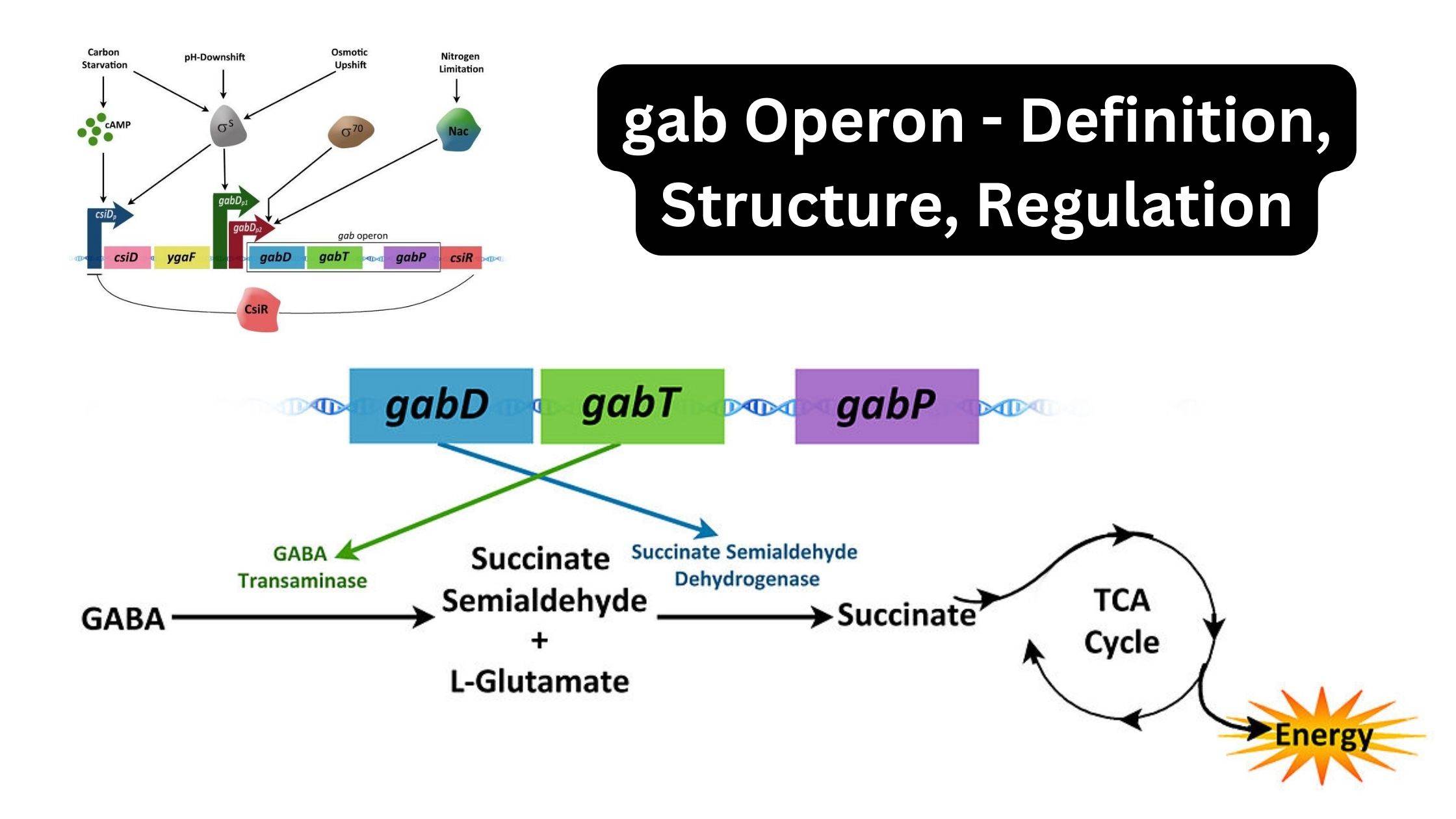
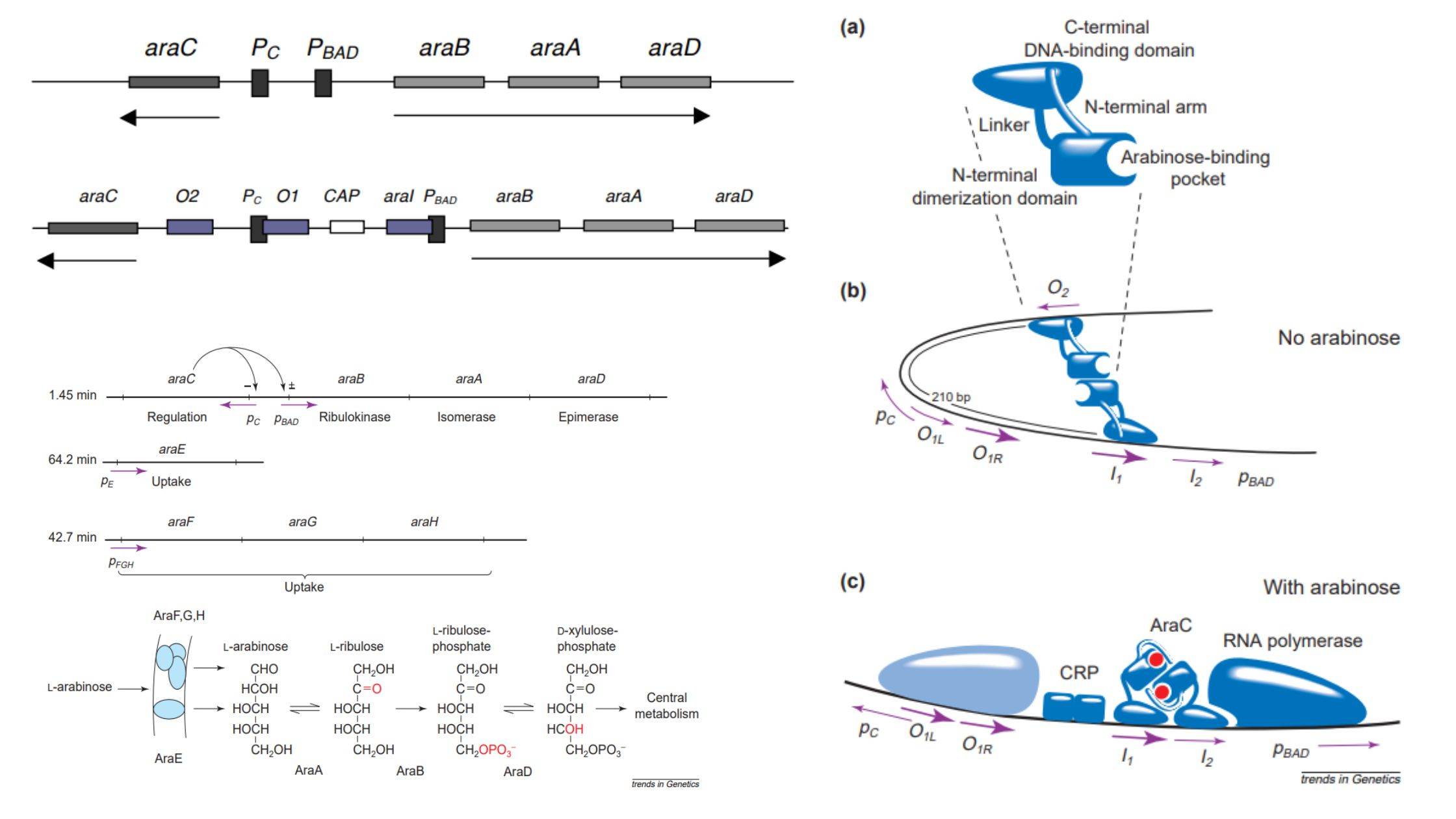
