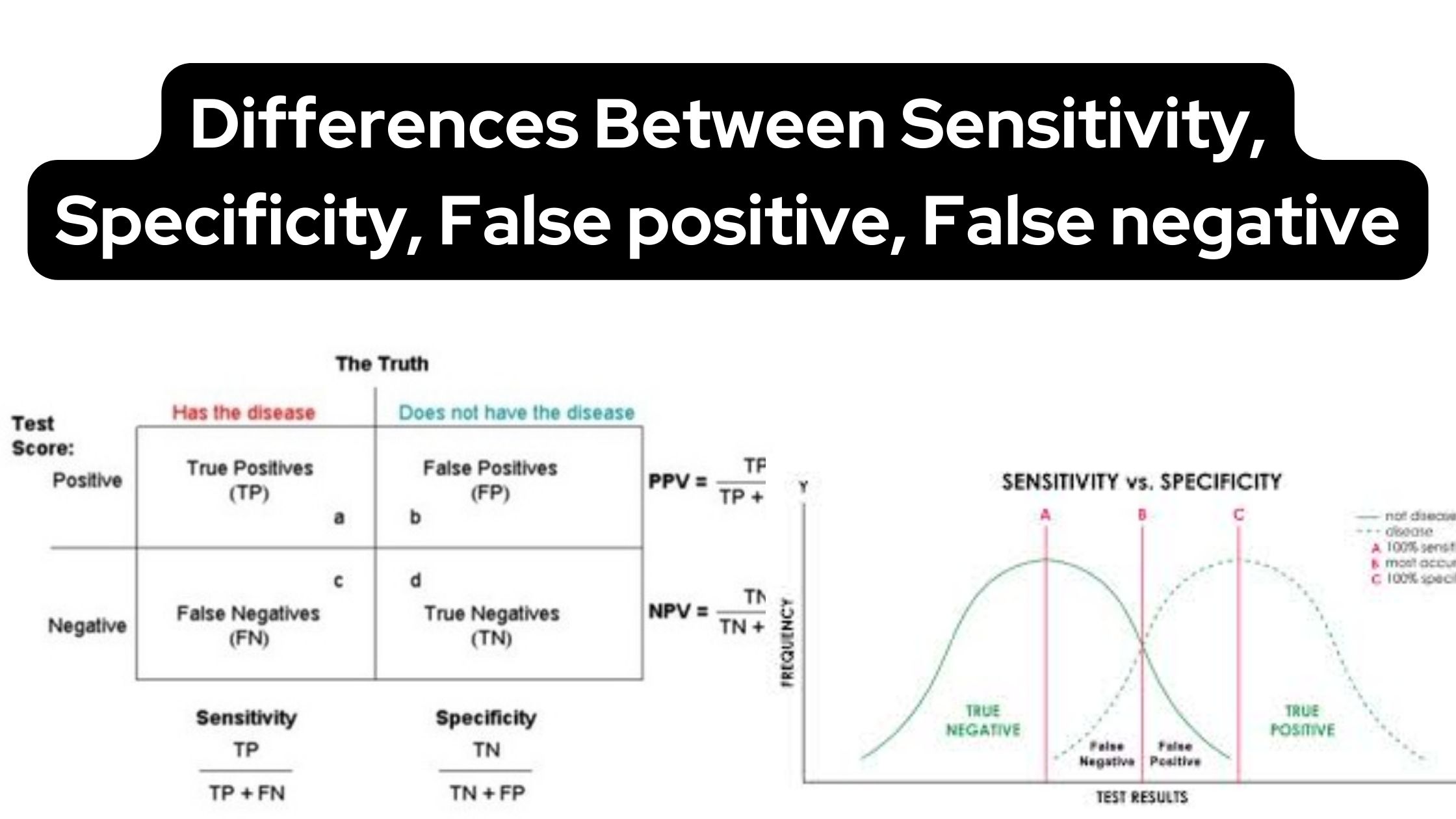
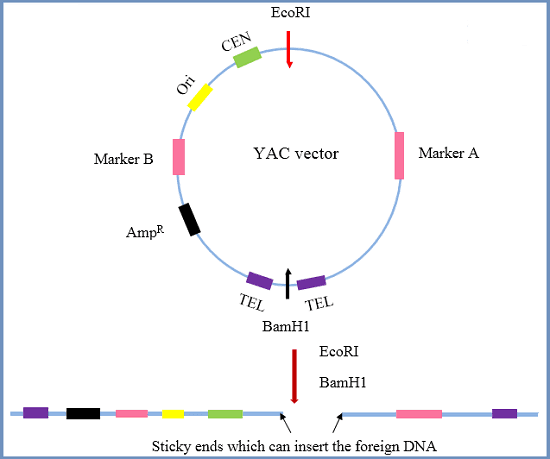
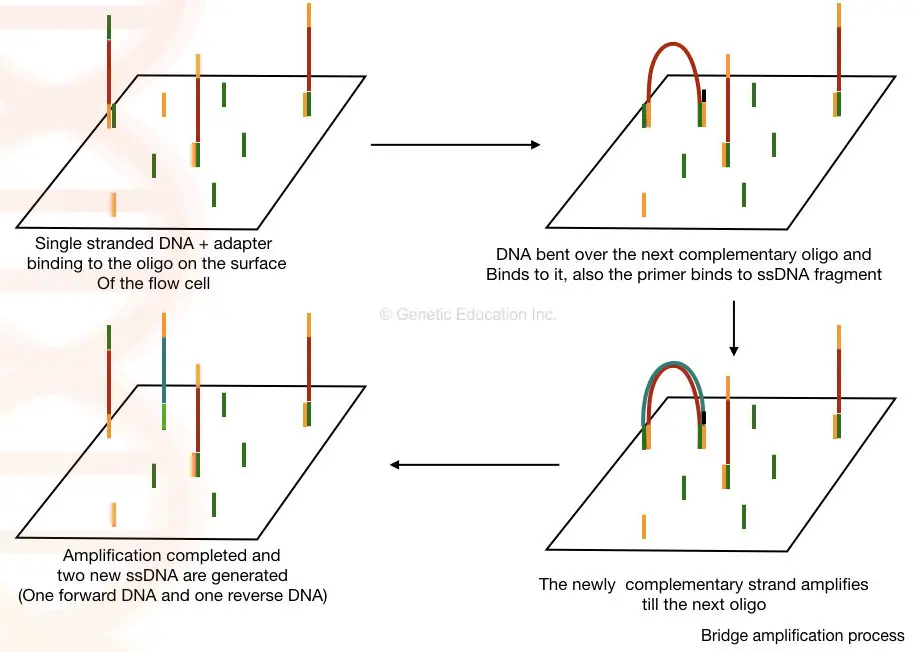
