic vortex that effectively homogenizes the sample. This principle allows for quick and reliable mixing of small volumes of liquid samples in laboratory settings.
Overall, the principle of the vortex mixer involves the use of an off-center, oscillating rubber piece to generate a vortex in the liquid sample. This vortex promotes vigorous mixing and blending, making the vortex mixer a valuable tool for various laboratory applications.
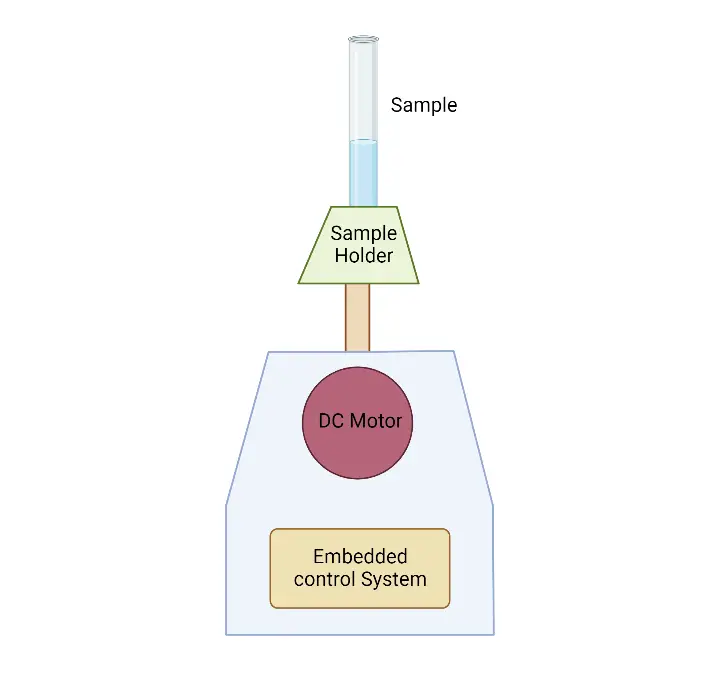
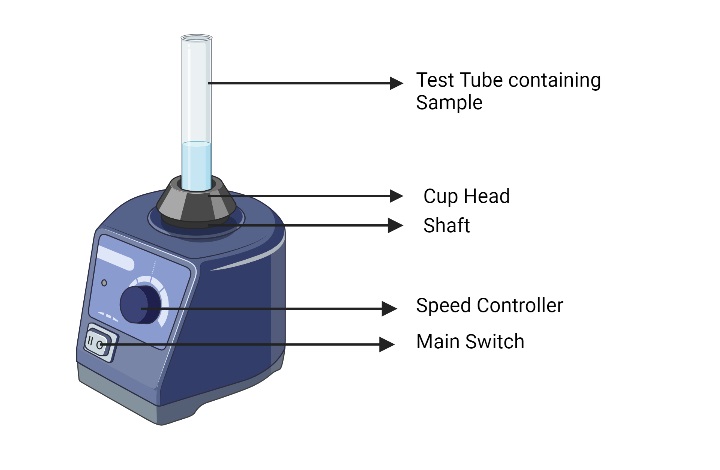
Parts of Vortex Mixer
In summary, a vortex mixer consists of several key parts that contribute to its functionality and versatility. These parts include:
- Main Switch: The main switch controls the power supply to the vortex mixer, allowing it to be turned on or off.
- Speed Controller Knob: The speed controller knob, located on the front panel of the machine, enables the adjustment of the rotational speed of the vortex mixer. Users can increase or decrease the speed by turning the knob.
- Operation Controller Button: The operation controller button is an embedded control unit that offers programming capabilities for the mixer’s operation. It allows users to choose between direct rotation or rotation when the vials are in contact with the well/cup head.
- Motor: The motor is a crucial component of the vortex mixer and is positioned directly below the cup head. It rotates in a circular motion, creating the necessary vortex effect in the liquid sample for proper homogenization.
