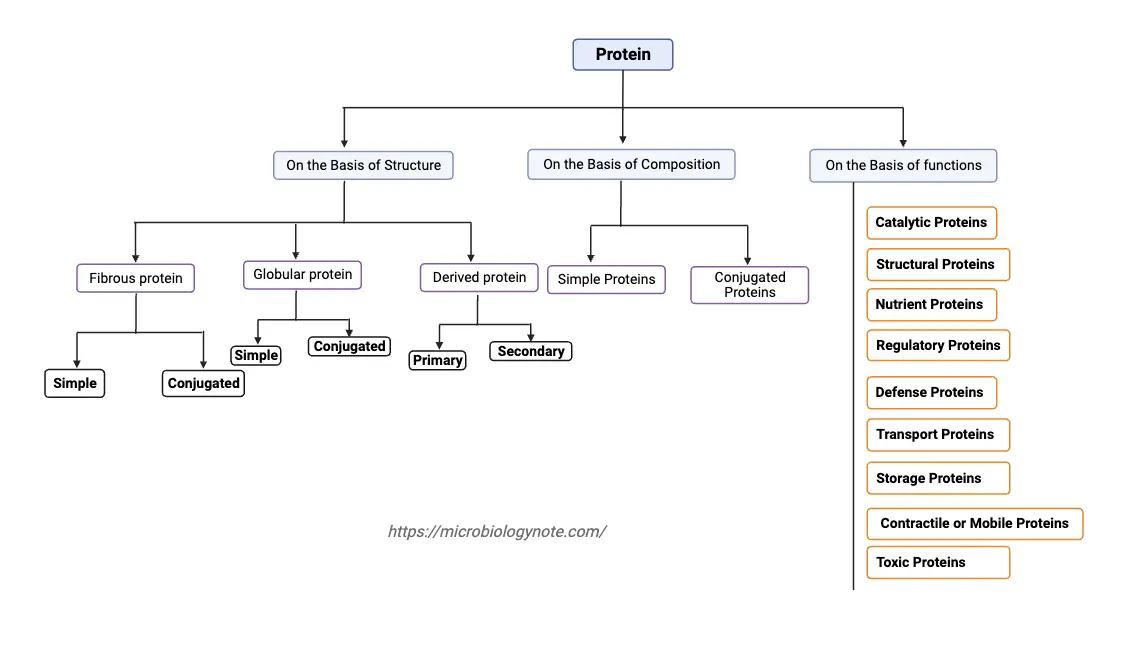
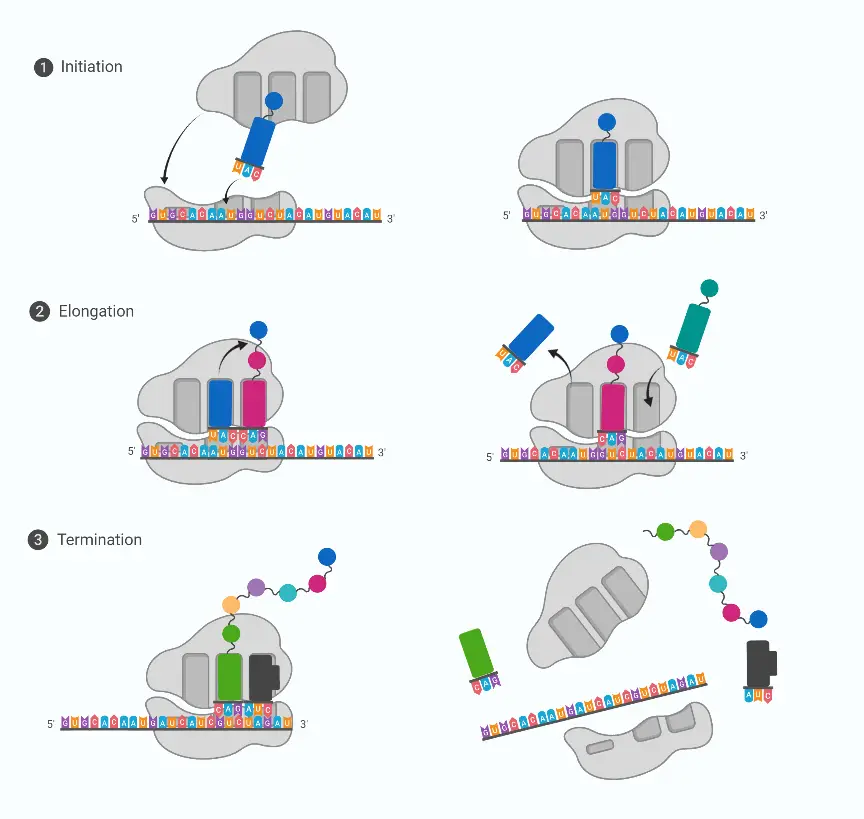
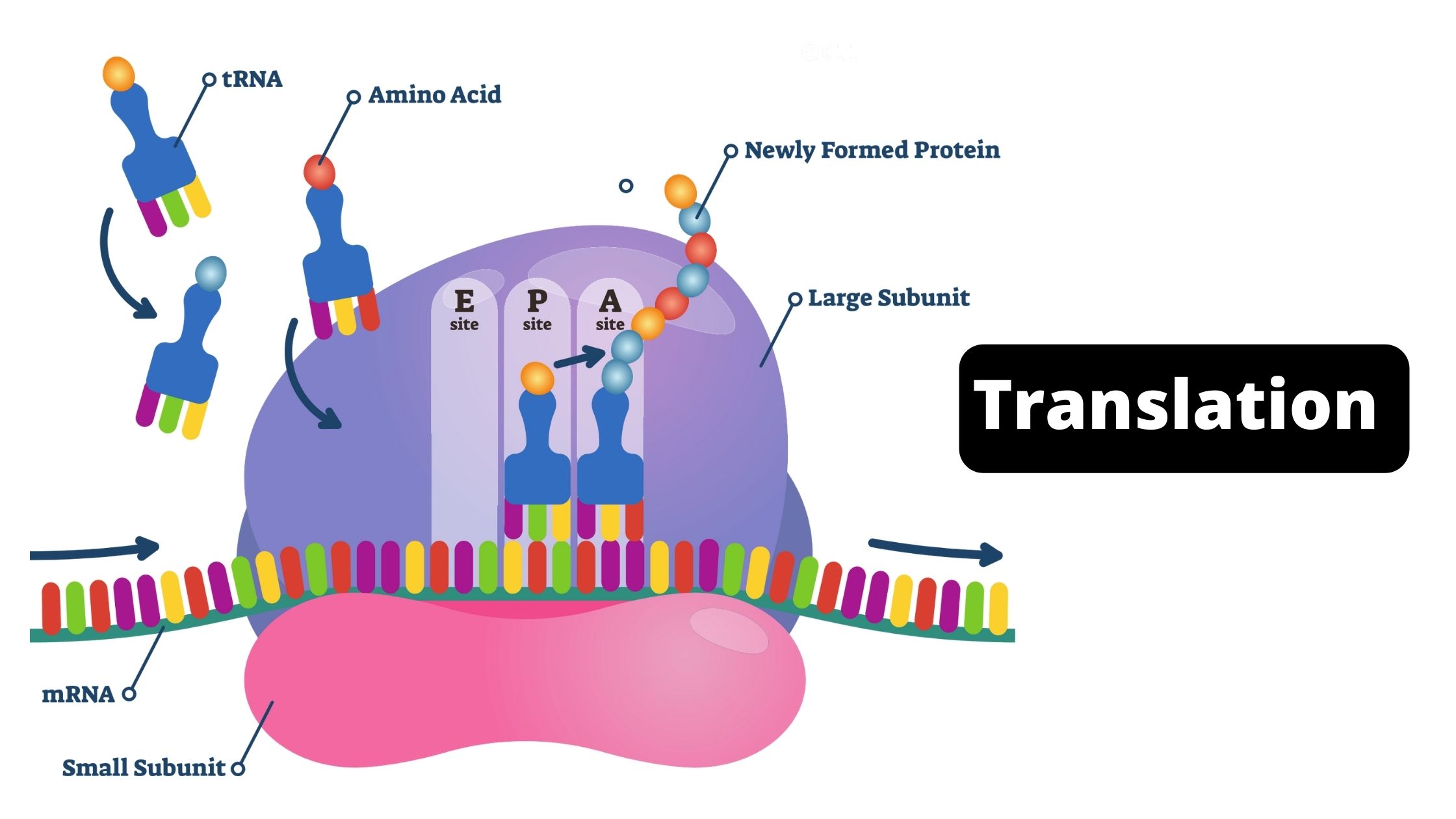
