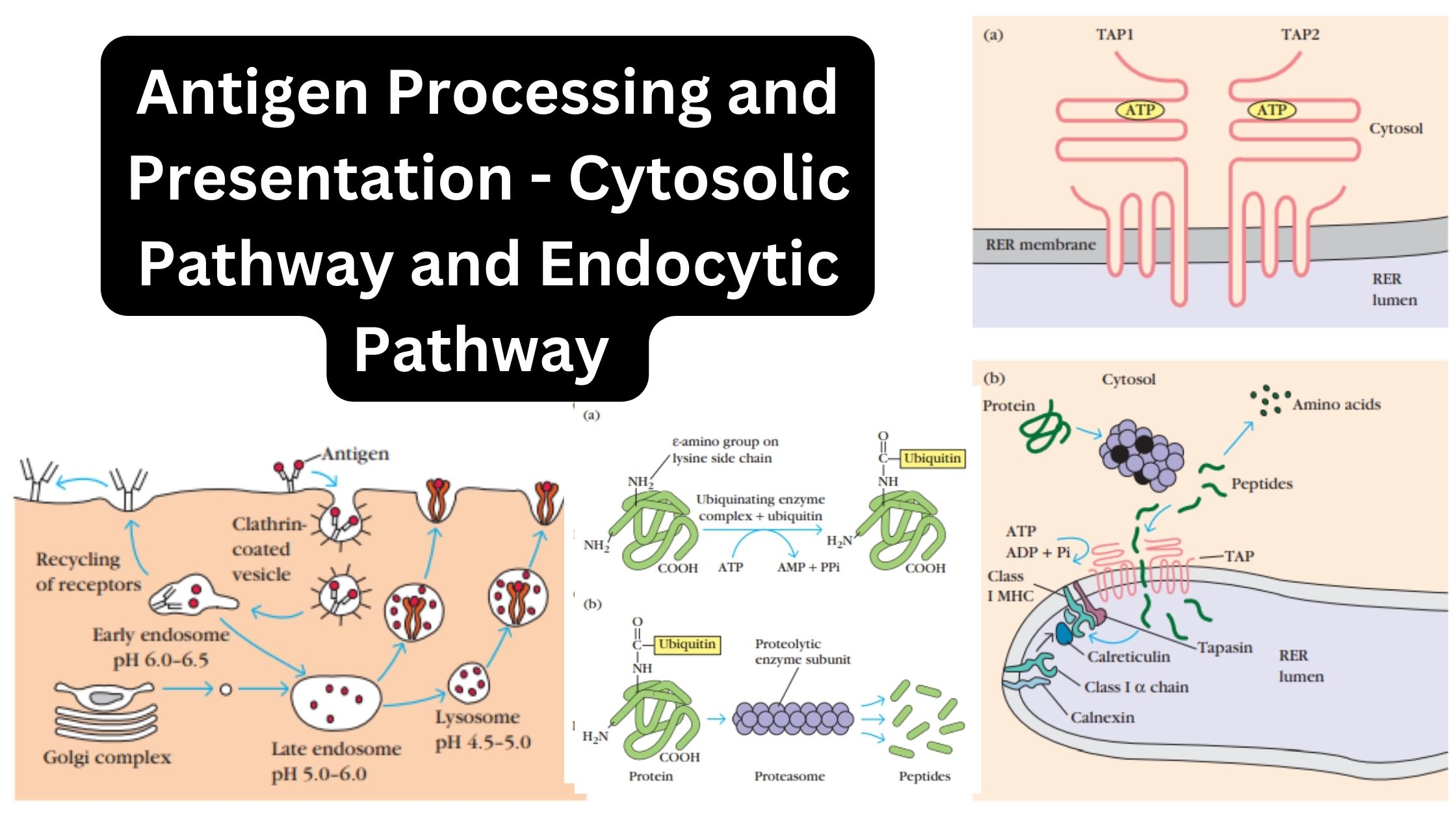
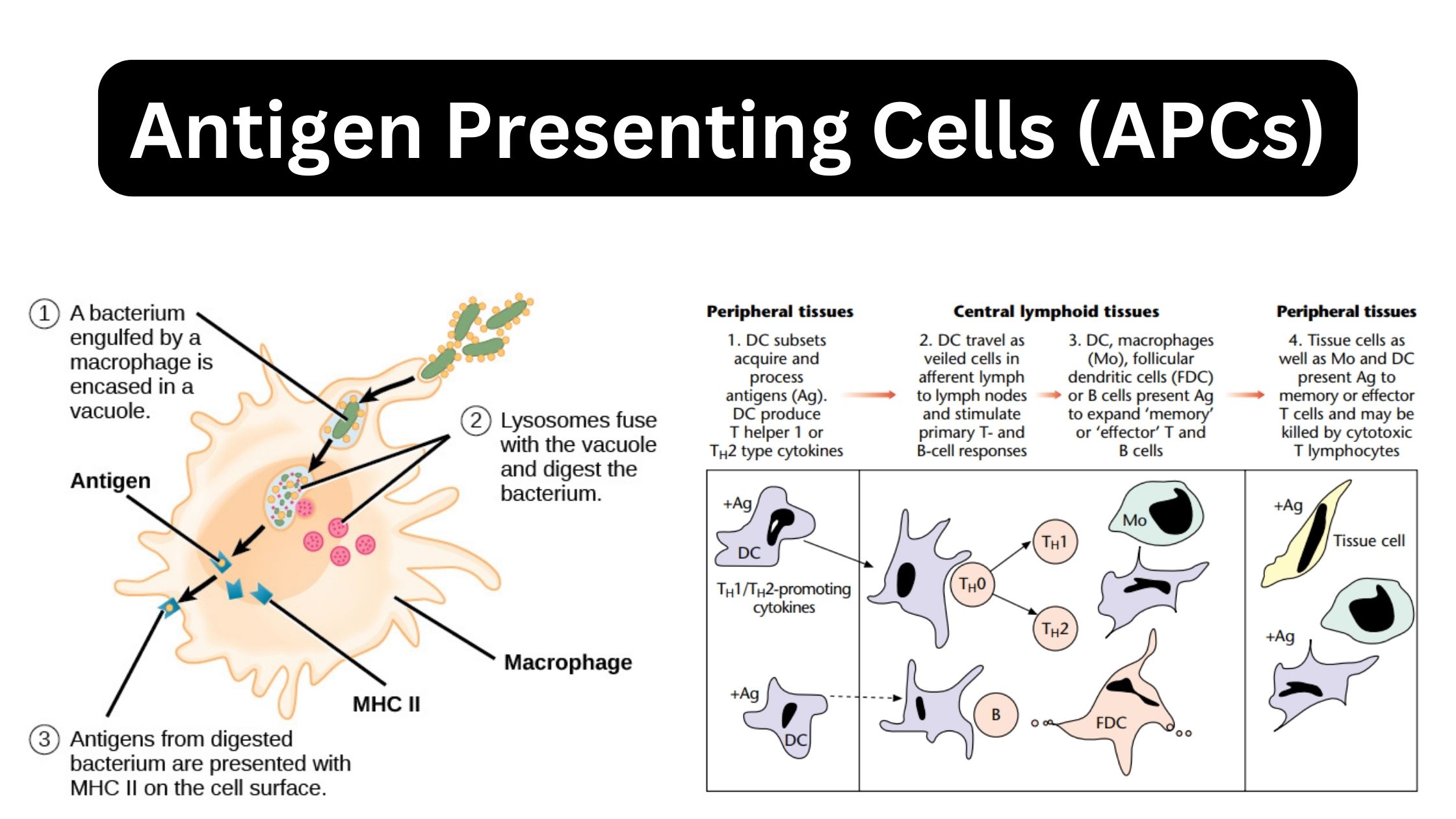
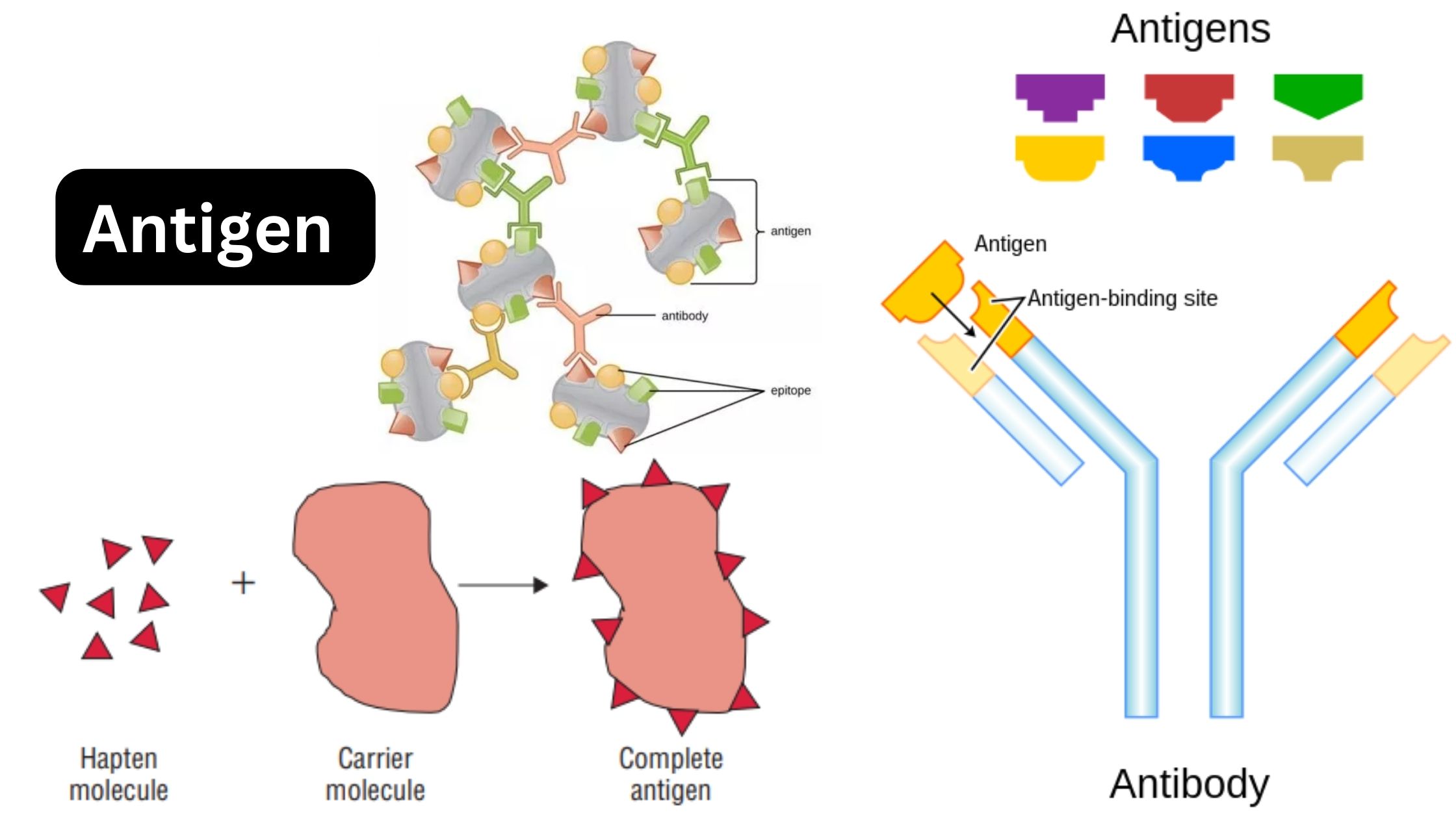