- Cup Head: The cup head is a replaceable component located above the motor. It is designed to hold the sample tubes securely in place during mixing. Cup heads are available in various sizes to accommodate different tube sizes, and they allow for rapid mixing. Typically made of rubber, the cup head provides a soft surface to hold glass test tubes used in vortex mixing.
Additional Accessories:
- Platform for Tubes: This accessory is used for holding tubes of different sizes simultaneously, allowing for the vortexing of multiple samples at once.
- Single Tube Holder: The single tube holder is a specialized accessory that assists in freehand vortexing of a single tube, providing stability and ease of use.
- Tube Insert: The tube insert serves as a holder for the tubes before and after vortexing, providing convenience and organization.
These extra accessories enhance the functionality and versatility of the vortex mixer, allowing for efficient and customized sample mixing based on specific laboratory needs.
Digital/Pulsing Vortex Mixer: In addition to the basic parts mentioned earlier, a digital/pulsing vortex mixer includes extra features:
- Time Display: It shows the elapsed time in continuous mode or the remaining time in timed mode. This feature allows users to monitor and control the duration of the mixing process.
- Speed Display: It indicates the rotational speed of the vortex mixer. Users can easily monitor the speed at which the mixer is operating.
Operating Procedure of Vortex Mixer
To operate a vortex mixer, follow these steps:
- Attach the power cable to the vortex mixer and connect it to a power supply.
- Secure the desired accessory, such as a cup head or tube holder, onto the cup head of the vortex mixer.
- Select the desired mode of operation. Some vortex mixers have different modes, such as continuous rotation or touch operation. Choose the appropriate mode based on your requirements.
- Turn on the main switch located on the front panel of the vortex mixer. This supplies the electrical power to the device.
- Adjust the speed of rotation by turning the speed control knob. Start at the lowest setting before gradually increasing the speed to the desired level. The speed control knob is typically located on the front panel.
- If the vortex mixer has a touch operation mode, apply gentle pressure to the cup head or accessory holder to initiate the mixing process. The mixer will start operating as soon as pressure is applied.
- Once the mixing is complete or when you want to stop the operation, release the pressure from the cup head or accessory holder. The vortex mixing will cease.
- After vortexing, turn the speed control knob to the lowest setting to reduce the rotation speed.
- Finally, switch off the main switch to stop the vortex mixer’s operation.
- Disconnect the power cable from the electrical source.
Difference Between Vortex Mixer and Centrifuge
Vortex mixers and centrifuges are both laboratory instruments that utilize centrifugal force, but they have distinct differences in their applications and functionalities. Here are the key differences between a vortex mixer and a centrifuge:
- Sample Types and Accessories: Vortex mixers are suitable for both single and multiple samples using various accessories. They are primarily used for mixing liquids and can accommodate different sizes of tubes or containers. On the other hand, centrifuges are mainly used for multiple samples with varying volumes, particularly for separating different components in fluids. Centrifuges typically require specialized rotors and tubes designed for specific applications.
- Size and Placement: Vortex mixers are generally compact and designed to fit on a laboratory benchtop. They have a small footprint, making them easily accessible during experiments. In contrast, centrifuges tend to be larger in size and require dedicated space in the laboratory due to their size and specialized equipment.
- Operation Time: Vortex mixers have a relatively quick operation time, usually requiring only a few seconds to mix samples thoroughly. Centrifuges, however, generally have longer operation times, as the separation process may require several minutes or more, depending on the specific application.
- Centrifugal Force: The centrifugal force generated by a vortex mixer is typically smaller compared to that of a centrifuge. Vortex mixers rely on the swirling motion created by the mixer head to mix samples effectively. Centrifuges, on the other hand, generate significantly higher centrifugal forces to separate particles or components based on their density.
- Movement of Samples: When using a vortex mixer, the movement occurs within the content of the tube or container. The sample is mixed by the rapid oscillating motion generated by the mixer head. In contrast, during centrifugation, the sample tubes or containers remain in a fixed position, while the rotor of the centrifuge rotates at high speeds to exert the centrifugal force needed for separation.
