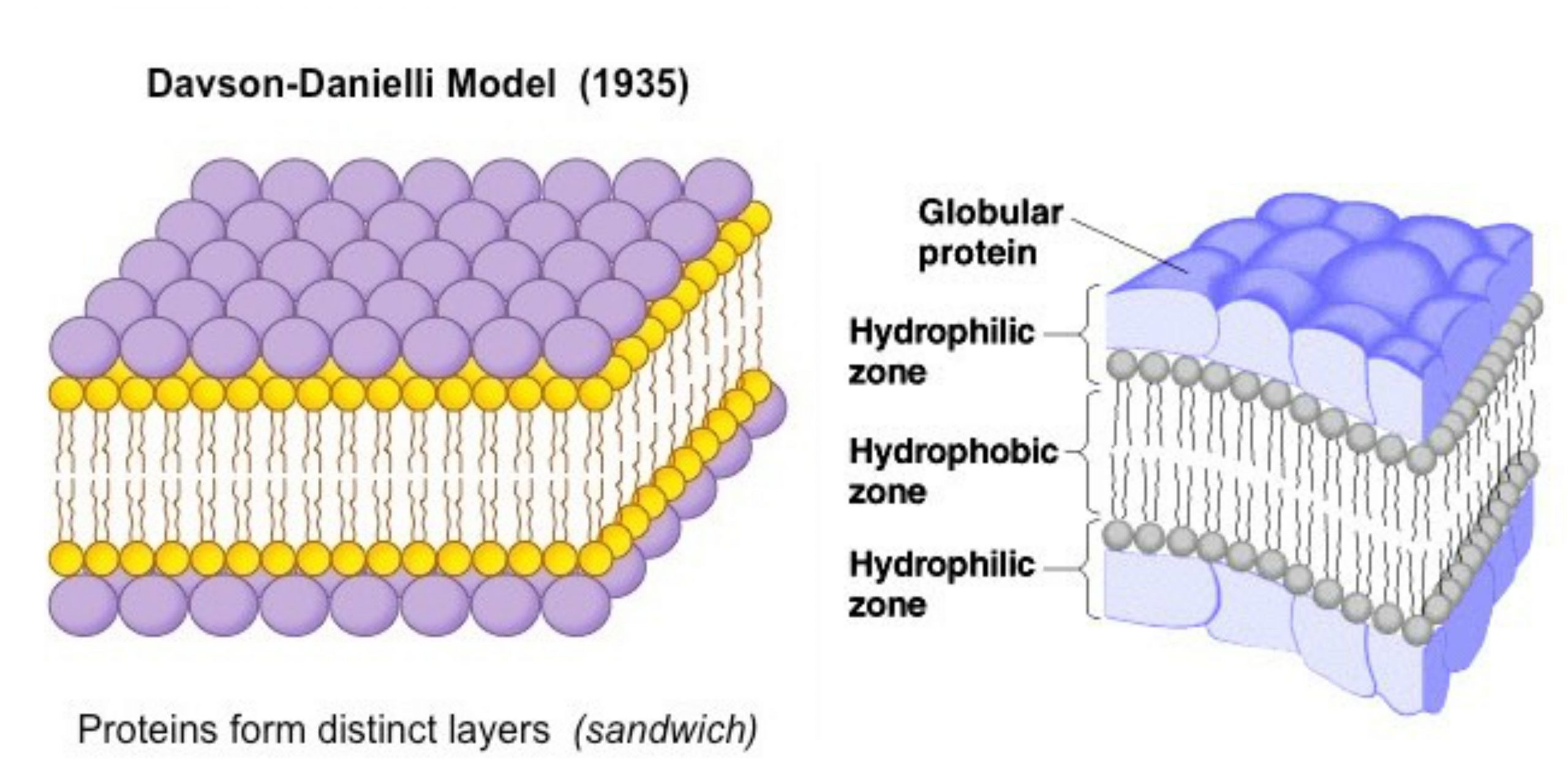
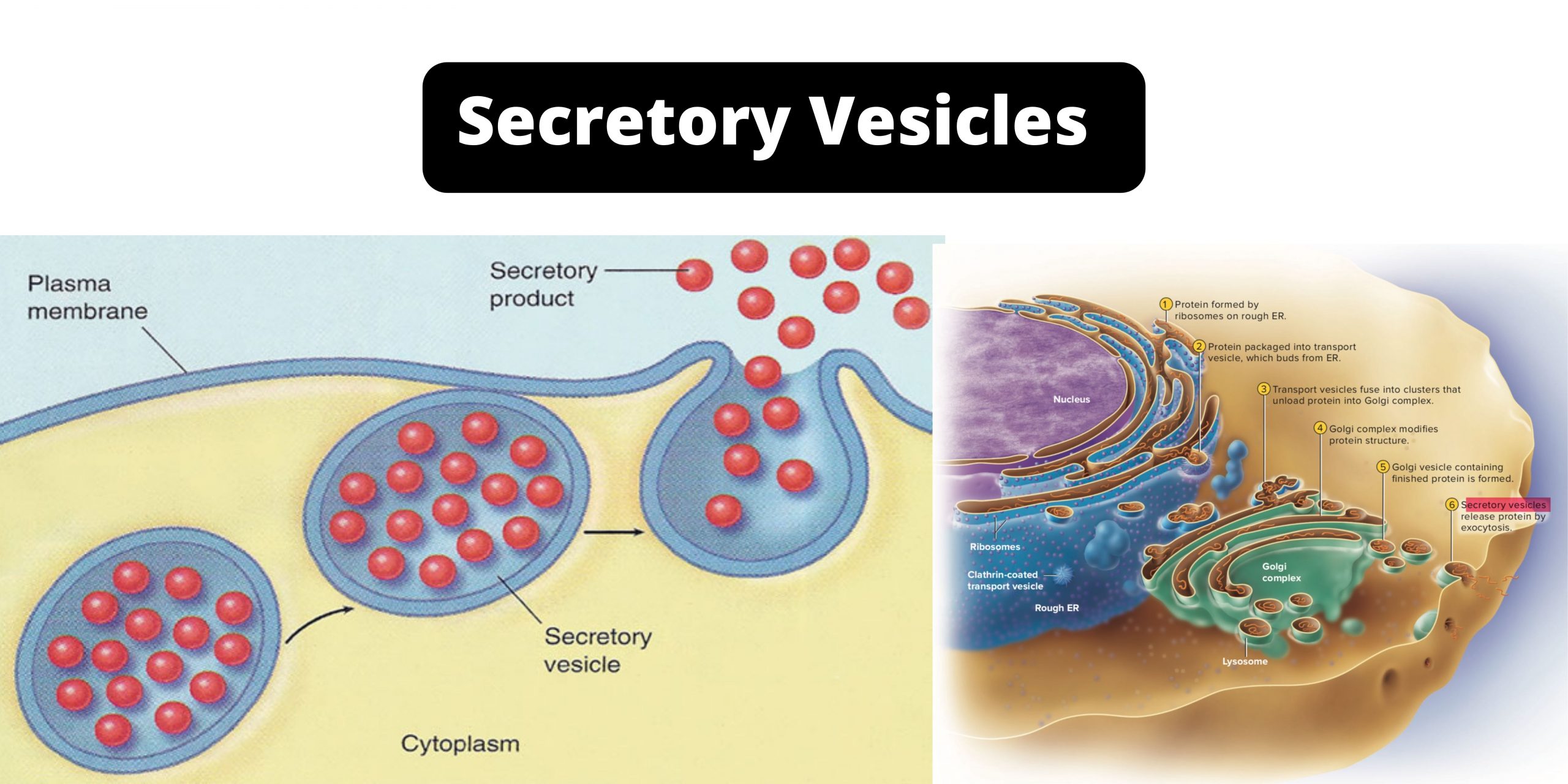
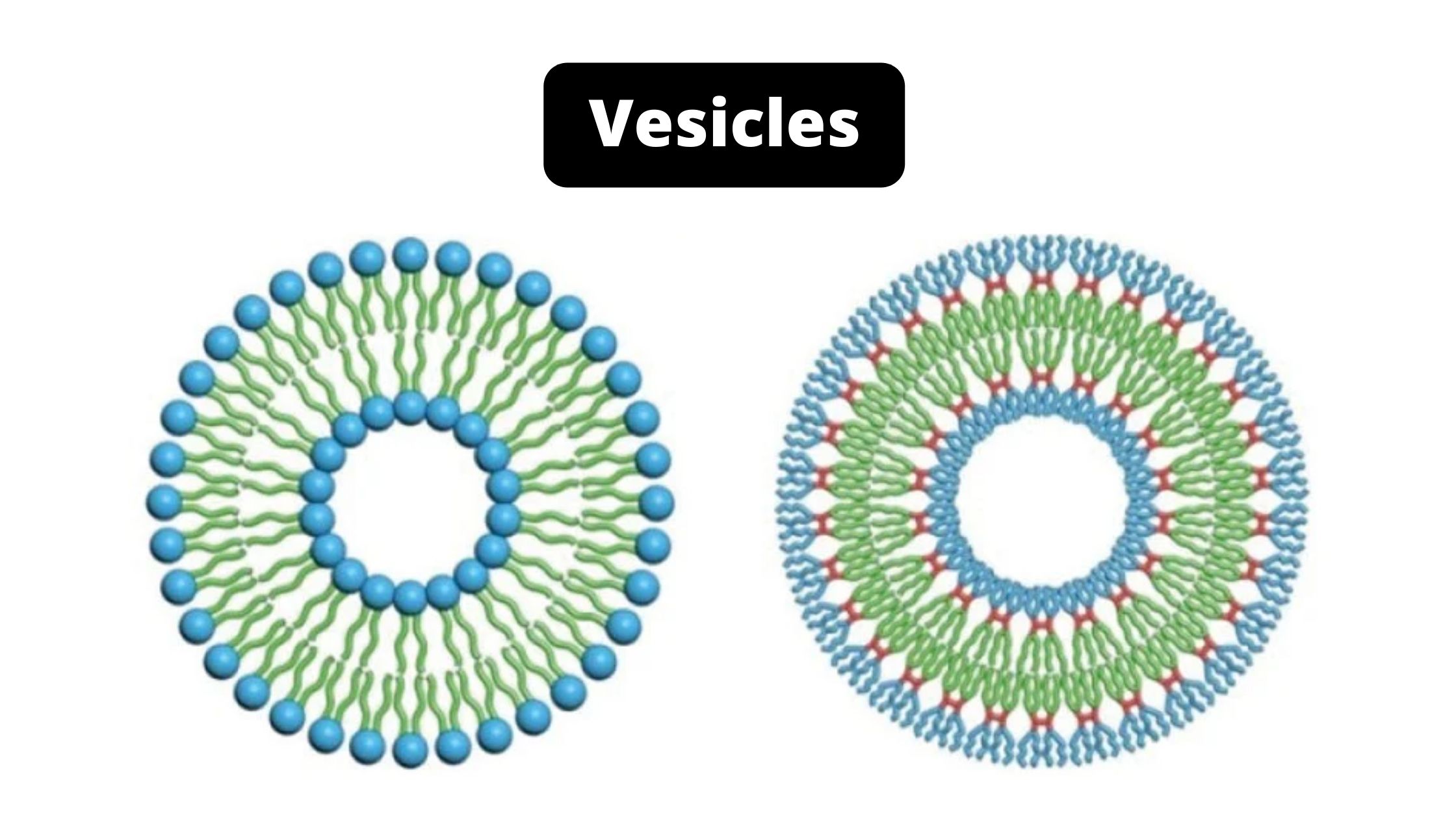