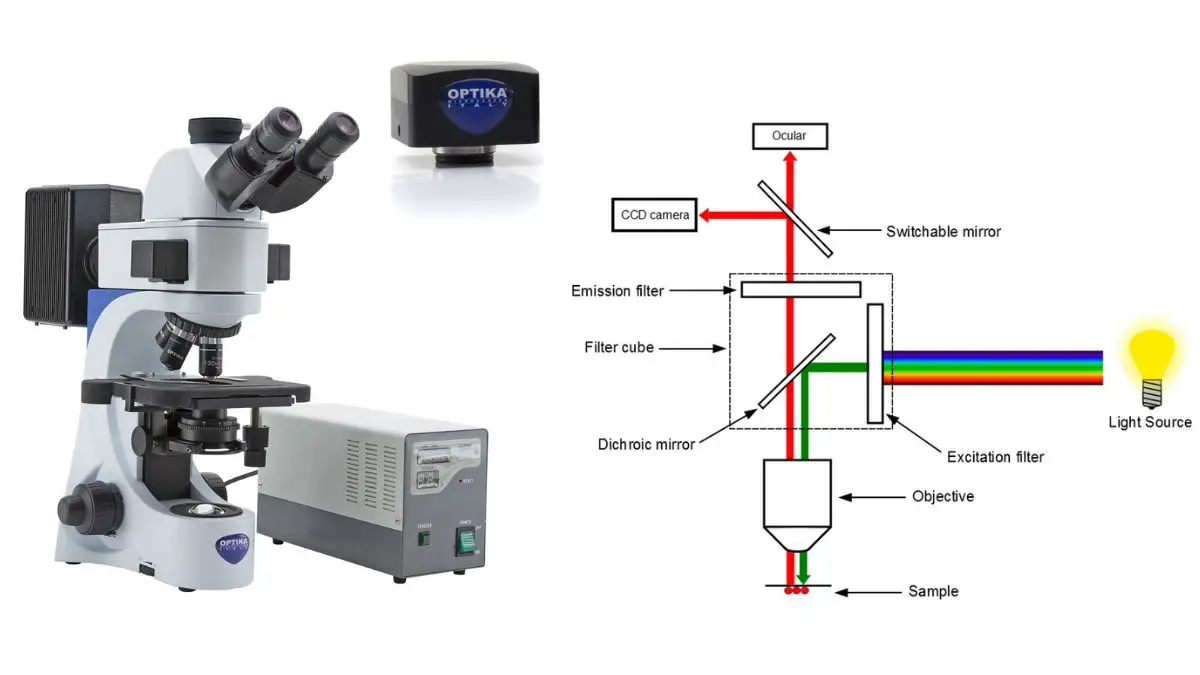
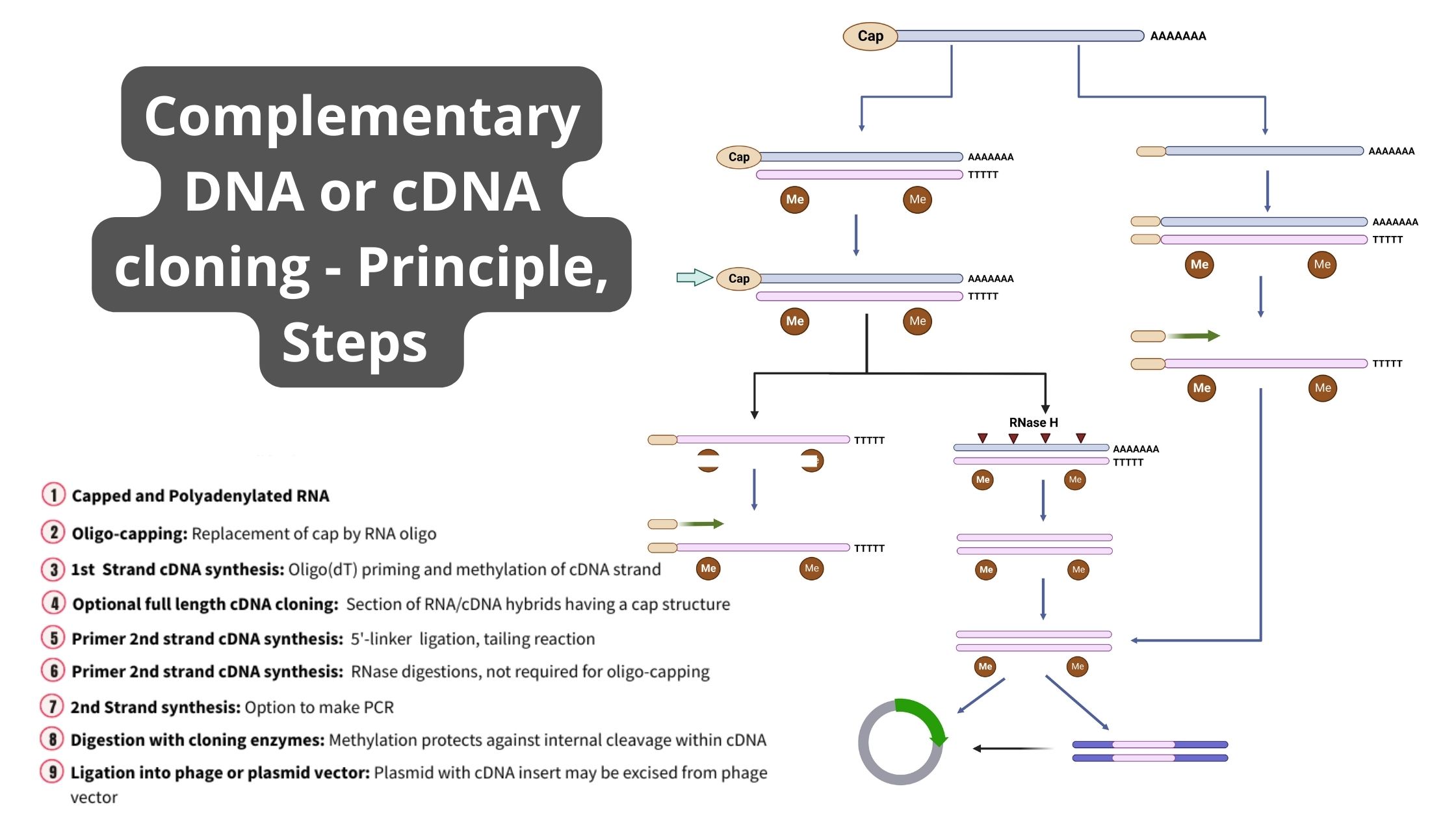
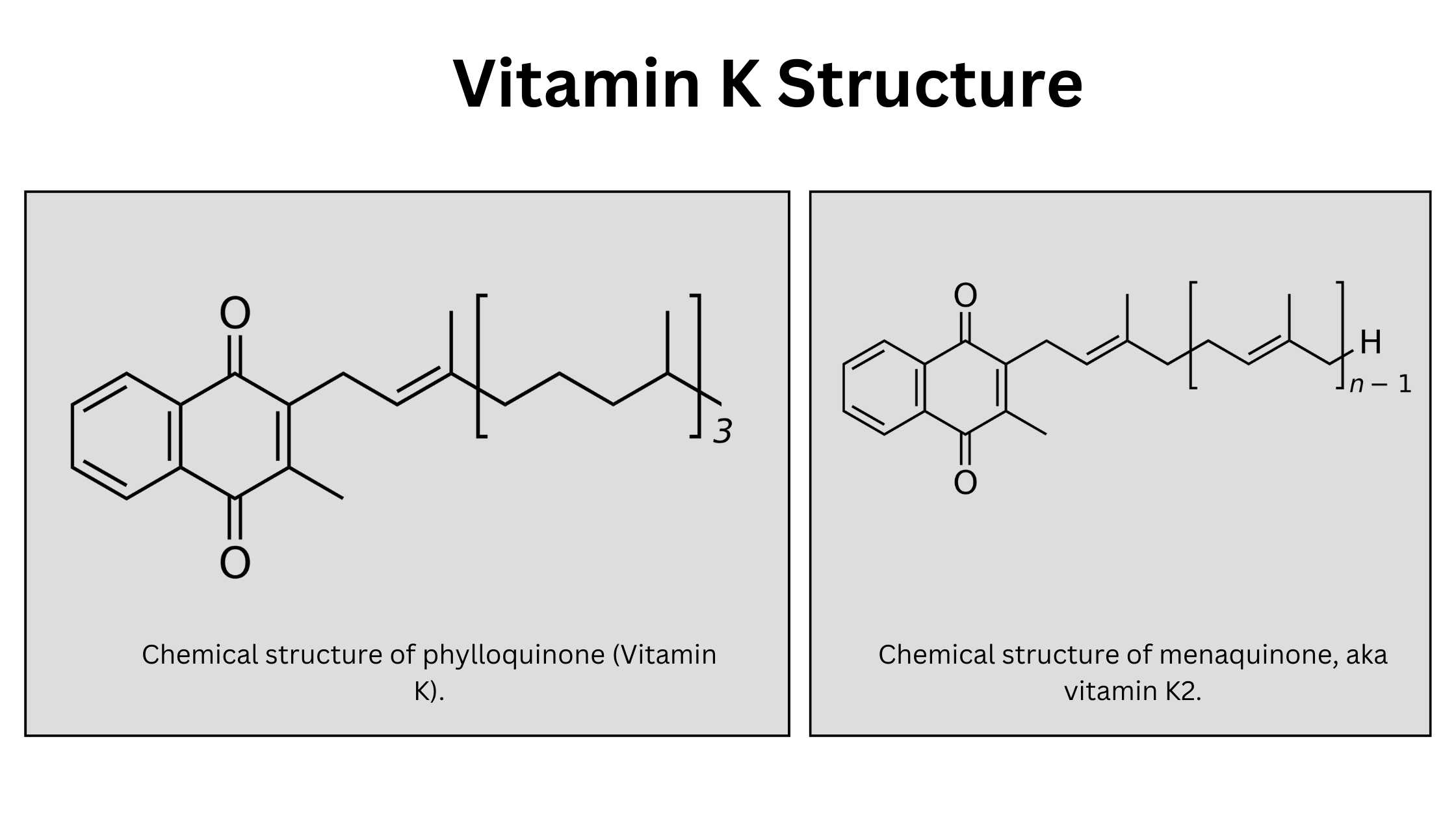
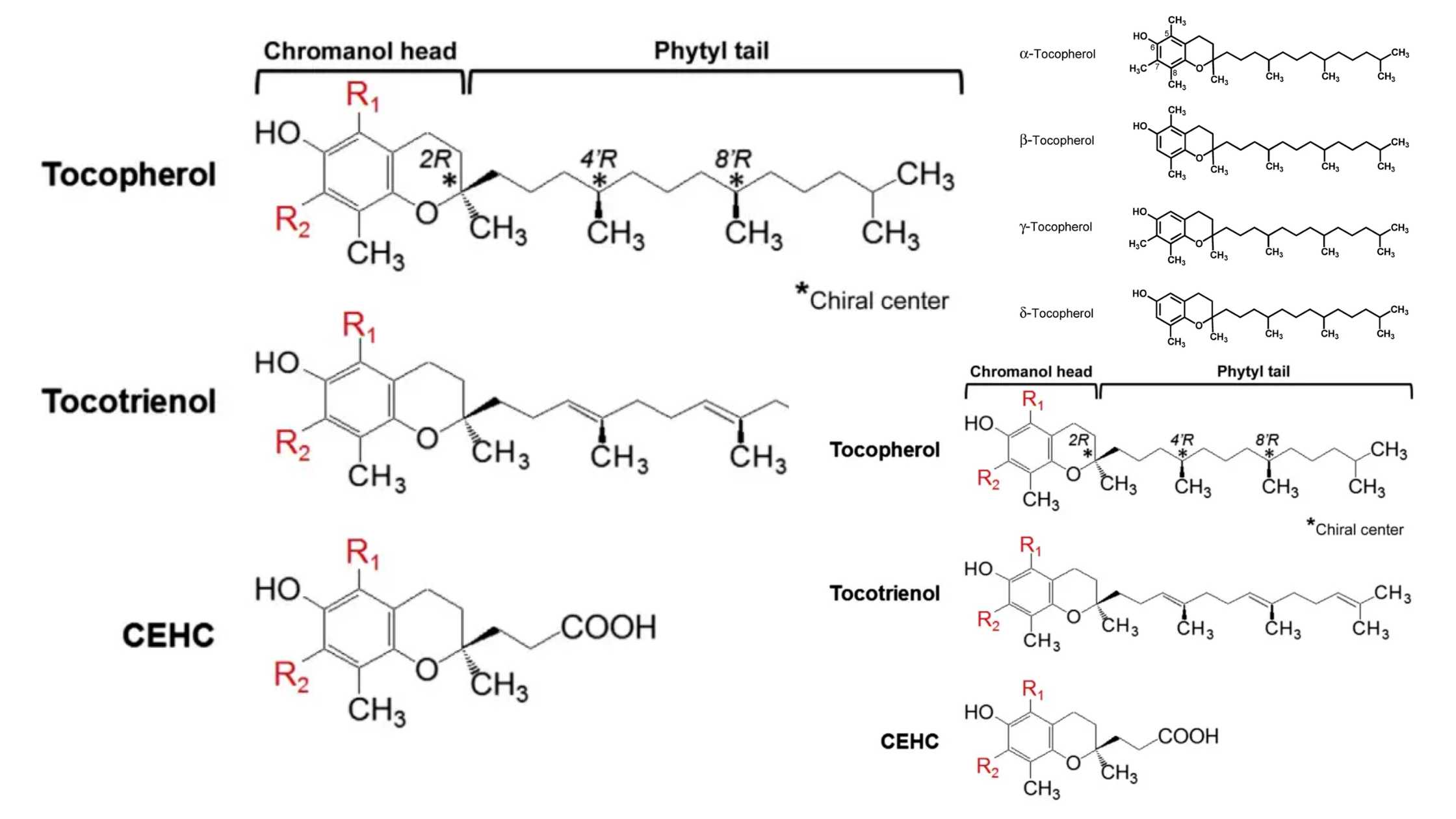