- Temperature Control: Vortex mixers generally do not offer temperature control options for samples being mixed. In contrast, many centrifuges provide temperature control features, allowing users to maintain specific temperature conditions during the separation process.
- Rotation Speed: Vortex mixers typically have a rotation speed range of around 100-3200 rpm, providing flexibility for different mixing requirements. Centrifuges, however, offer a wider range of rotation speeds, typically ranging from 300-15000 rpm, allowing for various separation needs depending on the sample type and application.
| Aspect | Vortex Mixer | Centrifuge |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Types and Accessories | Applicable for single and multiple samples using various accessories | Primarily used for multiple samples with varying volumes and requires specialized rotors and tubes |
| Application | Mixing liquids | Separating components in fluids |
| Size and Placement | Compact, fits on a benchtop | Larger size, requires dedicated space |
| Operation Time | Quick operation time | Longer operation time |
| Centrifugal Force | Smaller centrifugal force | Higher centrifugal force |
| Movement of Samples | Movement occurs within the tube/container contents | Tubes/containers remain in a fixed position, while the rotor rotates |
| Temperature Control | No temperature control options | Temperature control features available |
| Rotation Speed | Range: 100-3200 rpm | Range: 300-15000 rpm |
Safety Precautions
Safety precautions are essential when operating a vortex mixer to ensure the well-being of individuals and maintain a safe working environment. Here are some important safety precautions to follow:
- Secure Shaking Head: Never use the vortex mixer without a shaking head that is firmly fastened in place. Ensure that the shaking head is securely attached to the mixer to prevent any accidents or dislodging during operation.
- Wear Eye Protection: Always use impact-resistant eye protection, such as safety goggles or glasses, when operating the vortex mixer. This helps protect your eyes from any potential splashes or spills that may occur during mixing.
- Avoid Flammable and Hazardous Substances: It is crucial to avoid mixing or using solvents, flammables, or other hazardous substances near or on the vortex mixer. Mixing such substances in close proximity to the mixer can increase the risk of fire or chemical reactions. Ensure a safe distance between the vortex mixer and any flammable or hazardous materials.
- Use Proper Containment Vessels: When shaking potentially dangerous samples, ensure they are placed in appropriate containment vessels. Use containers that are designed to safely hold and contain the specific substances being mixed. This prevents leaks, spills, or exposure to harmful materials.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate hand and eye protection while using the vortex mixer. Gloves can help protect your hands from potential hazards or chemical exposure, while eye protection safeguards against any splashes or flying particles.
- Avoid Flammable Substances: Refrain from using flammable substances while operating the vortex mixer. Flammable materials pose a fire risk, and their use should be avoided in close proximity to the mixer. Follow proper storage and handling procedures for flammable substances in your laboratory.
- Use Sealed Containers for Hazardous Substances: When shaking hazardous substances, ensure they are contained in sealed vessels or containers. This helps prevent any accidental release or exposure to harmful fumes or substances.
- Securely Attach Cup Head: Before using the vortex mixer, always check that the cup head is securely attached. This prevents any potential detachment or movement during operation, ensuring safe and stable mixing.
- Timely Repair and Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain the vortex mixer to ensure its proper functioning and safety. Follow manufacturer guidelines for maintenance procedures and schedule any necessary repairs promptly. Faulty equipment should not be used until it has been properly serviced or repaired by qualified personnel.