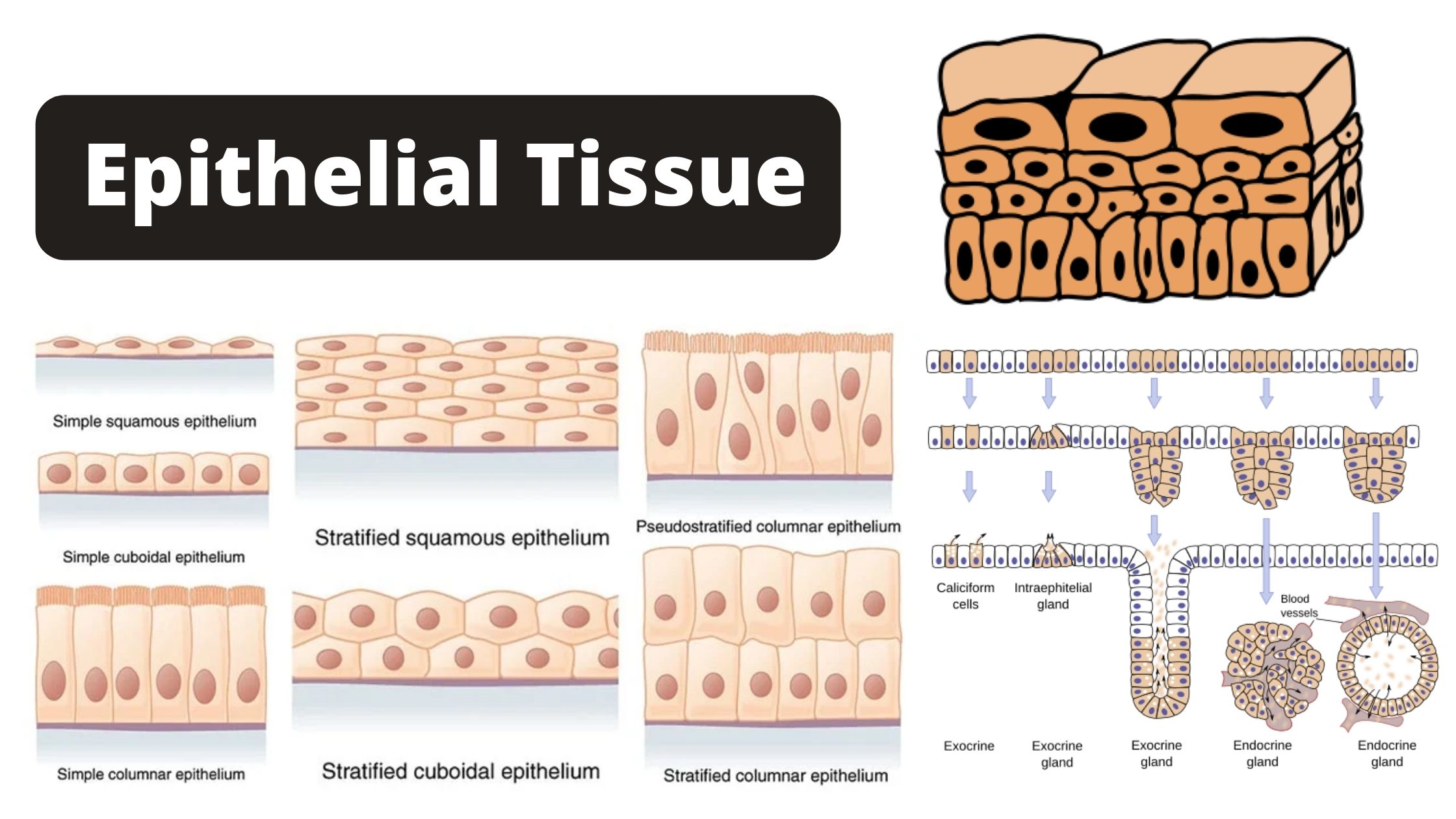
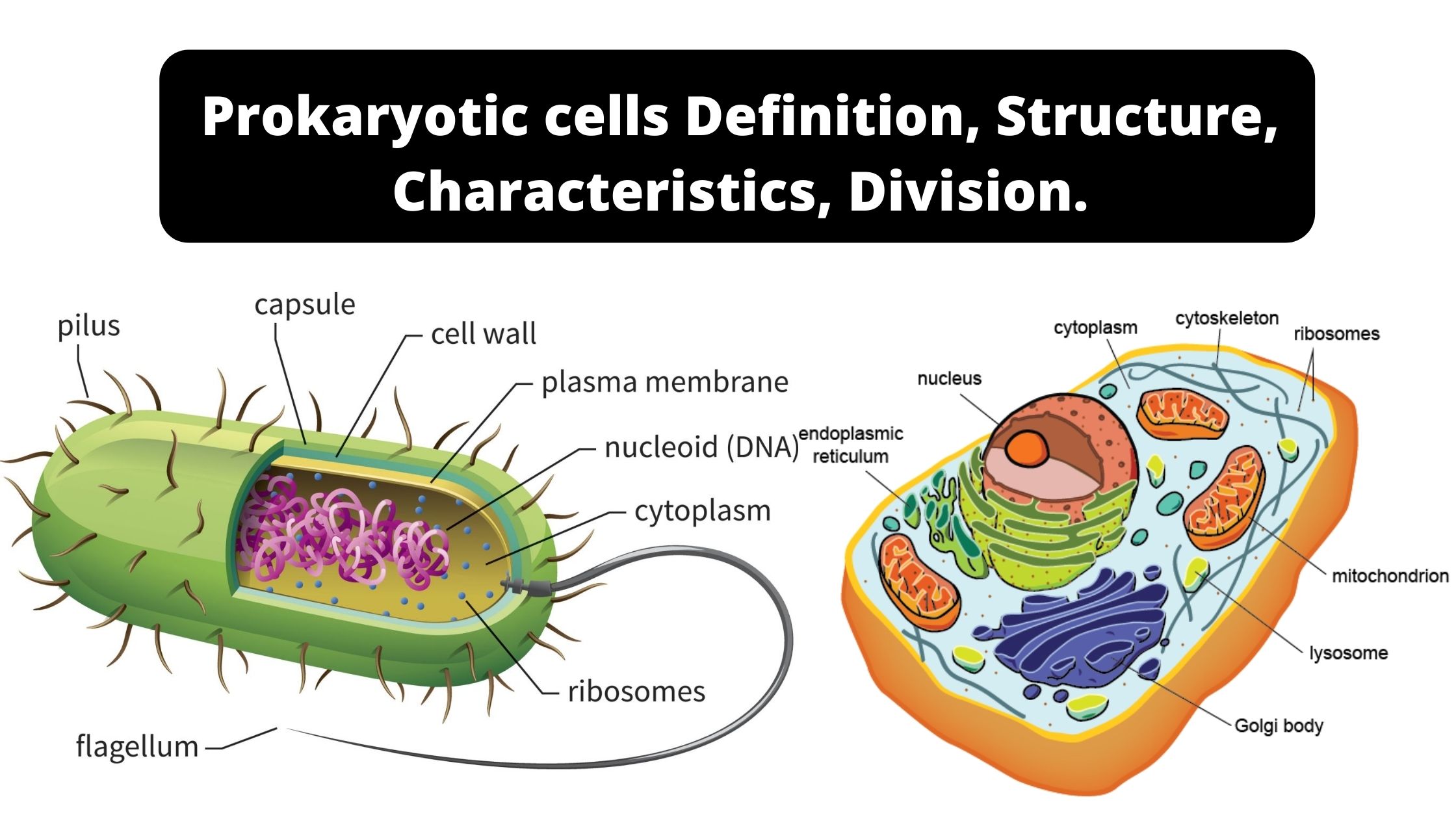
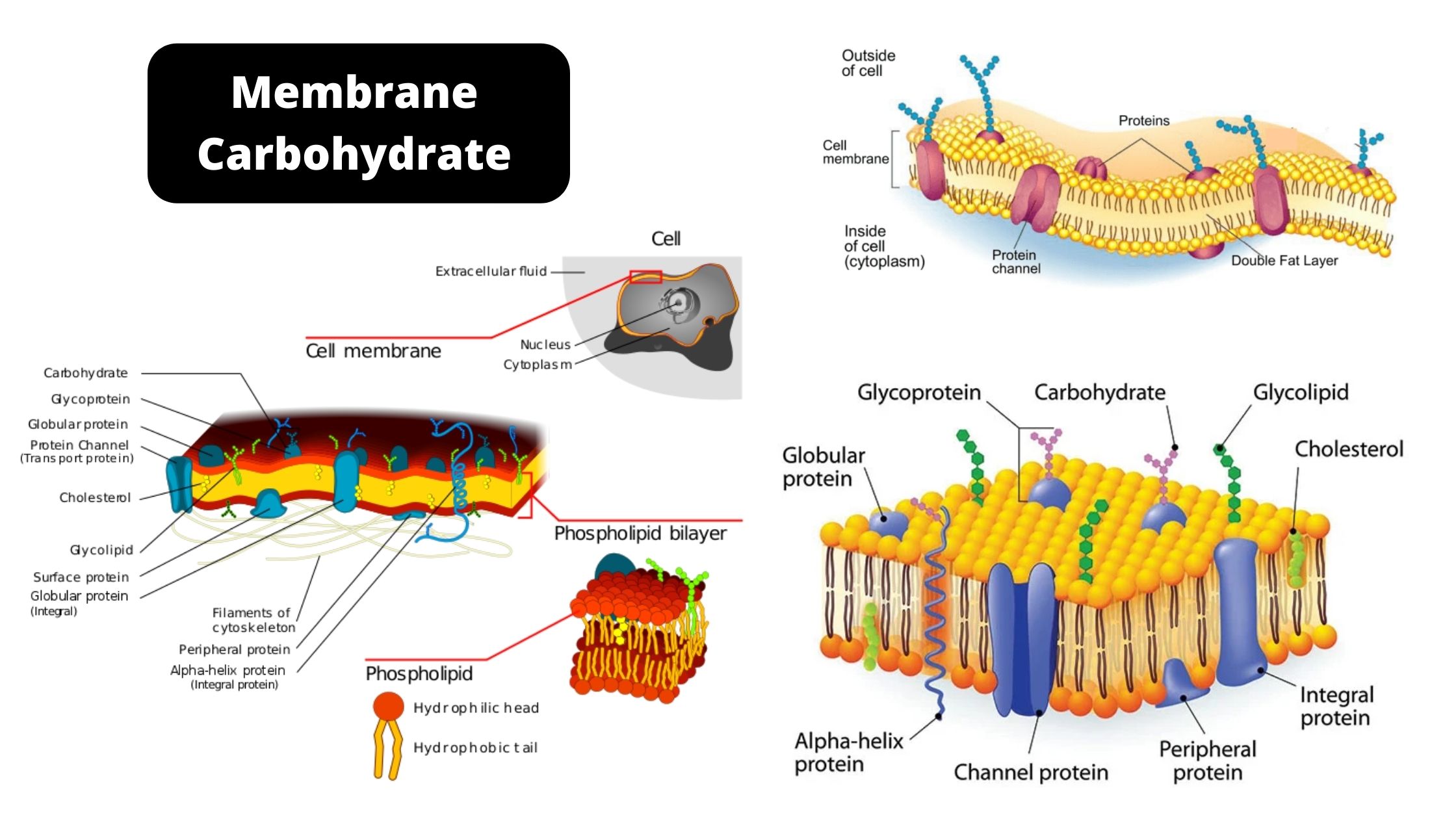
