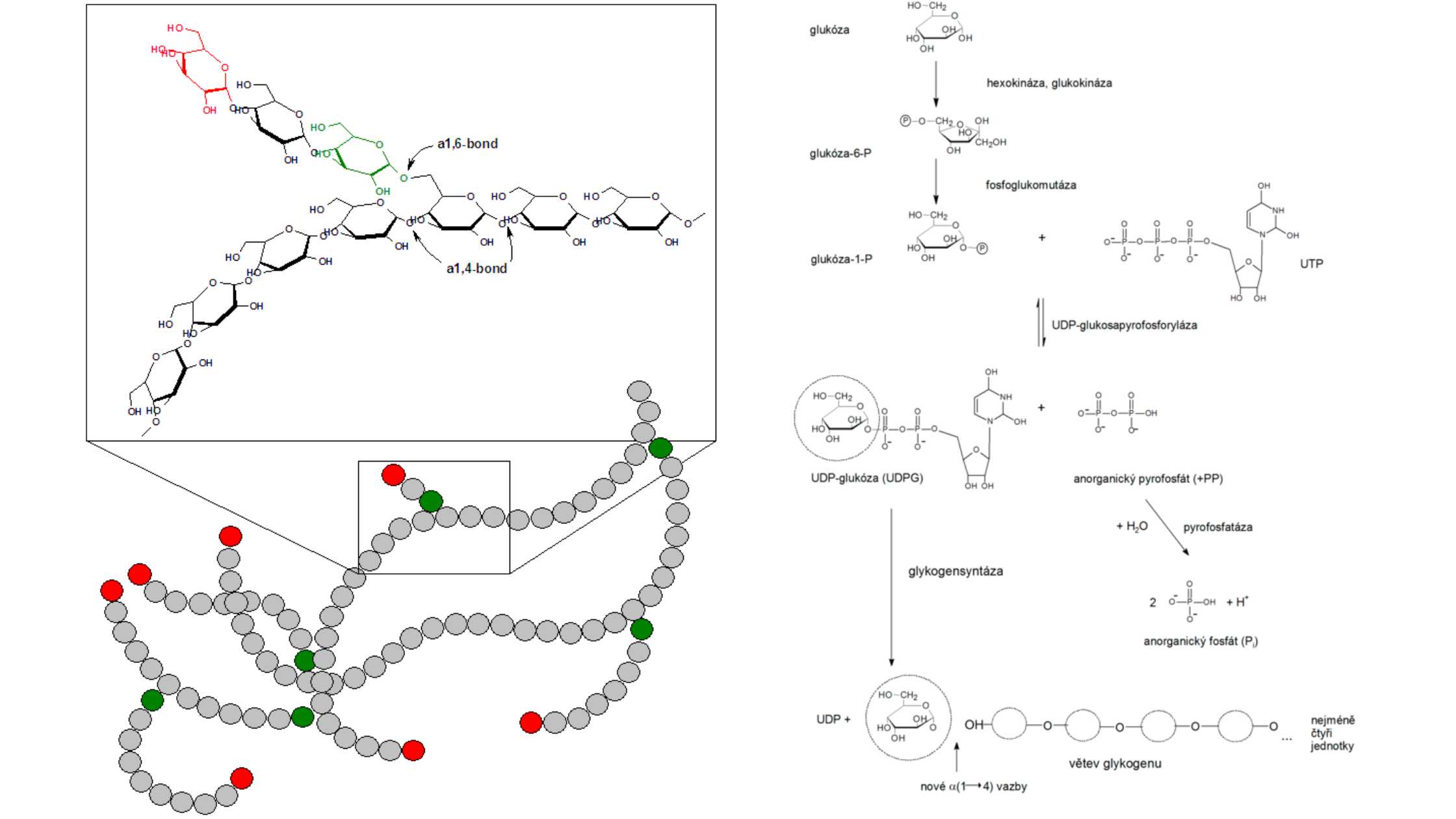
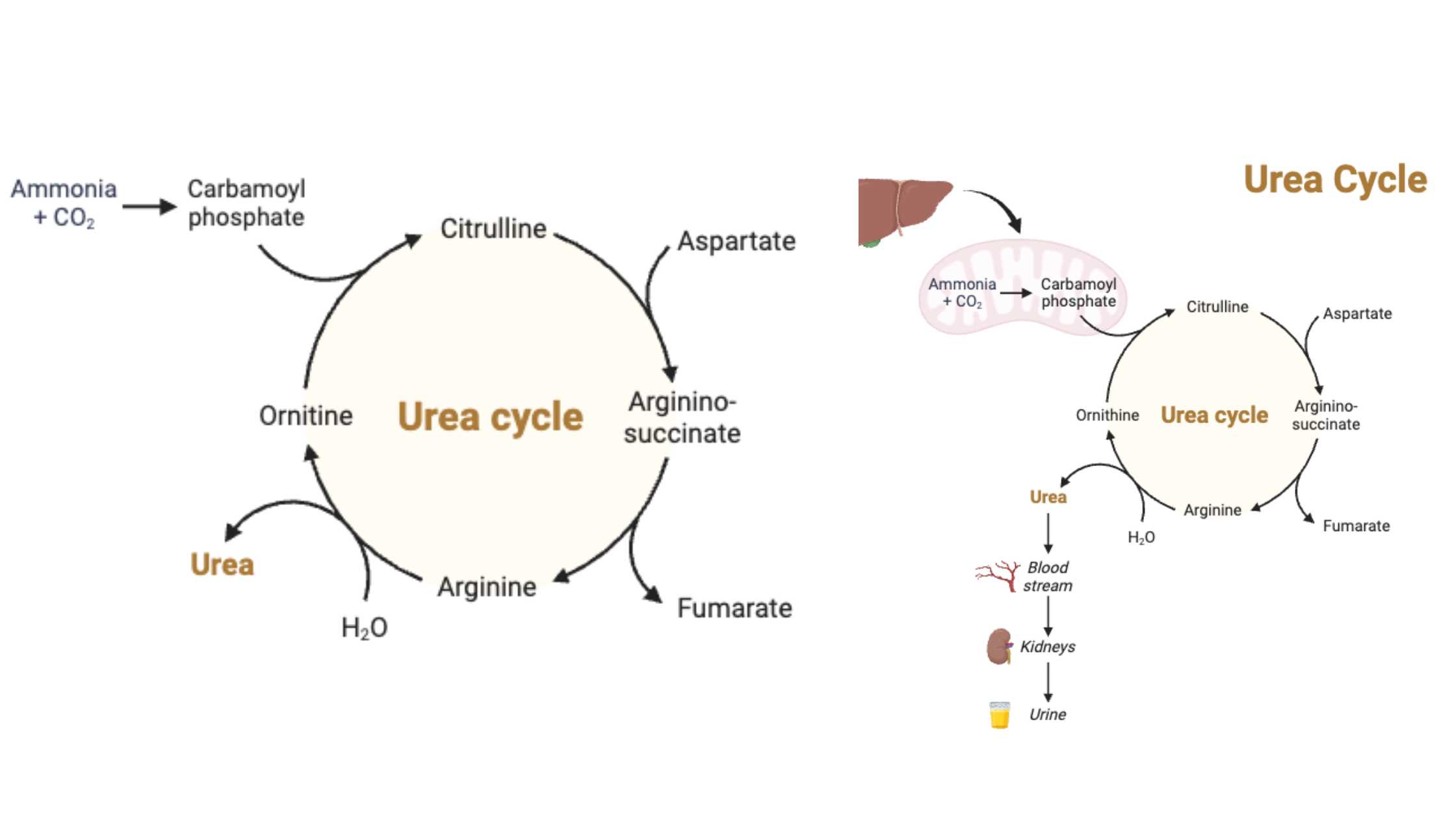
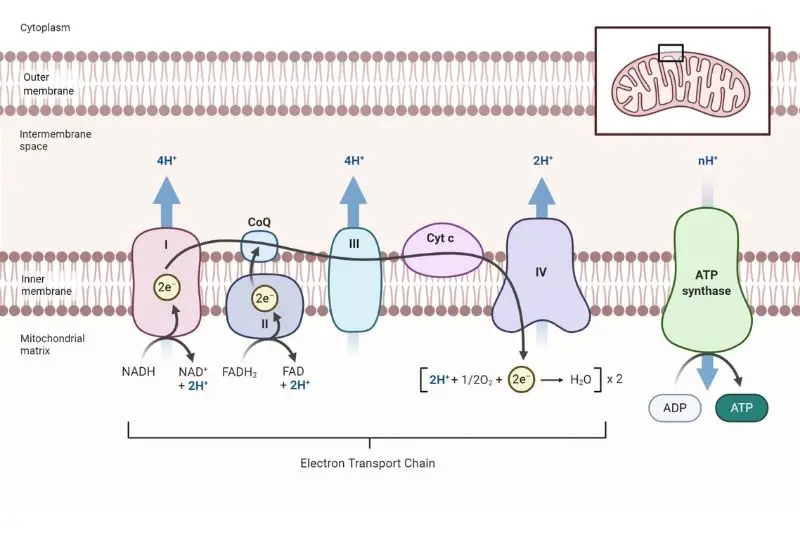