Types of Vortex Mixer
Based on technology, speed variation, and size, the vortex mixer has been subdivided into numerous varieties. Several types are described below:
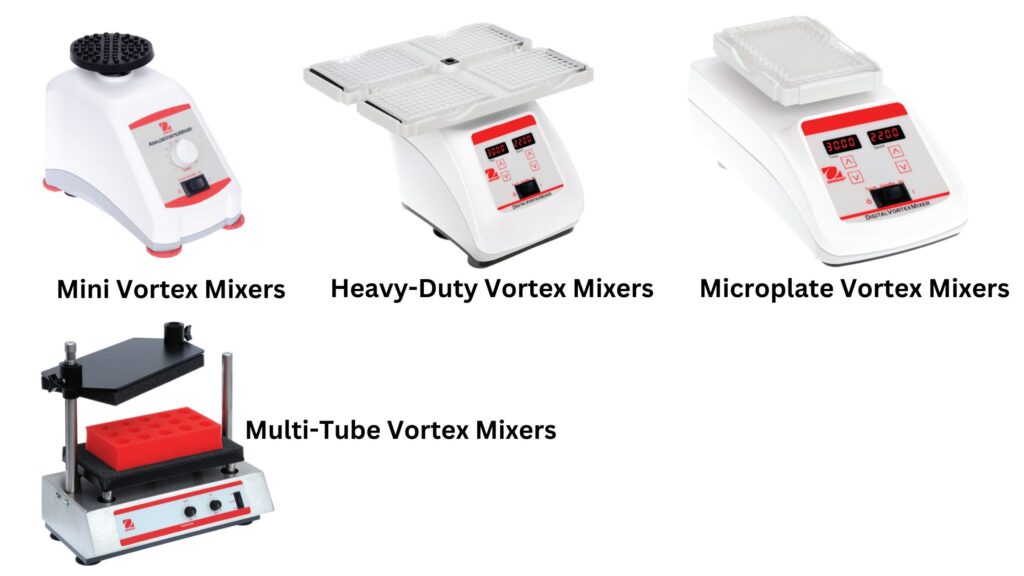

Vortex mixers come in various types, each with its own features and applications. Here are some common types of vortex mixers:
- Variable Speed Vortex Mixers: These vortex mixers offer a speed controller, allowing users to adjust the rotation speed within a range, typically from 100 to 3200 rpm. They often provide both touch and continuous modes, and with the use of accessories, they can handle multiple tubes simultaneously.
- Analog Vortex Mixers: Analog vortex mixers have speed control knobs that can be turned to adjust the mixing speed. They usually offer both continuous mode (when accessories are used) and touch mode (when the cup head is pressed down).
- Digital Vortex Mixers: Digital vortex mixers feature touchpad controls for adjusting the speed and other settings. They typically have an LED screen that displays the exact speed and time. Digital vortex mixers often offer both continuous operation with accessories and touch mode with the cup head. Some models also include a timer function.
- Fixed-Speed Vortex Mixers: Fixed-speed vortex mixers operate at a fixed high speed when the head is depressed. They are designed for powerful vortexing and often only offer the touch-down mode. Cup head accessories are commonly used with this type of vortex mixer.
- Mini Vortex Mixers: Mini vortex mixers are compact and portable devices suitable for vortexing small volumes, typically ranging from 0.2 to 50 mL. They can be found in both digital and analog versions and offer various operating modes based on the accessories used.
- Pulsing Vortex Mixers: Pulsing vortex mixers are equipped with glass beads for efficient cell disruption. The pulsing action reduces heat production during mixing. They can operate in both touch and continuous modes and are available in analog and digital technologies.
- Microplate Vortex Mixers: Designed specifically for mixing contents in microplates, these vortex mixers are available in digital and analog versions. They typically operate in a continuous mode and offer reliable mixing performance for microplate applications.
Each type of vortex mixer has its own advantages and is suited for different laboratory tasks. When selecting a vortex mixer, consider the specific requirements of your application and choose the appropriate type that best meets your needs.
Applications of Vortex Mixer
A vortex mixer finds a wide range of applications in various fields due to its ability to quickly and efficiently mix samples. Here are some common uses of a vortex mixer:
- Clinical and Medical Sectors: In the clinical and medical sectors, vortex mixers are used for thawing and mixing samples. They are essential for preparing samples for analysis, experiments, and diagnostic procedures.
- Cell and Tissue Analysis: Vortex mixers are utilized to suspend cell or tissue samples during tissue analysis and cell culture. The vortexing action helps in achieving a homogeneous mixture of cells or tissues with the required reagents and buffers.
