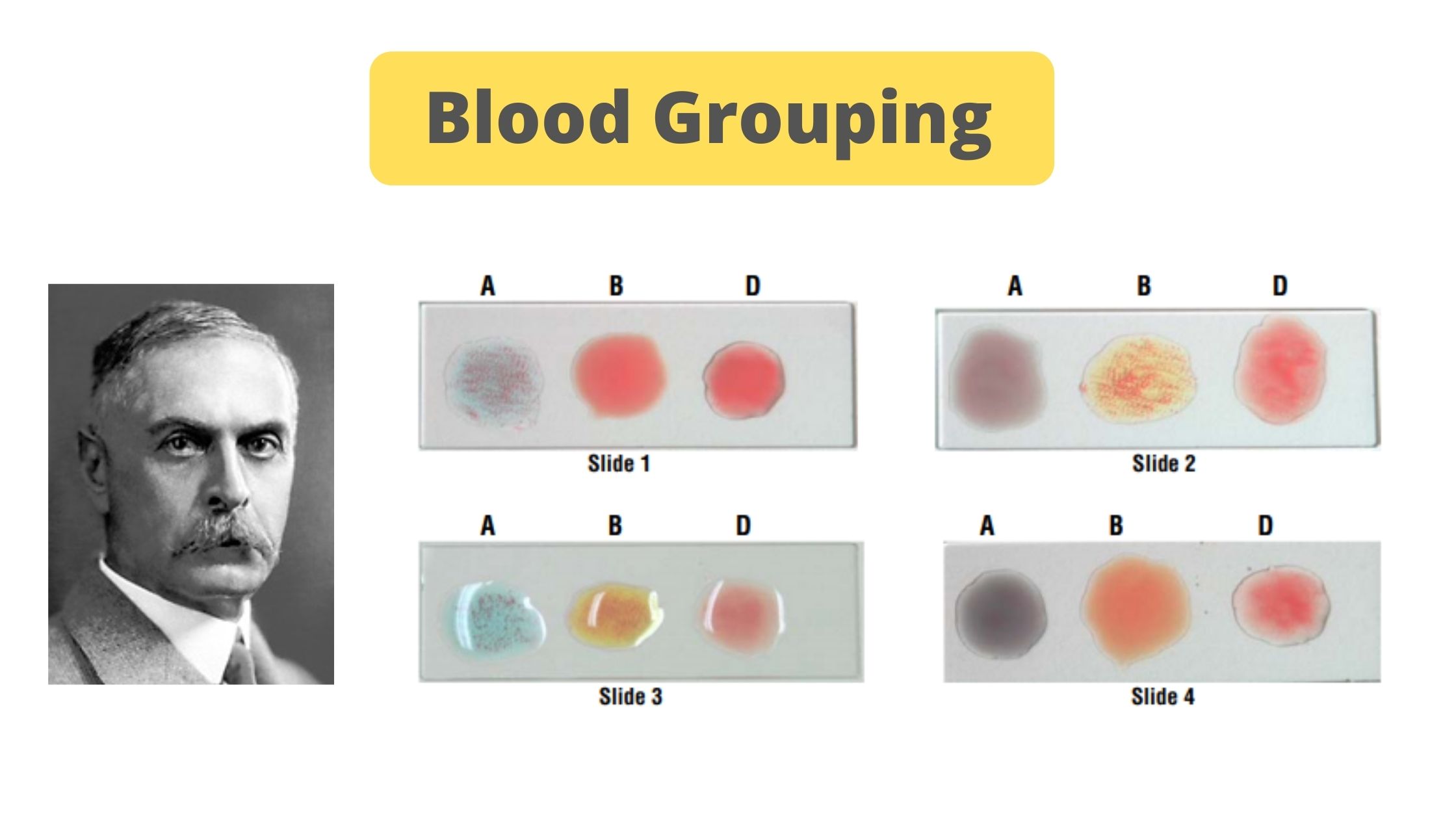
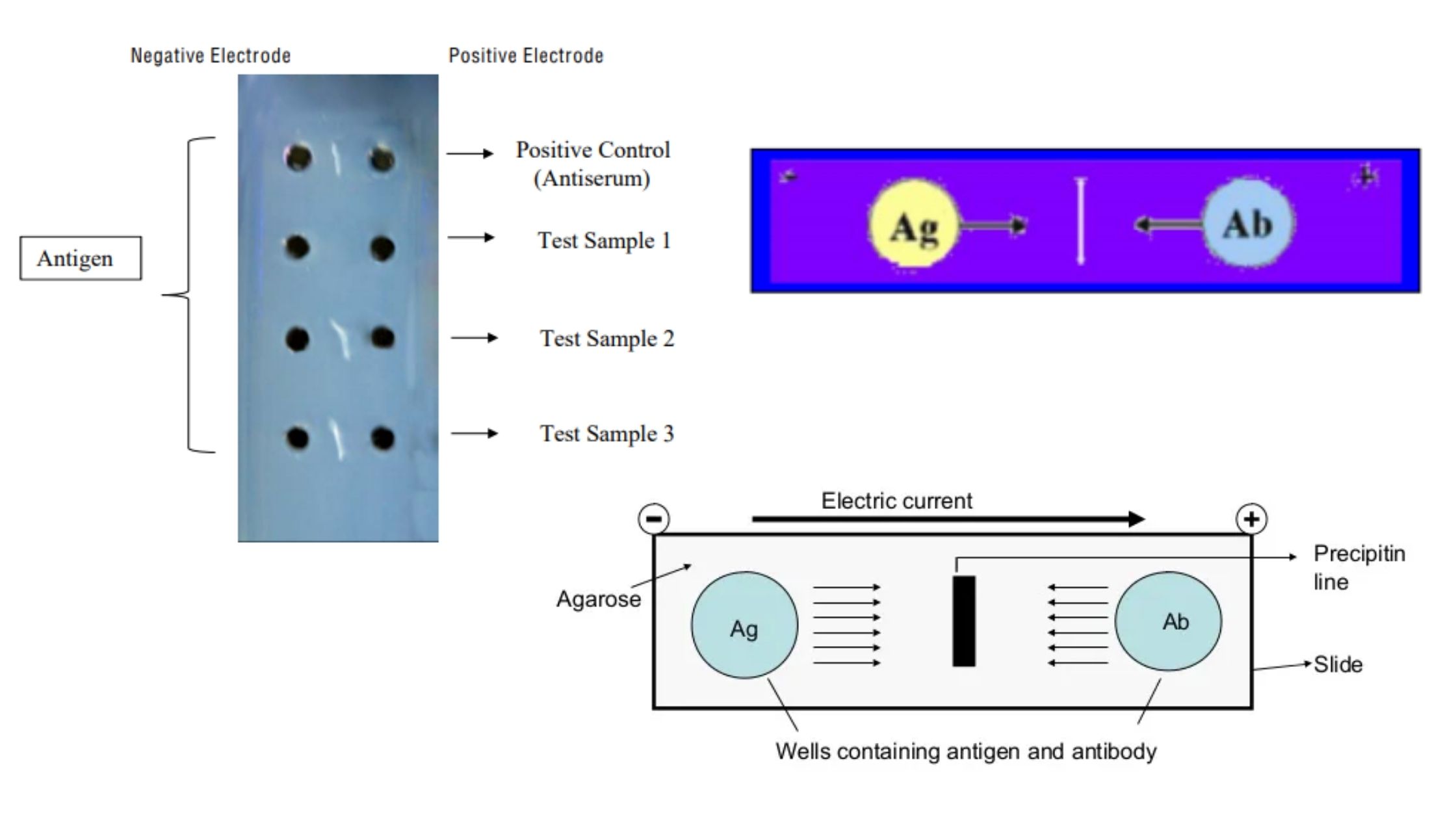
