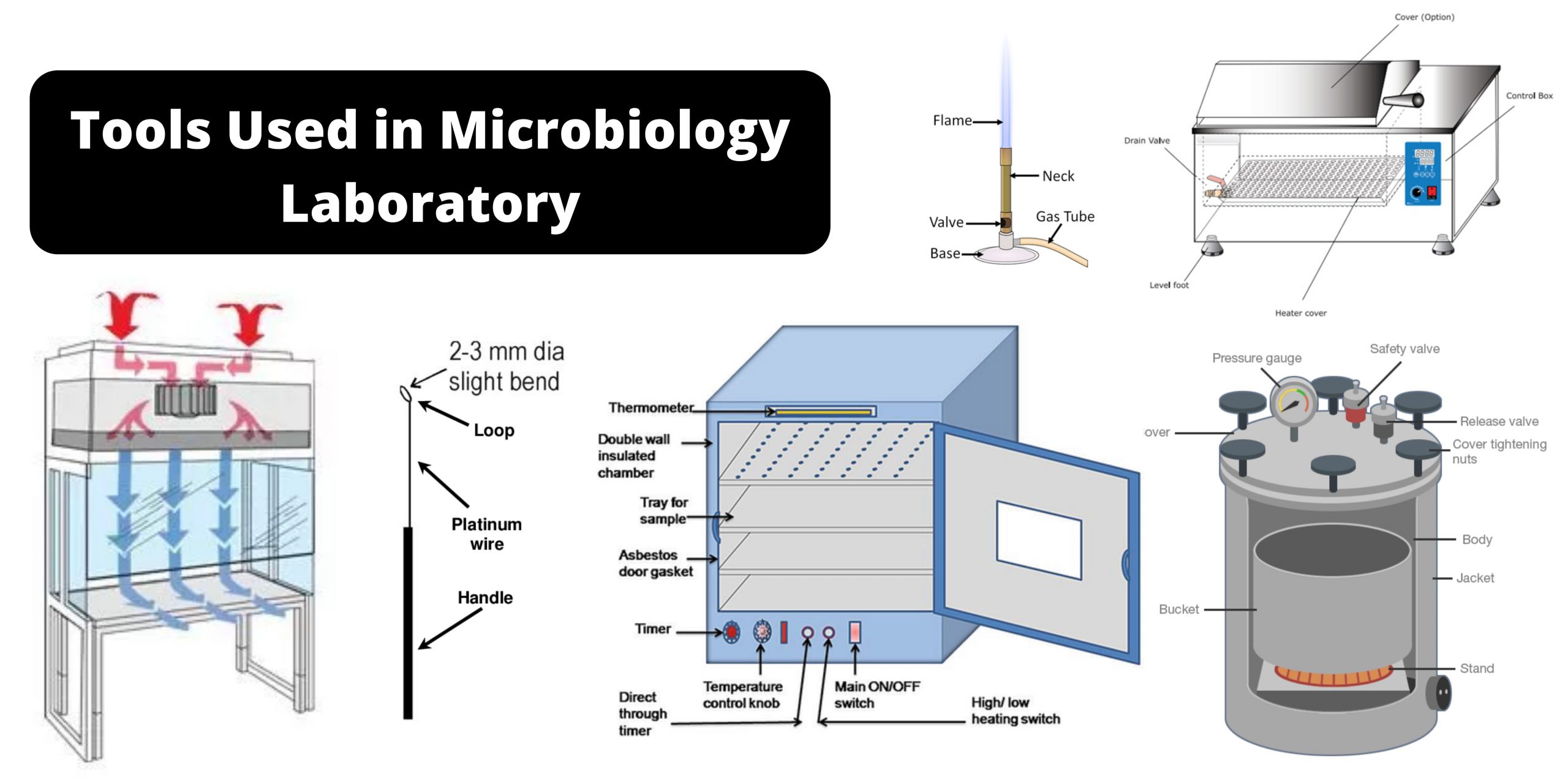
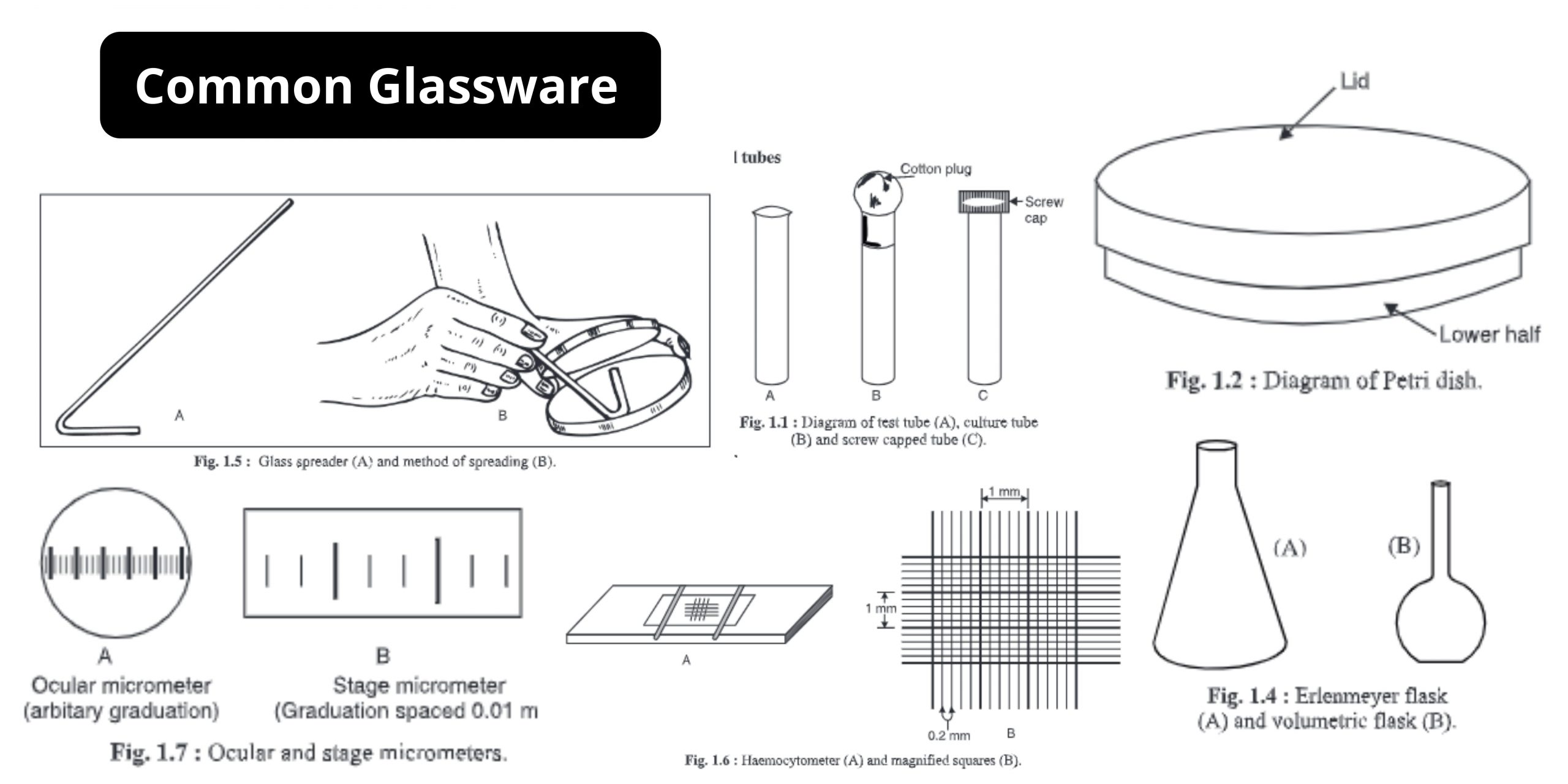
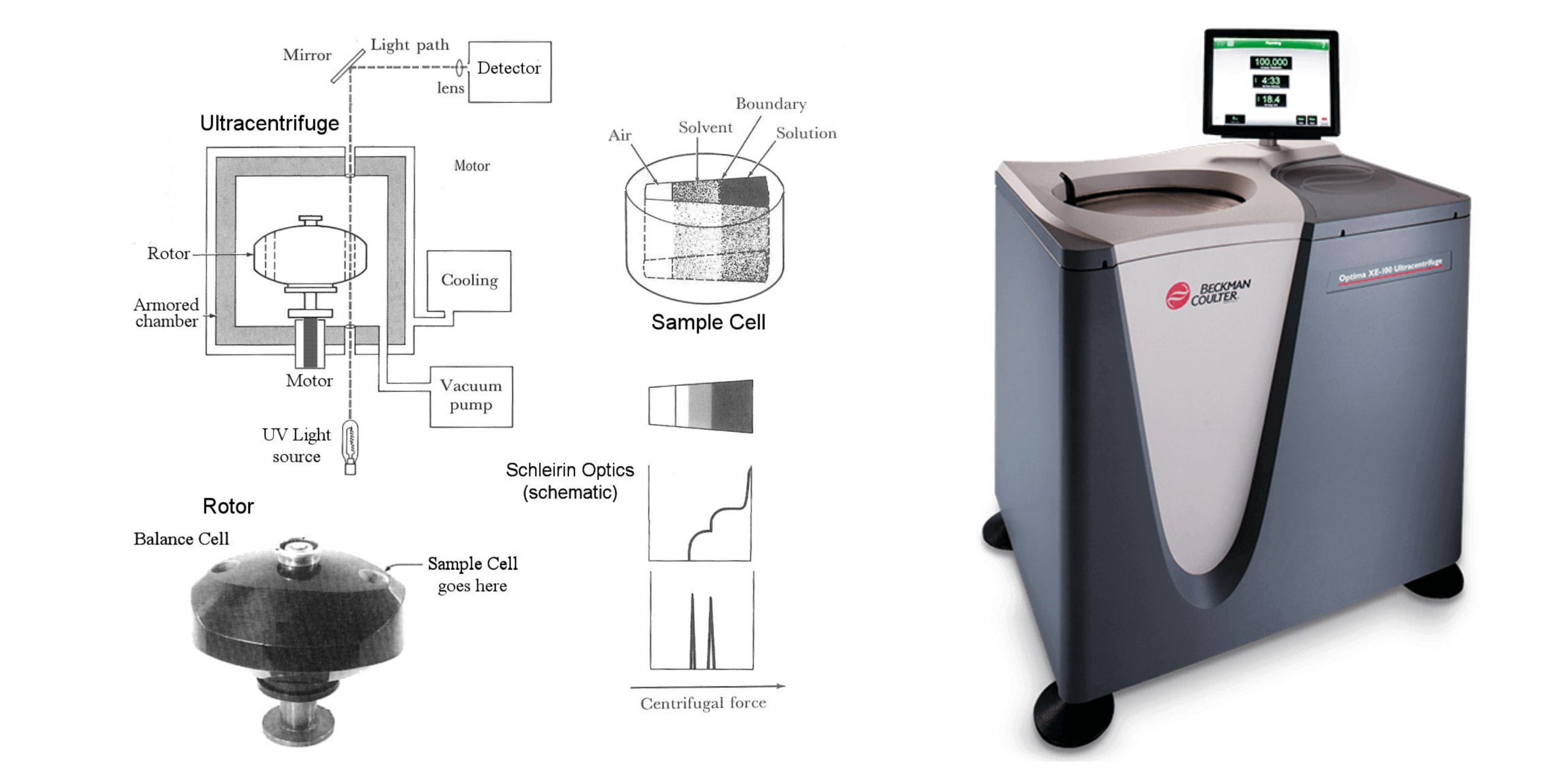
Centrifuge tube – Definition, Types, Applications, Sizes
What is a Centrifuge tube? A centrifuge tube is a thin, cylindrical tube with a round bottom and a cap, used in a laboratory centrifuge. Centrifuge tubes are made of plastic or glass and are used to separate substances based on their density. When placed in a centrifuge and spun at high speeds, the heavier … Read more