- Protein and Enzyme Research: When studying proteins and enzymes, it is crucial to mix samples with reagents and buffers to ensure accurate analysis. A vortex mixer facilitates the homogenization of samples, leading to proper mixing and interaction between the components.
- Pharmaceutical Applications: Vortex mixers play a role in heating and mixing samples in pharmaceutical laboratories. They are used in the preparation of various pharmaceutical formulations, ensuring uniform distribution of ingredients.
- Education: Vortex mixers are commonly used in schools and universities for practical demonstrations and experiments. They allow students to experience hands-on mixing of different substances and observe the effects of vortexing.
- Quality Control Testing: In industrial settings, vortex mixers are employed in quality control testing. They assist in sample preparation, ensuring that representative samples are obtained for accurate analysis and assessment.
- Chemical Mixing: Vortex mixers are widely used in laboratories for homogenous mixing of chemicals. The rapid mixing time offered by vortexing is often more efficient compared to other methods of mixing, such as manual shaking or stirring.
- DNA Extraction: During DNA extraction processes, vortex mixers are used to achieve homogenous sample mixing with extraction buffers. The vortexing action aids in the disruption of cells, facilitating the release of DNA for subsequent analysis.
The versatility and efficiency of vortex mixers make them invaluable tools in various scientific, medical, and industrial applications. They streamline sample preparation, enhance mixing accuracy, and contribute to reliable experimental results.
Advantages of Vortex Mixer
A vortex mixer offers several advantages that make it an effective and dependable tool for mixing samples. These advantages include:
- Consistent Speed Control: Vortex mixers are equipped with various speed options, allowing users to select the desired speed for their specific mixing needs. Once the speed is set, the vortex mixer maintains a constant and uniform mixing speed throughout the process. This ensures consistent and reliable mixing results, enhancing the reproducibility of experiments and analyses.
- Versatility in Sample Capacity: Vortex mixers can accommodate a range of sample sizes, from a single vial up to multiple vials at once. Depending on the specific model and design, vortex mixers can hold anywhere from one to a dozen vials simultaneously. This versatility in sample capacity allows for efficient batch processing and the simultaneous mixing of multiple samples, saving time and increasing productivity in the laboratory.
- Ease of Use and Minimal Resources: Vortex mixers are designed to be user-friendly and require minimal training or expertise to operate effectively. They typically have simple controls and intuitive interfaces, making them accessible to both experienced laboratory professionals and beginners. Additionally, vortex mixers operate using minimal resources, such as electricity, and do not require complex setups or additional equipment, making them convenient and cost-effective to use.
- Efficient Mixing Method: Vortex mixers provide an efficient mixing method, particularly for liquid samples. The rapid circular motion generated by the vortexing action creates a vortex or whirlpool effect in the sample, facilitating thorough mixing and dispersion of components. This results in homogenization and uniform distribution of substances within the sample, ensuring reliable and accurate analysis or downstream applications.
- Time-Saving and Increased Productivity: The efficient mixing capability of vortex mixers significantly reduces the mixing time compared to other manual or conventional methods. Vortex mixers can quickly achieve the desired mixing effect, allowing for faster sample preparation and processing. This time-saving feature contributes to increased productivity in the laboratory, enabling researchers and technicians to carry out their work more efficiently.
Limitation of Vortex Mixer
While a vortex mixer offers numerous benefits for liquid sample mixing, it also has certain limitations that need to be considered. These limitations include:
- Incompatibility with Solid-Liquid or Solid-Solid Mixing: The vortex mixer is primarily designed for homogenizing liquid samples. It is not suitable for mixing solid substances with liquids or combining solid components together. Other mixing techniques such as grinding, grinding, or stirring may be more appropriate for these scenarios.
- Risk of Spillage: Improper handling of the tubes can result in spillage. If the tube is not securely held or if excessive force is applied during vortexing, there is a possibility of the liquid sample splashing out of the tube. Care should be taken to ensure proper tube placement and secure attachment to minimize the risk of spillage.