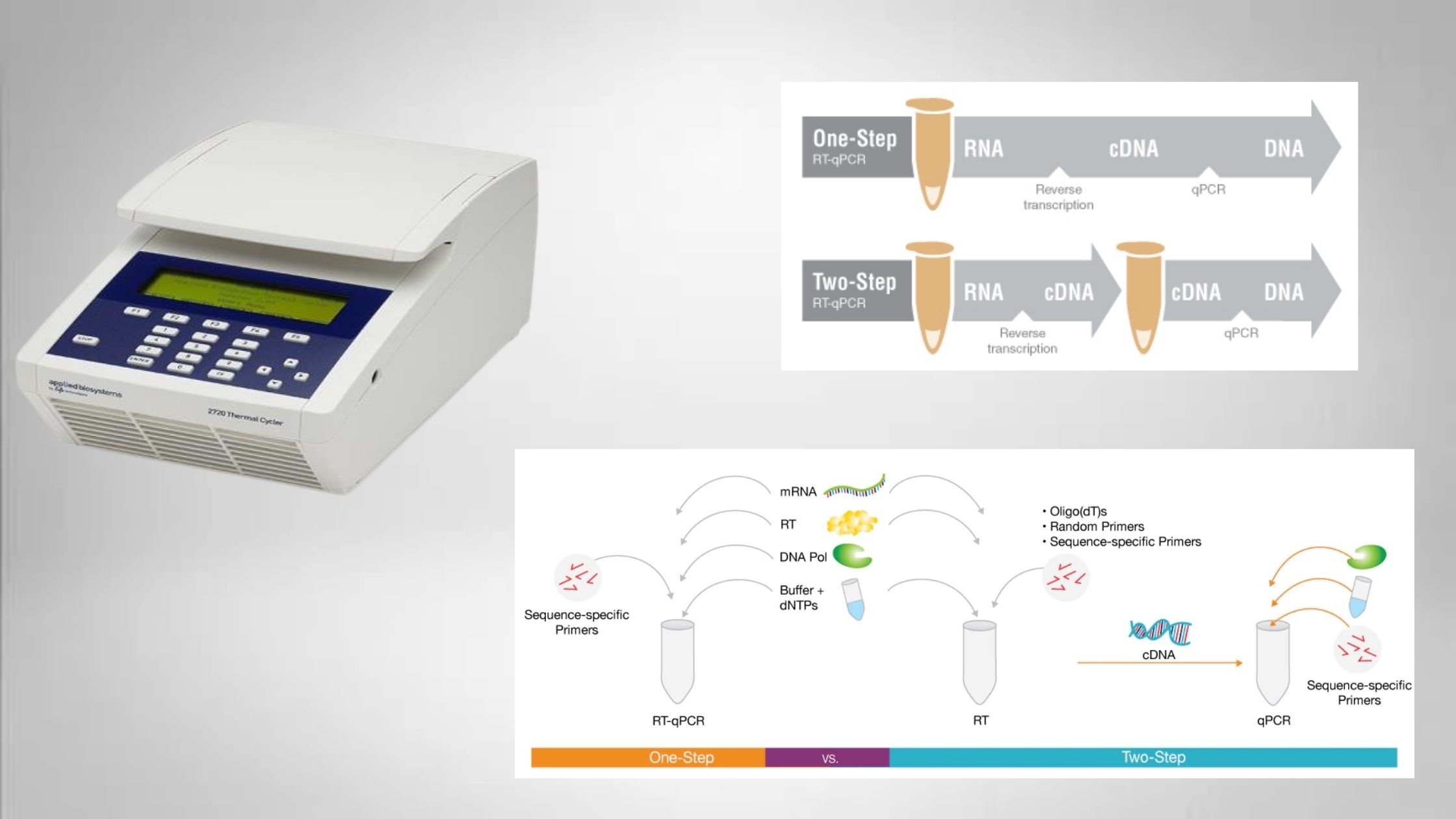
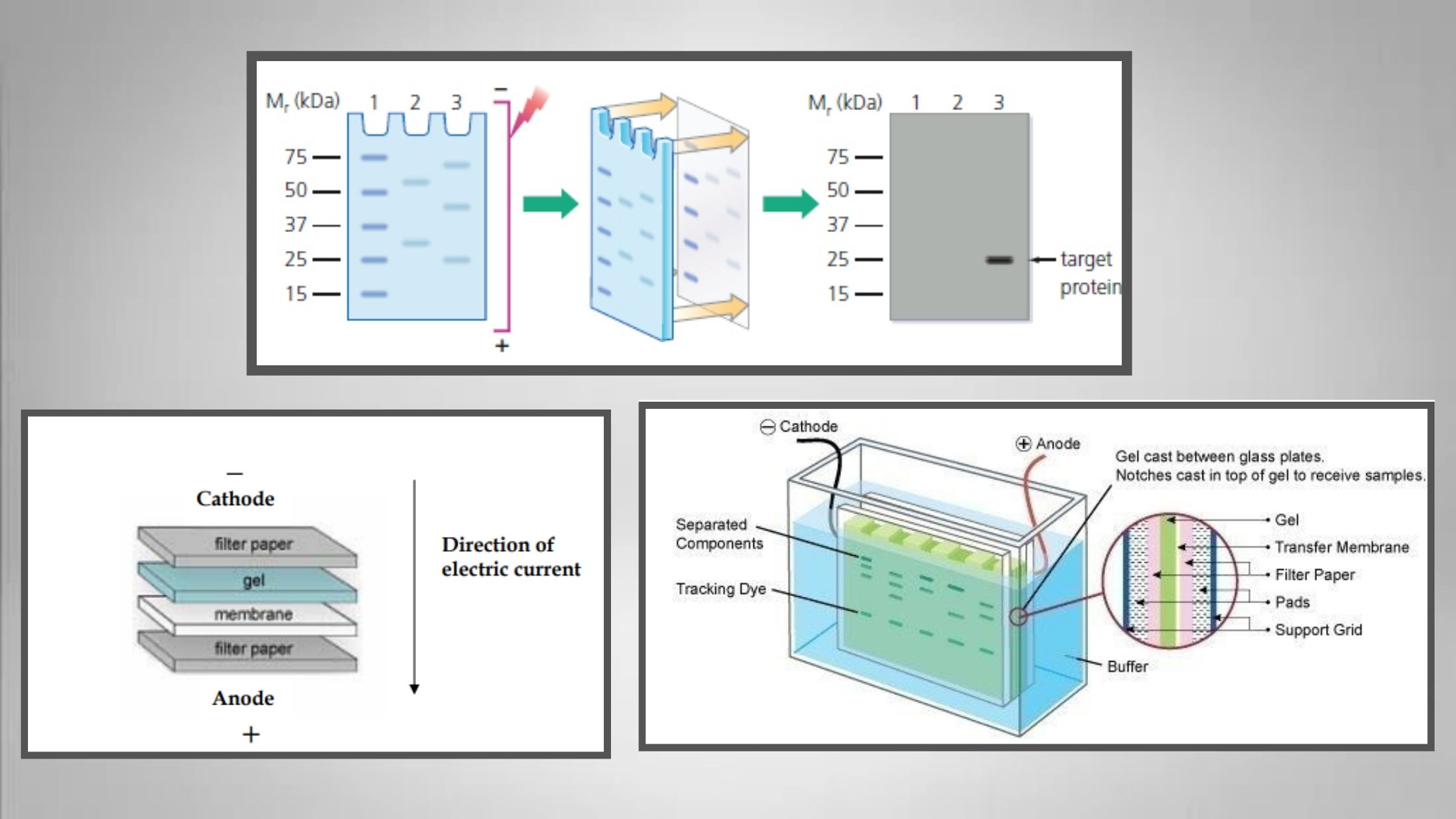
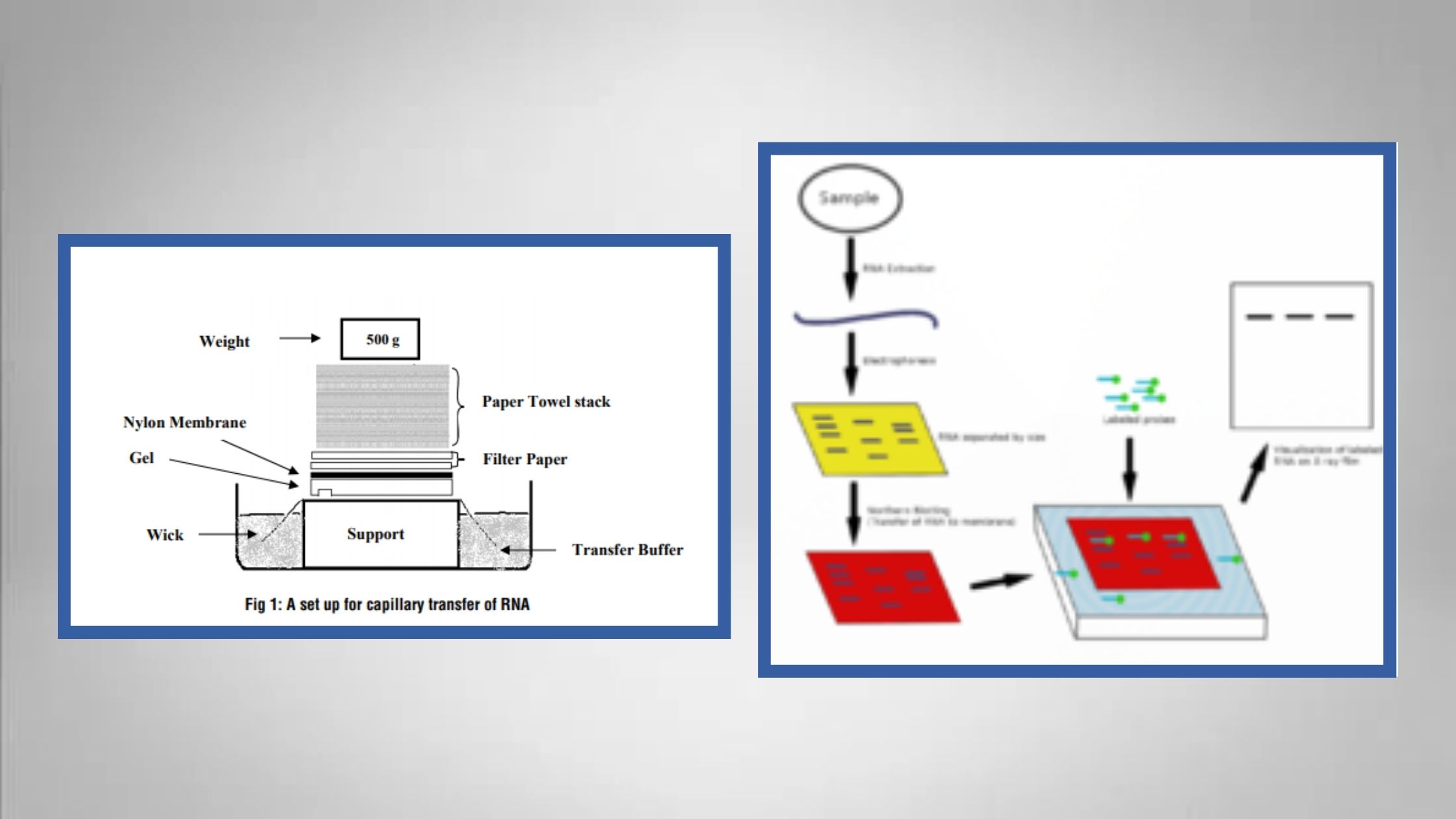
