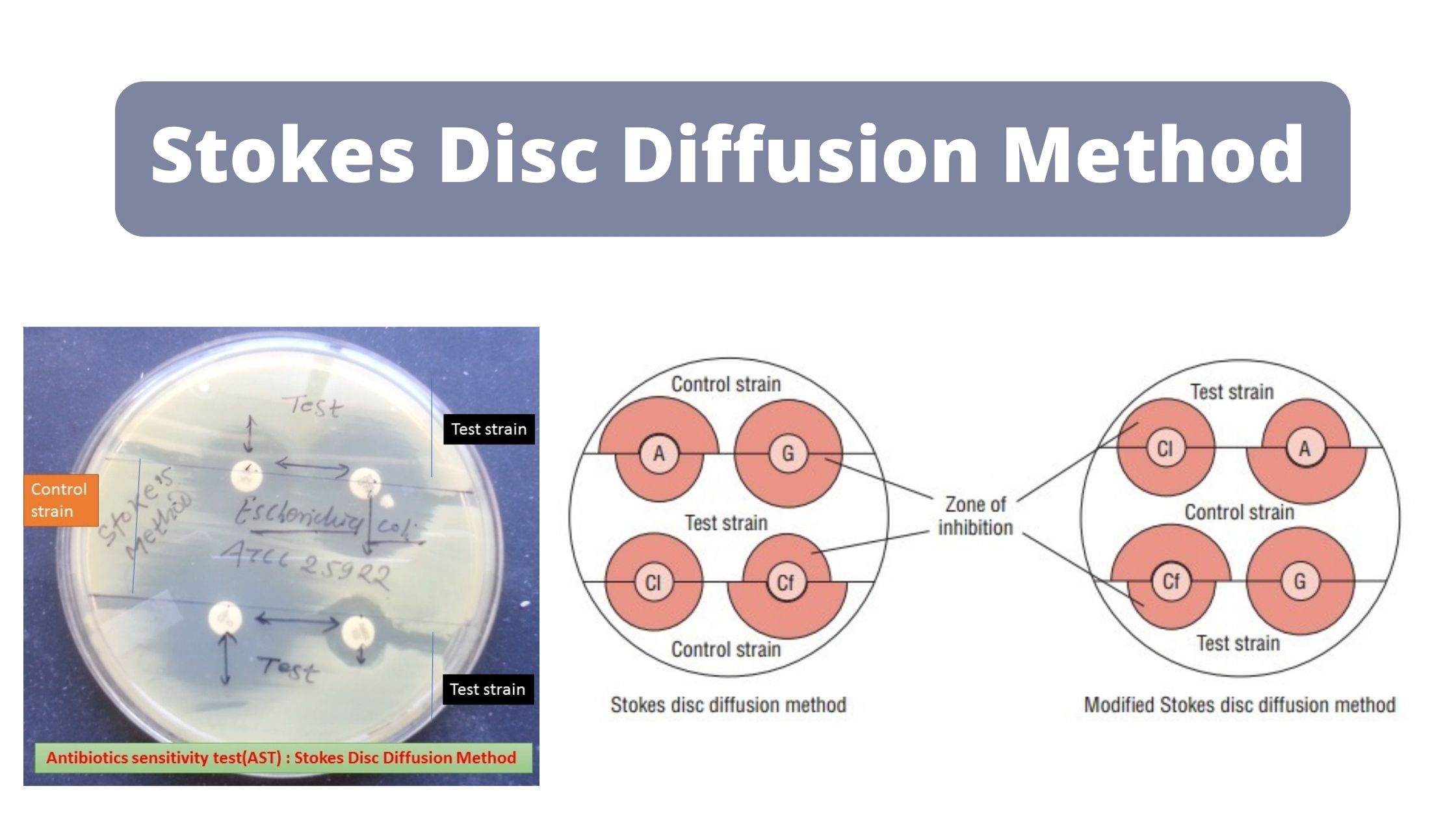
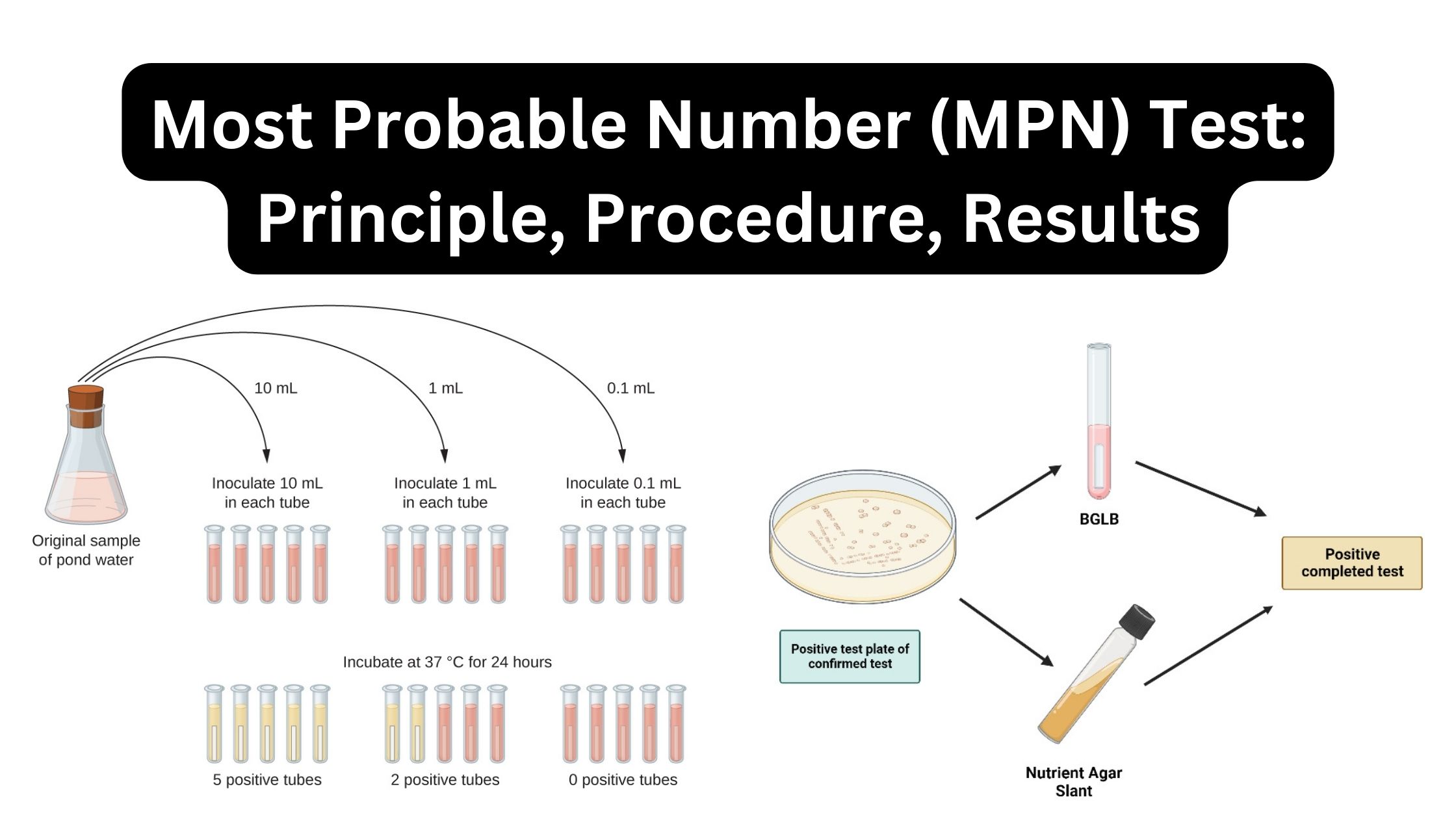
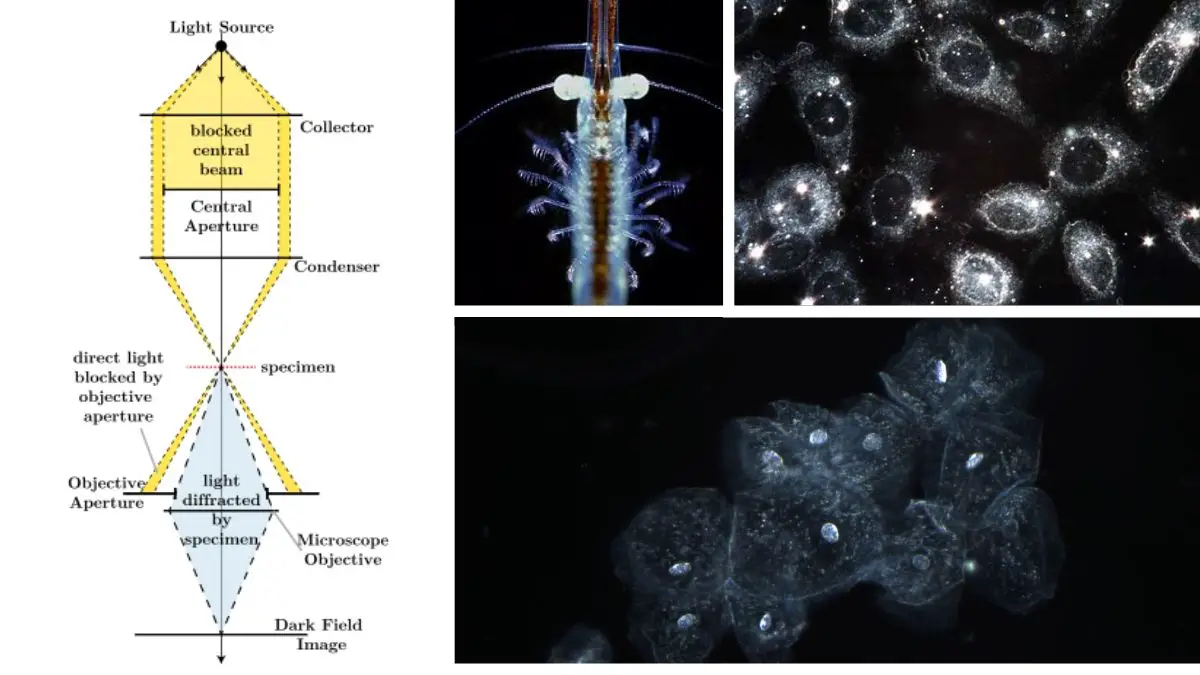