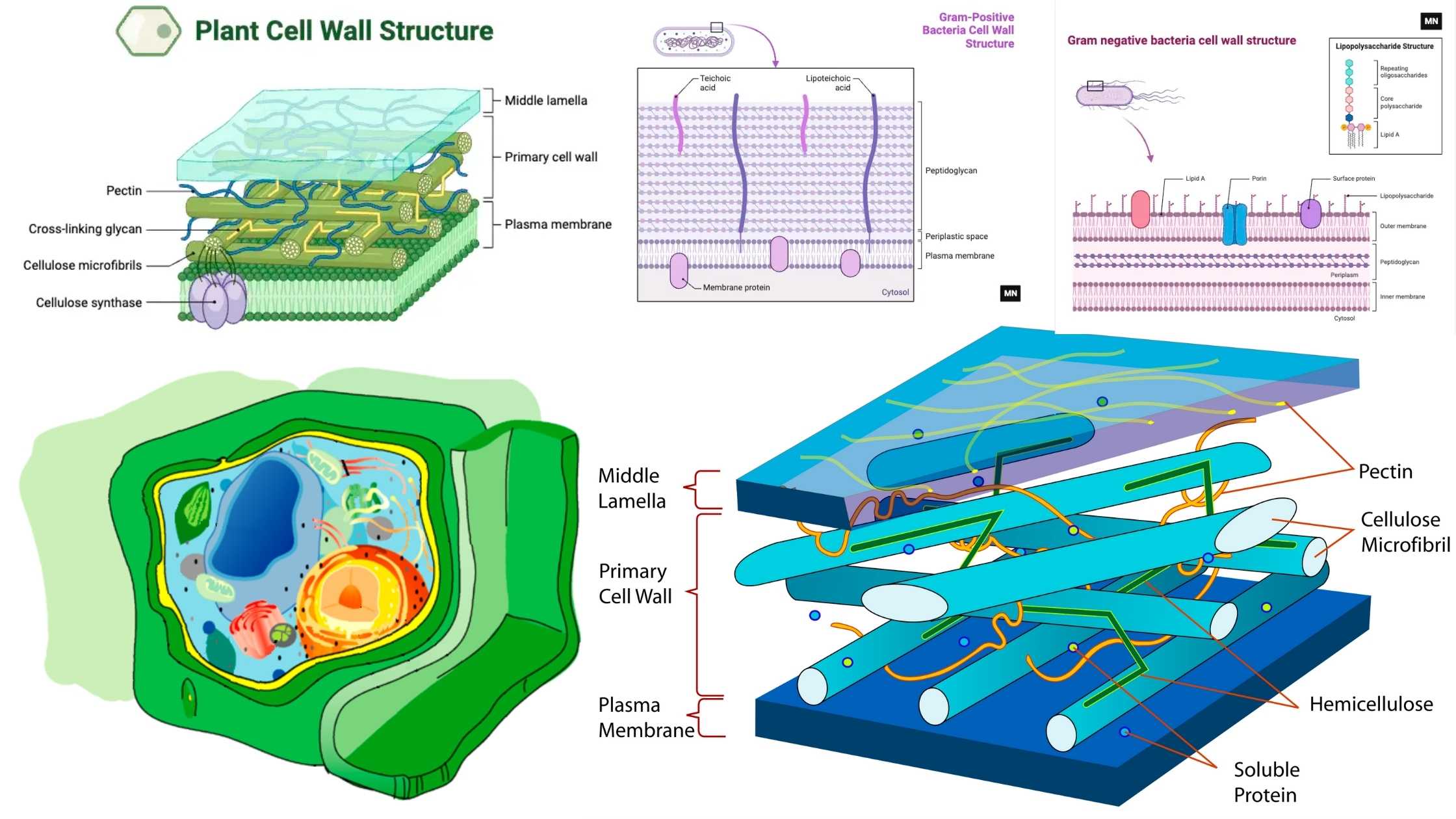
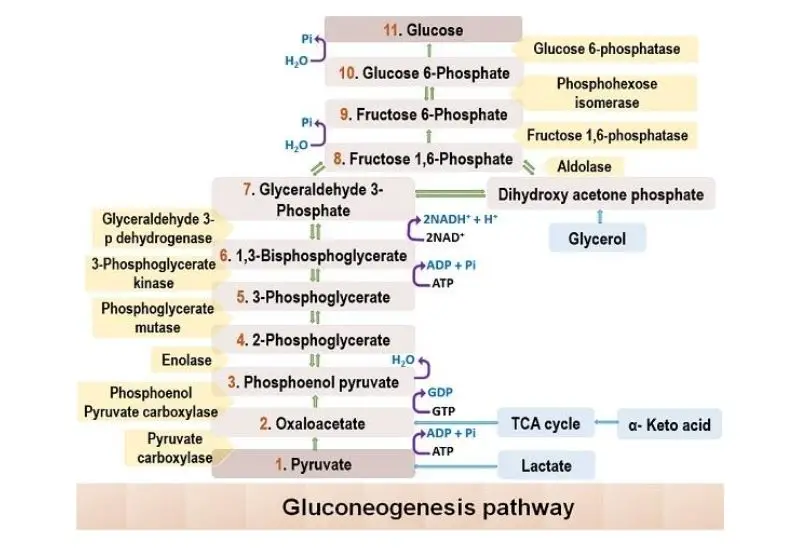
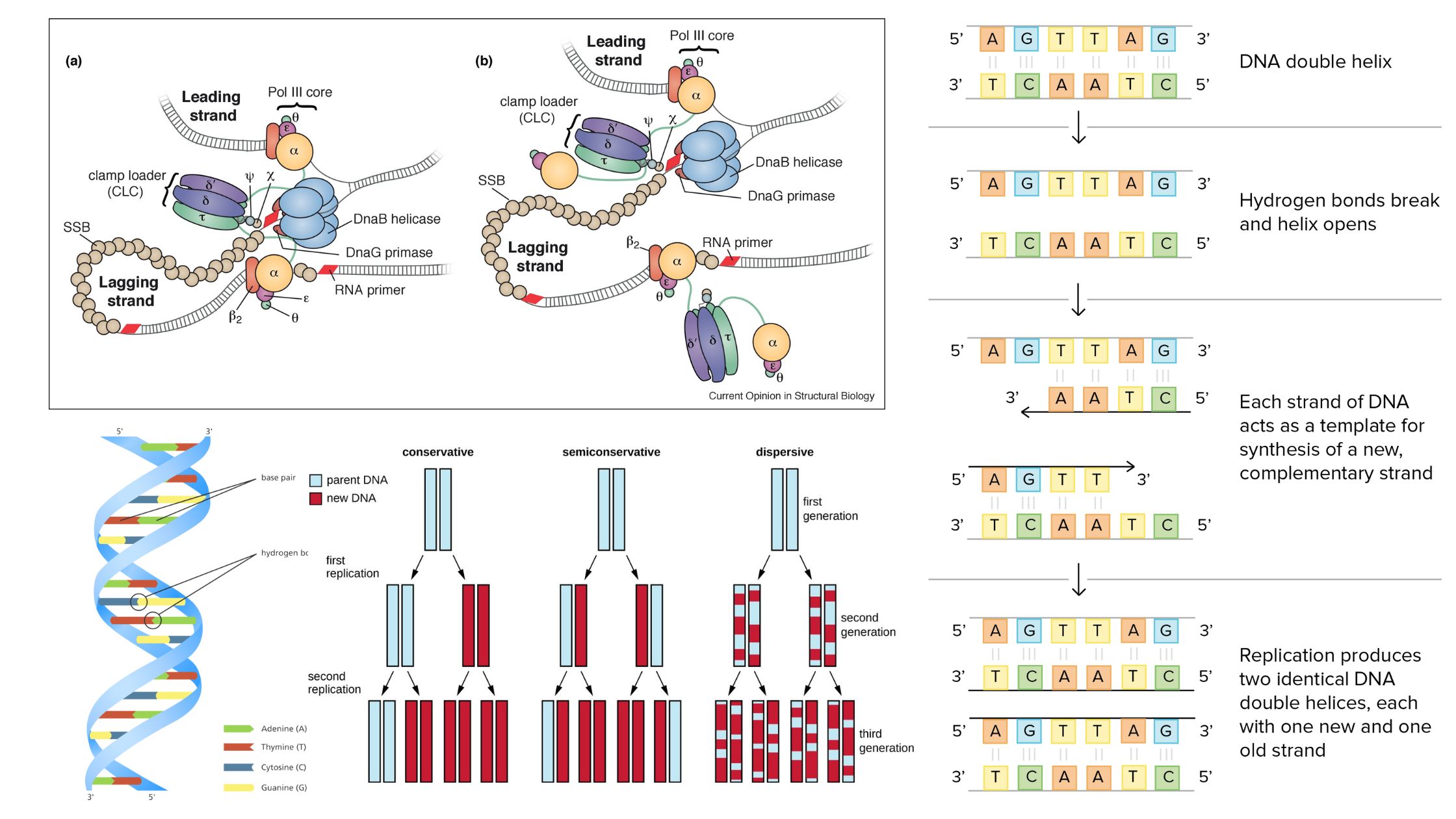
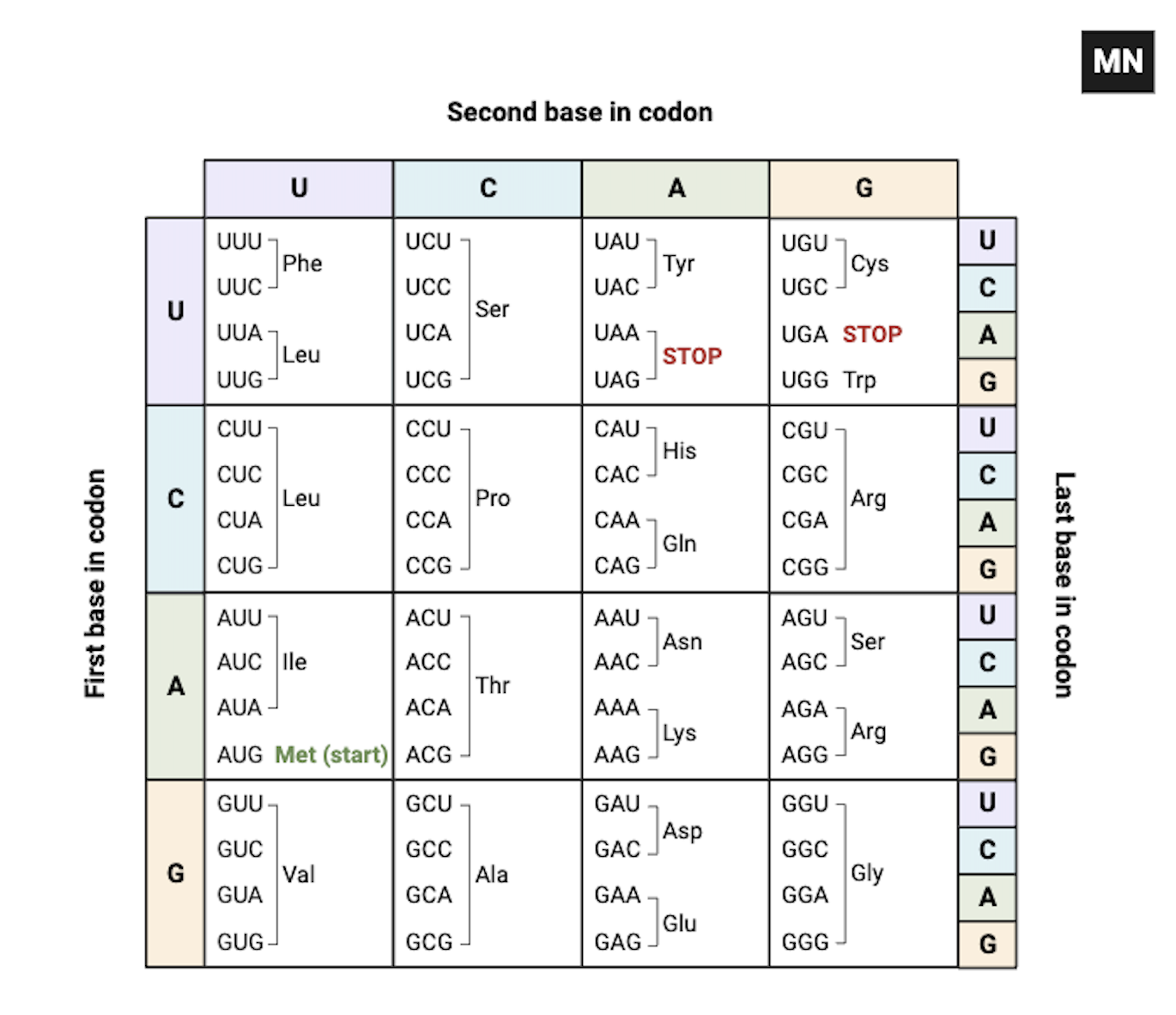
Glycogen Metabolism in Human Body
What is Glycogen? Structure And Function Of Glycogen The primary stores of glycogen within the human body are primarily located in skeletal muscle and the liver, although various other cells also maintain smaller glycogen reserves for their specific metabolic needs. The role of glycogen varies depending on its location, and it plays crucial functions in … Read more