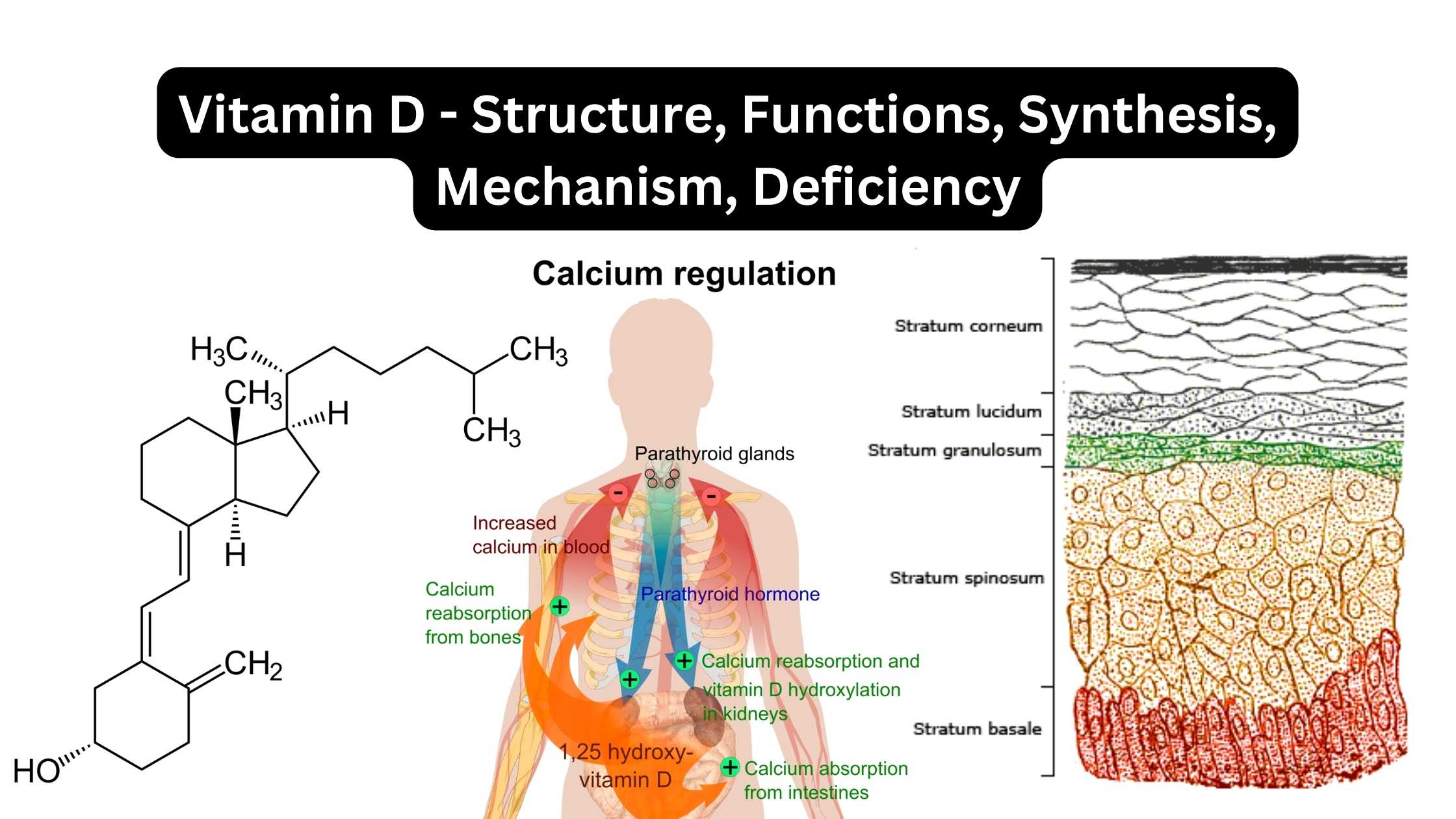
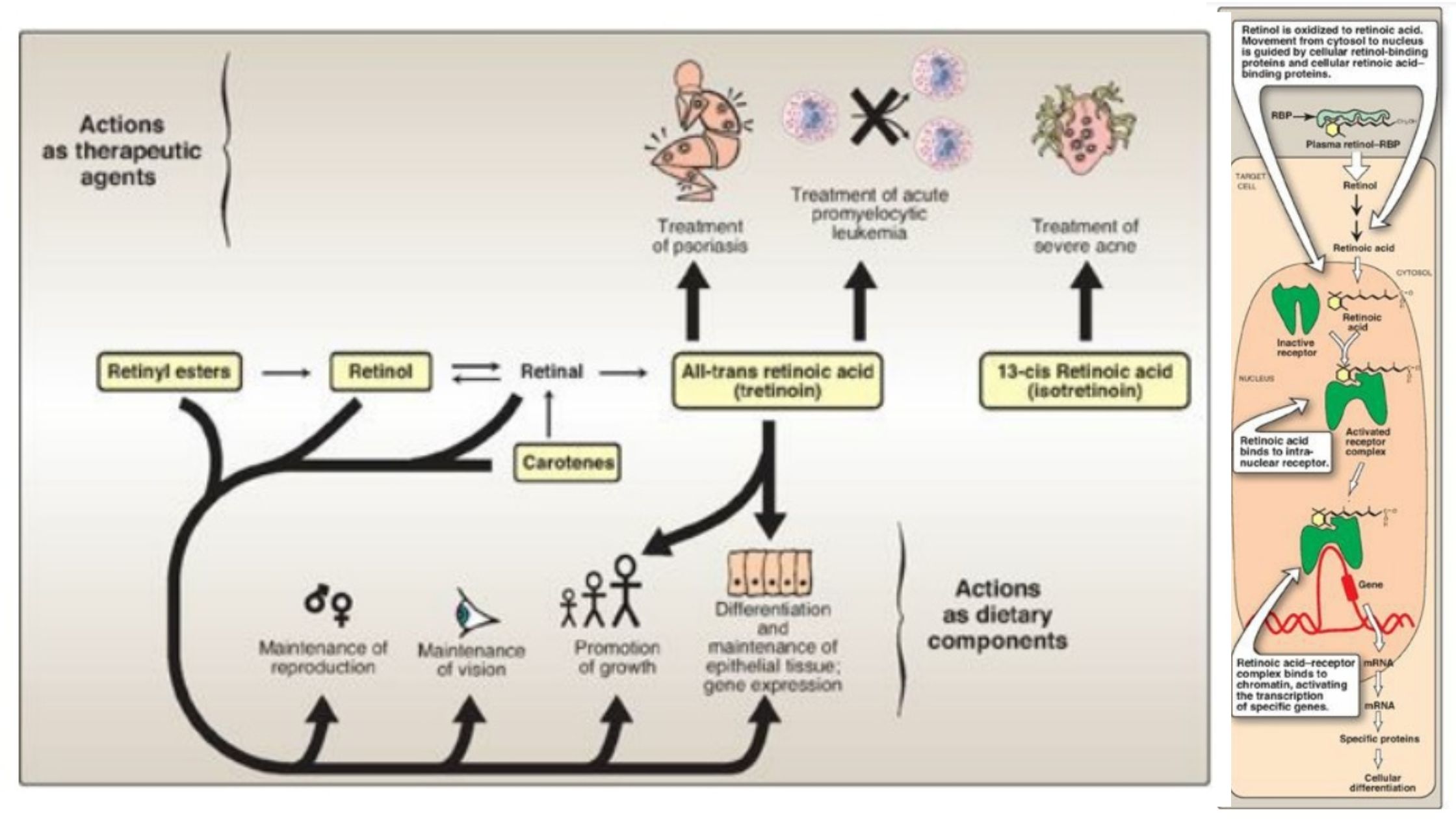
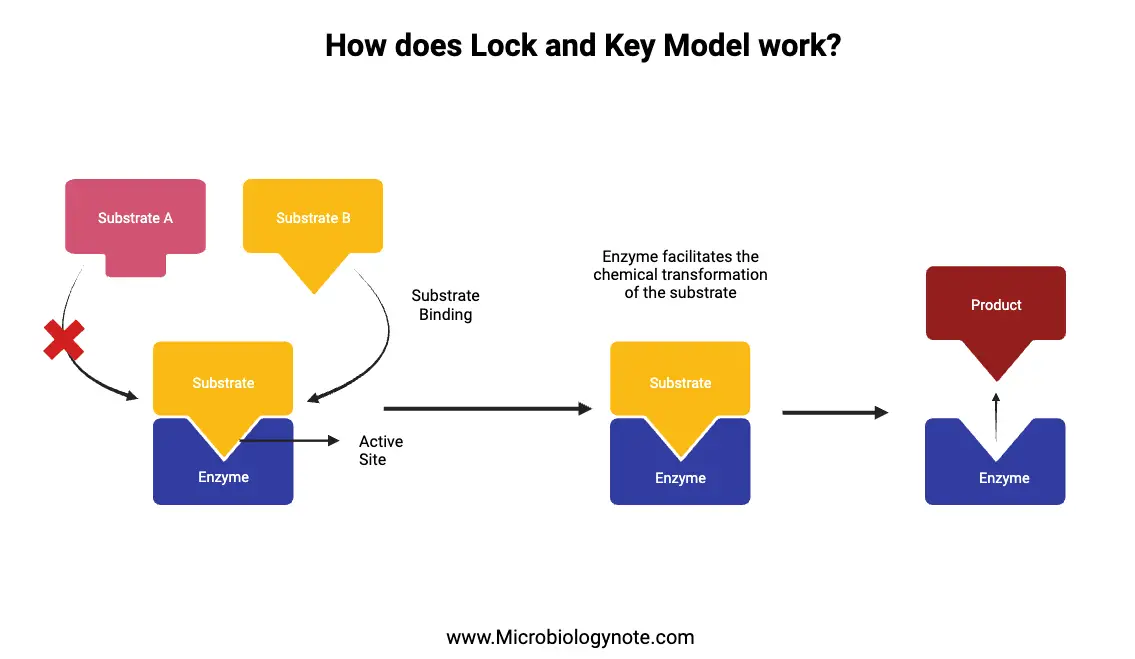
