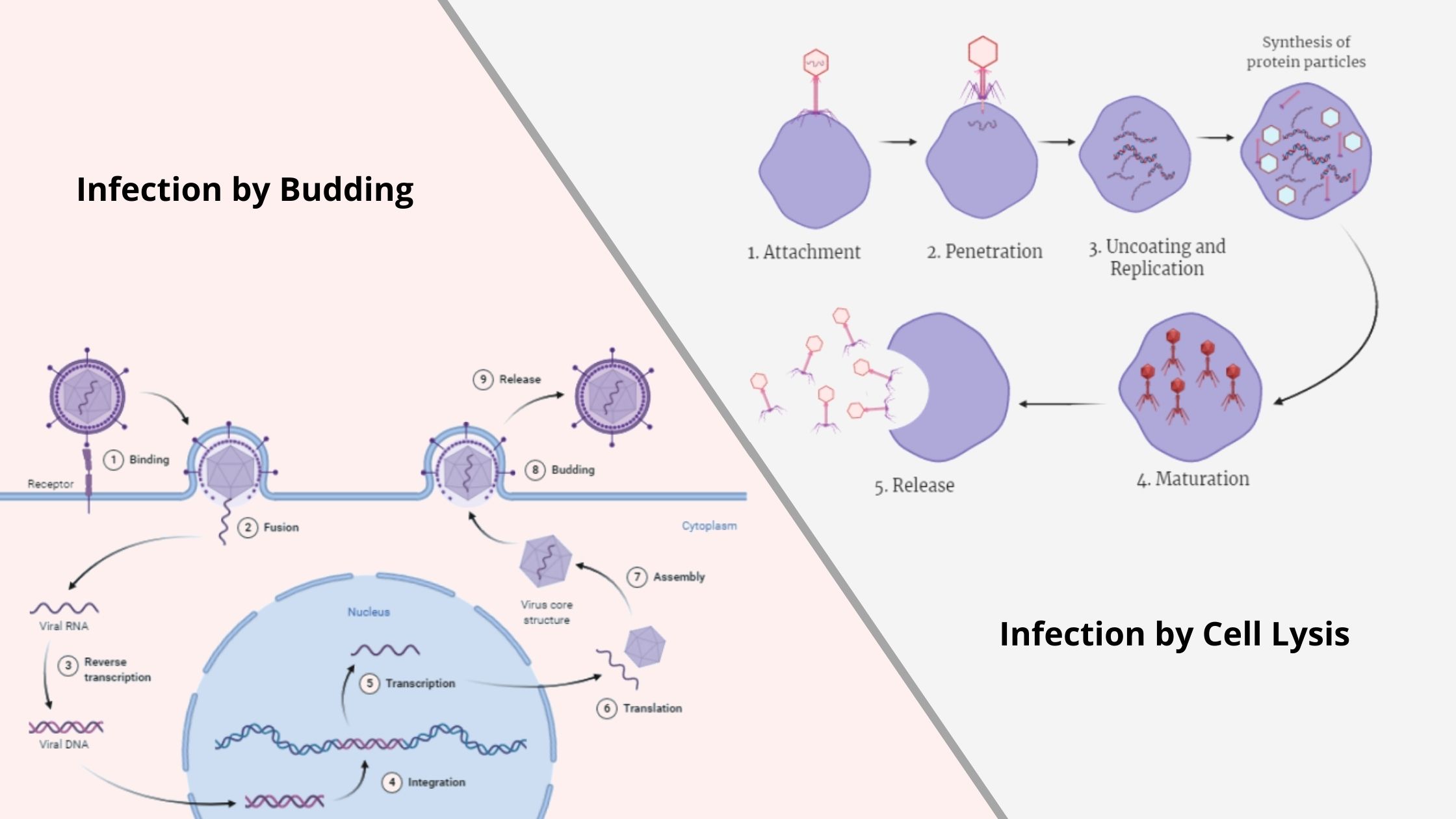
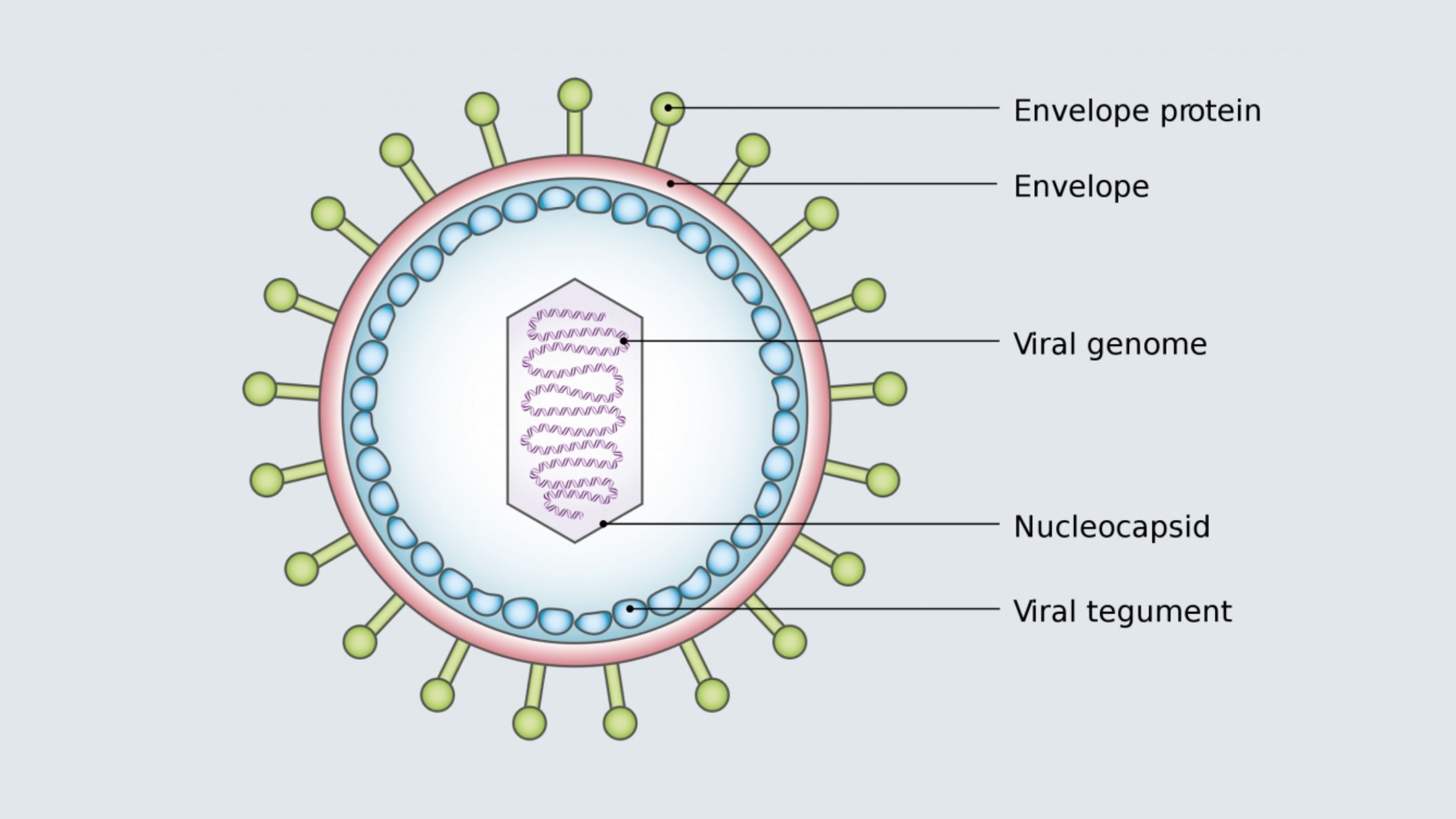
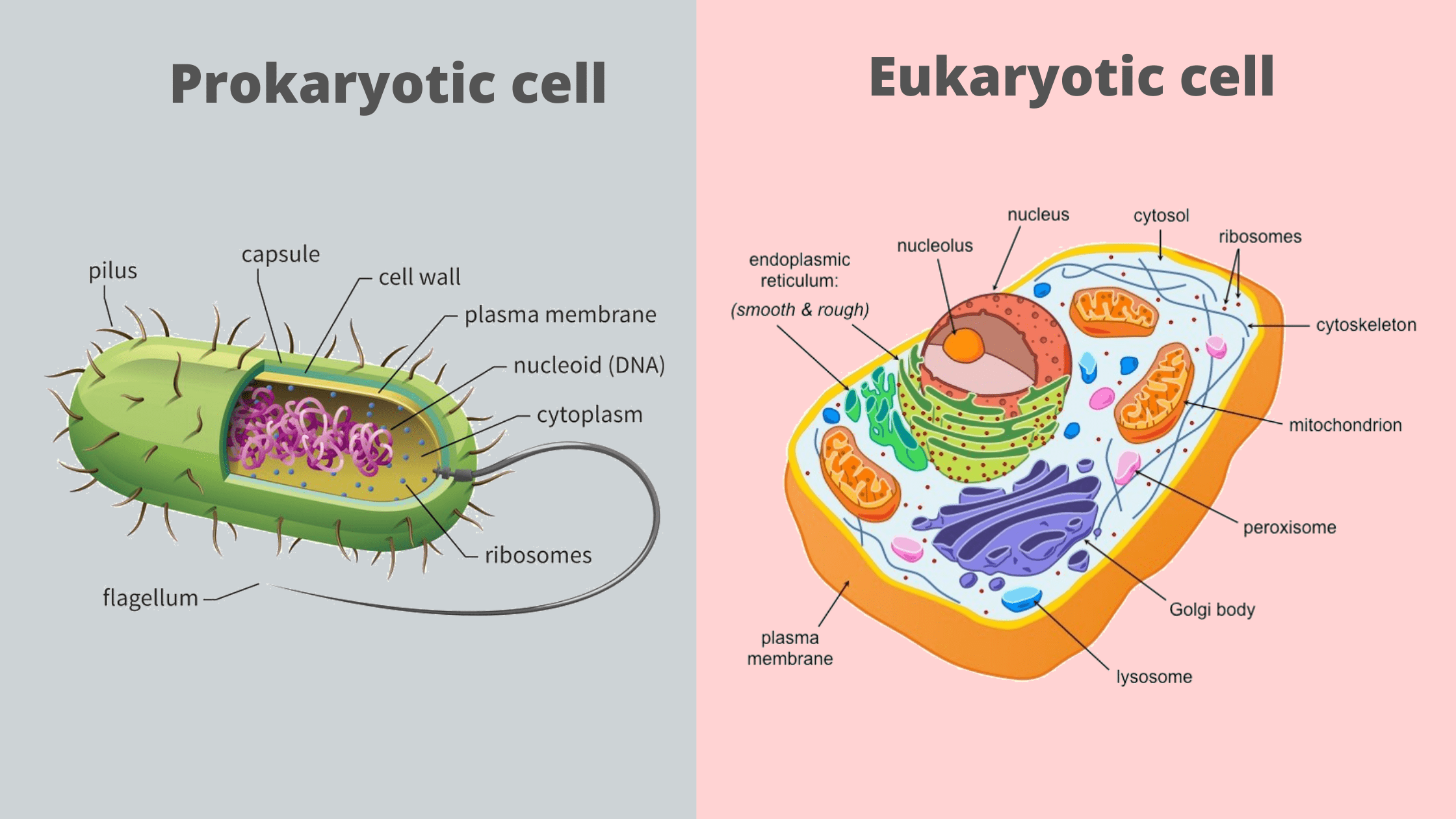