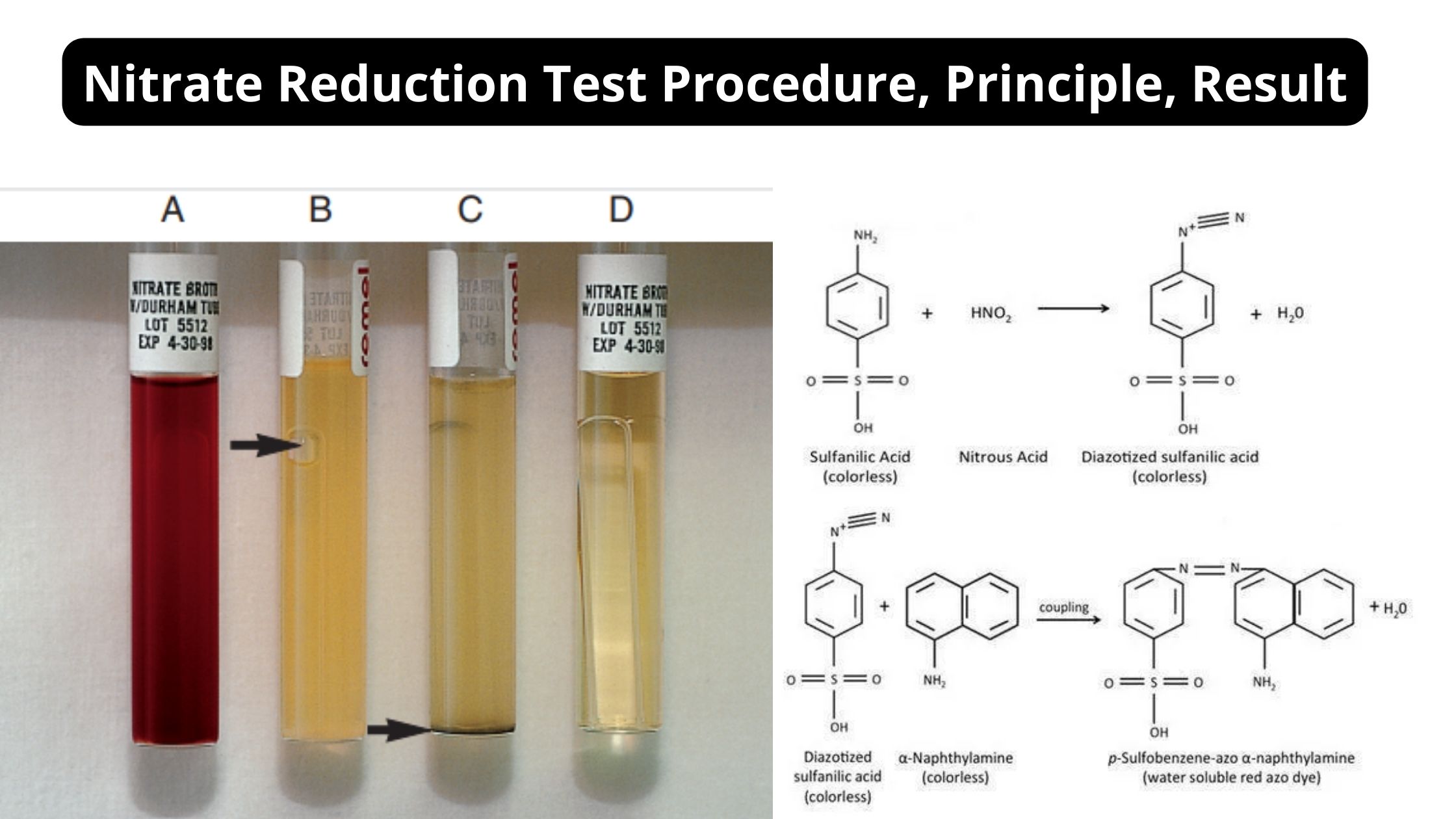
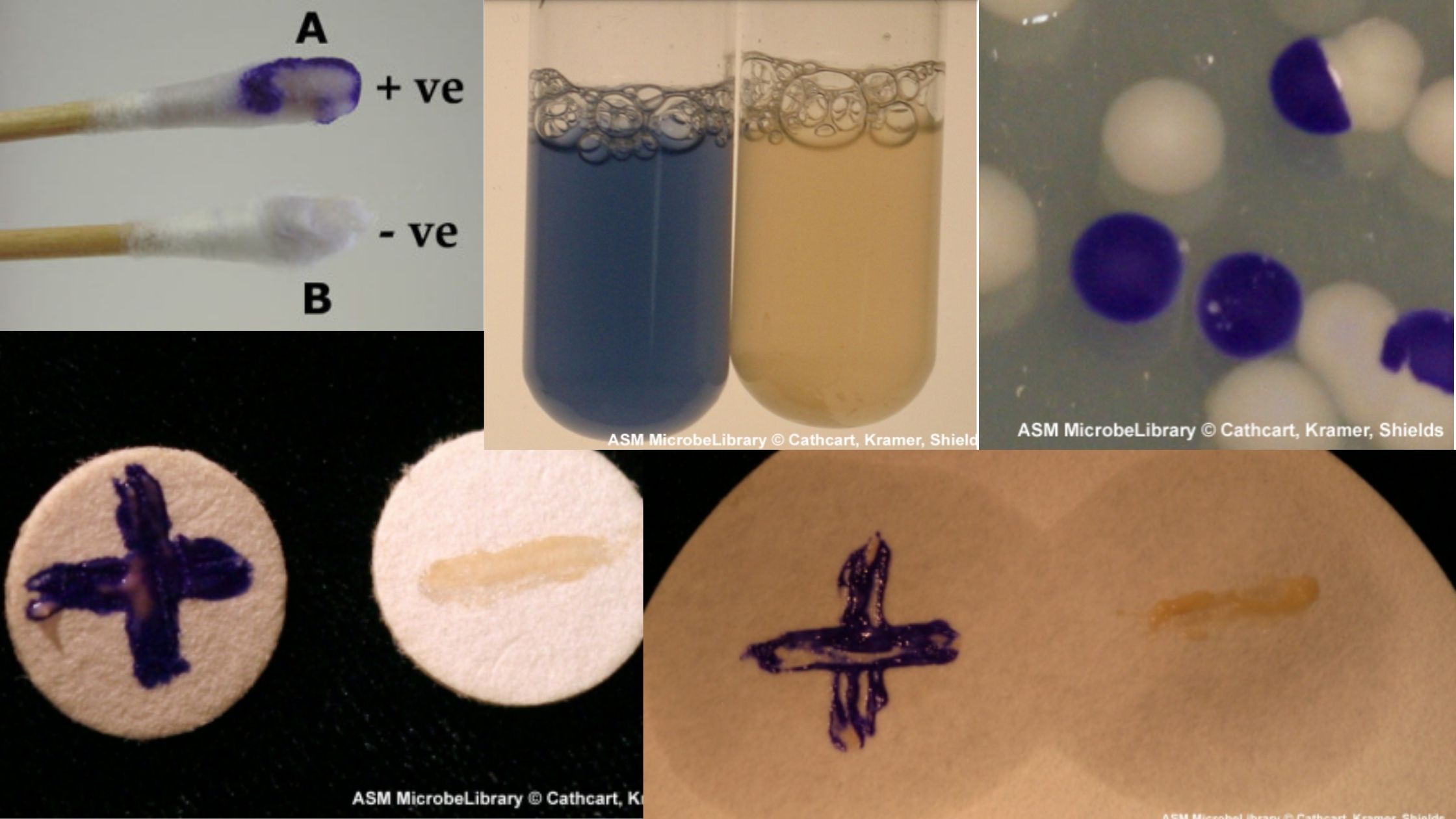