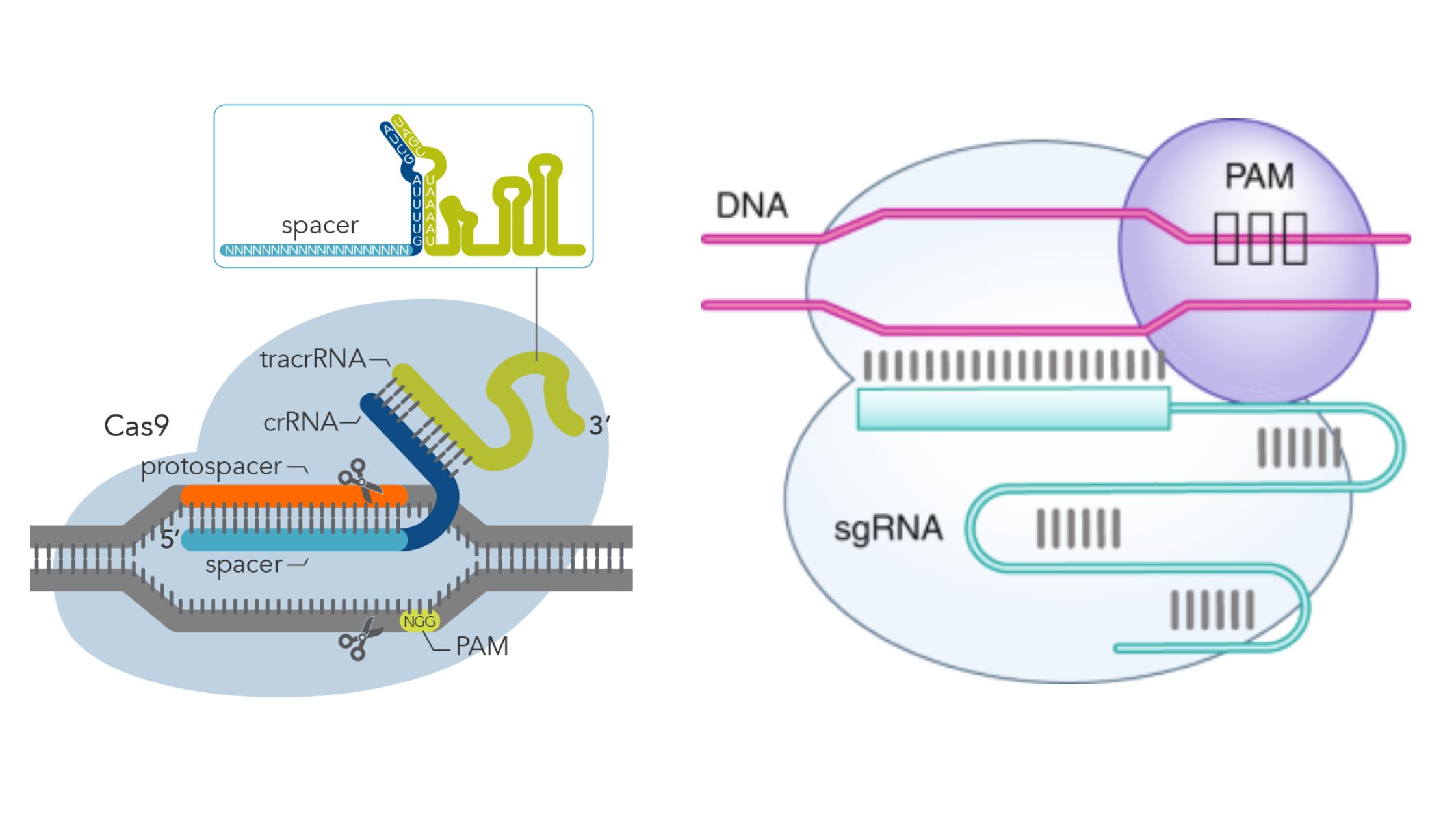
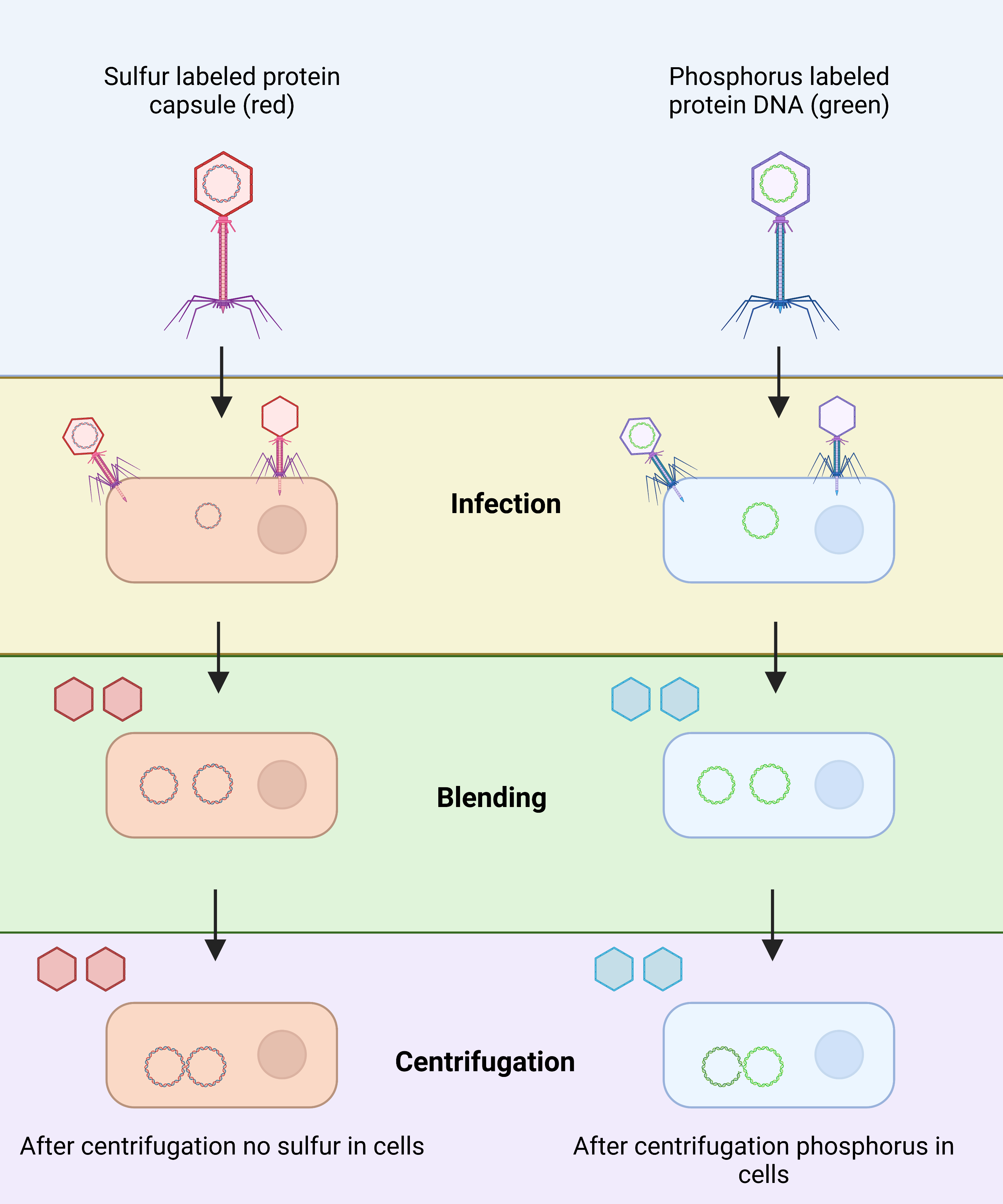
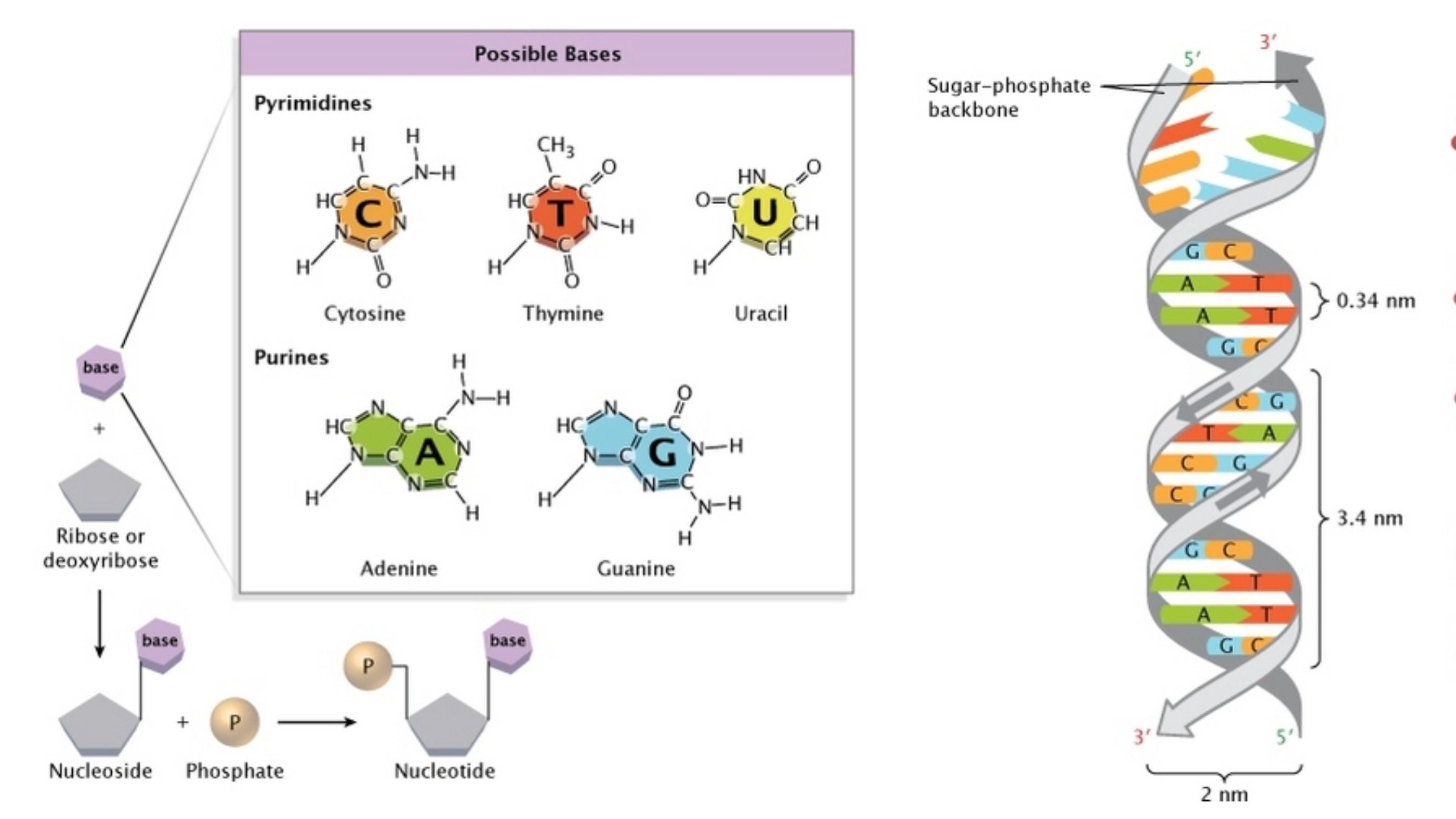