- Tedious Operation with Continuous Use: The touch method, where the vortexing action is initiated by pressing the tube against the cup head, is often the most efficient way to operate a vortex mixer. However, if the vortex mixer is used continuously for extended periods, repeatedly pressing down on the tube can become tedious and potentially strain the operator’s hand or wrist. It is important to take breaks and alternate between touch and non-touch methods to prevent discomfort or fatigue.
- Limited Mixing Capacity: Vortex mixers typically have a limited capacity for the number and size of tubes that can be accommodated simultaneously. Depending on the specific model and design, there may be restrictions on the maximum volume or number of tubes that can be effectively mixed at once. This limitation should be taken into consideration when working with large sample volumes or when requiring high-throughput mixing.
- Not Suitable for Delicate Samples: Some sensitive samples, such as fragile cells or easily denatured proteins, may be adversely affected by the vigorous vortexing action. In such cases, alternative gentle mixing methods should be considered to prevent damage or degradation of the samples.
It is important to be aware of these limitations and choose the appropriate mixing technique or equipment based on the nature of the samples and the desired mixing outcome.
FAQ
What is a vortex mixer?
A vortex mixer is a laboratory instrument used to mix or blend liquids by creating a vortex or whirlpool motion.
How does a vortex mixer work?
A vortex mixer works by applying a circular shaking motion to a sample or container, causing the liquid to spin rapidly in a vortex pattern.
What are the main applications of a vortex mixer?
Vortex mixers are commonly used in various applications such as mixing reagents, suspending cells, blending samples, DNA extraction, and protein analysis.
Can a vortex mixer handle multiple samples simultaneously?
Yes, many vortex mixers come with accessories like tube racks or plate holders that allow for simultaneous mixing of multiple samples.
What is the speed range of a vortex mixer?
The speed range of a vortex mixer typically varies from 100 to 3200 revolutions per minute (rpm), although this may vary depending on the specific model.
Can I control the speed of a vortex mixer?
Yes, most vortex mixers have adjustable speed controls, allowing users to set the desired speed for their mixing requirements.
Is a vortex mixer suitable for mixing solid materials?
No, vortex mixers are primarily designed for liquid mixing applications and are not suitable for mixing solid materials.
Are there any safety precautions to consider when using a vortex mixer?
Yes, it is important to securely fasten the shaking head, wear protective eyewear, avoid using flammable substances, and use proper containment vessels for hazardous samples.
Can a vortex mixer control the temperature of the sample?
Generally, vortex mixers do not have temperature control capabilities. They are mainly used for mixing at ambient temperature.
How does a vortex mixer differ from a centrifuge?
While both instruments utilize centrifugal force, a vortex mixer is used for mixing liquids, while a centrifuge is used for separating components in fluids through spinning at high speeds.
References
- https://www.gilson.com/pub/media/docs/VORTEX_UG_LT318403-01.pdf
- https://www.tillquist.se/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/Vortex-Mixers-Data-Sheet_AP_EN_Tillquist.pdf
- https://www.labnetinternational.com/sites/www.labnetinternational.com/files/product-documents/RY%20929929%20Vortex%20Mixer%20S0200.pdf
- https://www.fishersci.com/content/dam/fishersci/en_US/documents/programs/scientific/brochures-and-catalogs/catalogs/fisher-scientific-vortex-mixer-catalog.pdf
- https://camblab.info/what-does-a-vortex-mixer-do/
- https://ijrat.org/downloads/Vol-6/dec-2018/Paper%20ID-612201848.pdf
- https://microbeonline.com/vortex-mixer-principle-types-and-uses/
- https://www.mrclab.com/vortex
- https://www.azom.com/article.aspx?ArticleID=17282#:~:text=Vortex%20mixers%20are%20one%20of,with%20high%20degrees%20of%20precision.
- file:///C:/Users/Soura/Downloads/Documents/Beverage_Vortex-Mixer-E.pdf