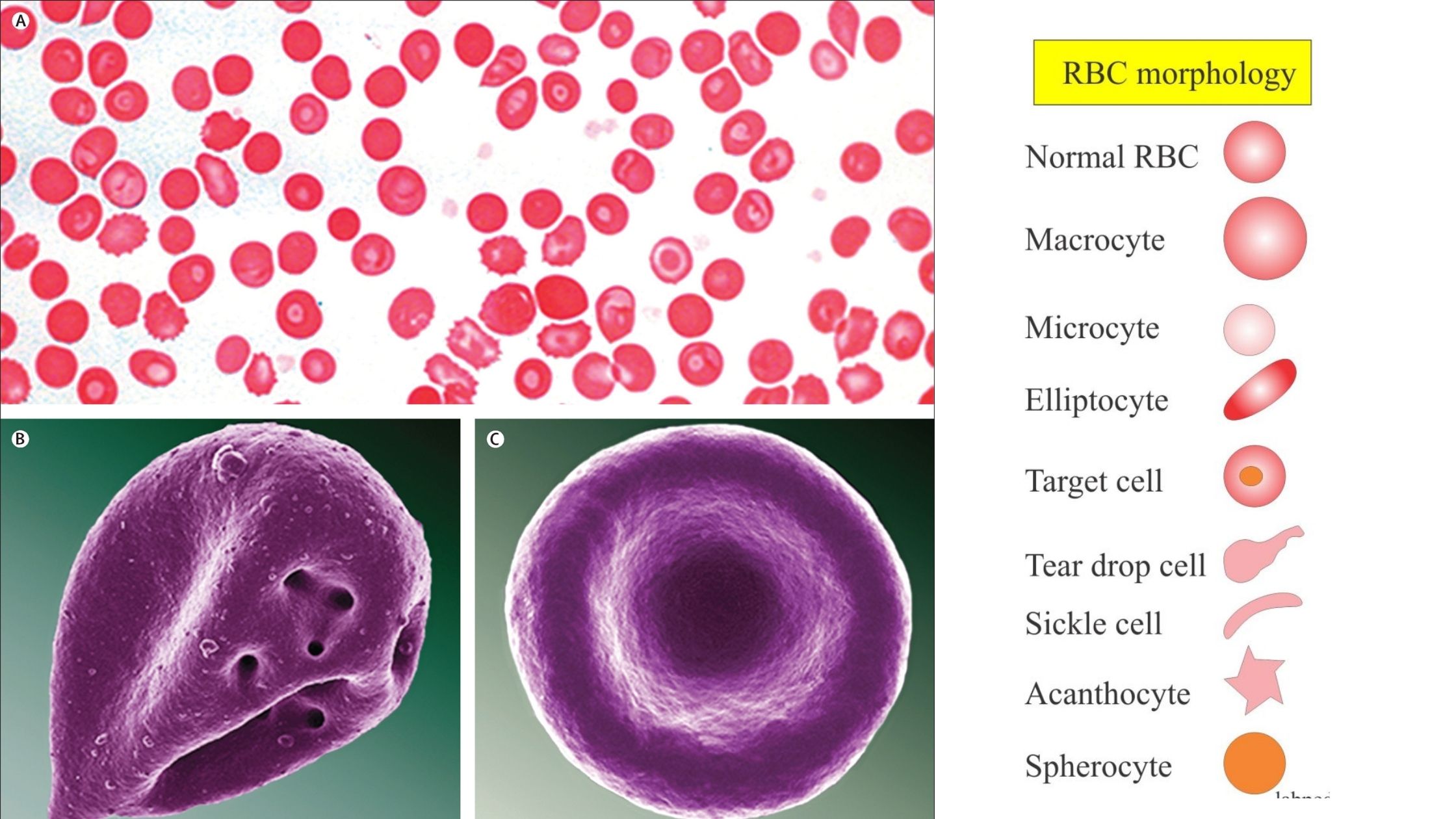
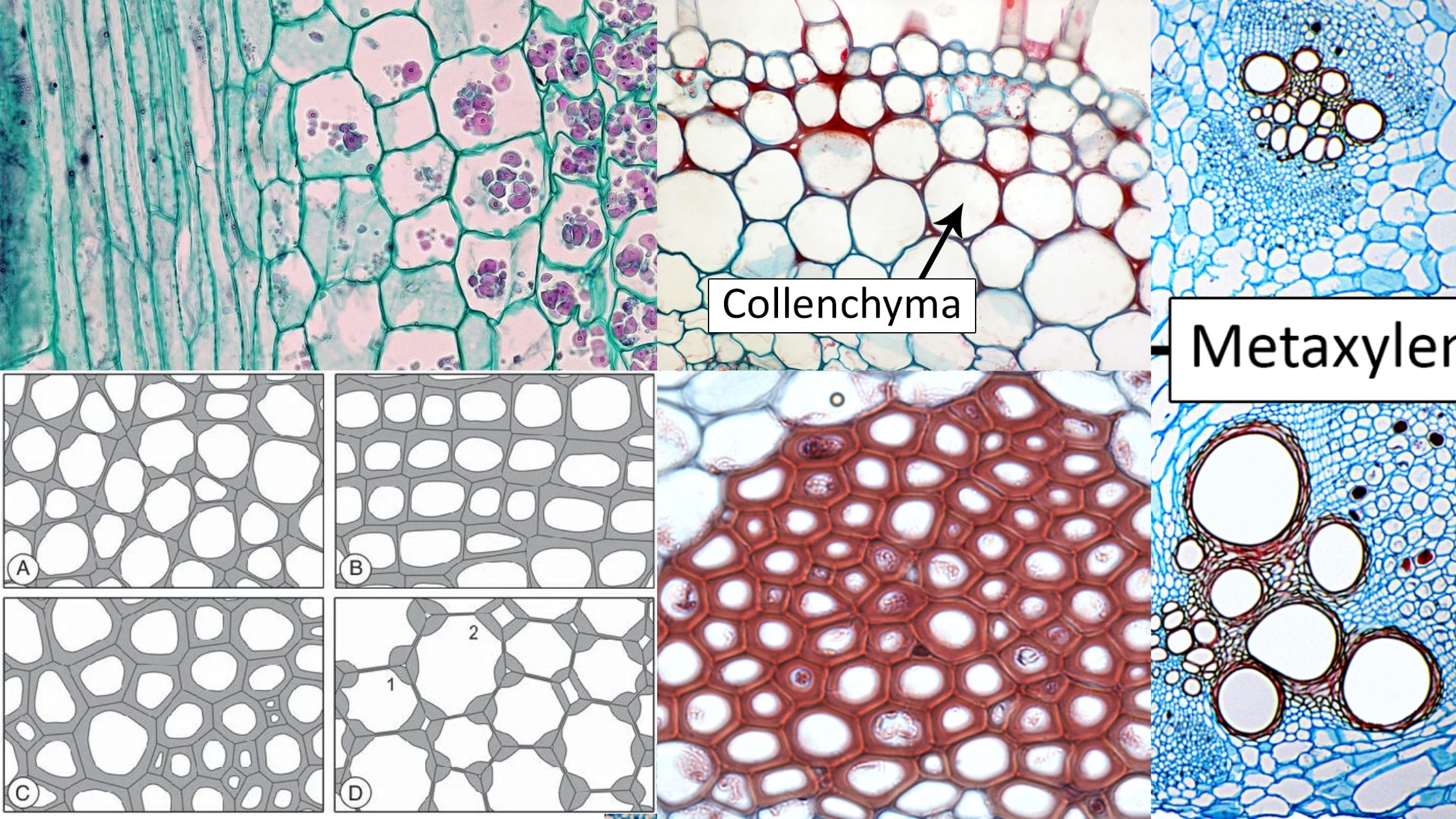