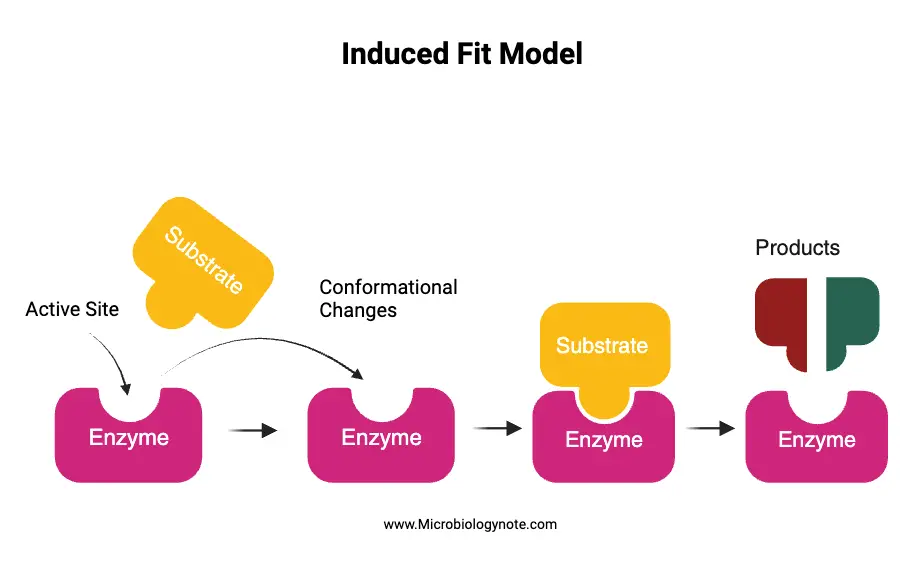
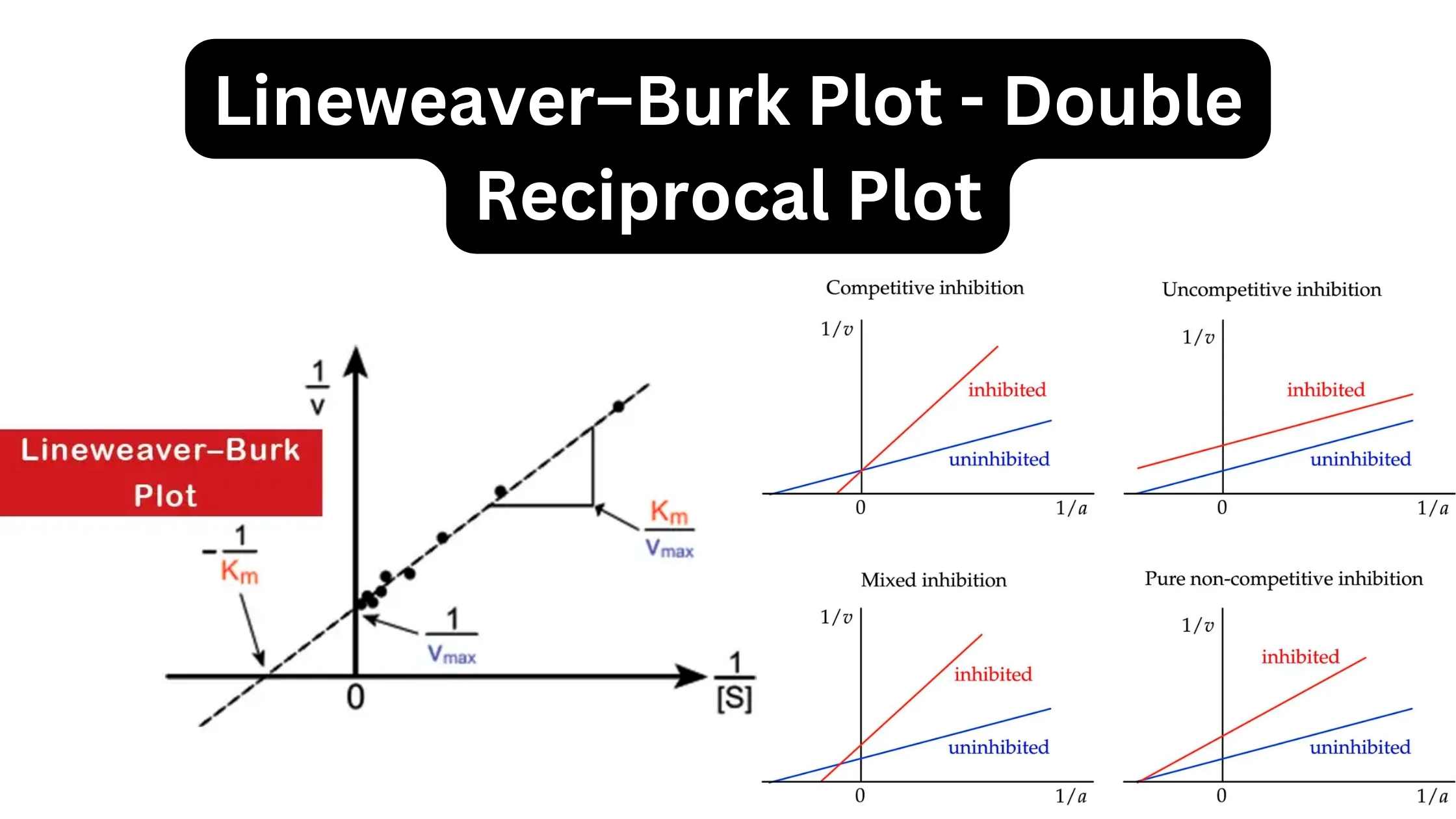
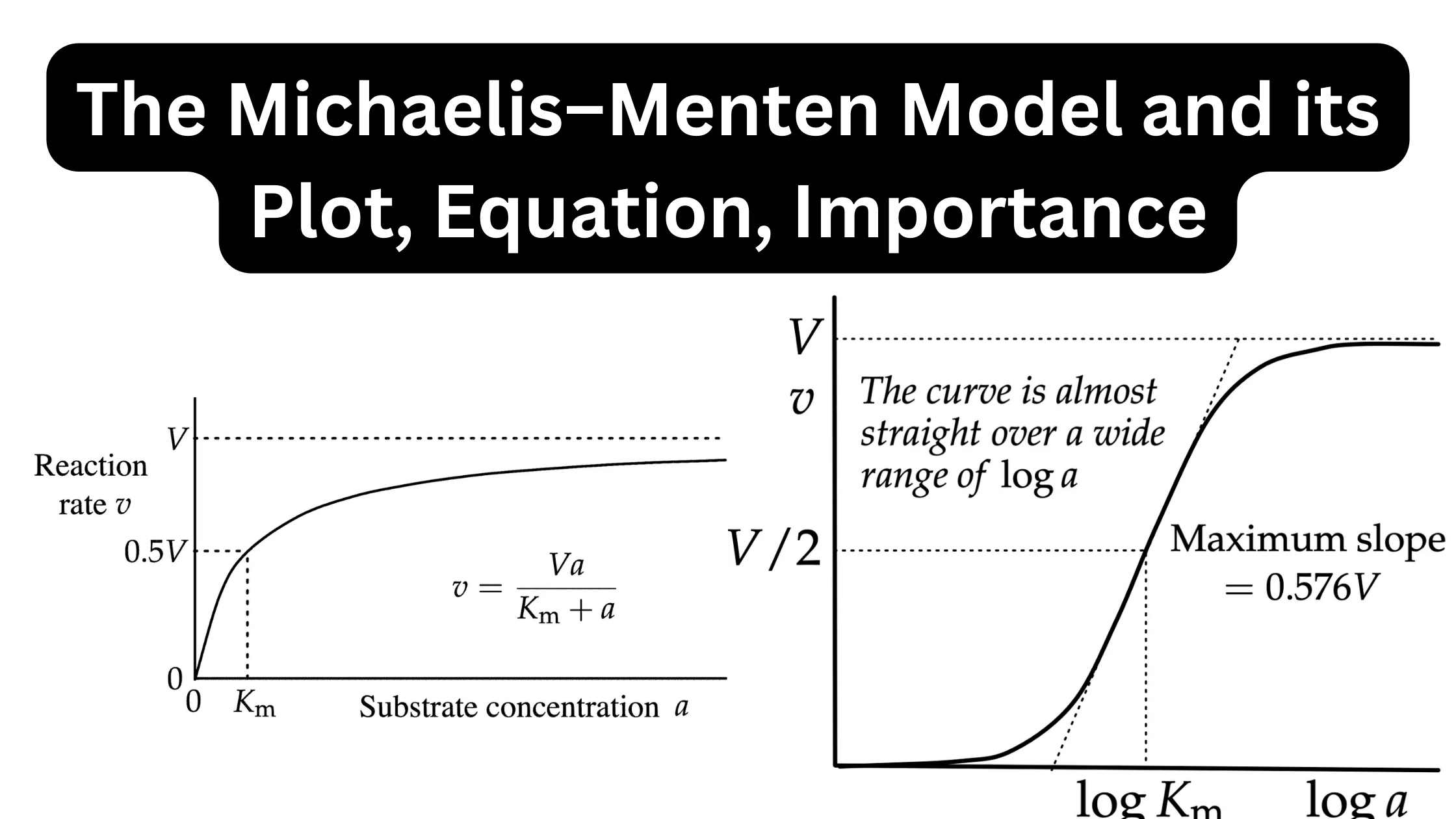