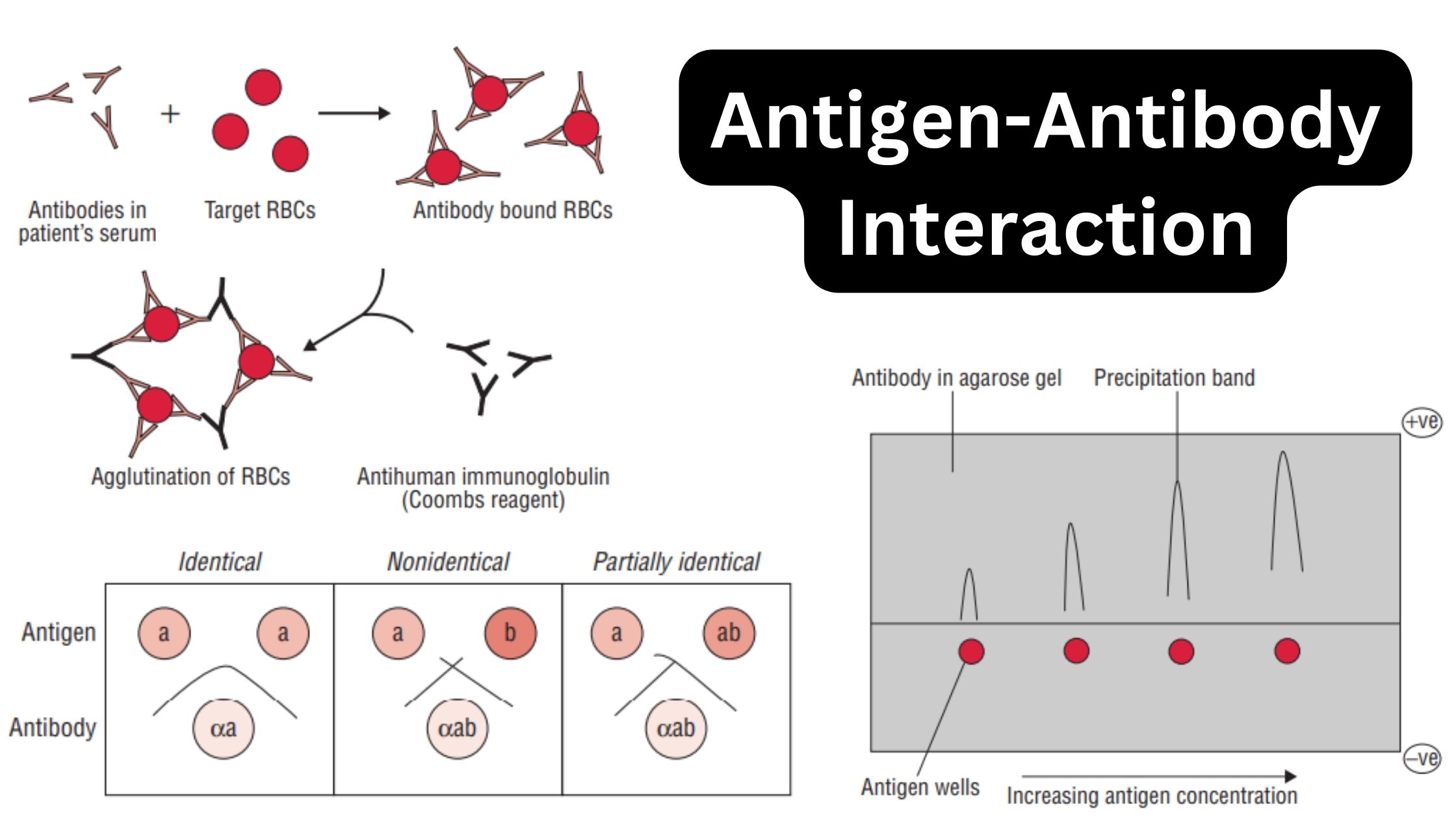
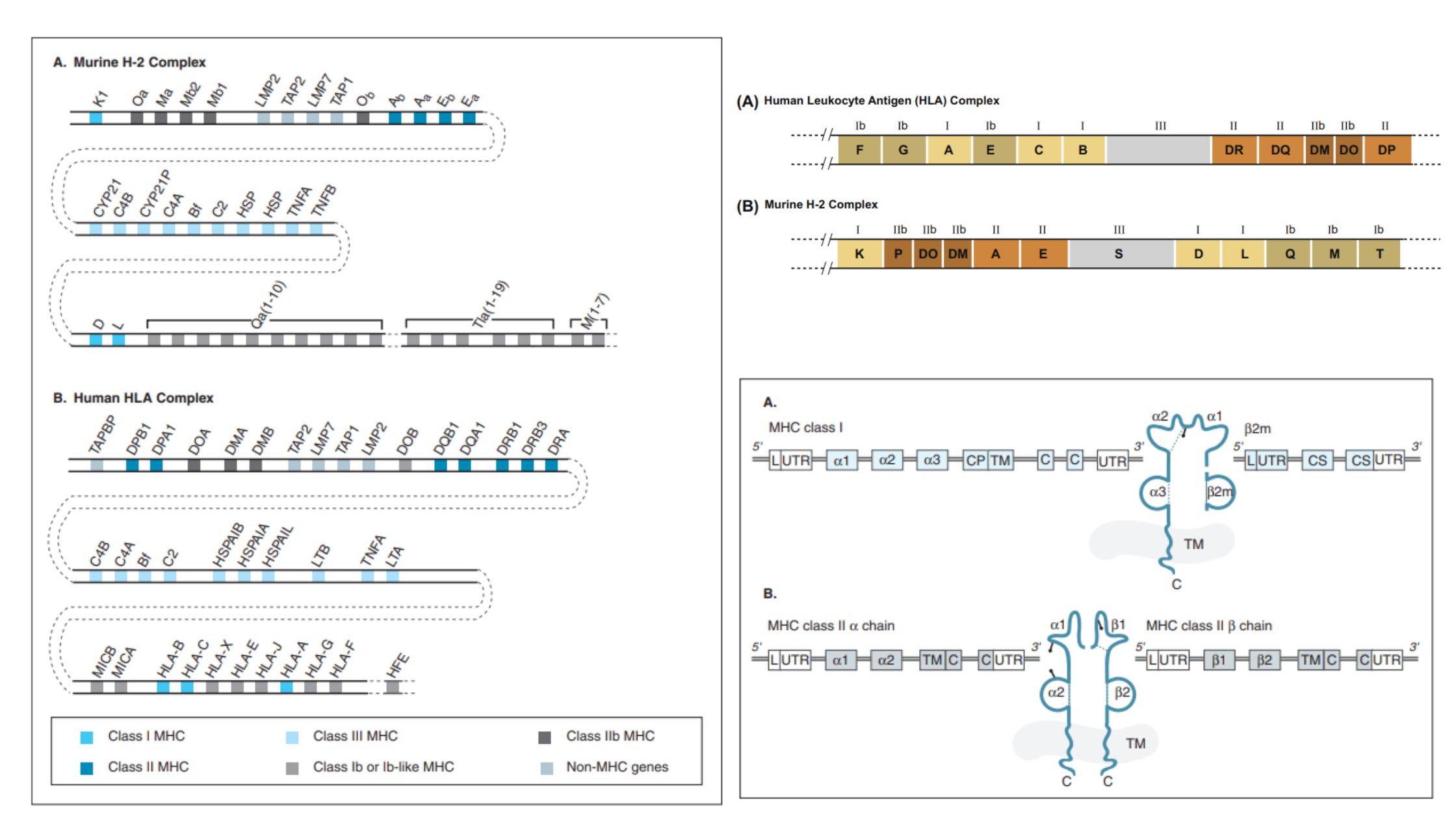
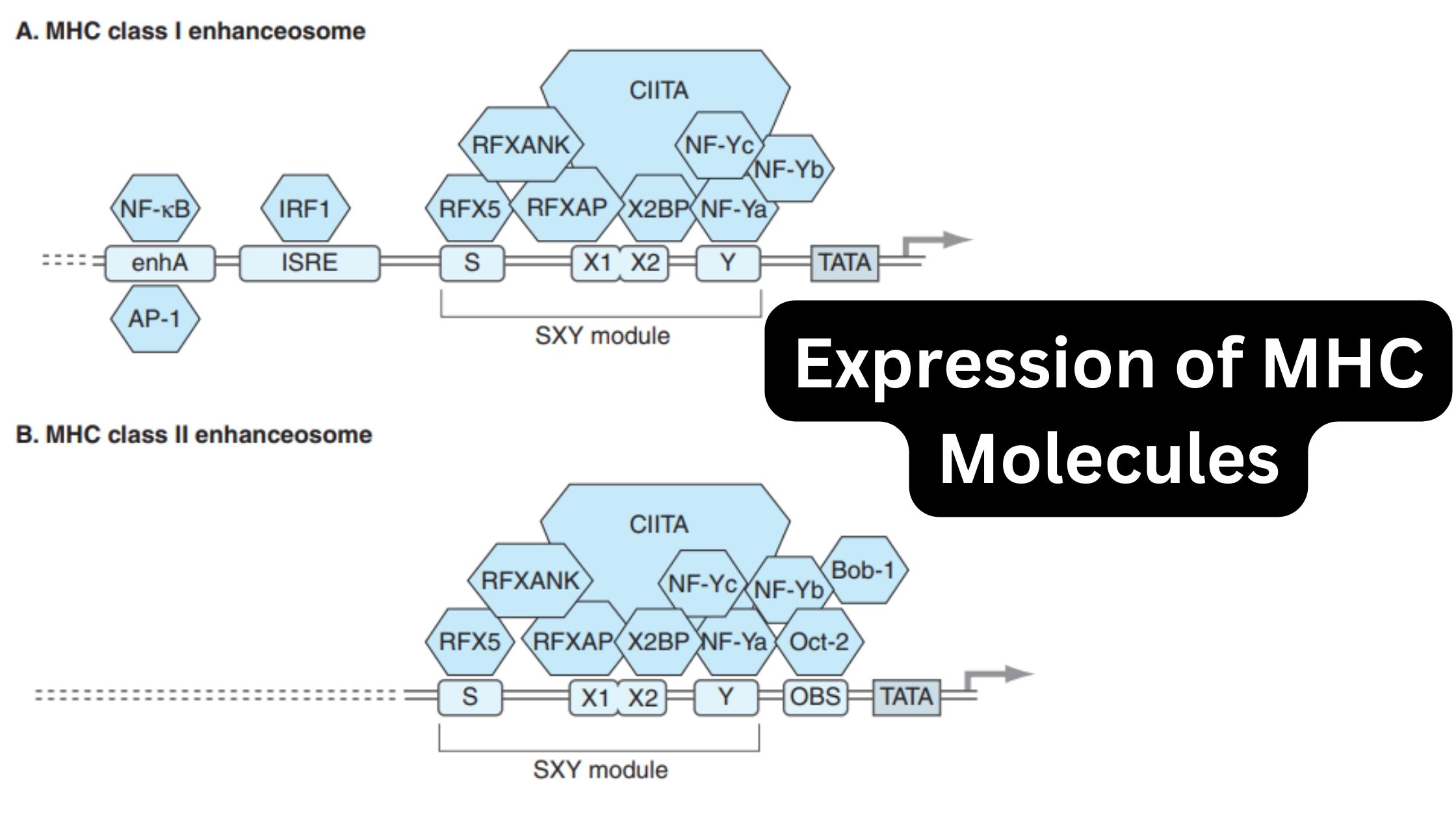