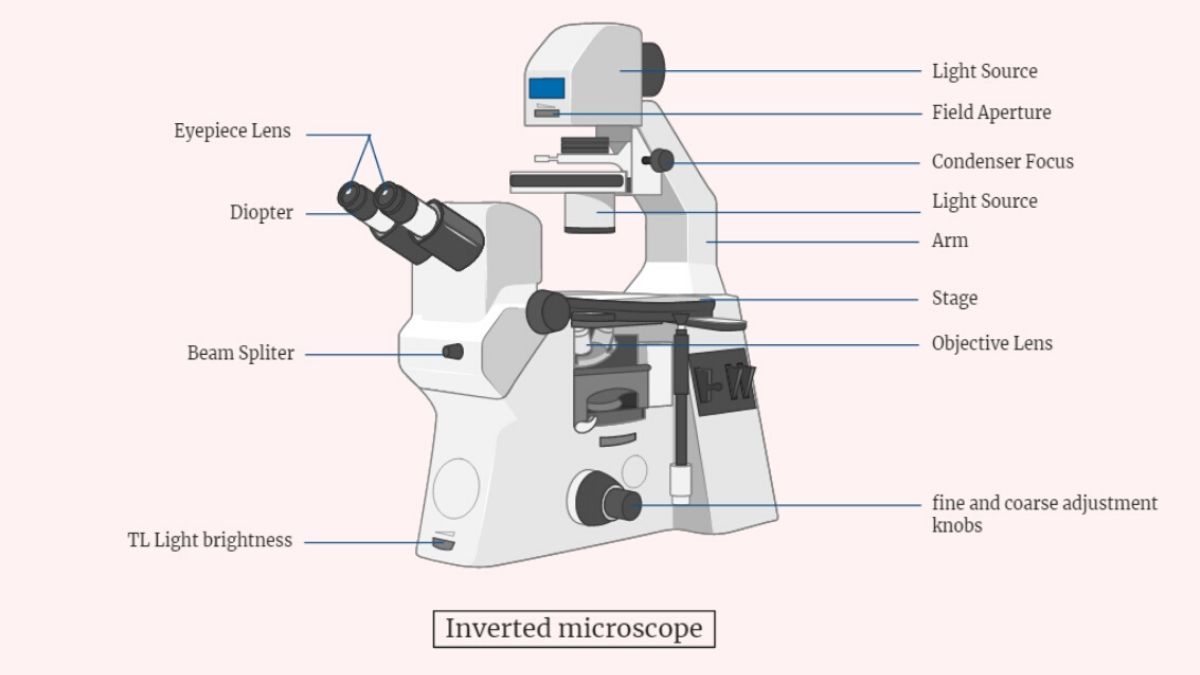
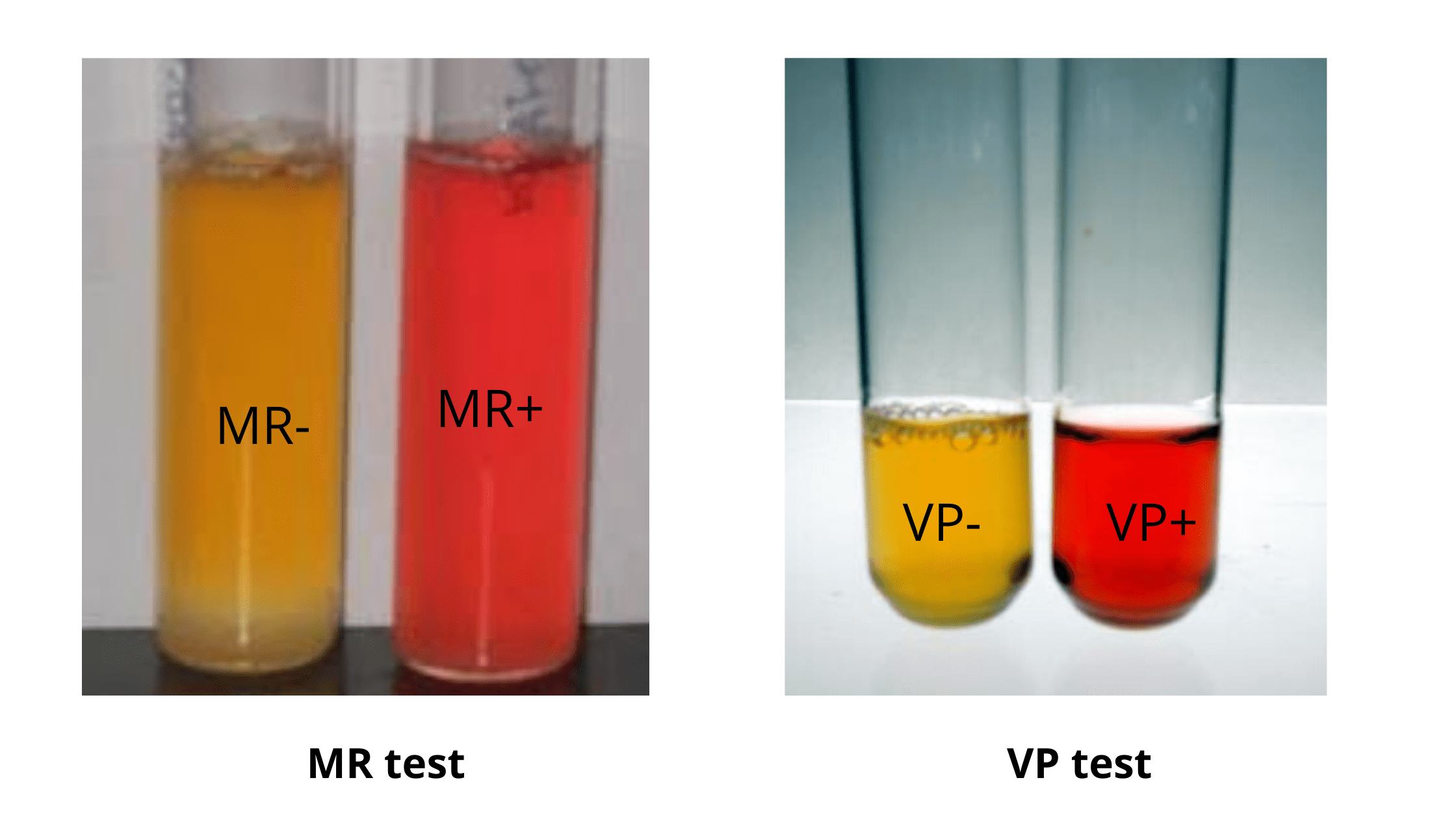
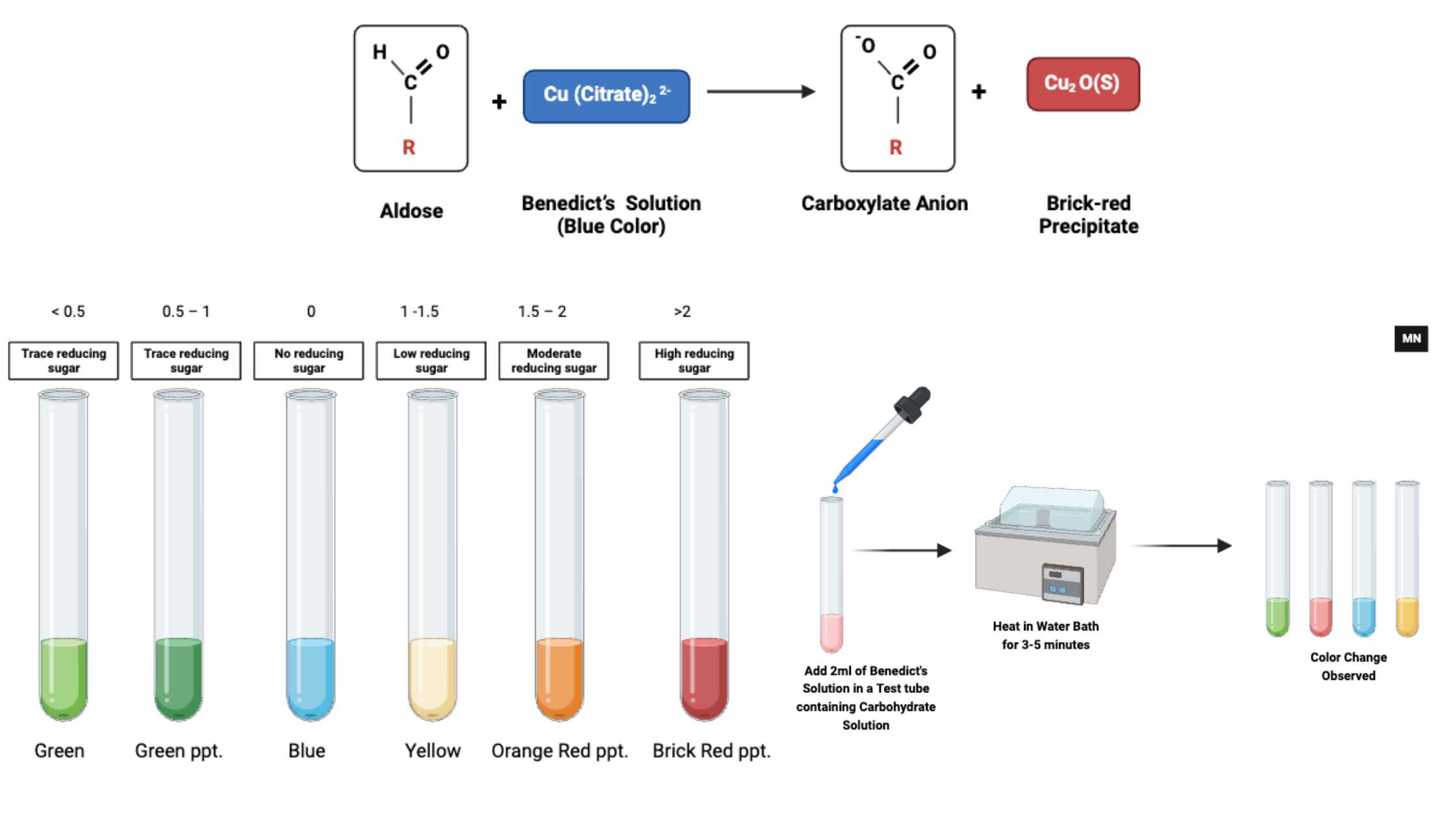