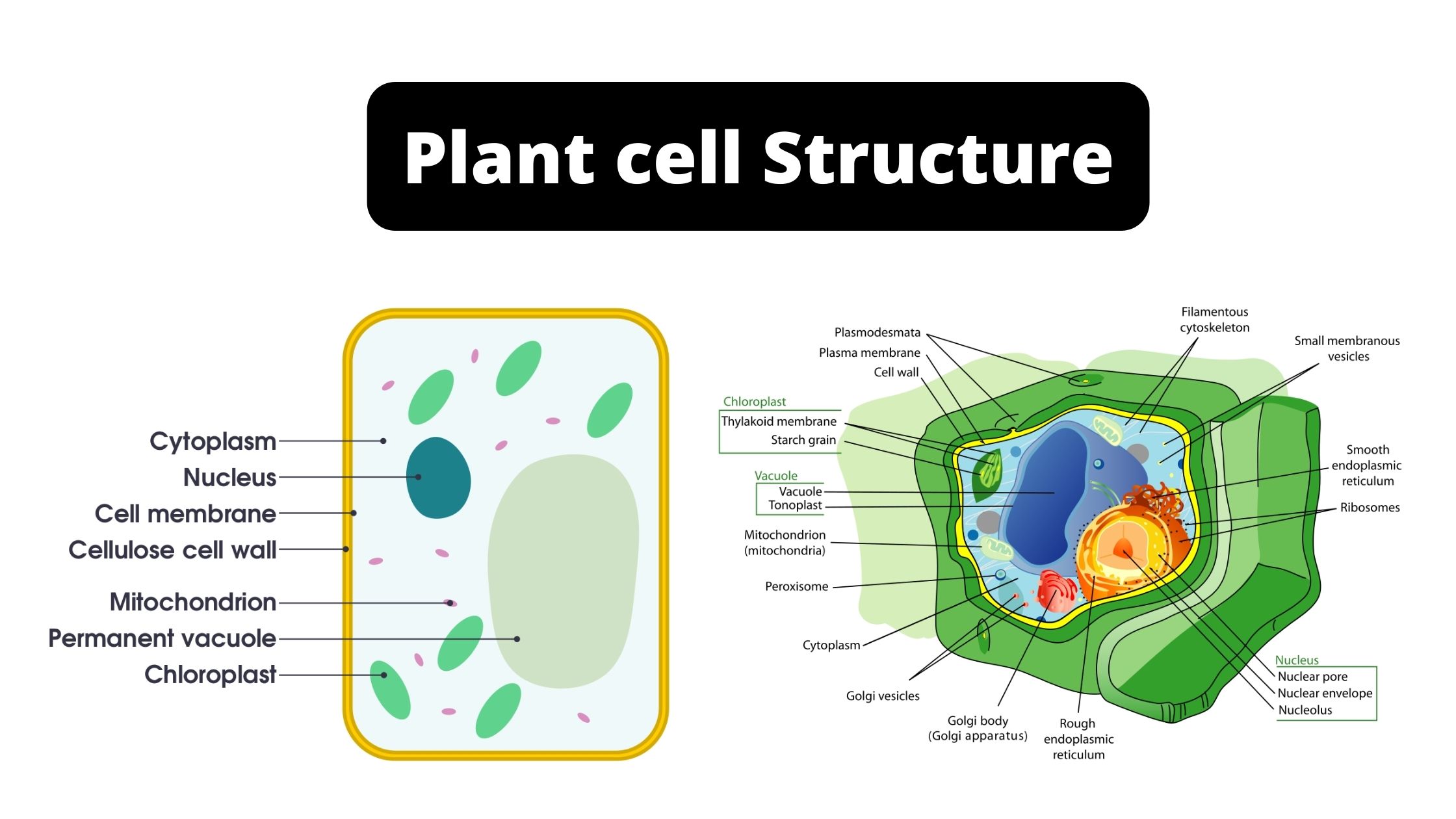
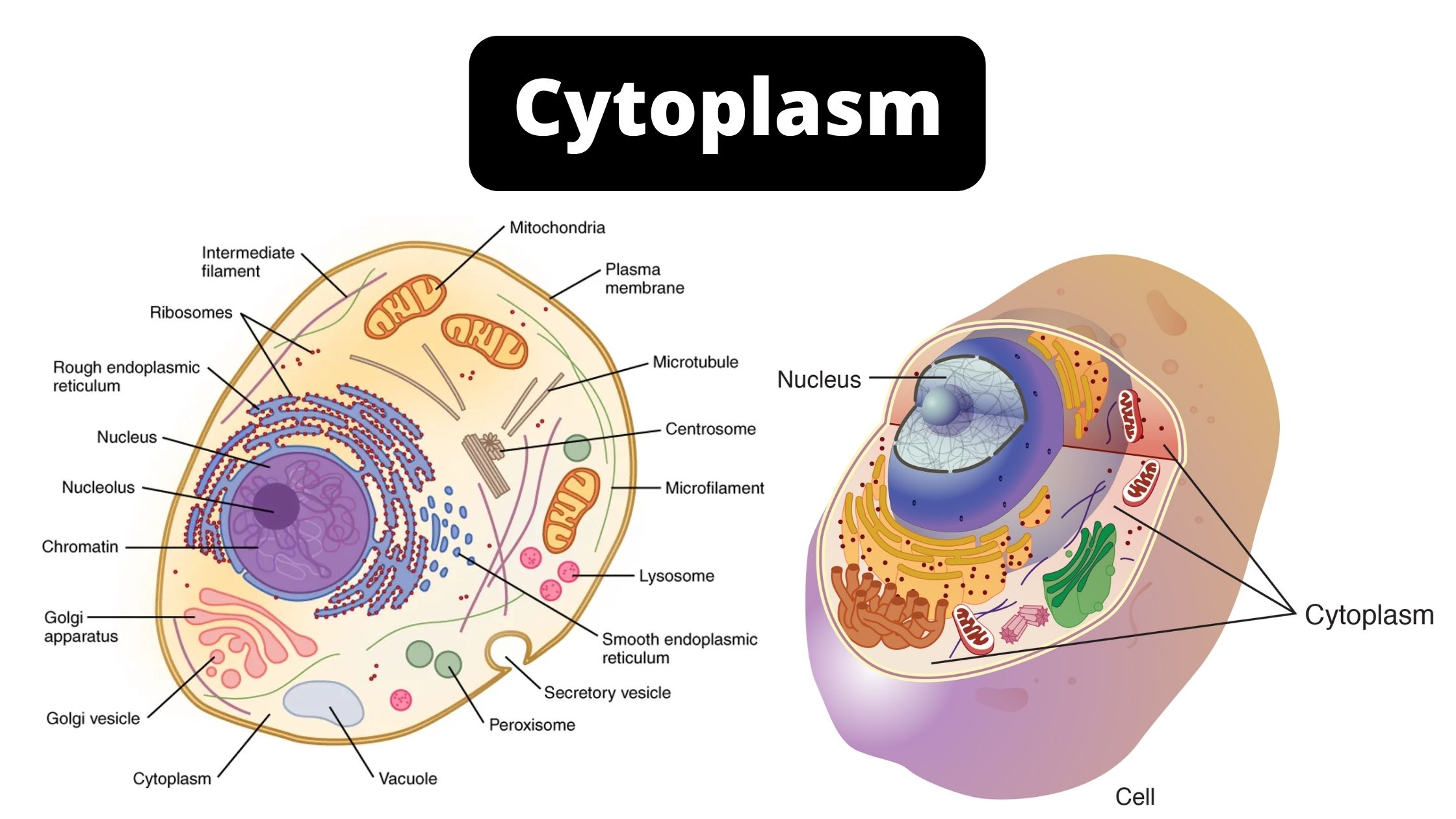
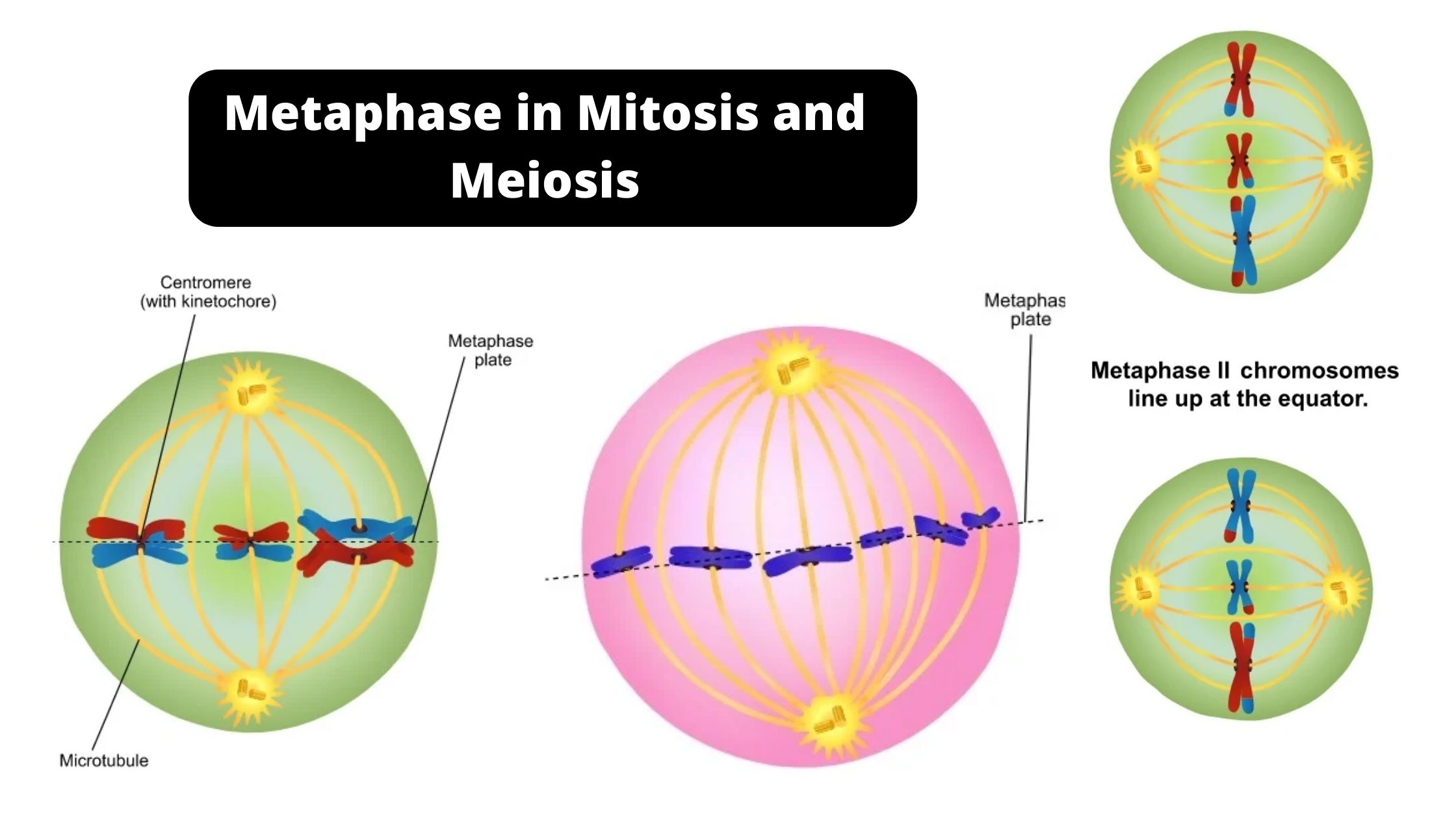