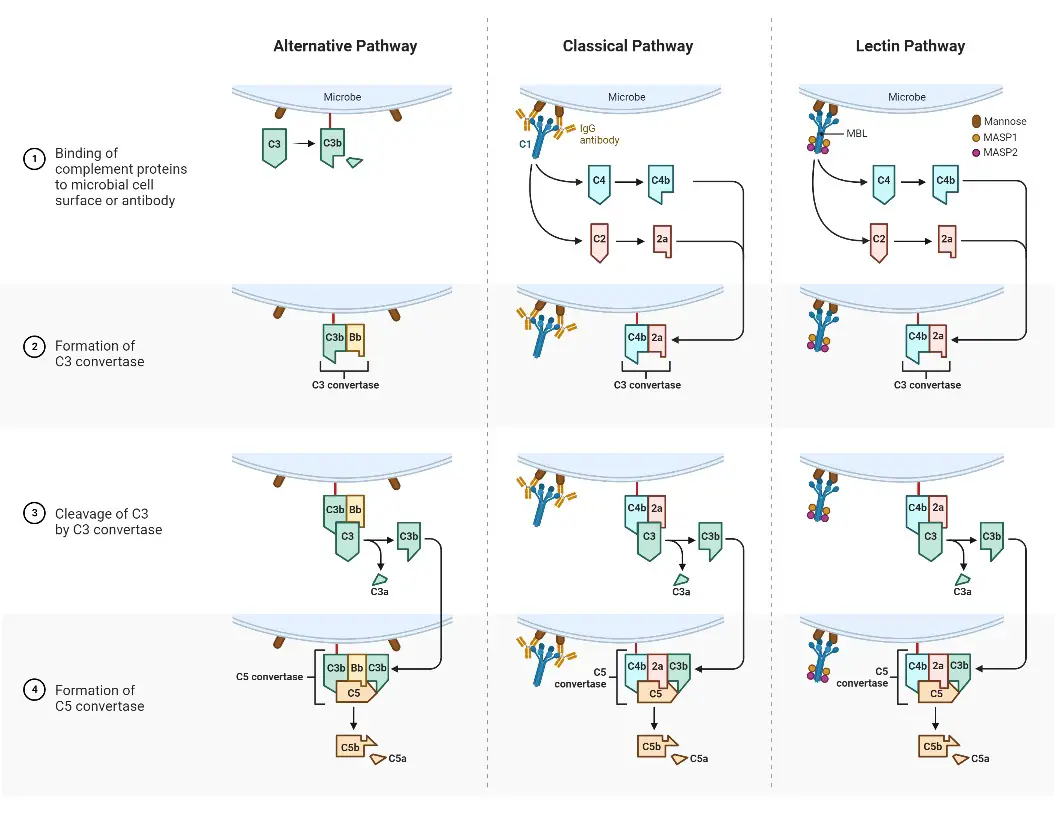
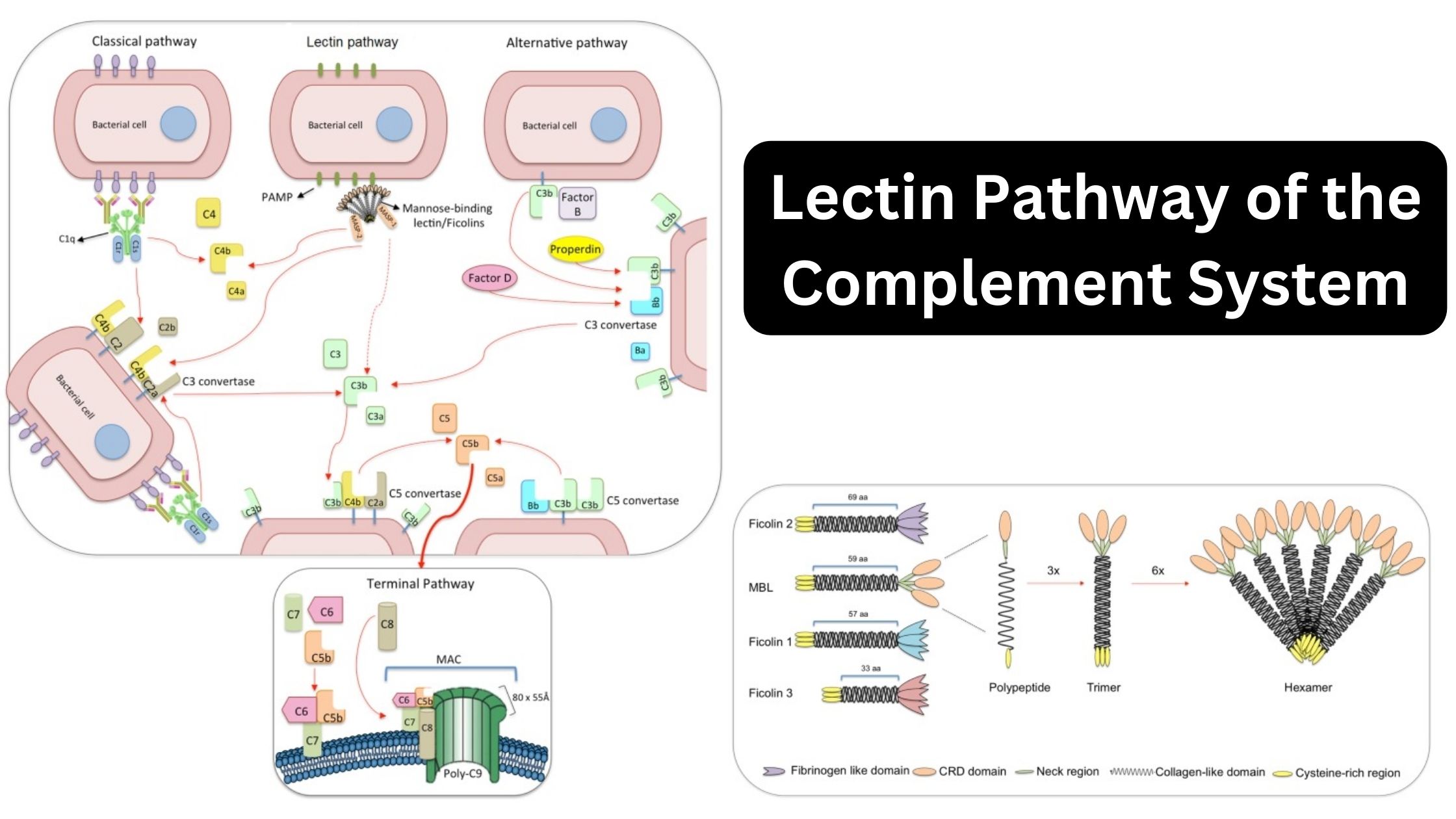
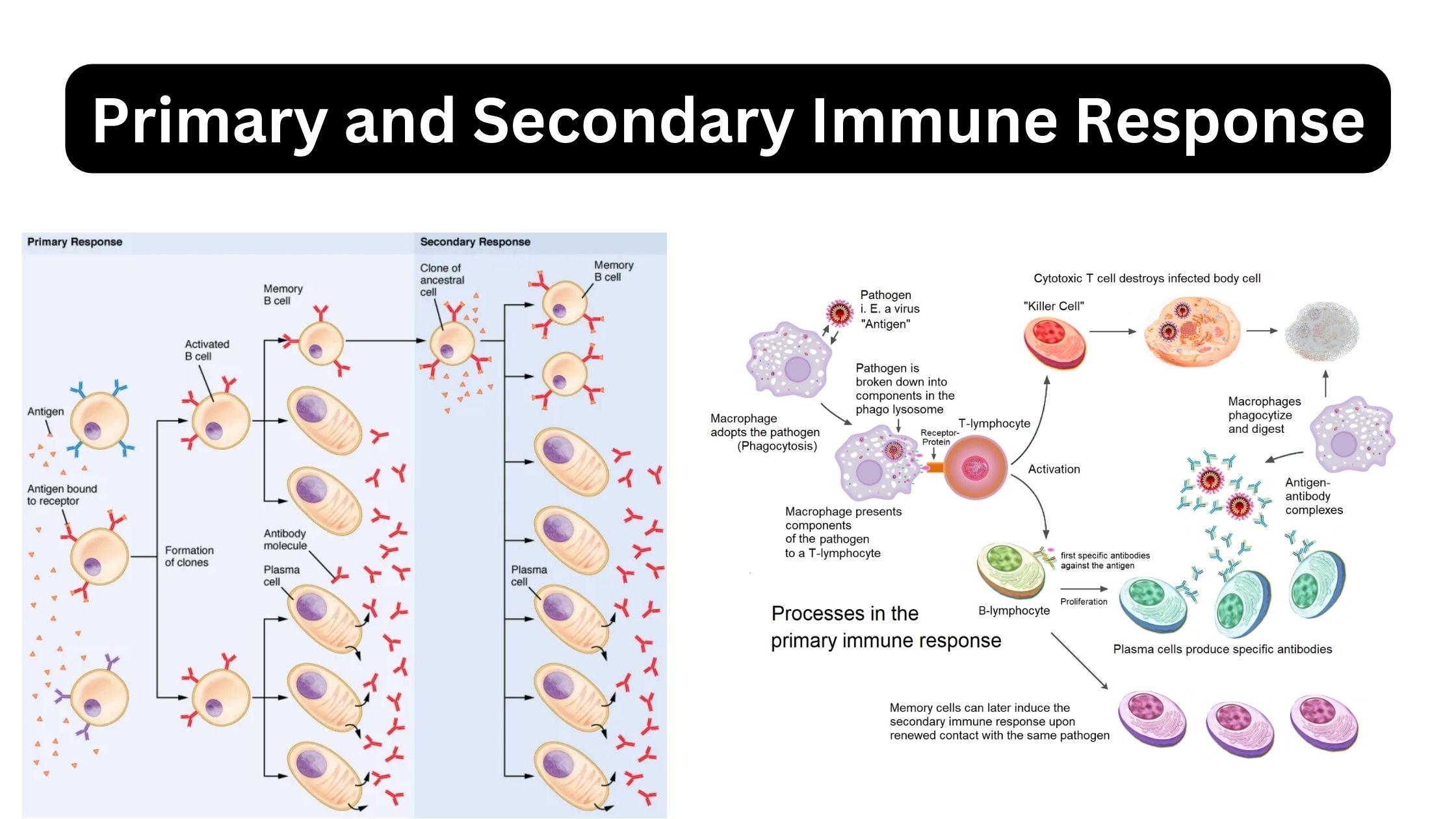
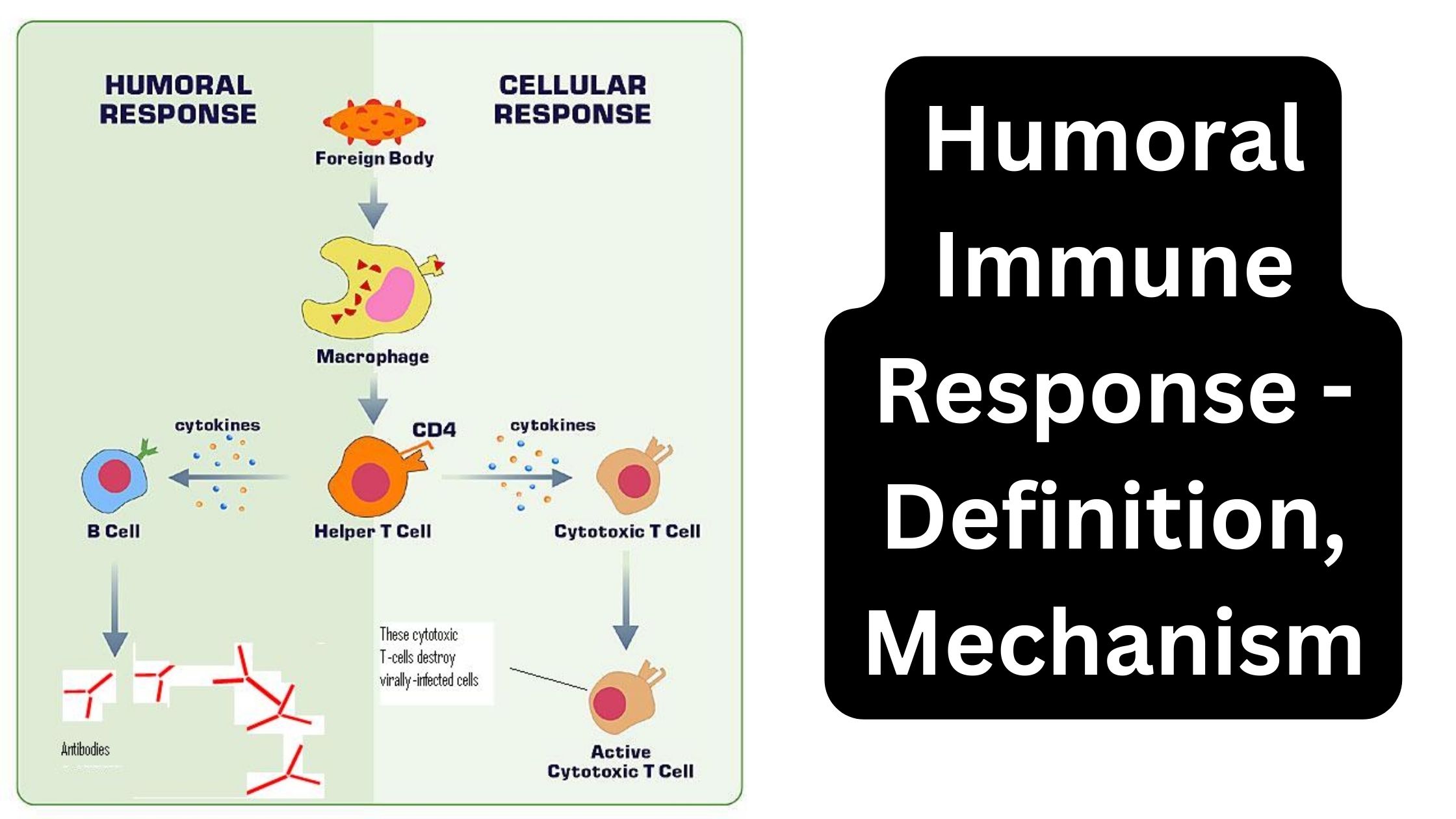