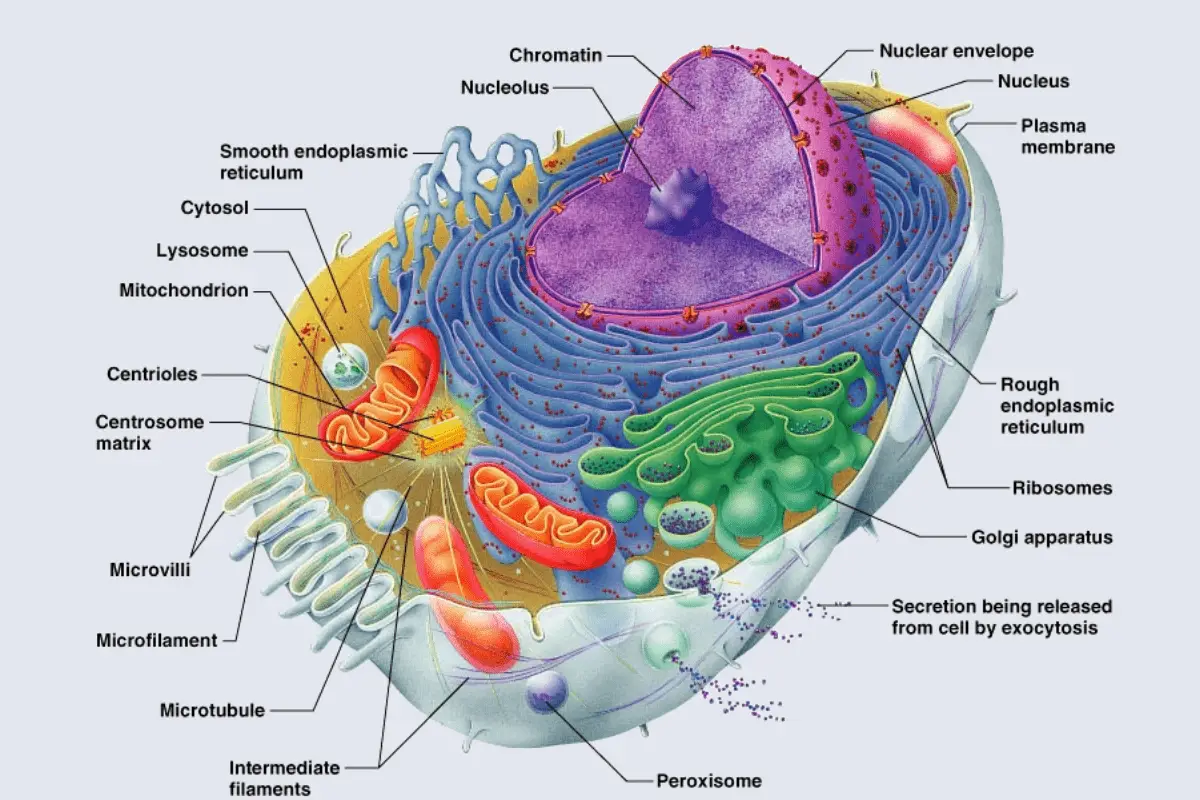
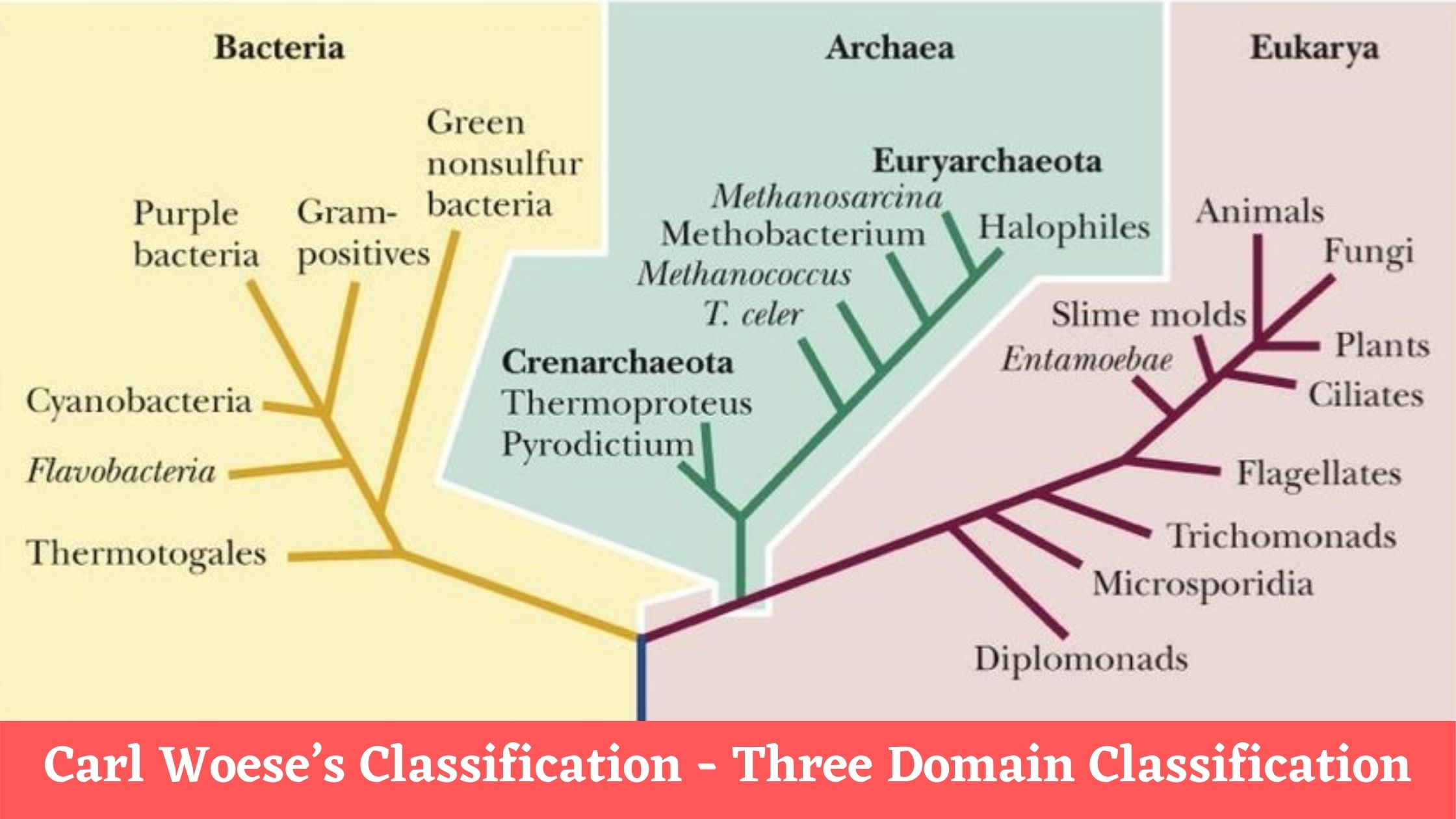