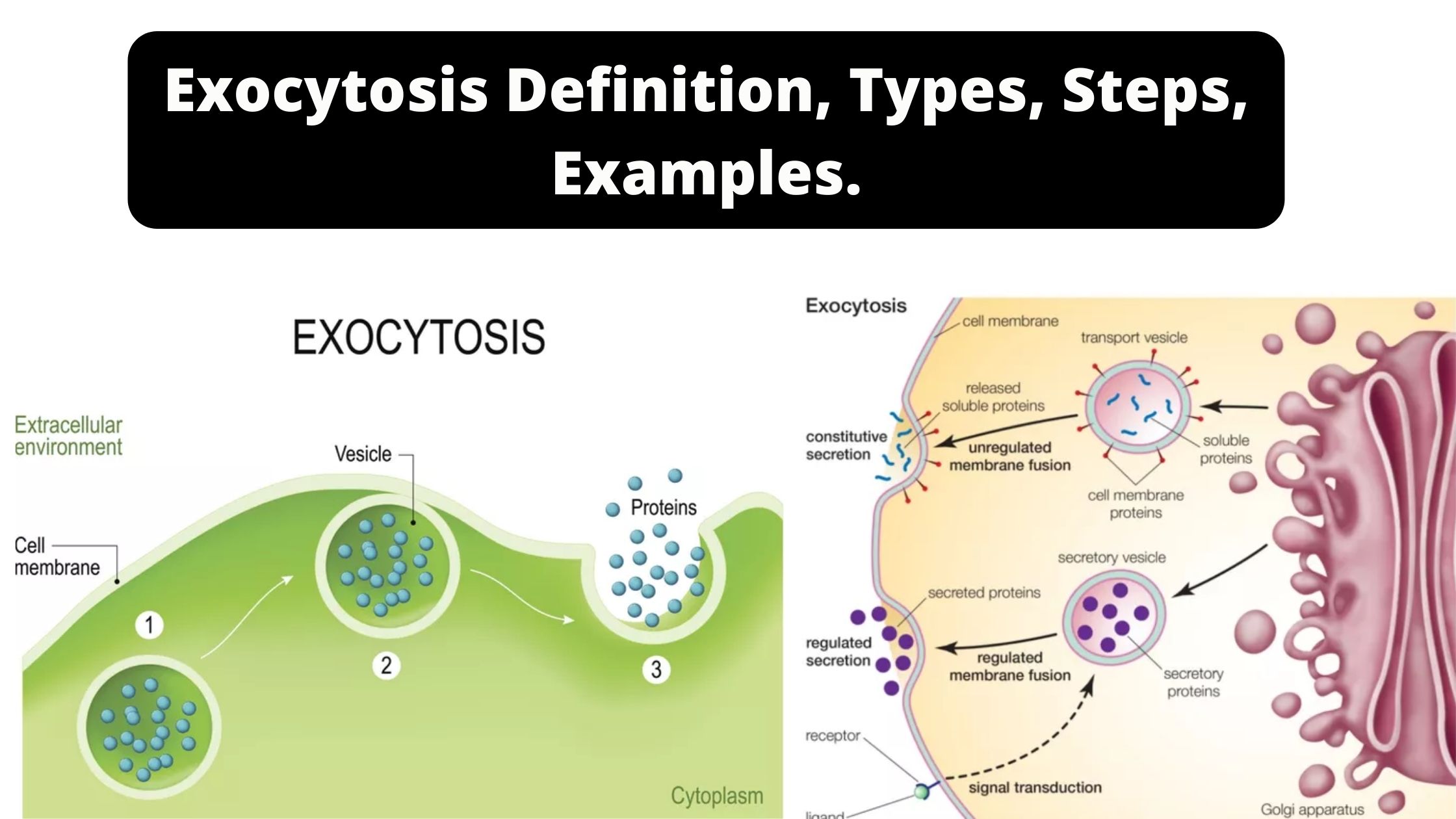
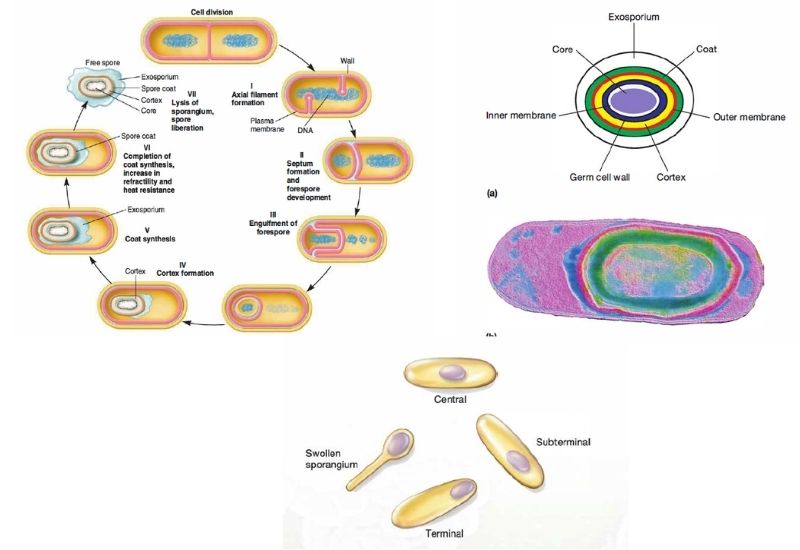
Sandwich (Davson–Danielli) model of cell membrane
The Davson Danielli model (or the paucimolecular model) was an illustration that depicts the membrane in cells. It was developed in the year 1935 by Hugh Davson and James Danielli The model is a bilayer of phospholipids which is located within two layers of protein globular. the model is trilaminar as well as lipoproteinous.