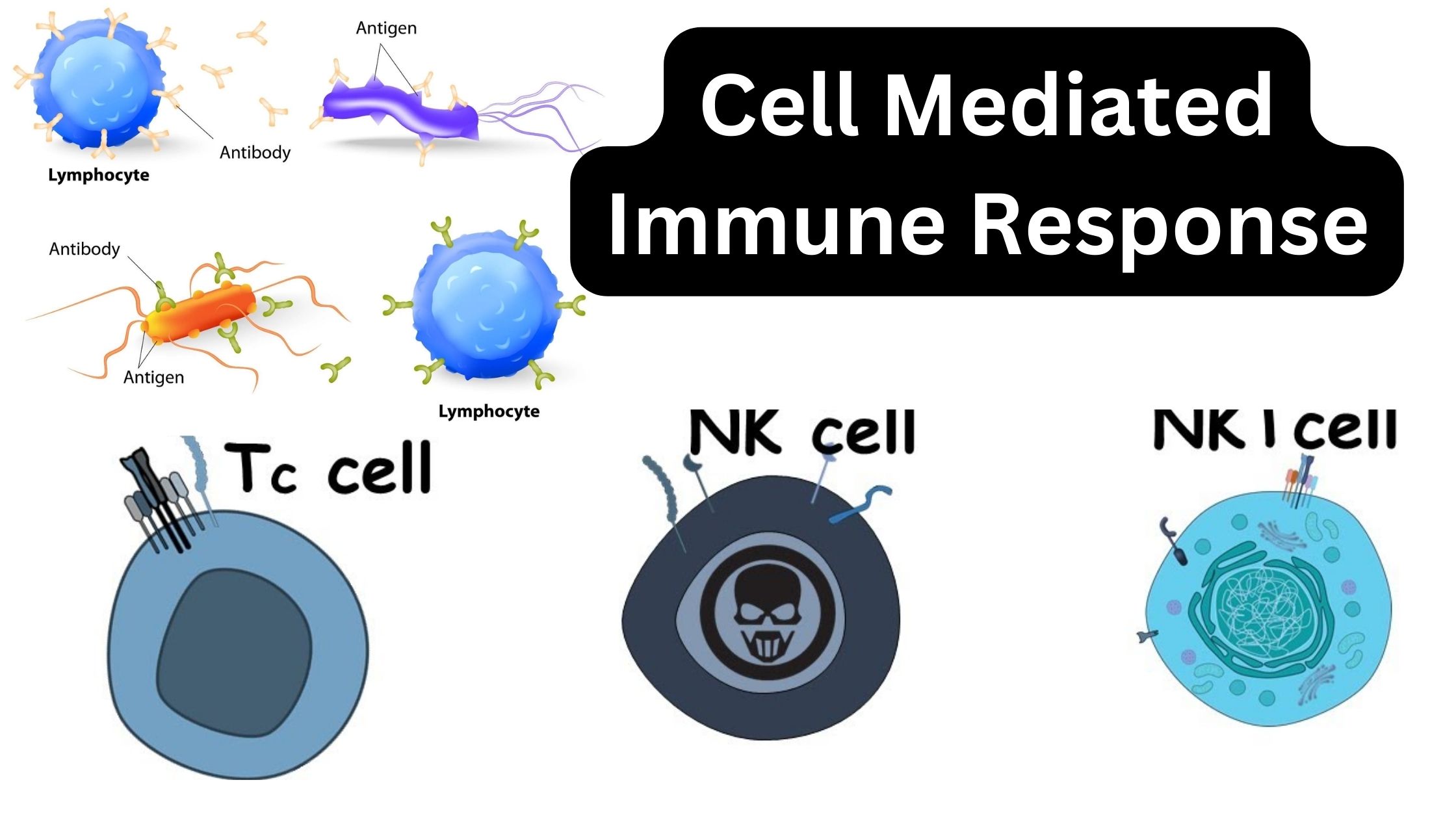
Immunity – Definition, Types, Mechanism, Components, and Immunization