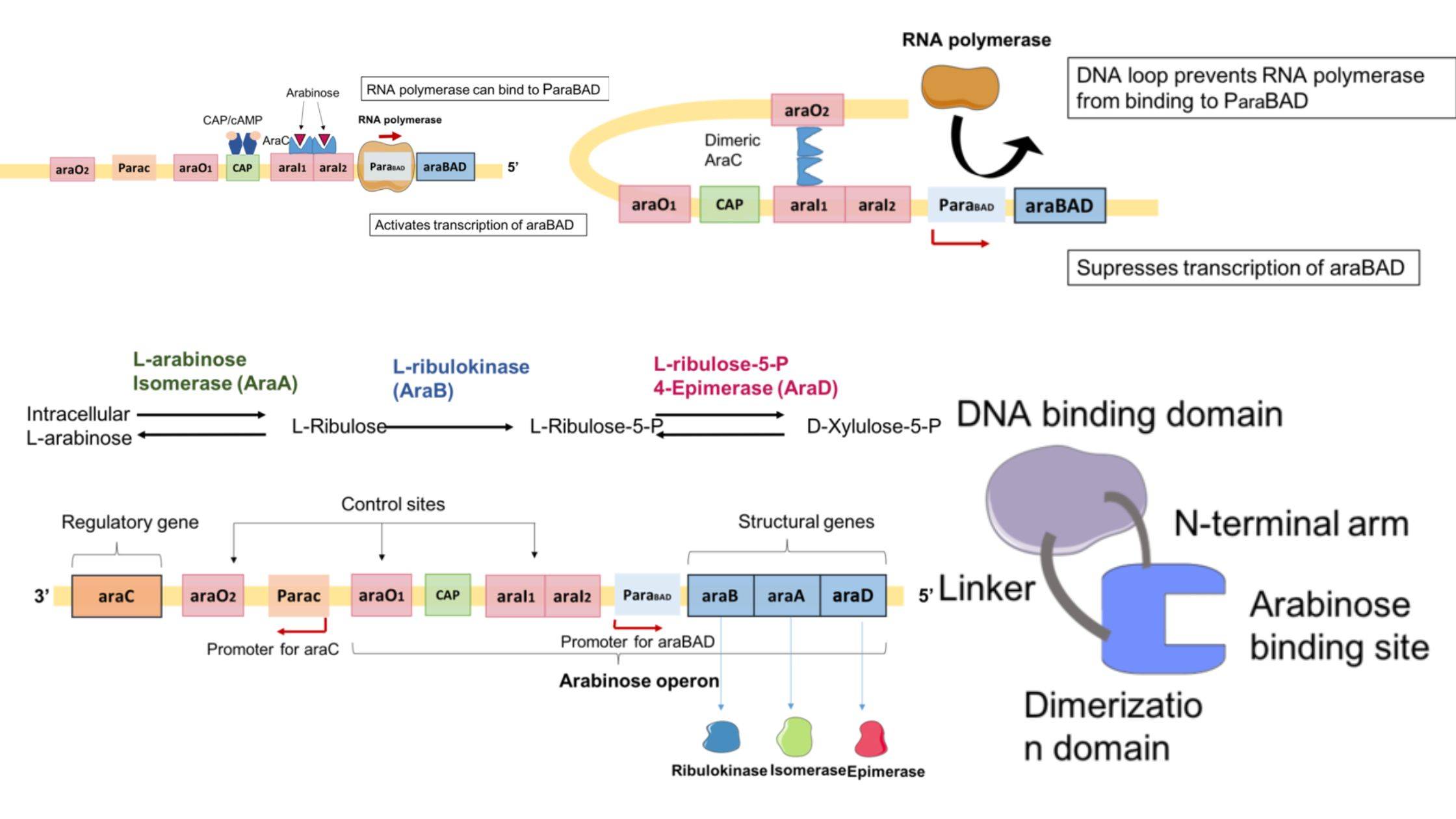
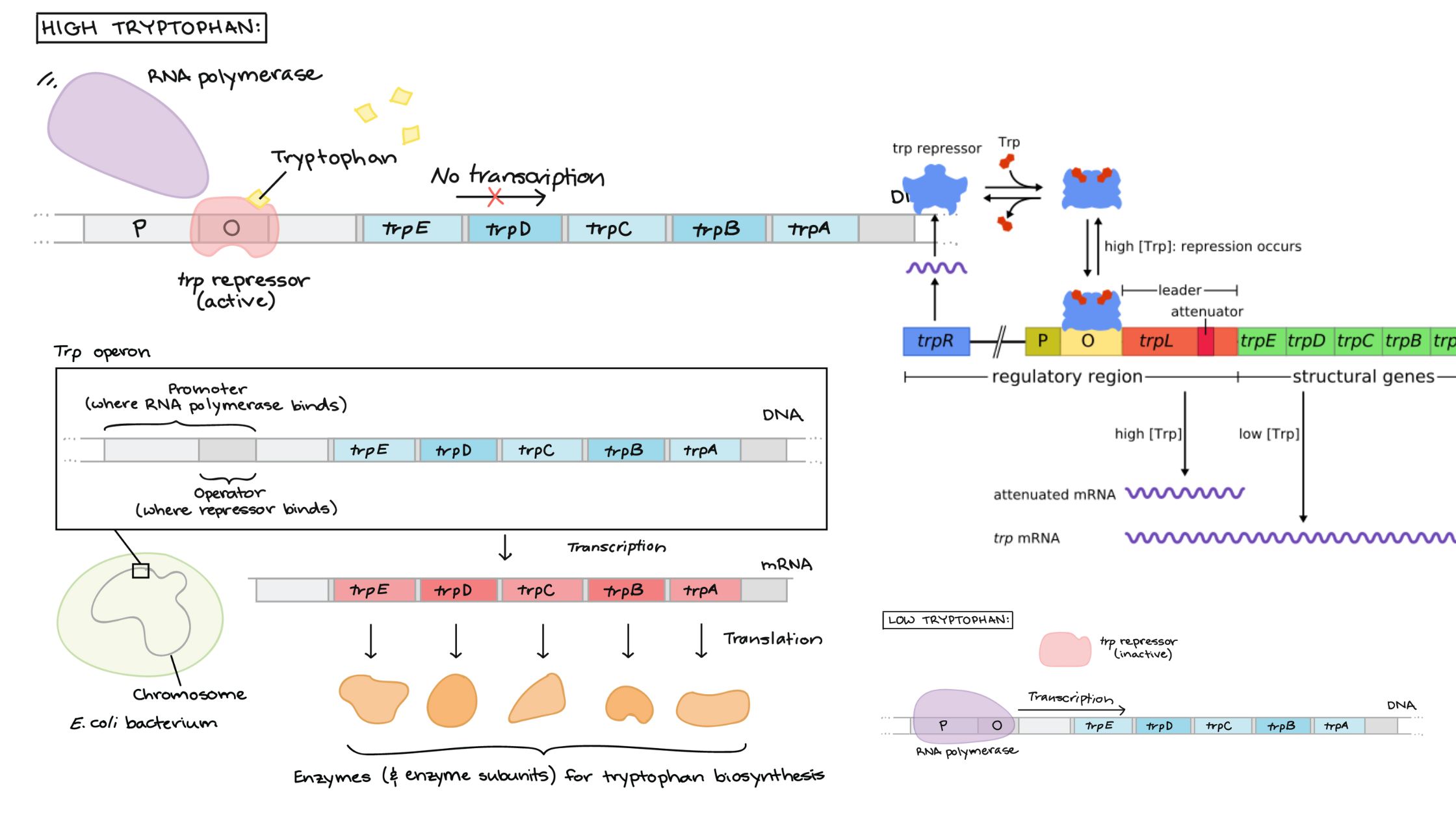
Parasitism – Definition, Types, Examples