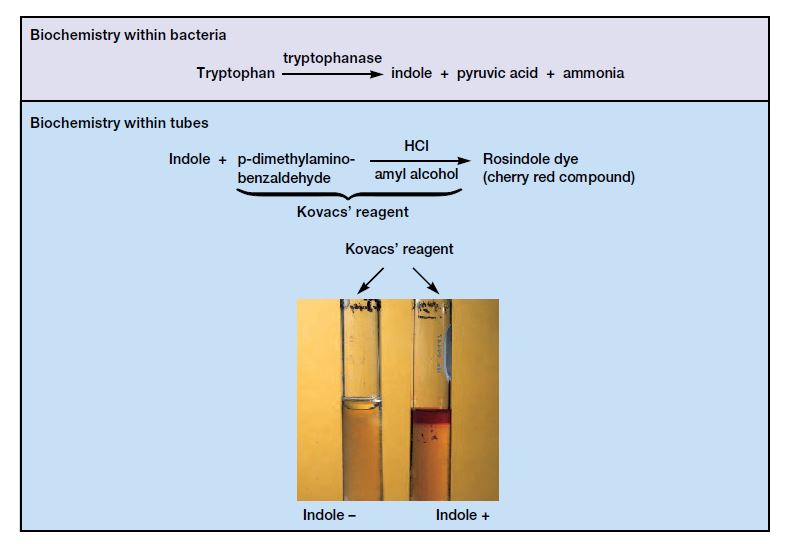
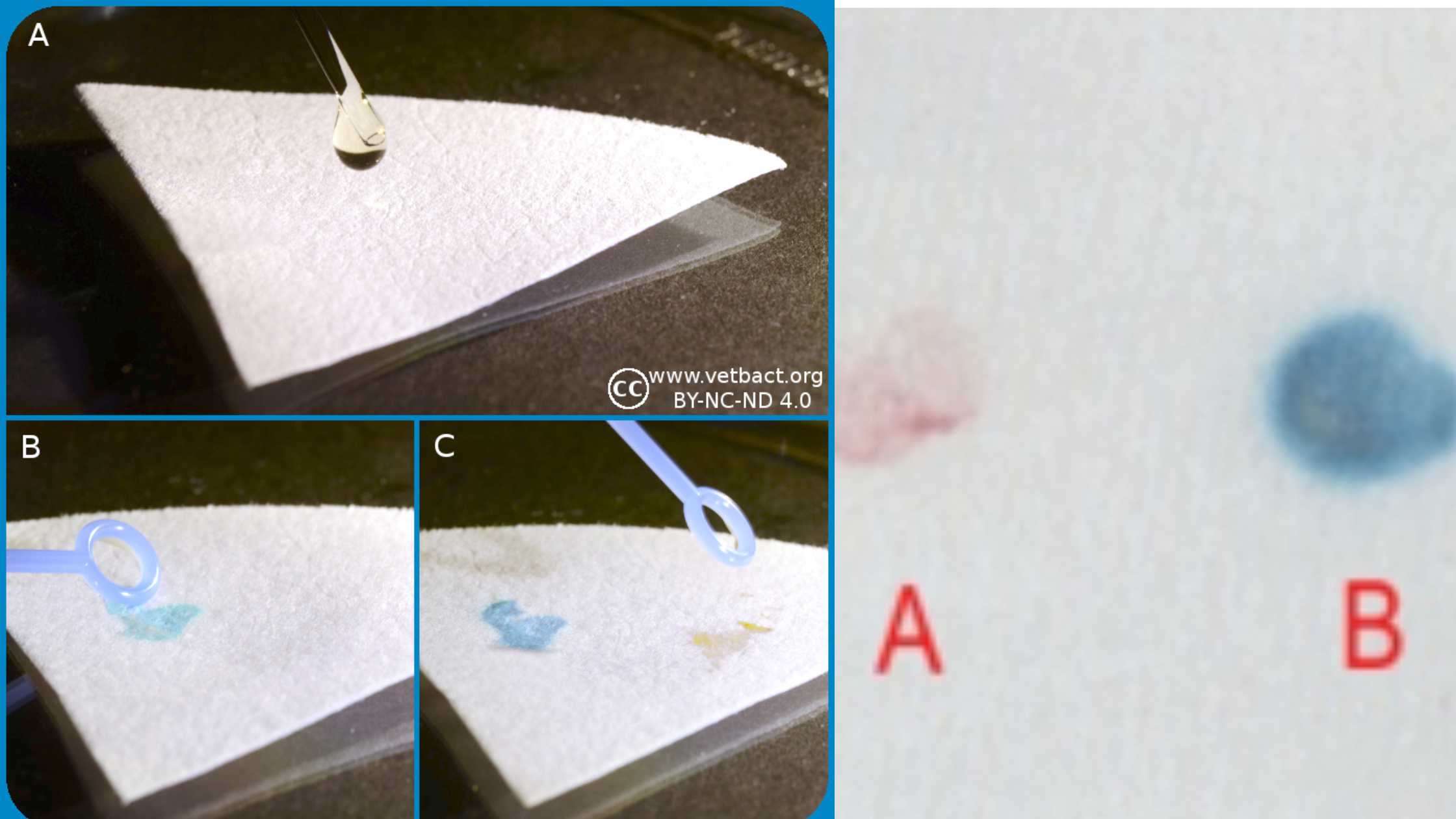
Stokes Disc Diffusion Method – Principle, Procedure, Result.
Stokes disc diffusion method isn’t as well-standardized as Kirby-Bauer’s method and is utilized in labs especially where the exact amount of antimicrobial present in discs isn’t known because of the difficulty in getting discs and correctly storing them or when other requirements needed for the Kirby-Bauer method cannot be fulfilled.