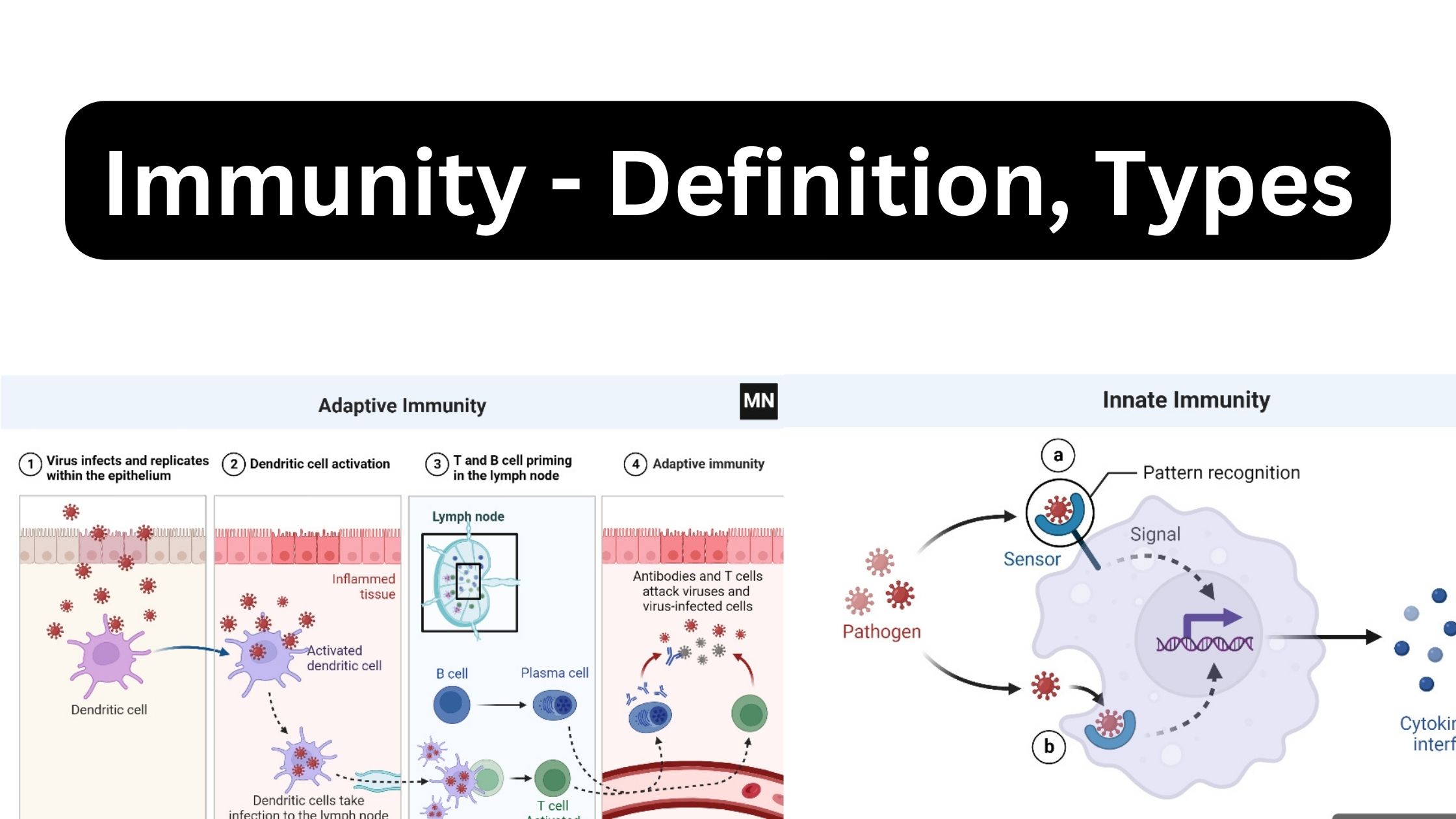
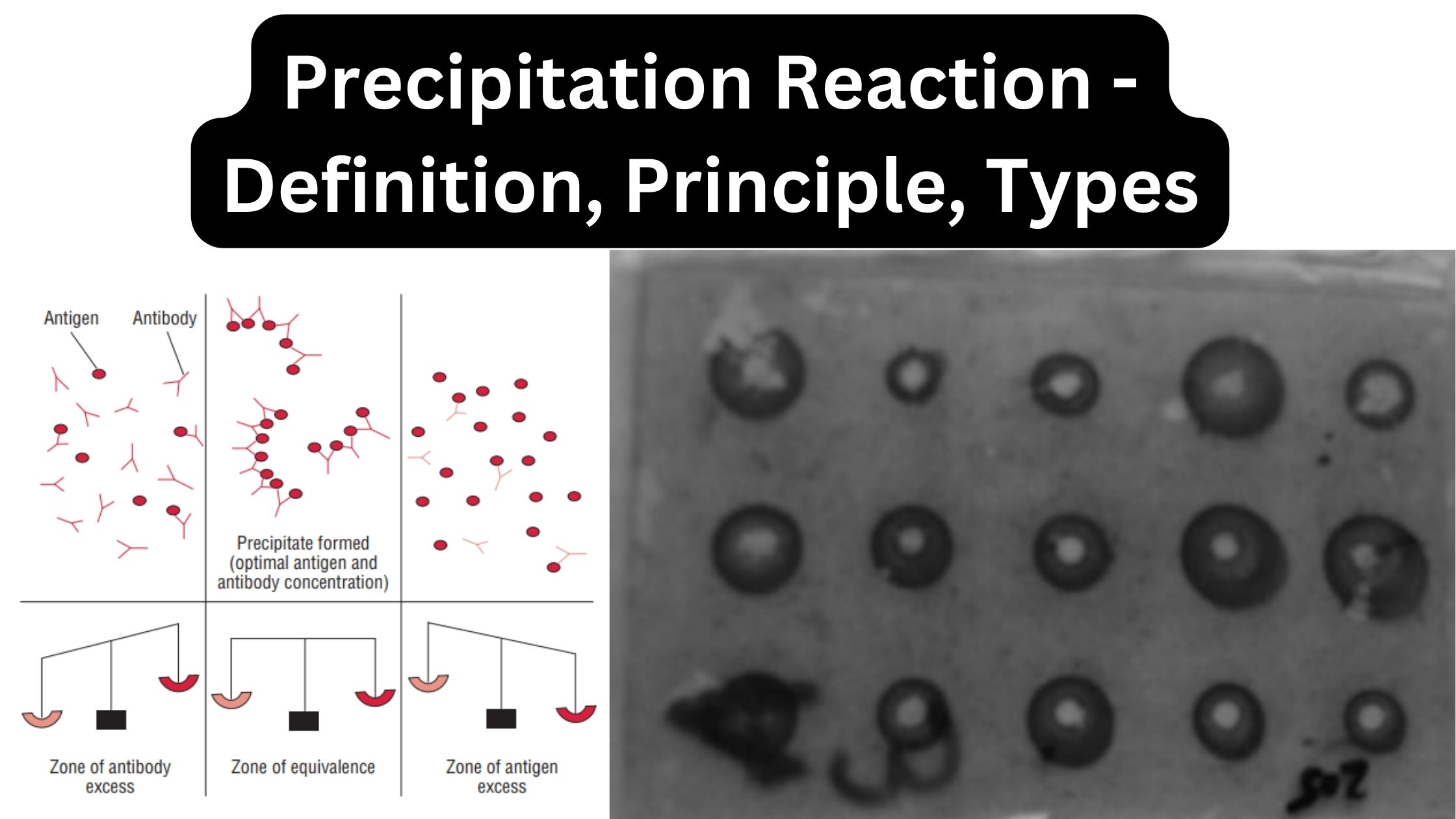
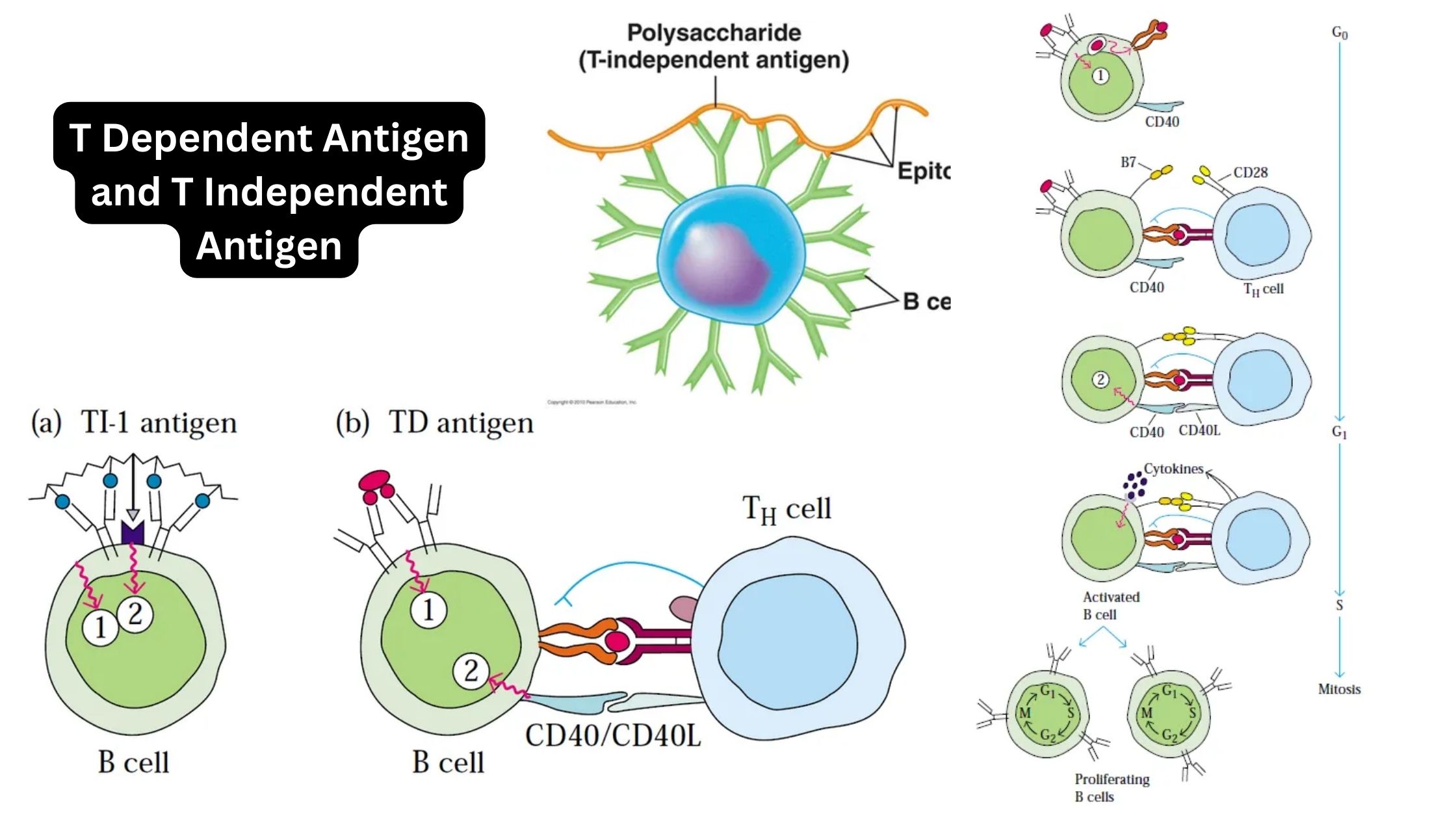