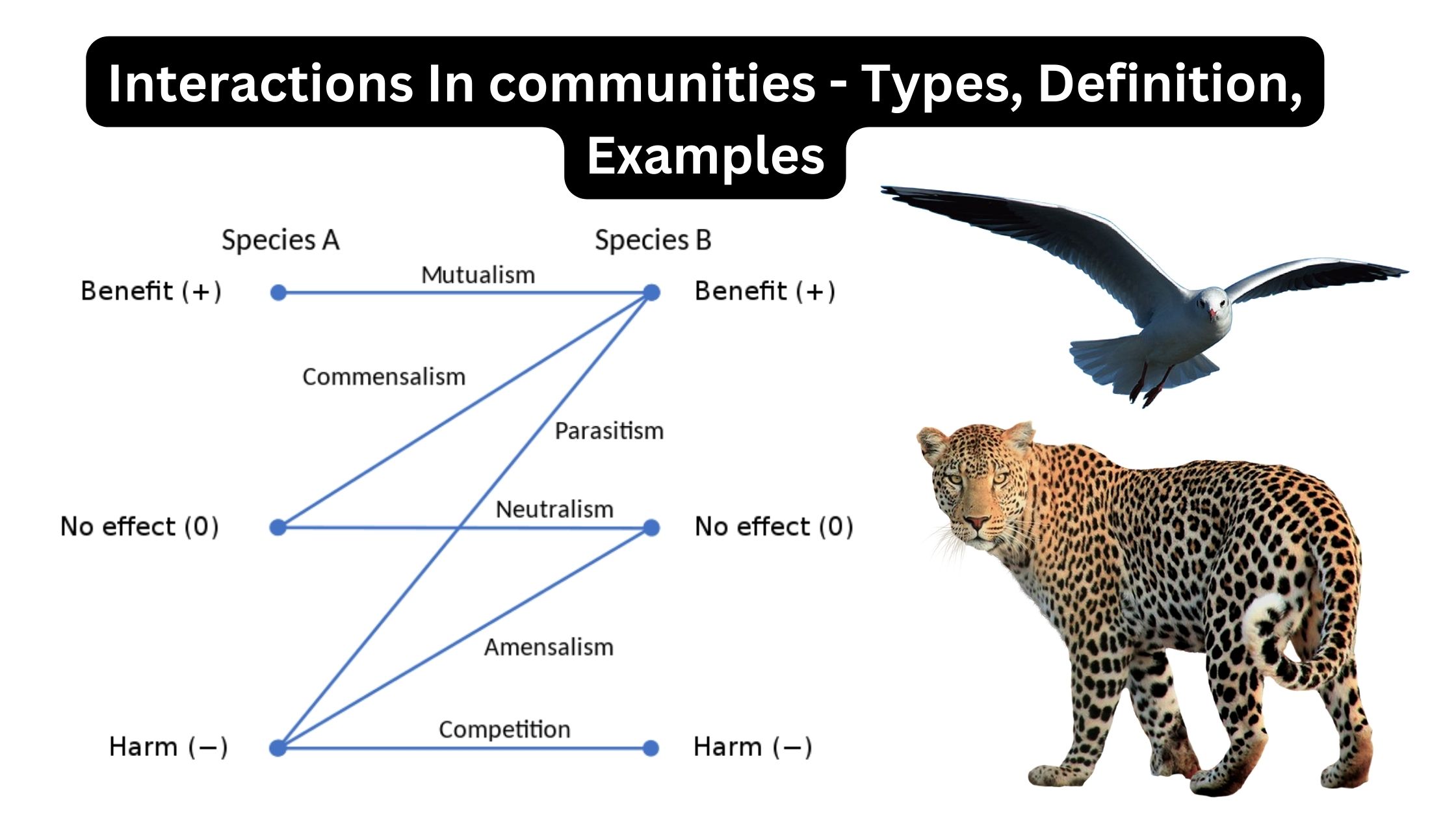
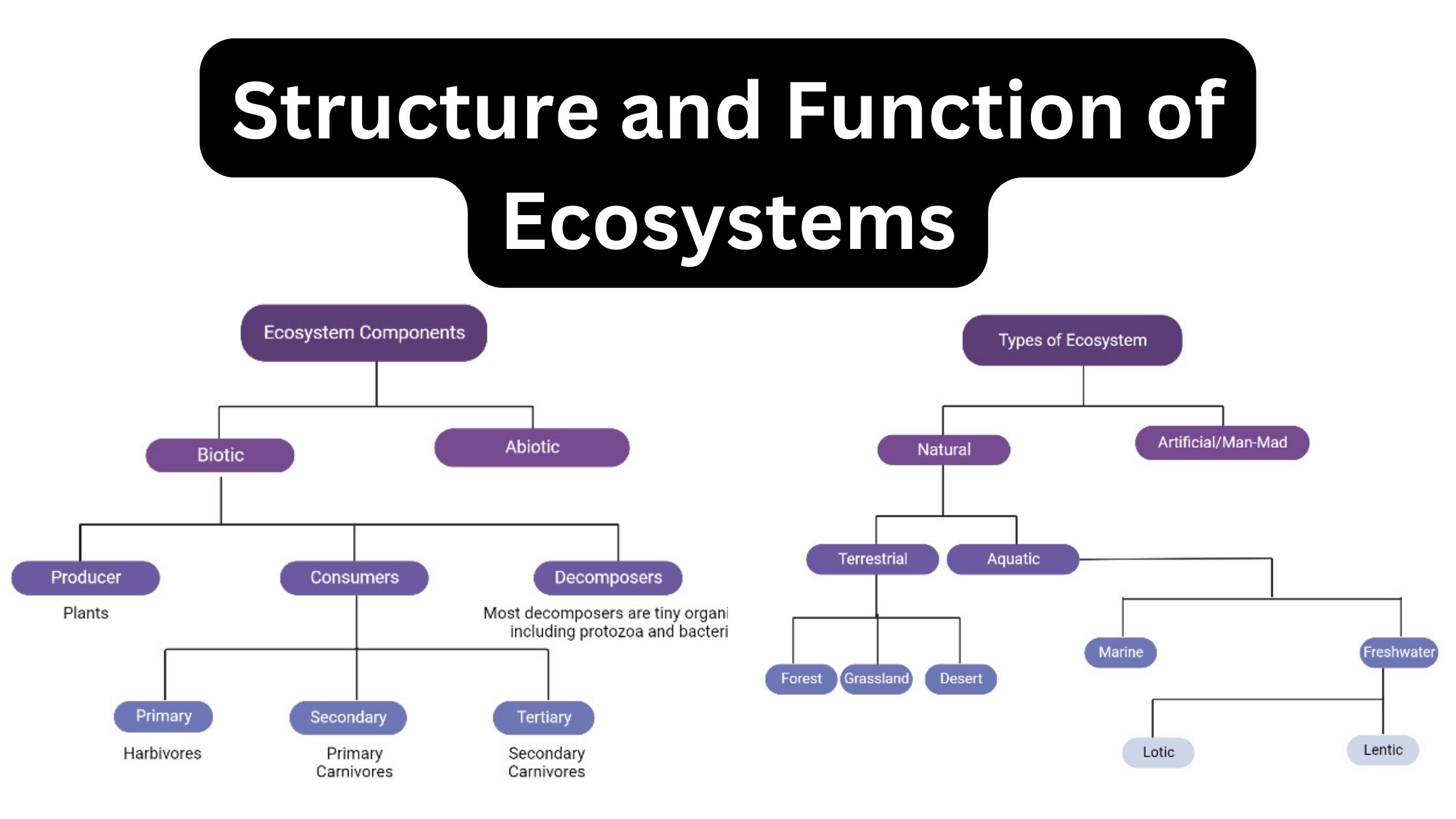