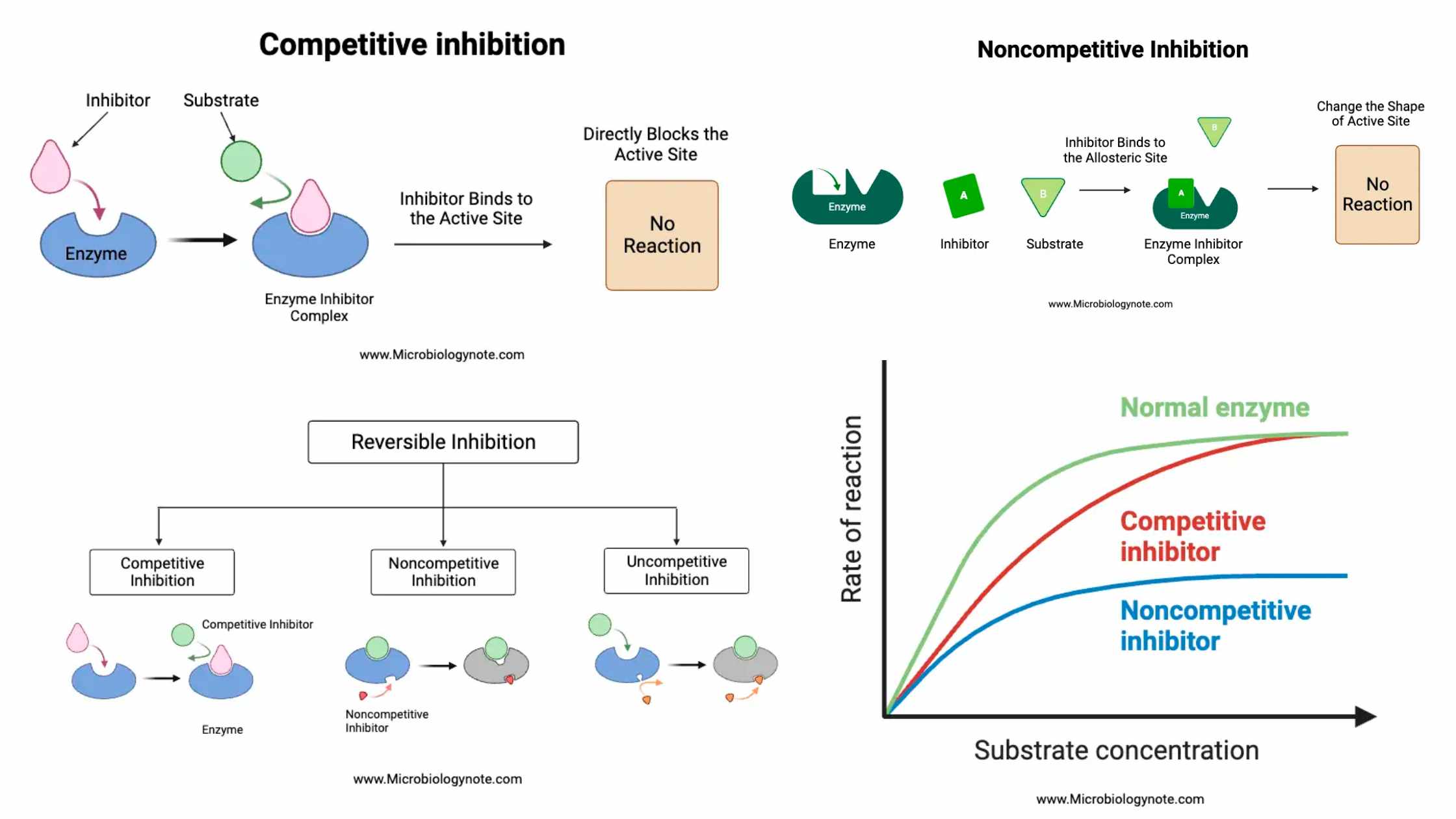
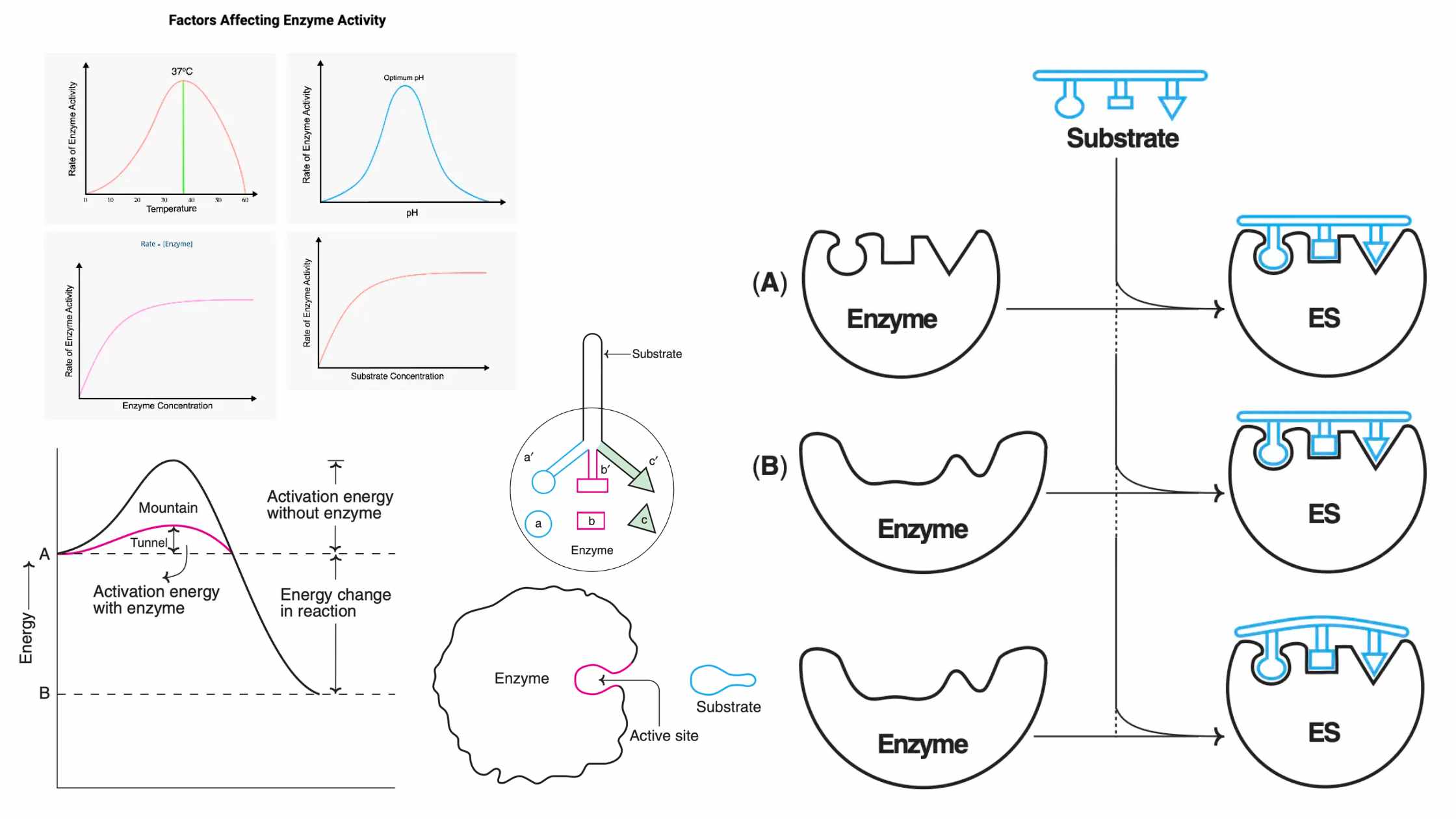
Classification of Protein On the Basis of Structure, Composition, Functions
What is Protein? Classification of protein On the Basis of Structure 1. Fibrous protein Fibrous proteins are a distinct category of proteins characterized by their elongated or fiber-like structure. These proteins are primarily found in animals and play specific roles in structural support. Therefore, understanding their nature, structure, and function is essential for a comprehensive … Read more