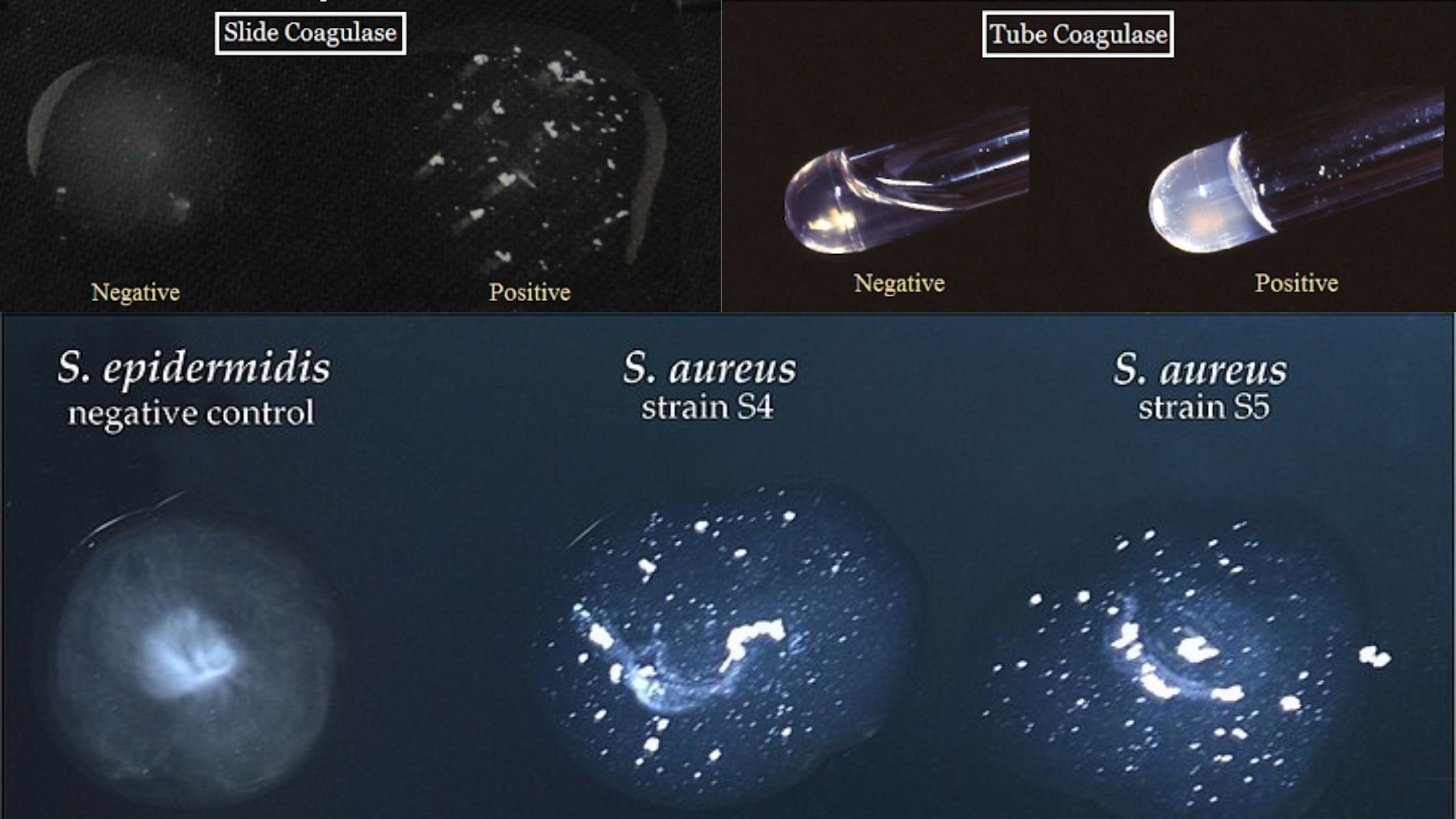
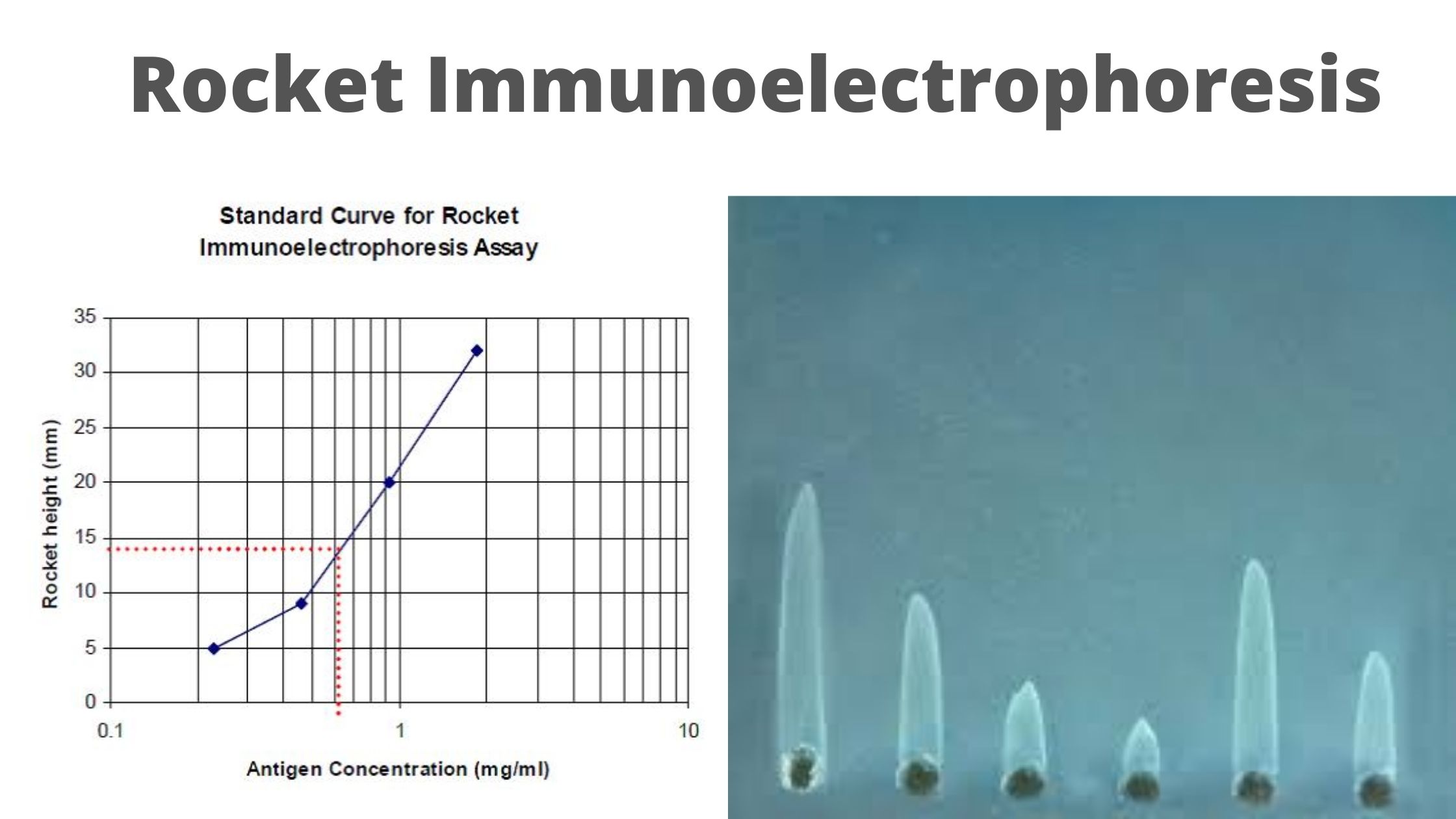