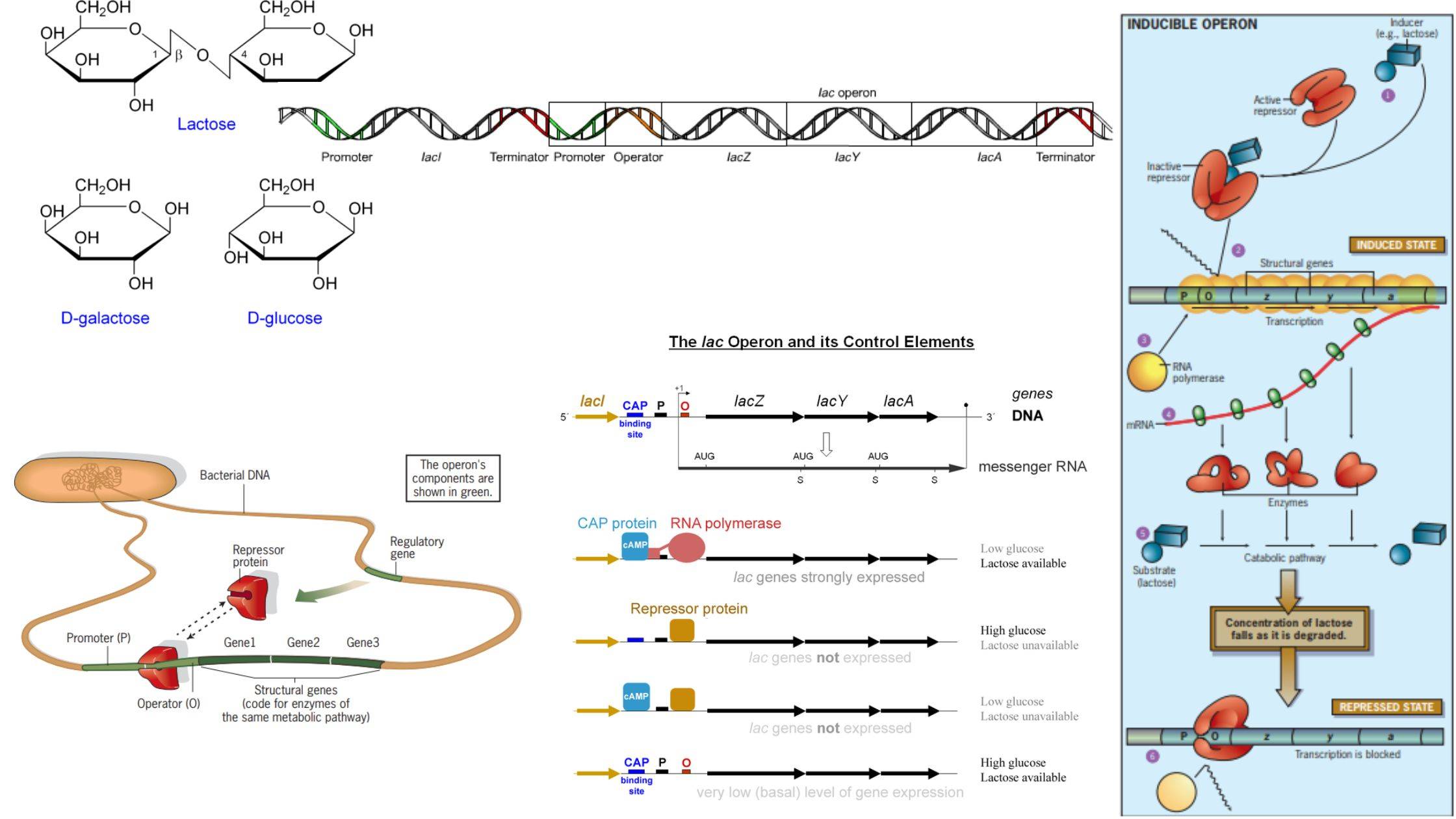
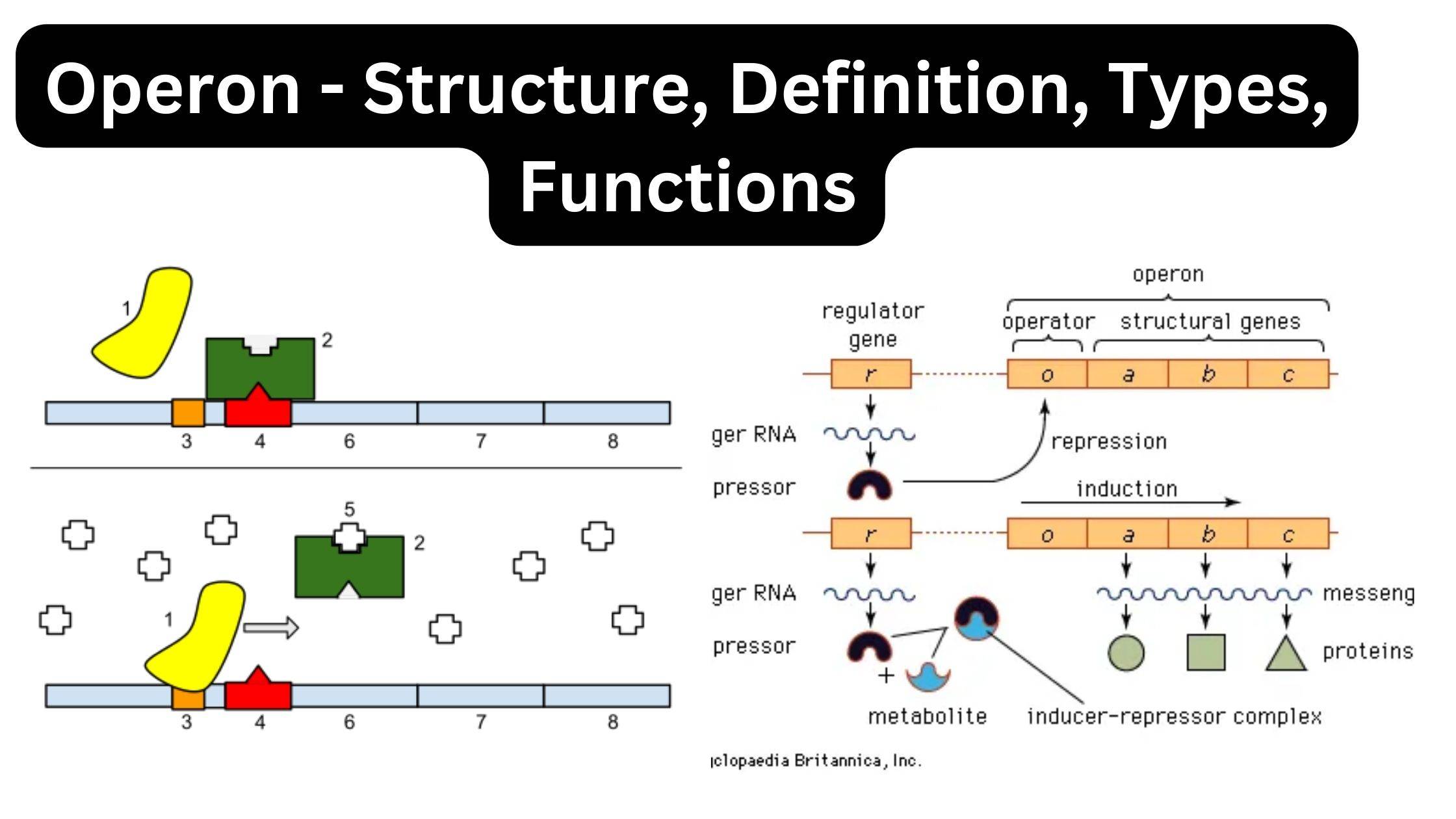
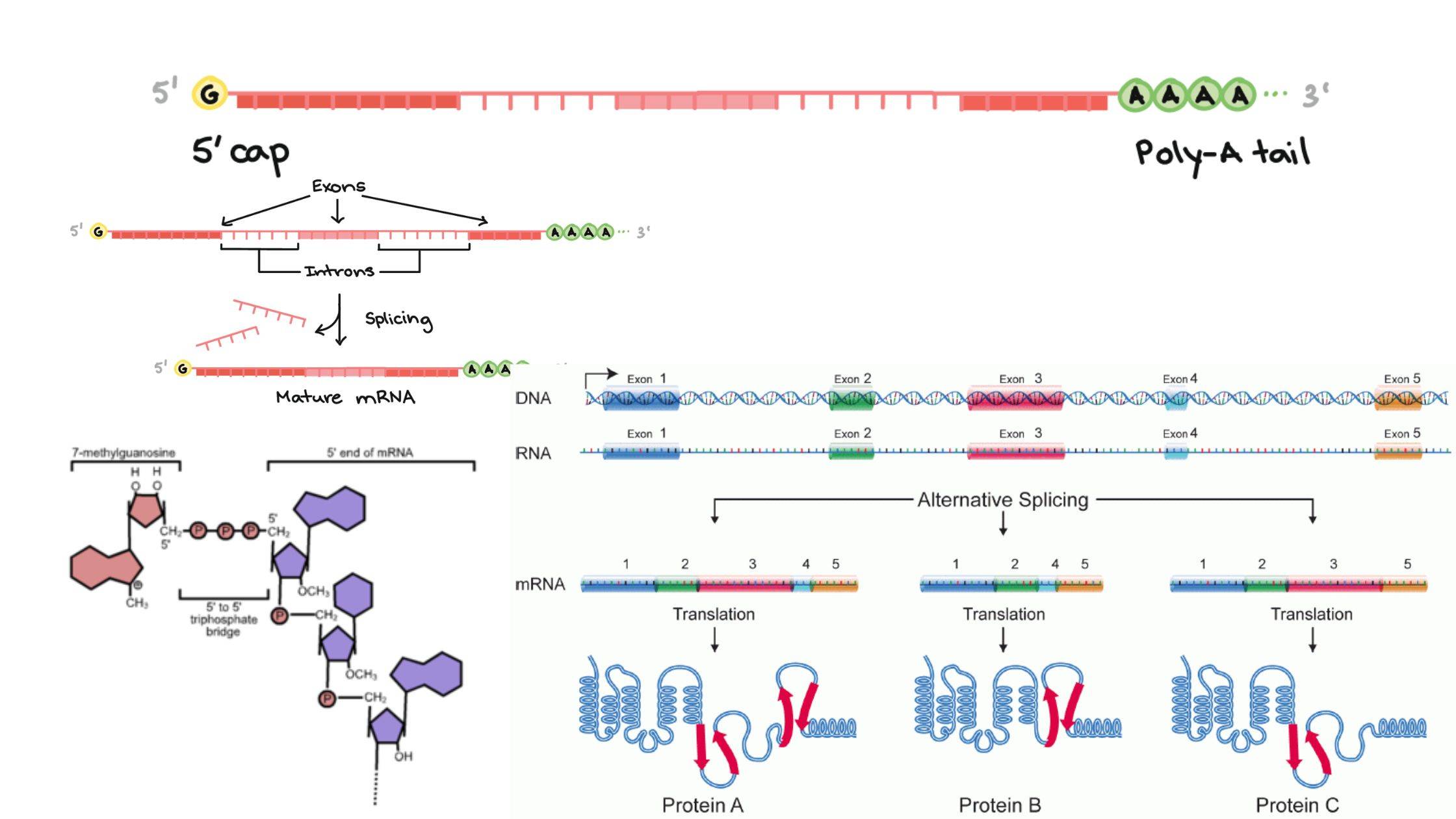
What is Parasitism? Definition of Parasitism Parasitism is a symbiotic relationship between two species in which one organism, the parasite, derives benefits at the expense of the other organism, the host, often causing it harm. Mechanisms of Dispersal Types of Parasitism Parasitism, a multifaceted biological interaction, can be classified based on various criteria, ranging from … Read more