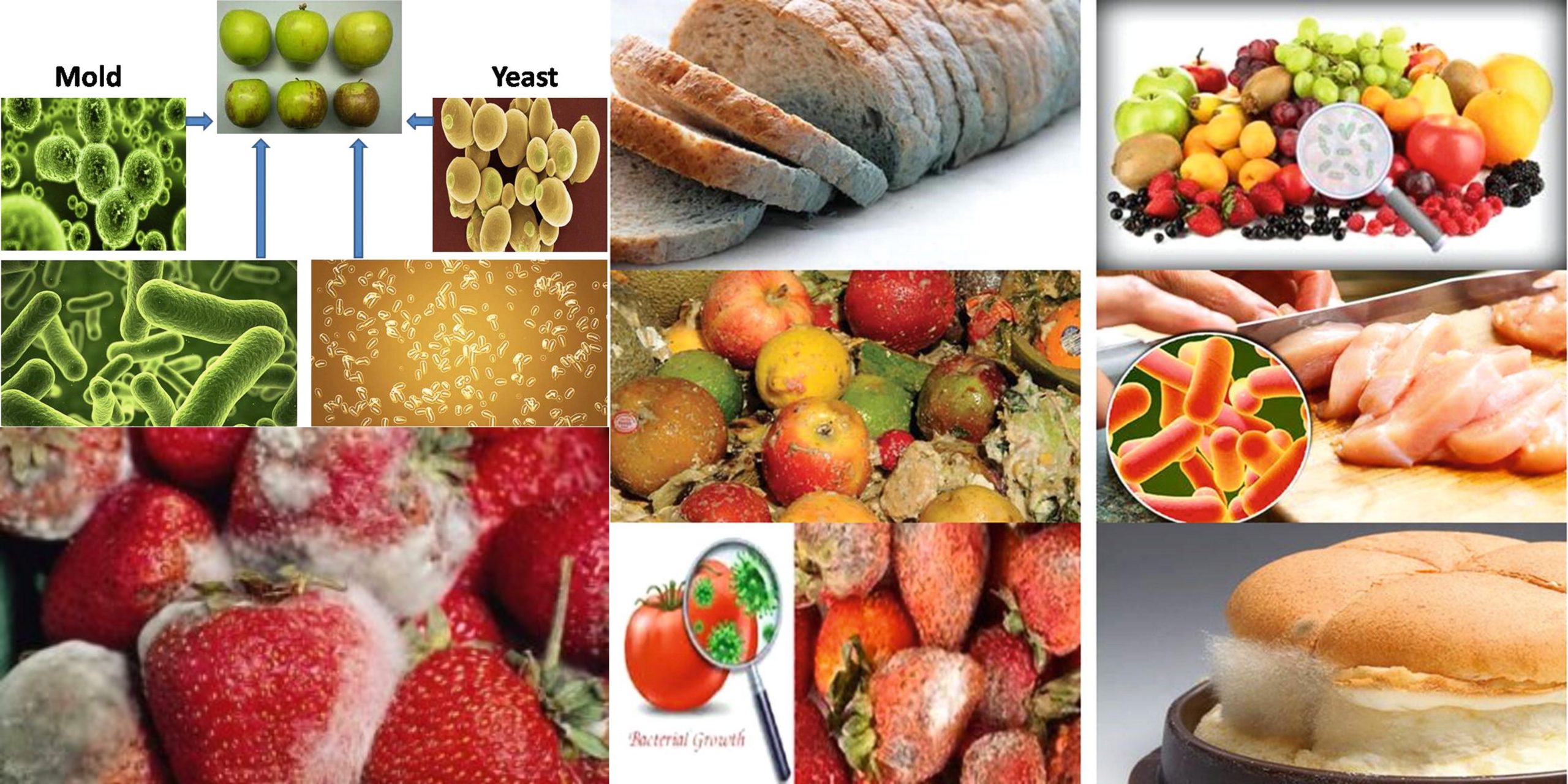
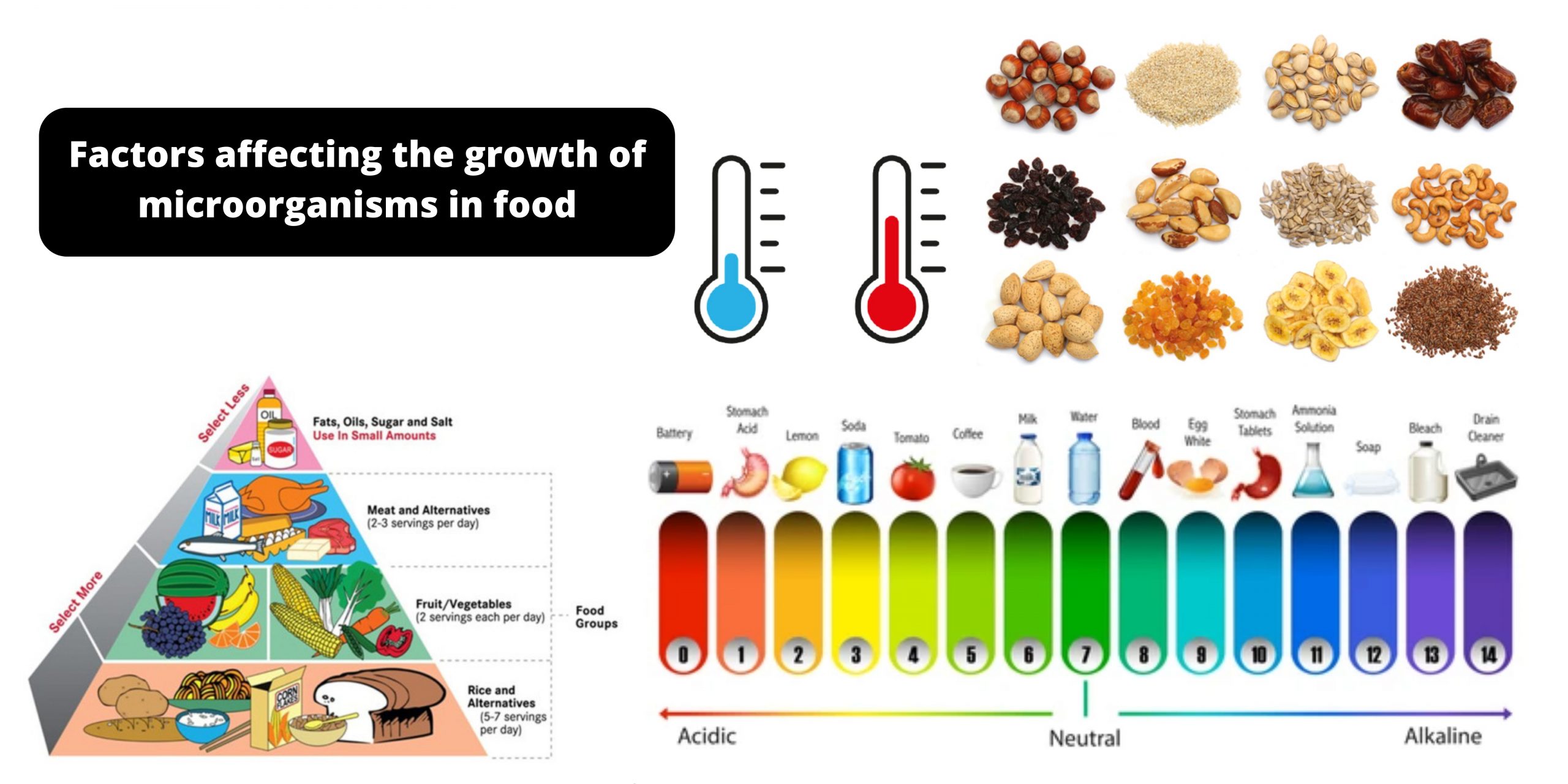
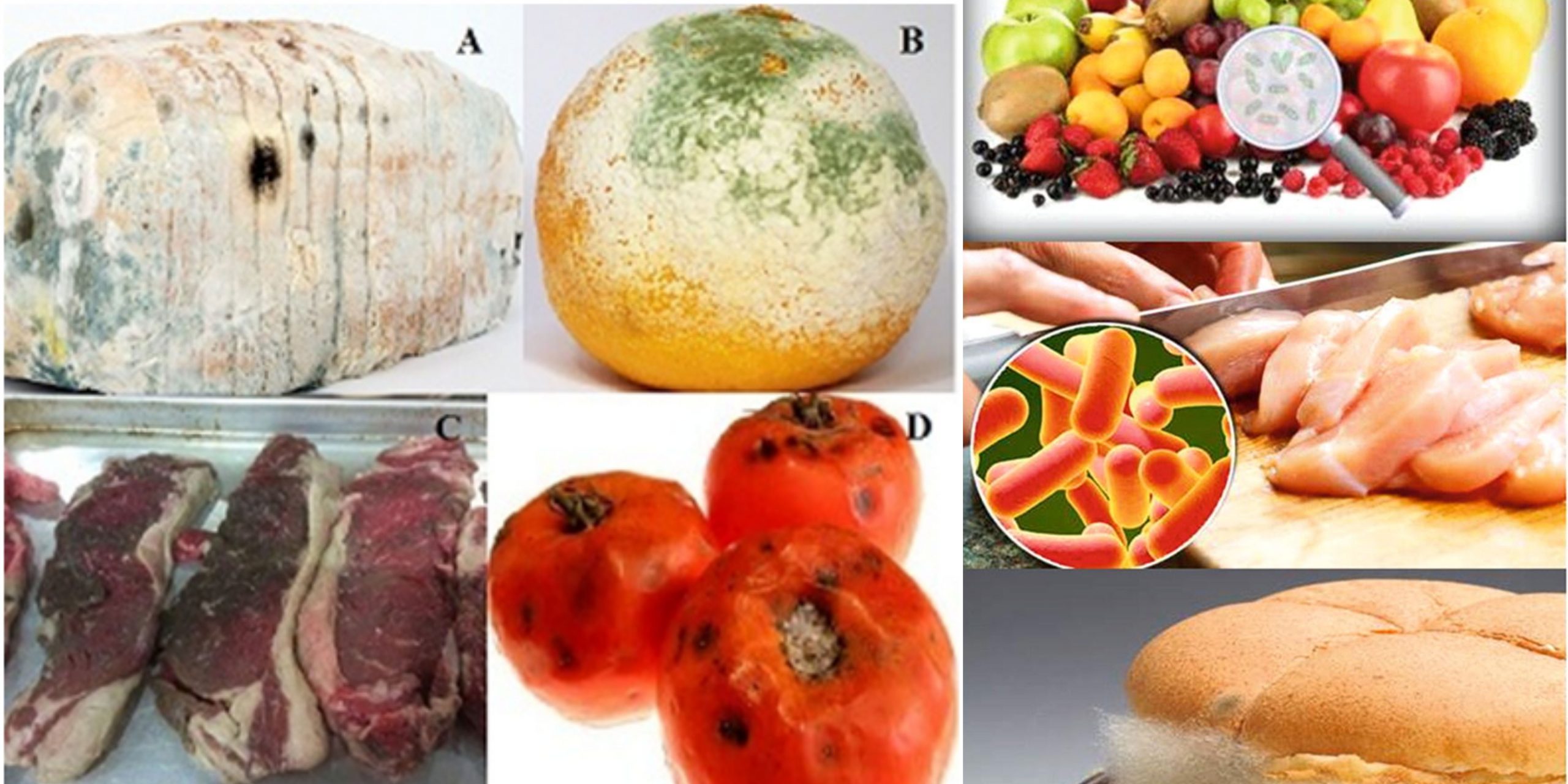