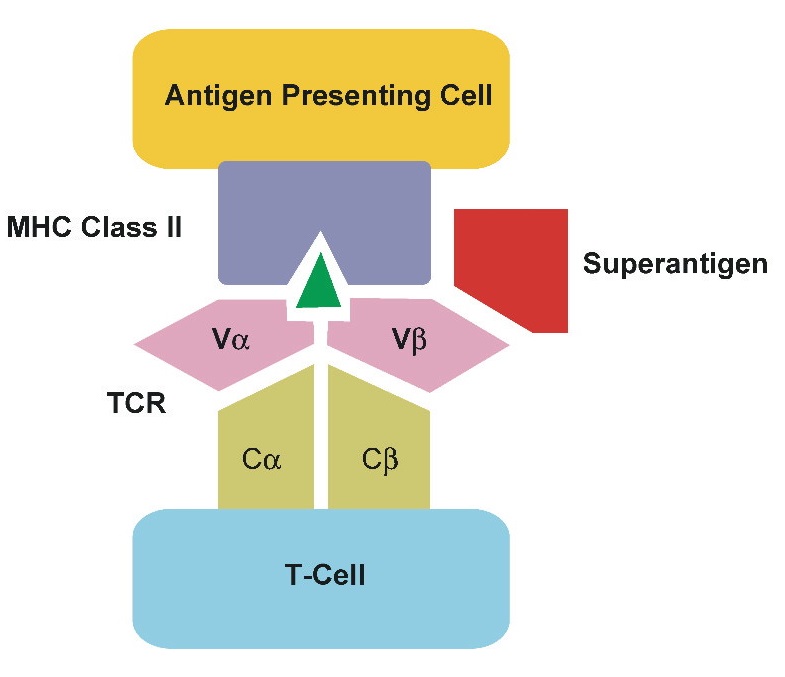
What is Immunity? Definition of Immunity Immunity is the body’s ability to resist or protect itself against harmful pathogens or diseases. What is Immune System? Lymphoid Organs Primary lymphoid organs Secondary lymphoid organs Tertiary lymphoid organs How does Immunity Work? Mechanism of Immunity Types of Immunity The primary purpose of the immune system is to … Read more