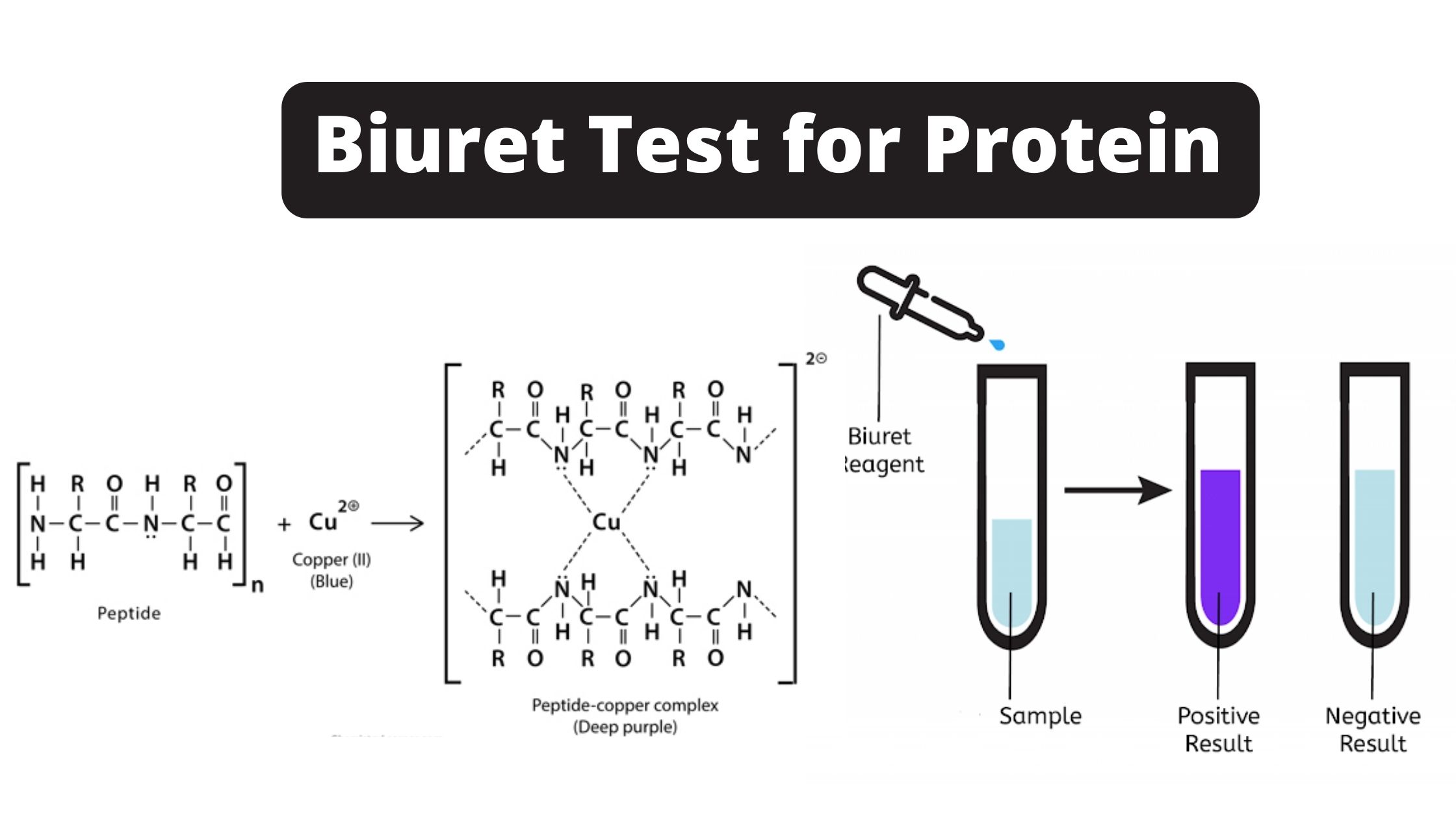
Biochemical Test of Bacillus cereus
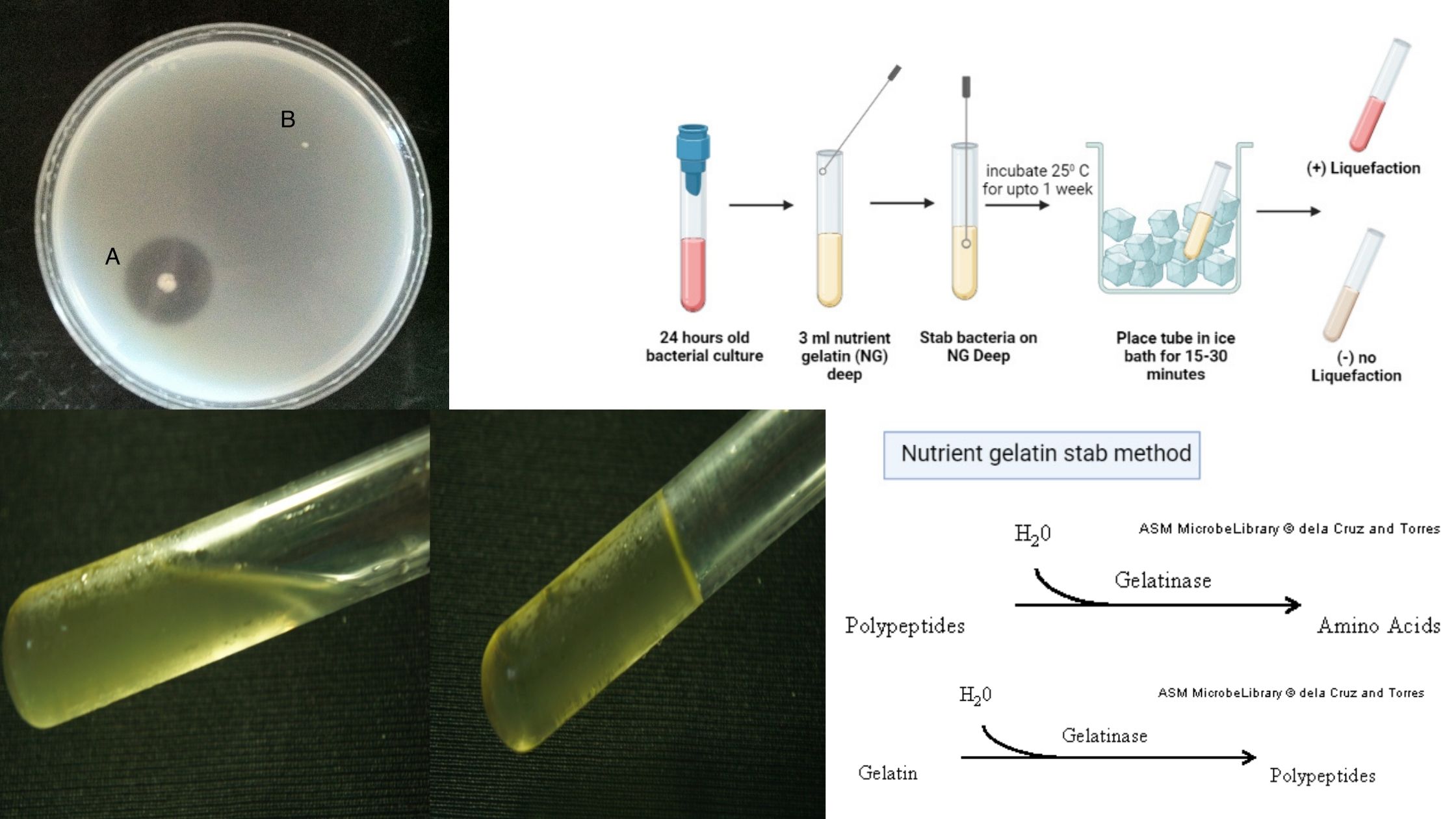
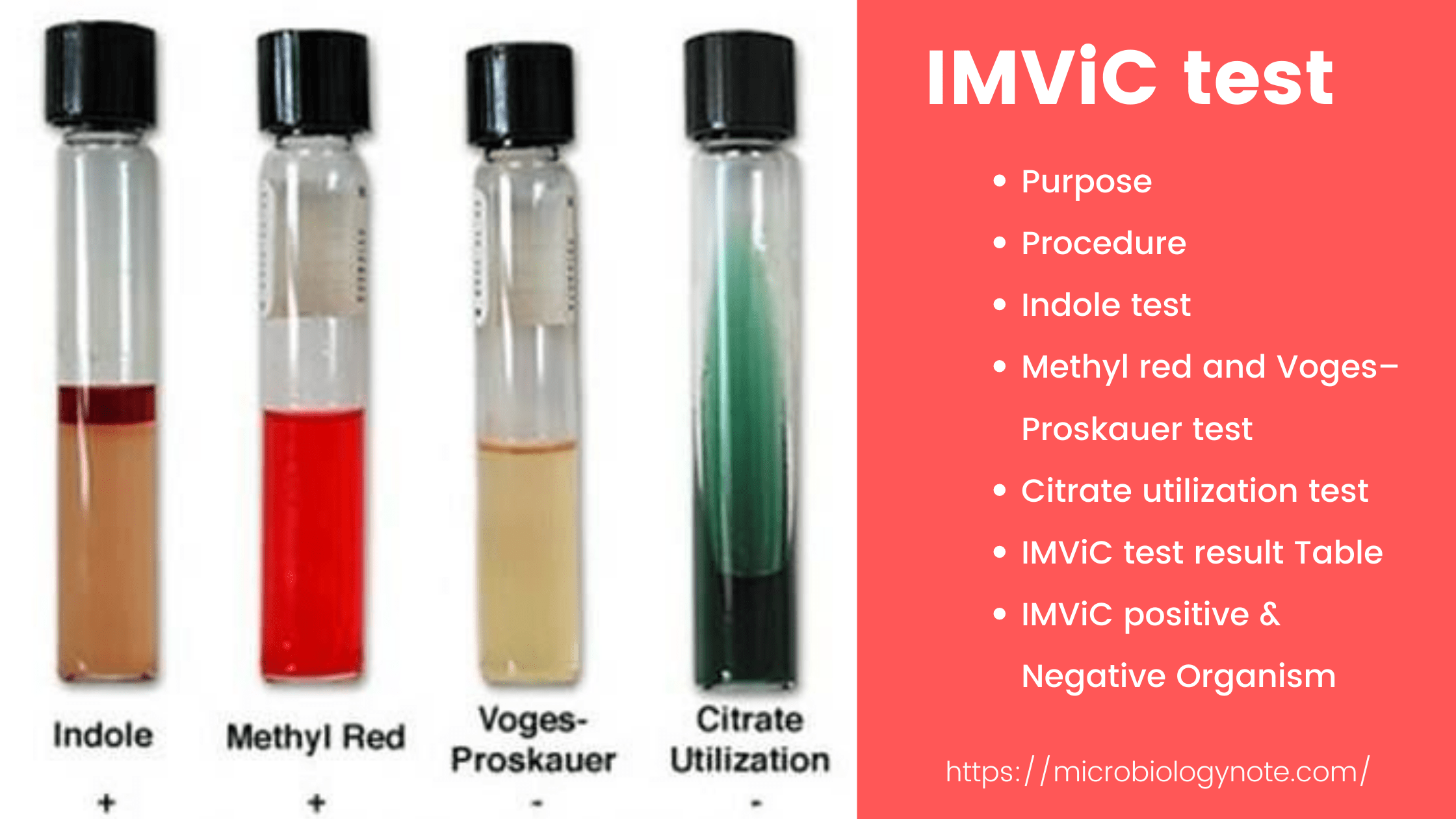
Biochemical Test of Bacillus cereus Basic Characteristics Properties (Bacillus cereus) Catalase Positive (+ve) Citrate Positive (+ve) Gelatin Hydrolysis Negative (-ve) Gram Staining Positive (+ve) Growth in KCN Positive (+ve) Hemolysis Positive (+ve) Indole Negative (-ve) Motility Positive (+ve) MR (Methyl Red) Negative (-ve) Nitrate Reduction Variable Oxidase Negative (-ve) Pigment Negative (-ve) Shape Rods Spore Positive … Read more