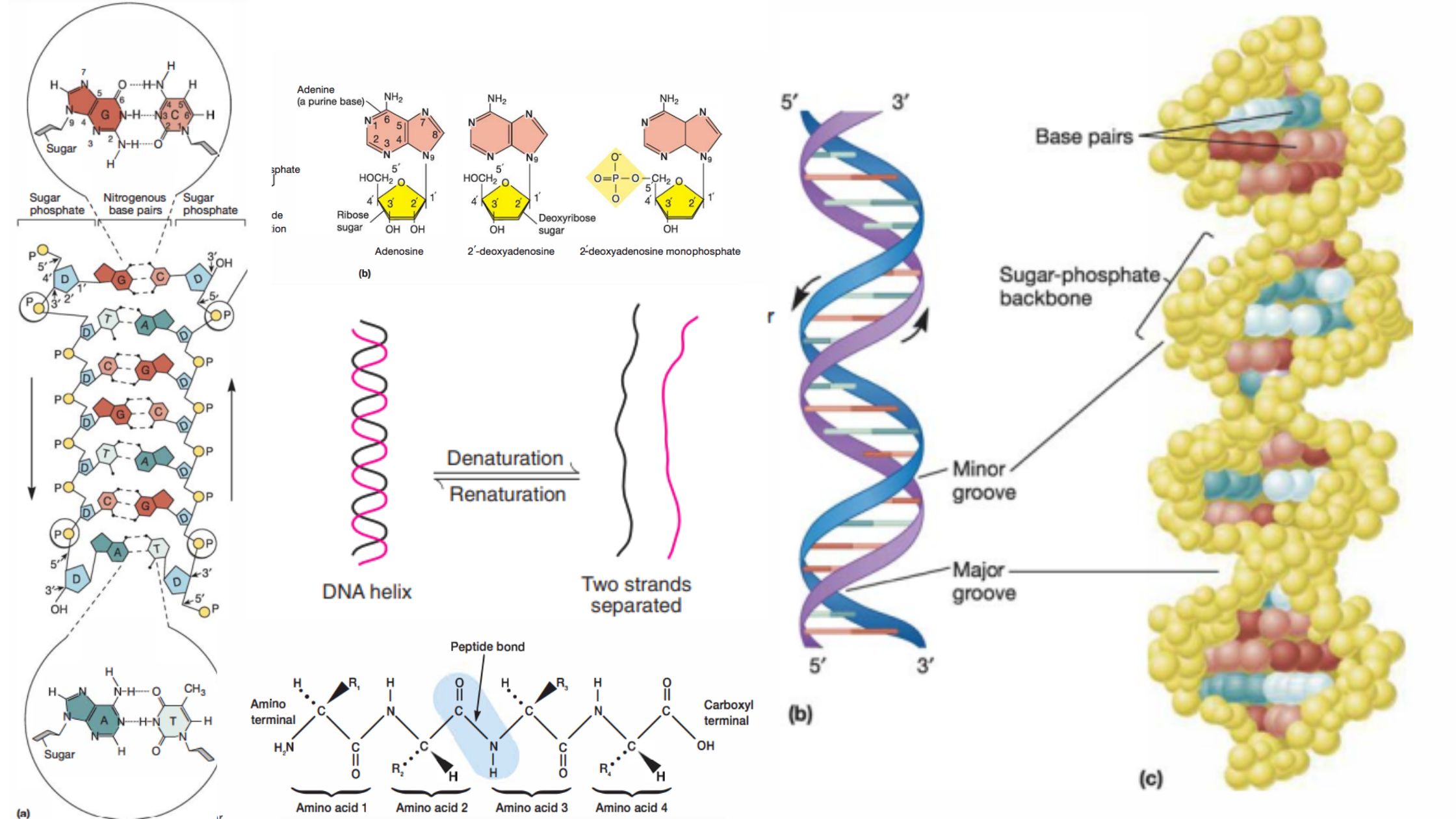
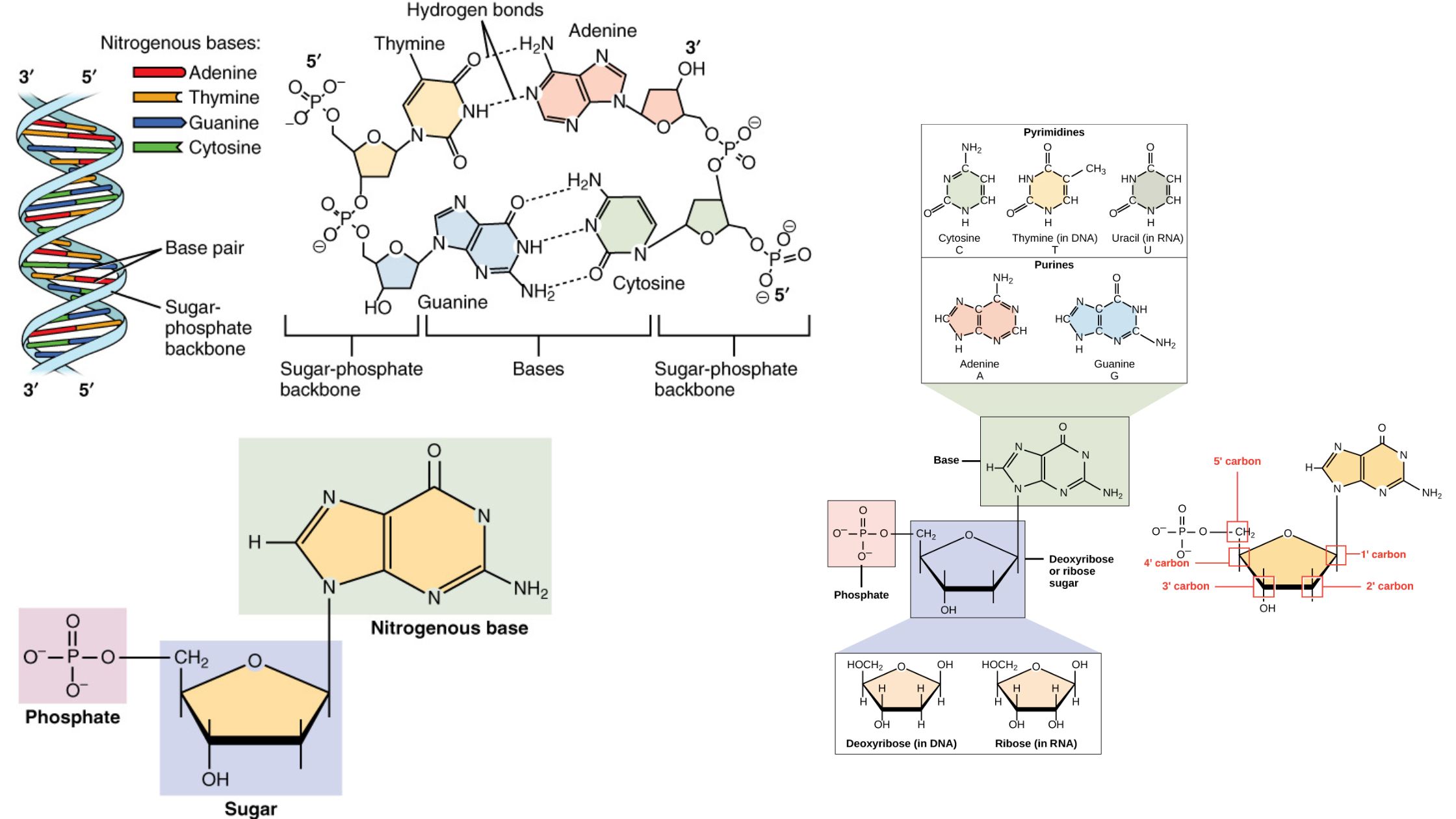
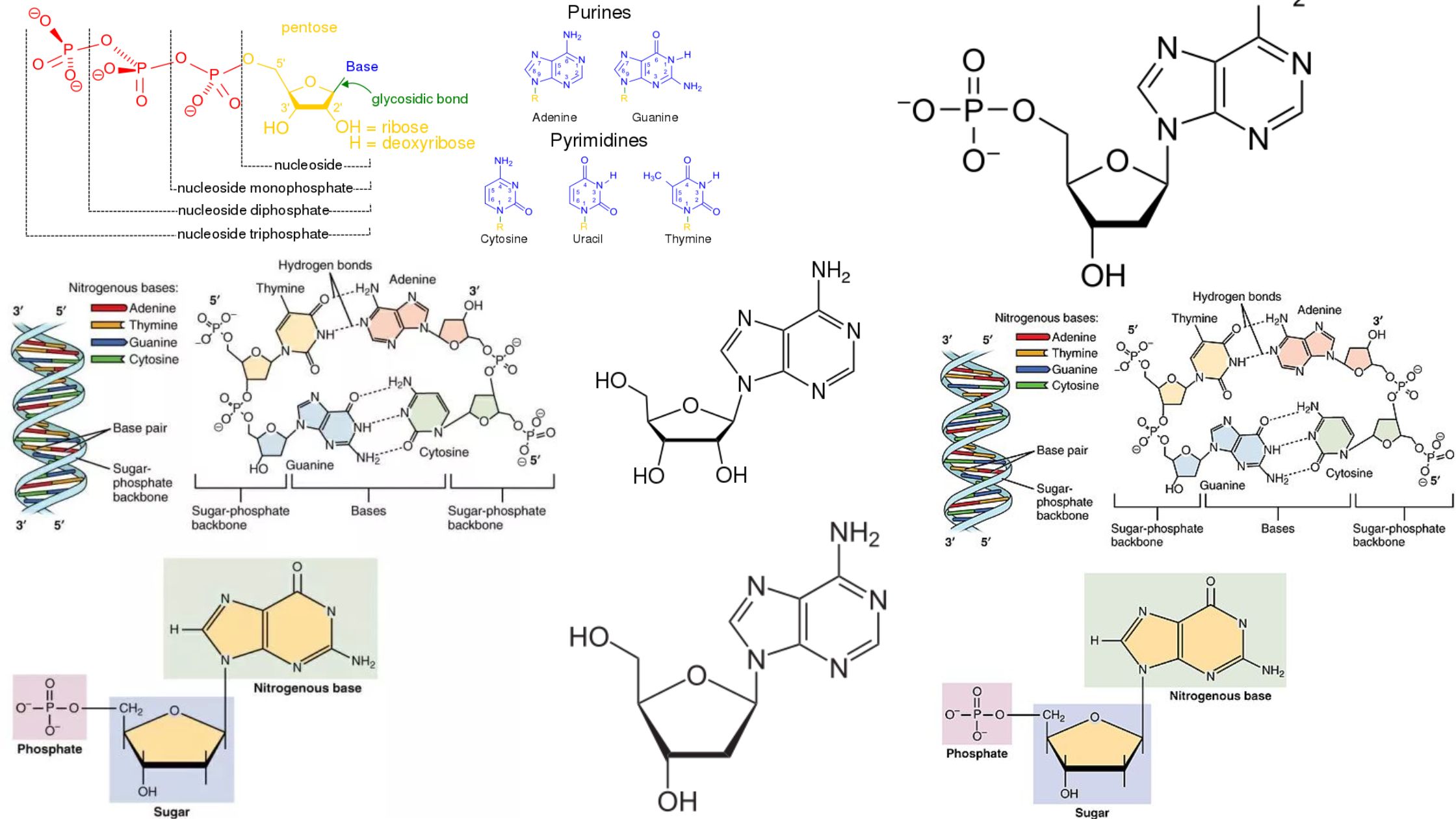