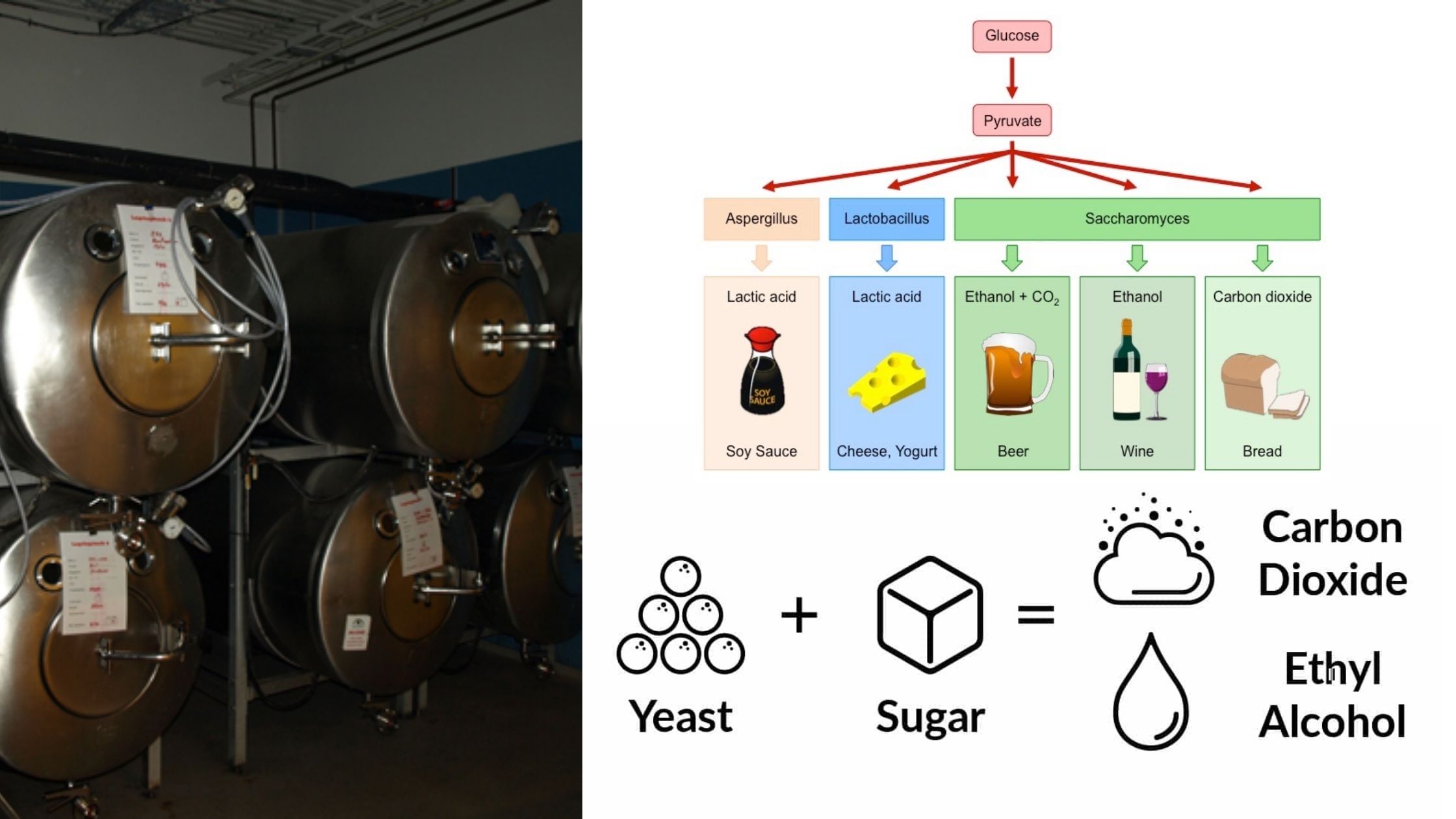
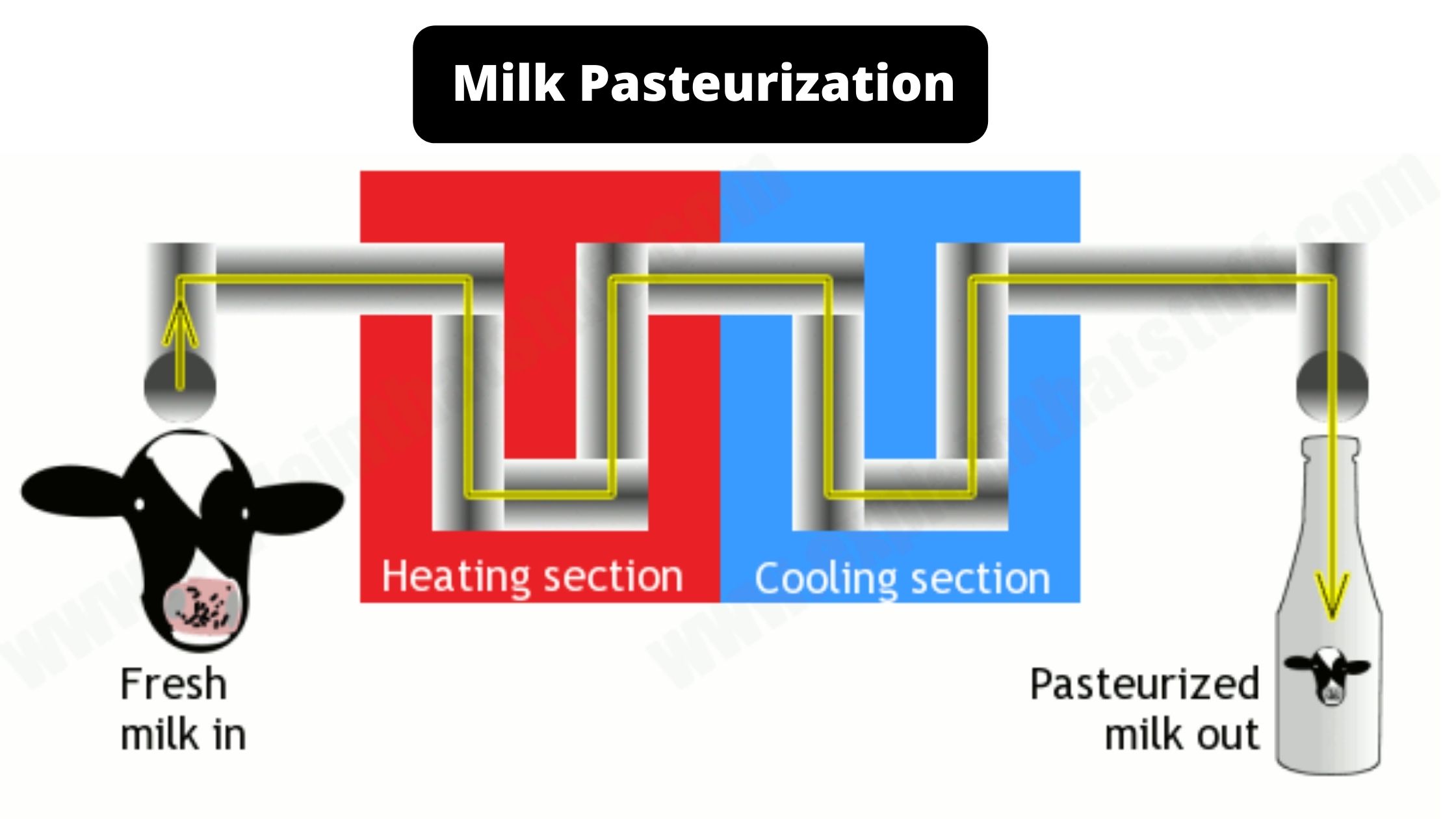
Food Preservation by chemicals – Food Additives
What are food additives? According to the Food Safety Standard Authority of India (FSSAI). Food additive may be defined as any substance not normally consumed as a food by itself or used as a typical ingredient of the food, whether or not it has nutritive value, the intentional addition of which to food for a … Read more