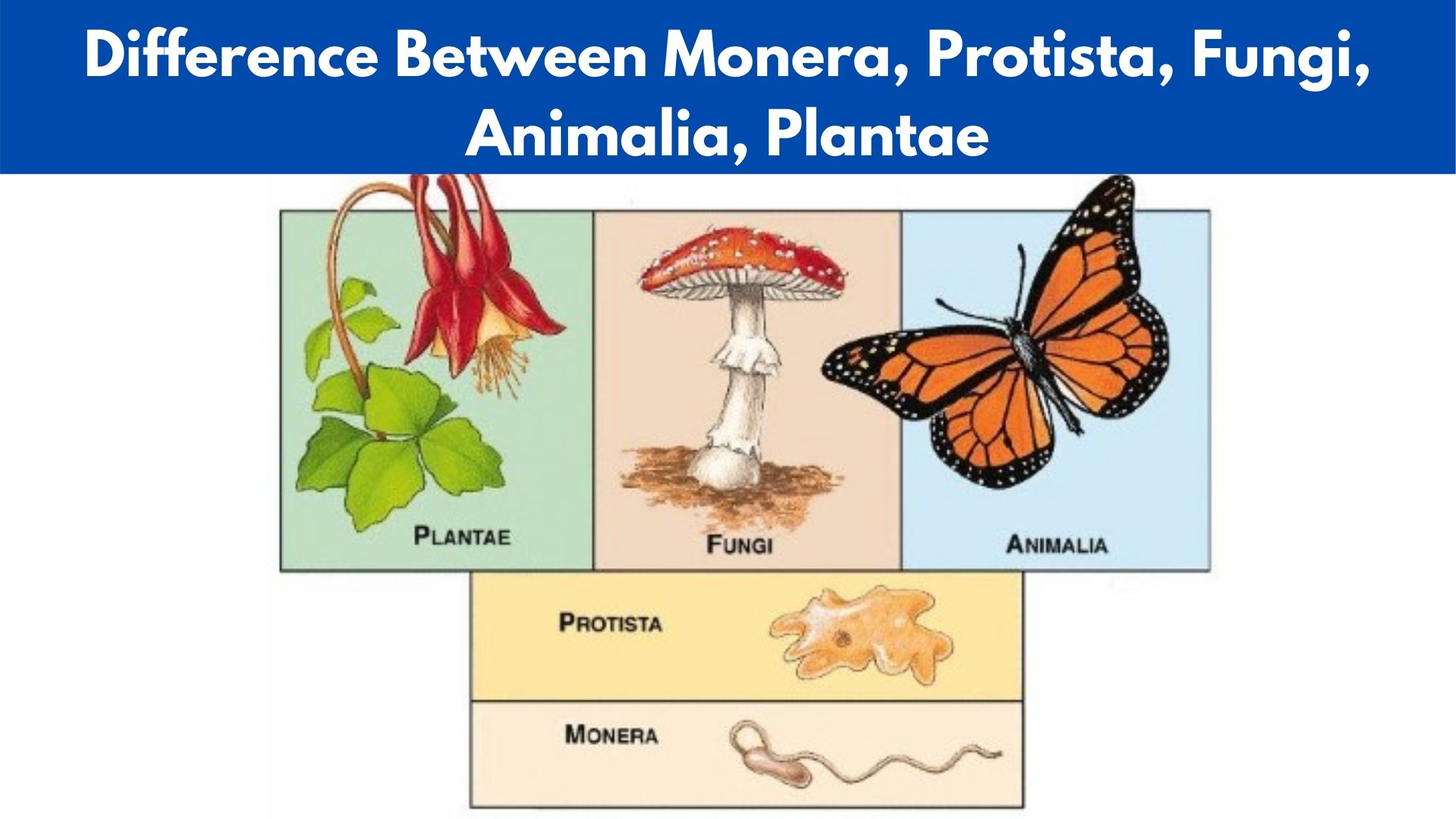
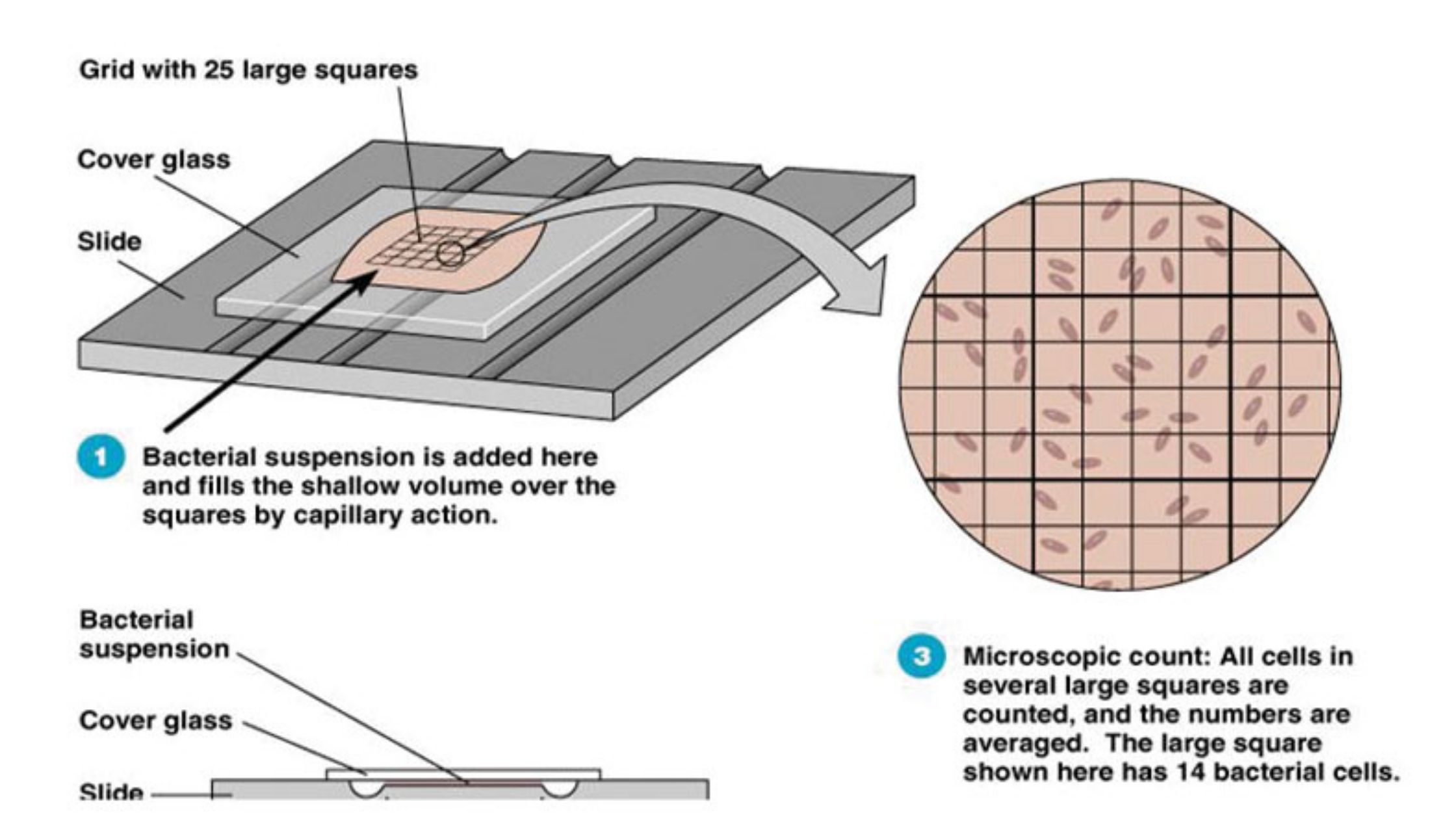
Viral Life Cycle: Steps of Viral Infection
Introduction In our daily life, we are thinking about Viral Infection and their symptoms, when we get infected by any infectious virus such as the flu or the chickenpox. But ever you ask, what’s actually happening in your body when you have been infected by a virus? In biology, viral infection means viruses are started … Read more