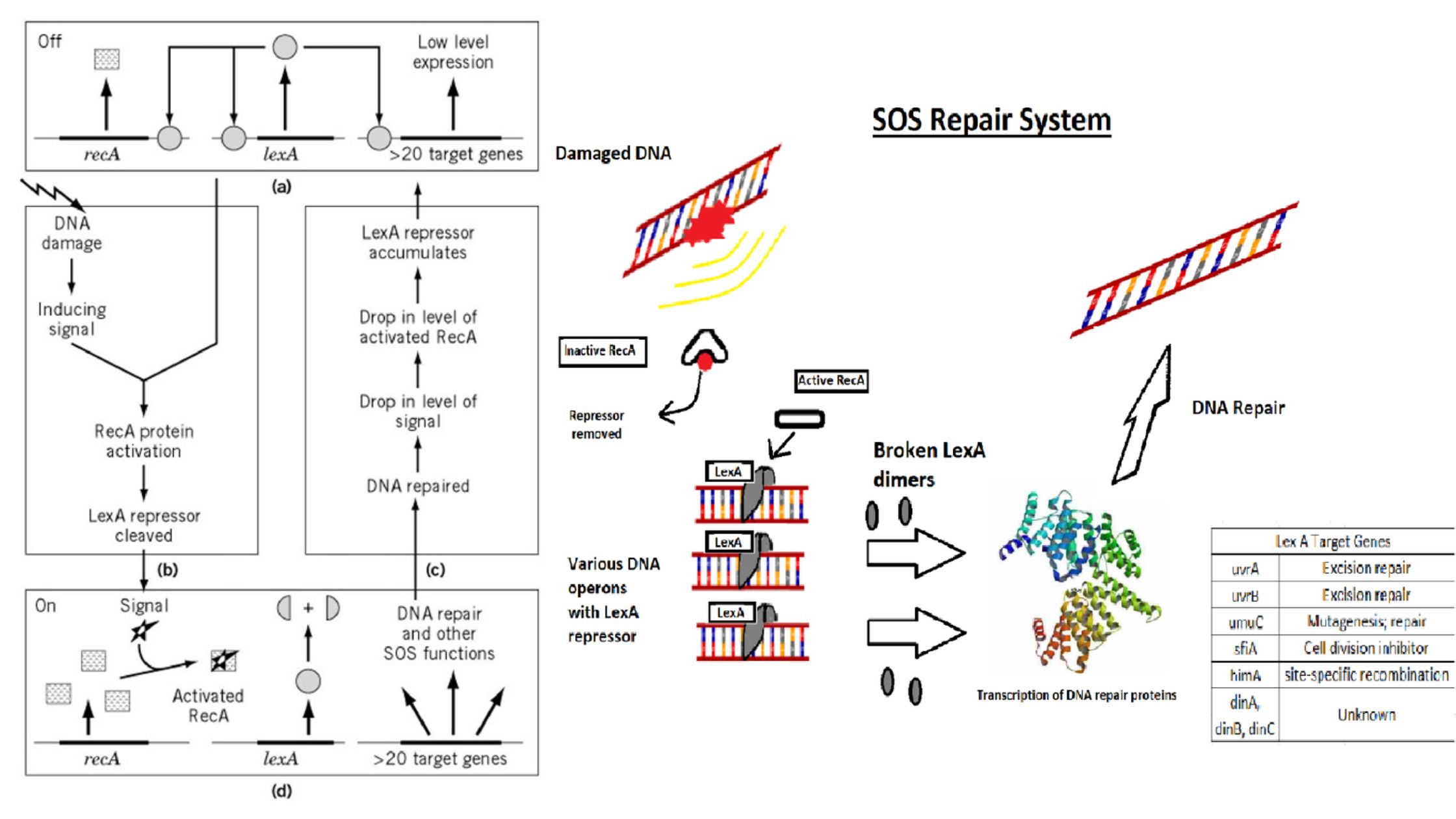
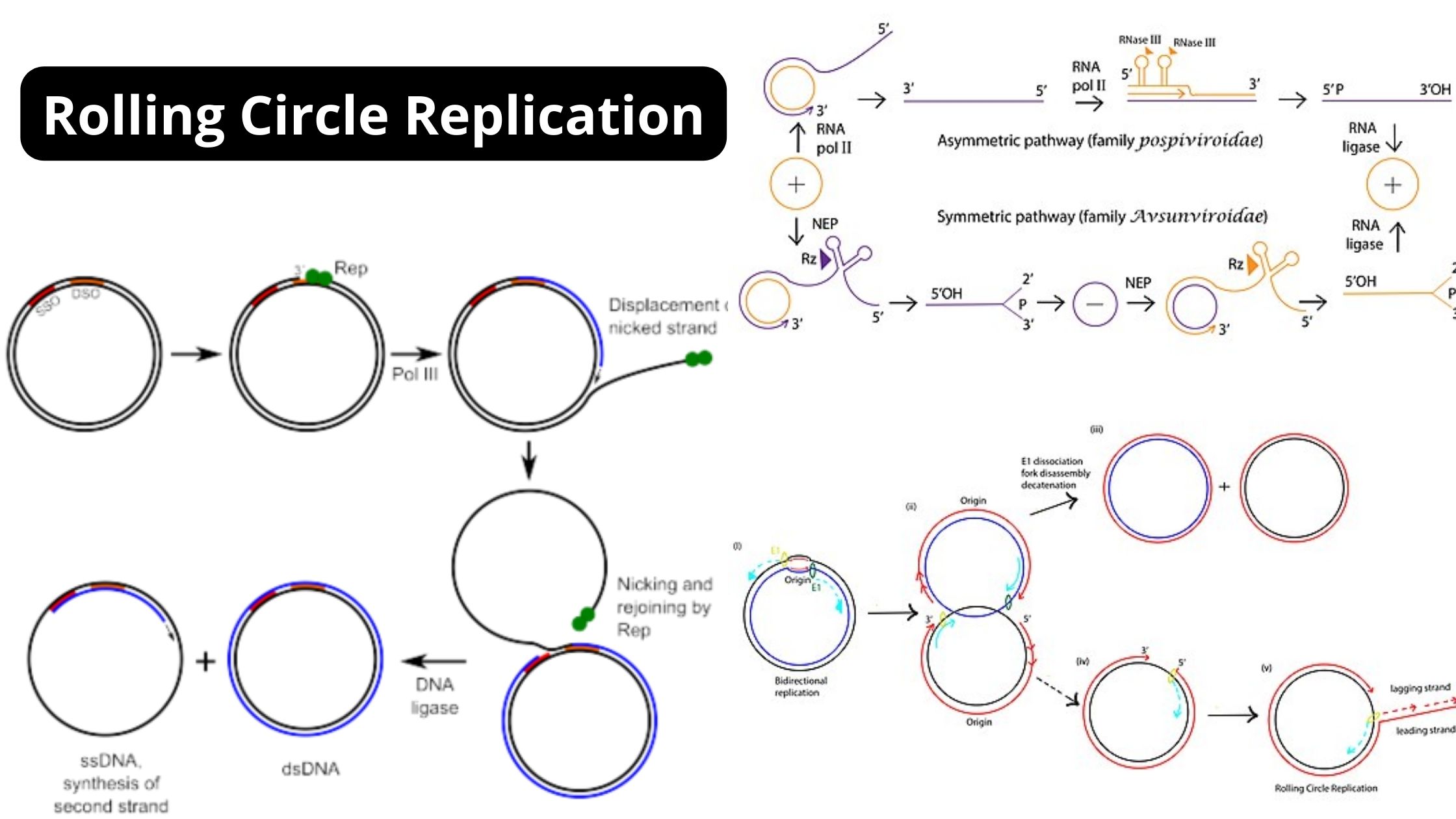
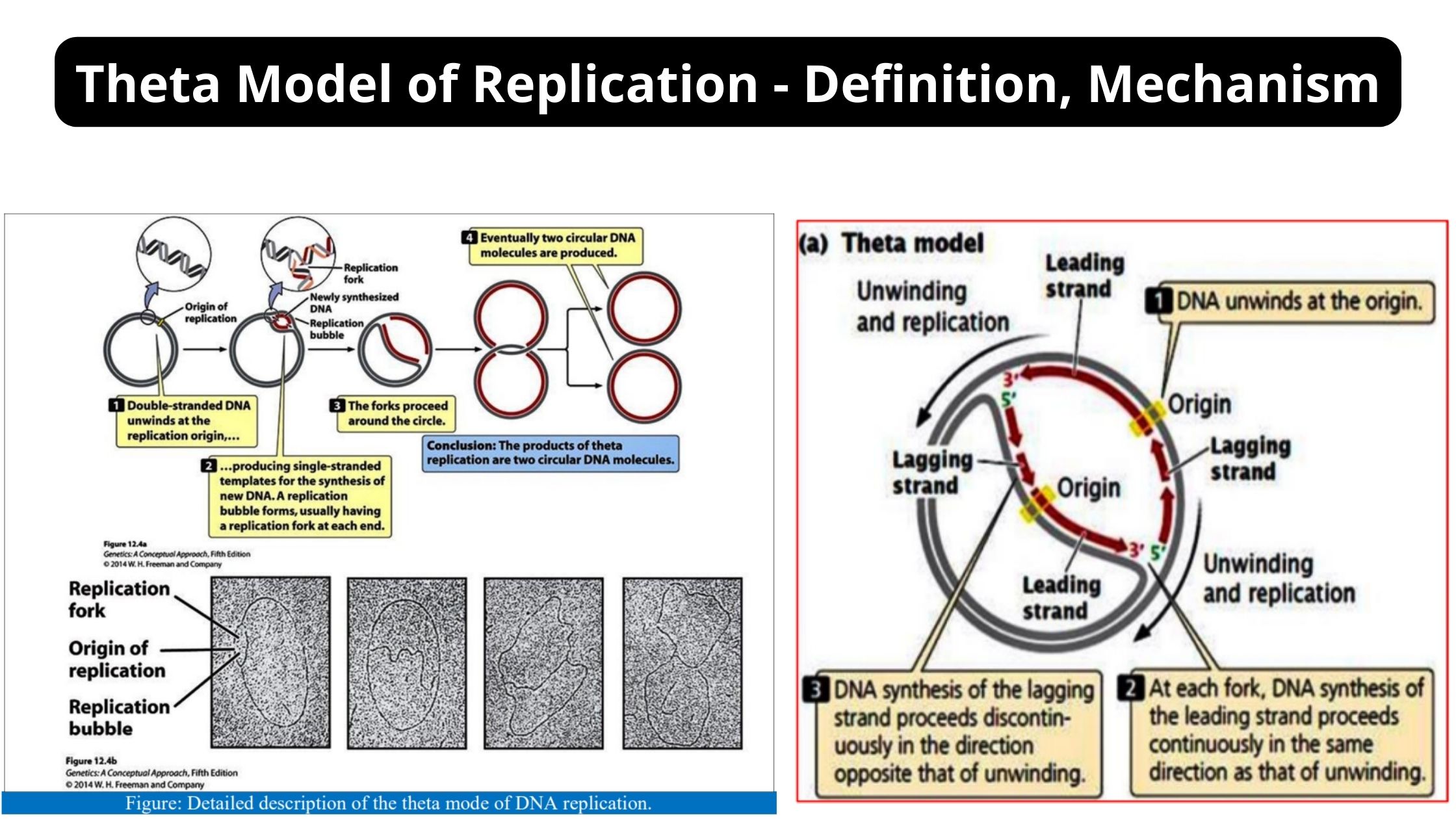