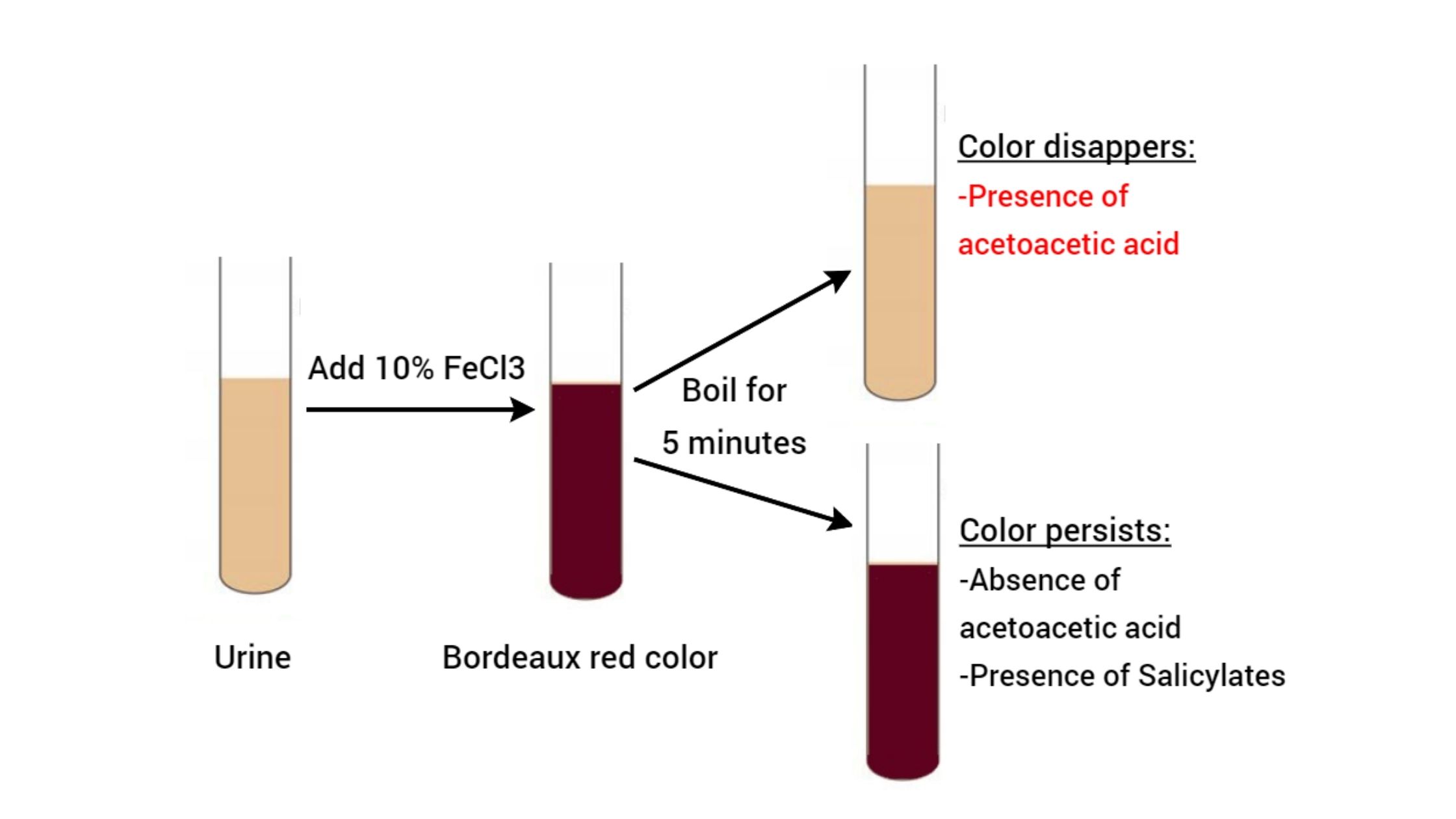
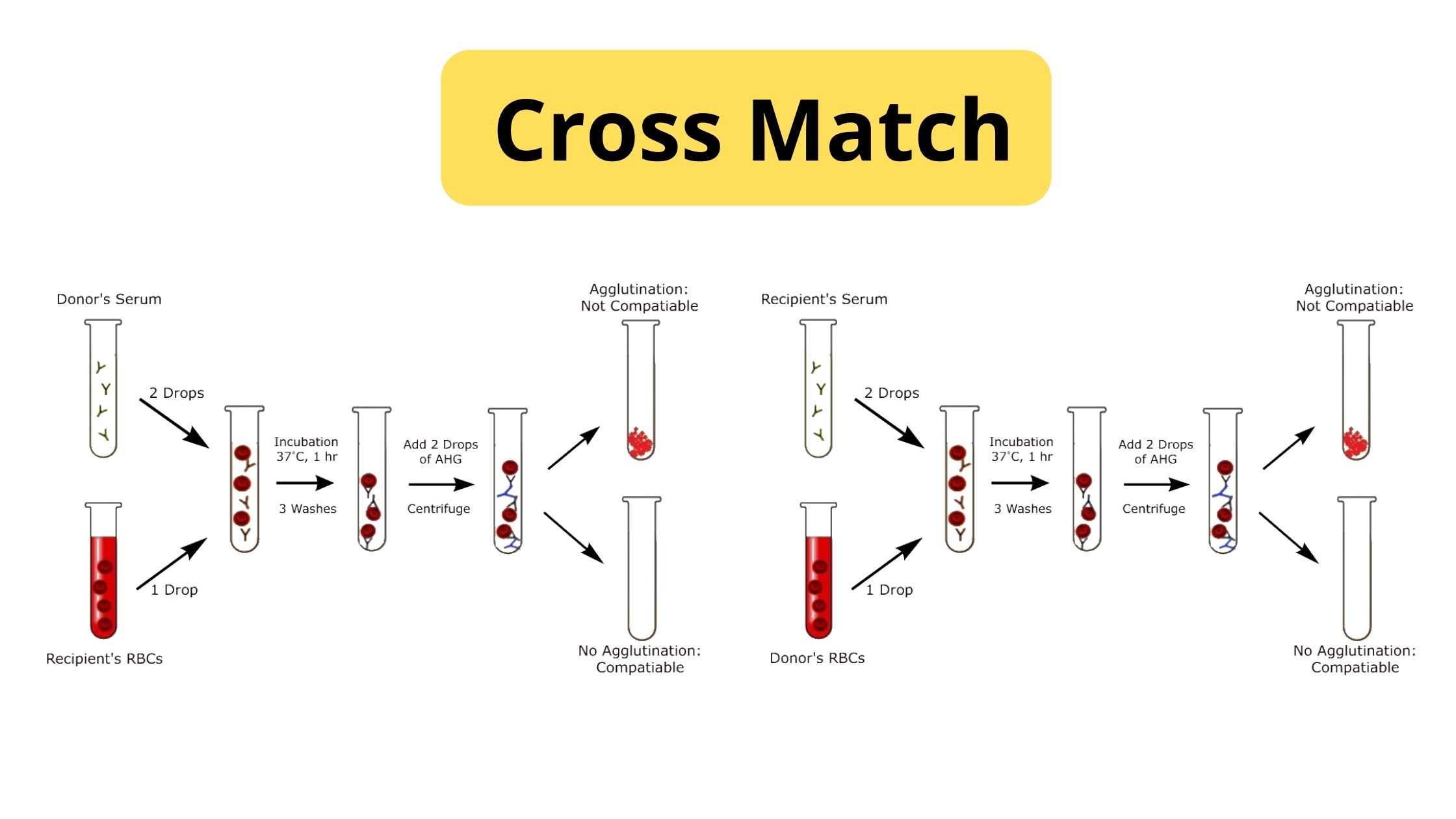
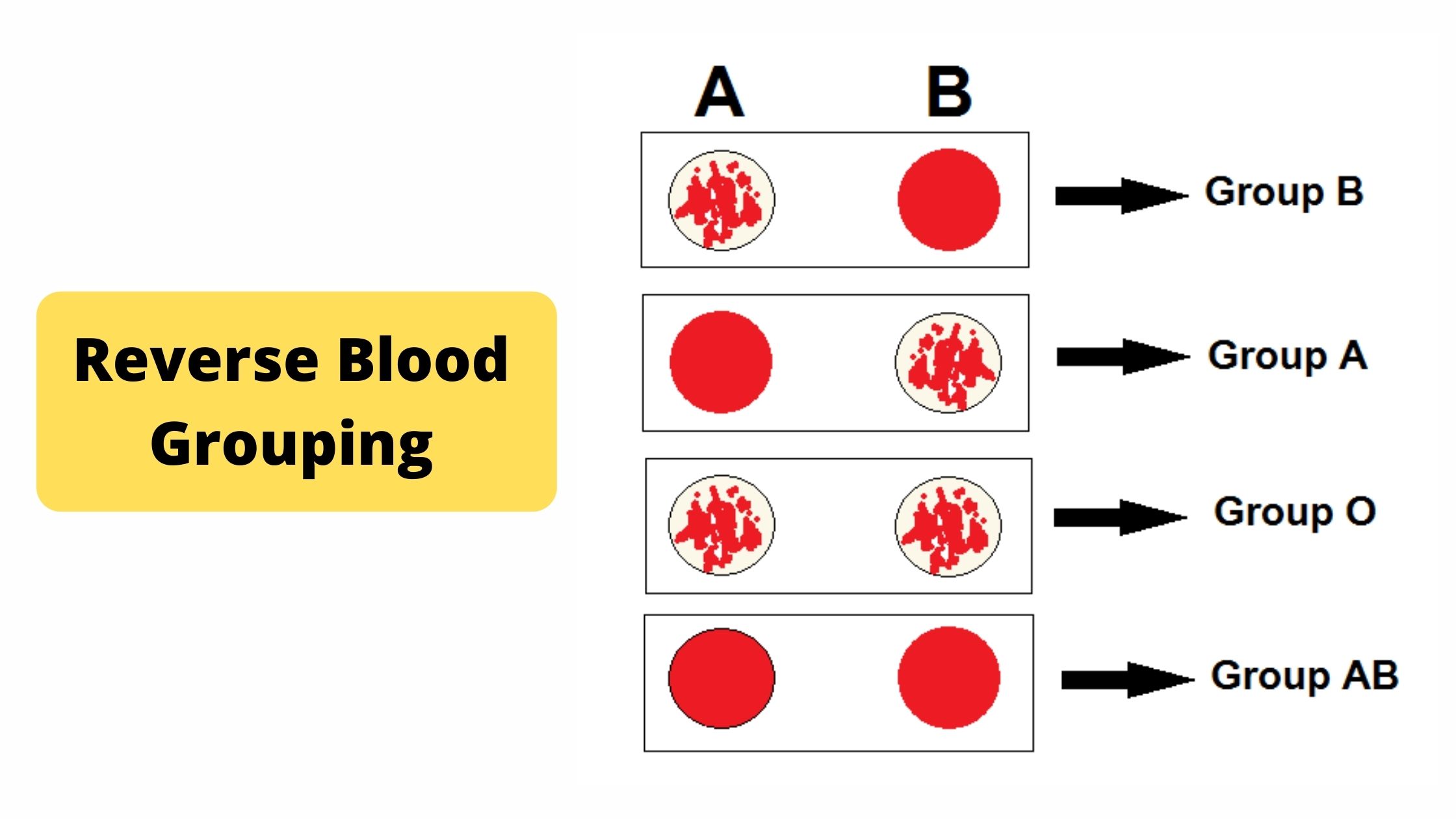
Blood Grouping Test – Principle, Procedure, Result
The concept of Blood grouping was first discovered by Karl Landsteiner in 1901, who was an Austrian-American immunologist and pathologist. He received Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1930 for this discovery.