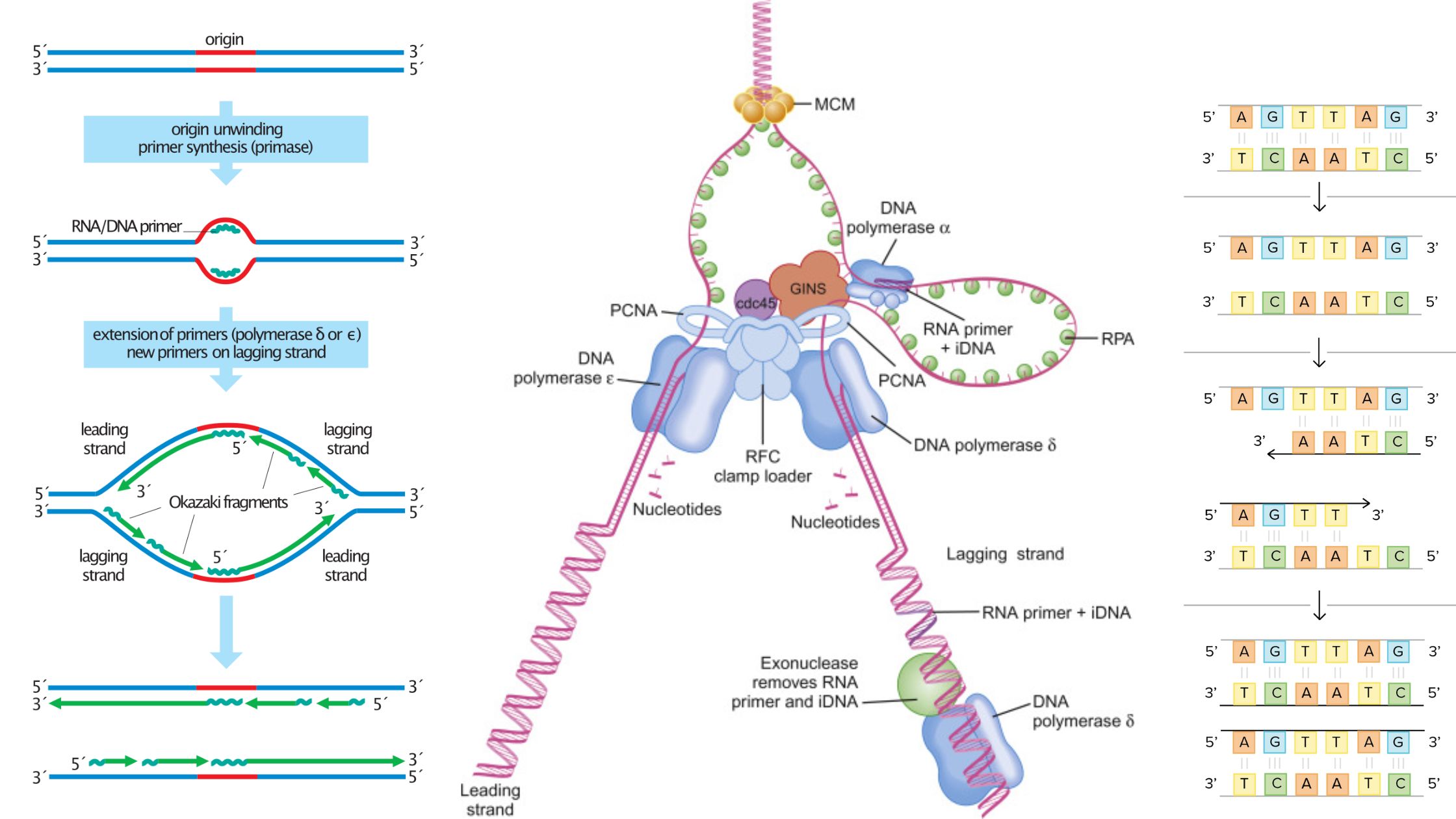
Bacterial Conjugation – Definition, Steps, Methods
Bacterial conjugation is the transfer of genetic material between bacterial cells through direct cell-to-cell contact or a bridge-like connection.This is accomplished via a pilus.It is a parasexual mode of bacterial reproduction. Since acterial conjugation involves the exchange of genetic material, it is often compared to sexual reproduction or mating in bacteria. However, this is not … Read more